Water Loss Due to Increasing Planted Vegetation over the Badain Jaran Desert, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Terrestrial Total Water Storage
2.3. Precipitation
2.4. In Situ Lake Level Measurements
2.5. Other Supplementary Data
2.6. Vegetation Extraction
2.7. Lake Area Mapping
2.8. Identification of the Increase in Planted Vegetation
2.9. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Spatial-Temporal TWS Change Patterns over the BJD Region
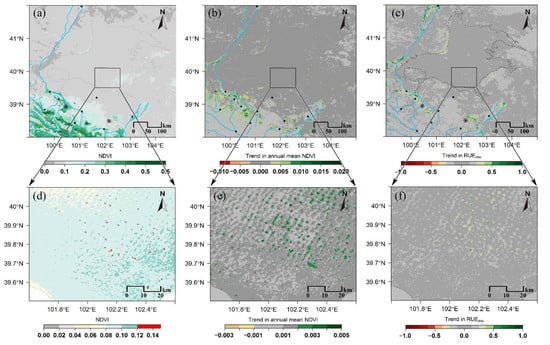
3.2. Trends in Planted Vegetation over the Study Area
3.3. The Changes in Lake Area Associated with the Decline in TWS
3.4. Water Level and Vegetation Changes of Four Local Lakes in the BJD Hinterland
4. Discussion
4.1. TWS Decline Despite the Stable Precipitation
4.2. Eco-Hydrological Changes of the BJD and Adjacent Region
4.3. The Impact of the Increasing Tourism on Desert Lakes
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reynolds, J.F.; Smith, D.M.; Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L., 2nd; Mortimore, M.; Batterbury, S.P.; Downing, T.E.; Dowlatabadi, H.; Fernandez, R.J.; Herrick, J.E.; et al. Global desertification: Building a science for dryland development. Science 2007, 316, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, R.K. Sensitivity of evapotranspiration to global warming: A case study of arid zone of rajasthan (India). Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 69, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M. Human domination of earth’s ecosystems. Science 1997, 277, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Wu, Z.; Huang, J.; Chassignet, E.P. Evolution of land surface air temperature trend. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Shen, Y.; Kang, E.; Li, D.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, R. Recent and future climate change in northwest China. Clim. Chang. 2007, 80, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Deng, H.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Xu, C. Abrupt change of temperature and precipitation extremes in the arid region of northwest China. Quat. Int. 2014, 336, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y.; et al. The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Fan, Y.; Wang, H.; Deng, H. Progress and prospects of climate change impacts on hydrology in the arid region of northwest China. Environ. Res. 2015, 139, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, Z.; Dai, X.; Feng, S.; Kang, S.; Huang, G. Effect of climate change on reference evapotranspiration and aridity index in arid region of China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 492, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, J.W.; Zheng, Q.-H.; Yu, Y.-J. A preliminary study of oasis evolution in the tarim basin, Xinjiang, China. J. Arid Environ. 2003, 55, 545–553. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.Z.; Zhao, W.Z.; Su, P.X.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, T.; Ram, R. Ecological effects of desertification control and desertified land reclamation in an oasis–desert ecotone in an arid region: A case study in Hexi corridor, northwest China. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 29, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cheng, G. The characteristics of water resources and the changes of the hydrological process and environment in the arid zone of northwest China. Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenhua, L. Degradation and restoration of forest ecosystems in China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 201, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Innes, J.L.; Lei, J.; Dai, S.; Wu, S.W. China’s forestry reforms. Science 2007, 318, 1556–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Chen, L.; Shankman, D.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H. Excessive reliance on afforestation in China’s arid and semi-arid regions: Lessons in ecological restoration. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2011, 104, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Kang, S.; Zhang, L.; Tong, L.; Su, X. Analysis of impacts of climate variability and human activity on streamflow for a river basin in arid region of northwest China. J. Hydrol. 2008, 352, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhang, L. Hydrological responses to conservation practices in a catchment of the loess plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 1885–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.D. Landscapes and riverscapes: The influence of land use on stream ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2004, 35, 257–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delin, H. The progress of research on oasis in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 1999, 19, 313–319. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, C.; Fang, C. Water resources constraint force on urbanization in water deficient regions: A case study of the Hexi Corridor, arid area of NW China. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 62, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goward, S.N.; Tucker, C.J.; Dye, D.G. North american vegetation patterns observed with the NOAA-7 advanced very high resolution radiometer. Plant Ecol. 1985, 64, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justice, C.O.; Townshend, J.; Holben, B.; Tucker, E.C. Analysis of the phenology of global vegetation using meteorological satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1985, 6, 1271–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townshend, J.R.; Goff, T.E.; Tucker, C.J. Multitemporal dimensionality of images of normalized difference vegetation index at continental scales. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1985, GE-23, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J.; Vanpraet, C.L.; Sharman, M.; Van Ittersum, G. Satellite remote sensing of total herbaceous biomass production in the senegalese sahel: 1980–1984. Remote Sens. Environ. 1985, 17, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J.; Nicholson, S.E. Variations in the size of the sahara desert from 1980 to 1997. Ambio 1999, 28, 587–591. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, J.; Geerken, R. Discrimination between climate and human-induced dryland degradation. J. Arid Environ. 2004, 57, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, L.; Eklundh, L.; Ardö, J. A recent greening of the sahel—Trends, patterns and potential causes. J. Arid Environ. 2005, 63, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Dent, D.; Olsson, L.; Schaepman, M. Global Assessment of Land Degradation and Improvement: 1. Identification by Remote Sensing; FAO-Food and Agriculture Organization/ISRIC-World Soil Information: Rome, Italy; Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nkonya, E.; Gerber, N.; Baumgartner, P.; von Braun, J.; De Pinto, A.; Graw, V.; Kato, E.; Kloos, J.; Walter, T. The Economics of Desertification, Land Degradation, and Drought toward An Integrated Global Assessment; Center for Development Research(ZEF): Bonn, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fensholt, R.; Rasmussen, K.; Kaspersen, P.; Huber, S.; Horion, S.; Swinnen, E. Assessing land degradation/recovery in the African sahel from long-term earth observation based primary productivity and precipitation relationships. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 664–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dardel, C.; Kergoat, L.; Hiernaux, P.; Grippa, M.; Mougin, E.; Ciais, P.; Nguyen, C.-C. Rain-use-efficiency: What it tells us about the conflicting sahel greening and sahelian paradox. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3446–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yengoh, G.T.; Dent, D.; Olsson, L.; Tengberg, A.E.; Tucker, C.J. Use of the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) to Assess Land Degradation at Multiple Scales: Current Status, Future Trends, and Practical Considerations; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 9–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, Y.; Balzter, H.; Kaduk, J.; Tucker, C. Land degradation assessment using residual trend analysis of gimms NDVI3g, soil moisture and rainfall in sub-saharan west Africa from 1982 to 2012. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5471–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Houerou, H.N. Rain use efficiency: A unifying concept in arid-land ecology. J. Arid Environ. 1984, 7, 213–247. [Google Scholar]
- Symeonakis, E.; Drake, N. Monitoring desertification and land degradation over sub-saharan Africa. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 573–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fensholt, R.; Rasmussen, K. Analysis of trends in the sahelian ‘rain-use efficiency’ using gimms NDVI, RFE and GPCP rainfall data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Satellite-based estimates of groundwater depletion in the Badain Jaran Desert, China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, Z.; Huete, A.; Ma, X.; Restrepo-Coupe, N.; Devadas, R.; Clarke, K.; Lewis, M. Landsat and grace observations of arid wetland dynamics in a dryland river system under multi-decadal hydroclimatic extremes. J. Hydrol. 2016, 543, 818–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyisa, G.L.; Meilby, H.; Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Automated water extraction index: A new technique for surface water mapping using landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulbure, M.G.; Broich, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Kommareddy, A. Surface water extent dynamics from three decades of seasonally continuous landsat time series at subcontinental scale in a semi-arid region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, N.; Chen, H.; Dong, C.; Zhang, H. Study on the boundary and the area of Badain Jaran Desert based on remote sensing imagery. Prog. Geogr. 2010, 29, 1087–1094. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, X. Geomorphology of the megadunes in the Badain Jaran Desert. Geomorphology 2004, 60, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Edmunds, W.M. Groundwater and lake evolution in the Badain Jaran Desert ecosystem, Inner Mongolia. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Williams, M.A. The ion chemistry of lakes and late holocene desiccation in the Badain Jaran Desert, inner mongolia, China. Catena 2003, 51, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Lu, Y.; Lü, X.; Chang, J. Hydrochemical characteristics and recharge sources of lake nuoertu in the Badain Jaran Desert. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.A.; Ning, K.; Li, Z.L.; Wang, Y.X.; Jia, P.; Ma, L. Holocene high lake-levels and pan-lake period onBadain Jaran Desert. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2016, 59, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, S.C. GRACE Monthly Land Water Mass Grids NETCDF RELEASE 5.0. Available online: https://podaac.jpl.nasa.gov/dataset/TELLUS_LAND_NC_RL05 (accessed on 5 December 2017).
- Gent, P.R.; Danabasoglu, G.; Donner, L.J.; Holland, M.M.; Hunke, E.C.; Jayne, S.R.; Lawrence, D.M.; Neale, R.B.; Rasch, P.J.; Vertenstein, M.; et al. The community climate system model version 4. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 4973–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, D.M.; Oleson, K.W.; Flanner, M.G.; Thornton, P.E.; Swenson, S.C.; Lawrence, P.J.; Zeng, X.; Yang, Z.-L.; Levis, S.; Sakaguchi, K.; et al. Parameterization improvements and functional and structural advances in version 4 of the community land model. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2011, 3, M03001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landerer, F.W.; Swenson, S.C. Accuracy of scaled grace terrestrial water storage estimates. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Yang, Y.; Wada, Y.; Hong, Y.; Liang, W.; Chen, Y.; Yong, B.; Hou, A.; Wei, J.; Chen, L. Deriving scaling factors using a global hydrological model to restore grace total water storage changes for China’s Yangtze river basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 168, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Meteorological Data Service Center (CMDC). Available online: http://data.cma.cn/data/detail/dataCode/SURF_CLI_CHN_PRE_MON_GRID_0.5/ (accessed on 5 December 2017).
- Bookstein, F.L. Principal warps: Thin-plate splines and the decomposition of deformations. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1989, 11, 567–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Y.; Li, X.; Lu, L. Land Cover Products of China. Available online: http://westdc.westgis.ac.cn/data/f1aaacad-9f42-474e-478aa474-d437f437d6482f (accessed on 5 December 2017).
- NASA LP DAAC, STRM. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/data_access/data_pool (accessed on 5 December 2017).
- Rouse, J.W., Jr.; Haas, R.; Schell, J.; Deering, D. Monitoring vegetation systems in the great plains with erts. NASA Spec. Publ. 1974, 351, 309. [Google Scholar]
- NASA LP DAAC, MODIS. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/data_access/data_pool (accessed on 5 December 2017).
- Solano, R.; Didan, K.; Jacobson, A.; Huete, A. Modis Vegetation Index User’s Guide (Mod13 Series); Vegetation Index and Phenology Lab, The University of Arizona: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2010; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- USGS, GloVis. Available online: https://glovis.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 5 December 2017).
- Jiang, H.; Feng, M.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, N.; Huang, J.; Xiao, T. An automated method for extracting rivers and lakes from landsat imagery. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 5067–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.; Flood, N.; Danaher, T. Comparing landsat water index methods for automated water classification in eastern Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justice, C.; Dugdale, G.; Townshend, J.; Narracott, A.; Kumar, M. Synergism between NOAA-AVHRR and meteosat data for studying vegetation development in semi-arid west Africa. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1991, 12, 1349–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, S.D.; Colstoun, D.; Brown, E.; Kravitz, L. Evidence from rain-use efficiencies does not indicate extensive sahelian desertification. Glob. Chang. Biol. 1998, 4, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, S.D.; Justice, C.O. Coarse resolution remote sensing of the Sahelian environment. Int. J. Remote Sens 1991, 12, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, M.S. Developing simple, operational, consistent NDVI-vegetation models by applying environmental and climatic information: Part I. Assessment of net primary production. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 97–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fensholt, R.; Sandholt, I.; Rasmussen, M.S.; Stisen, S.; Diouf, A. Evaluation of satellite based primary production modelling in the semi-arid sahel. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.; Vanpraet, C.; Boerwinkel, E.; Gaston, A. Satellite remote sensing of total dry matter production in the senegalese sahel. Remote Sens. Environ. 1983, 13, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verón, S.R.; Oesterheld, M.; Paruelo, J.M.; Díaz, S. Production as a function of resource availability: Slopes and efficiencies are different. J. Veg. Sci. 2005, 16, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malo, A.R.; Nicholson, S.E. A study of rainfall and vegetation dynamics in the African sahel using normalized difference vegetation index. J. Arid Environ. 1990, 19, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Rich, P.M.; Price, K.P. Temporal responses of NDVI to precipitation and temperature in the central great plains, USA. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 2345–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, R.B.; Cleveland, W.S.; McRae, J.E.; Terpenning, I. Stl: A seasonal-trend decomposition procedure based on loess. J. Off. Stat. 1990, 6, 3–73. [Google Scholar]
- Donchyts, G.; Baart, F.; Winsemius, H.; Gorelick, N.; Kwadijk, J.; van de Giesen, N. Earth’s surface water change over the past 30 years. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 810–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Famiglietti, J.S.; Rodell, M. Water in the balance. Science 2013, 340, 1300–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richey, A.S.; Thomas, B.F.; Lo, M.H.; Reager, J.T.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Voss, K.; Swenson, S.; Rodell, M. Quantifying renewable groundwater stress with GRACE. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 5217–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wilson, C.; Tapley, B.; Scanlon, B.; Güntner, A. Long-term groundwater storage change in Victoria, Australia from satellite gravity and in situ observations. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 139, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Zhang, Z.; Save, H.; Wiese, D.N.; Landerer, F.W.; Long, D.; Longuevergne, L.; Chen, J. Global evaluation of new GRACE mascon products for hydrologic applications. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 9412–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, S.; Yeh, P.J.F.; Wahr, J.; Famiglietti, J. A comparison of terrestrial water storage variations from grace with in situ measurements from Illinois. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L16401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, G.S.; Sadler, R.; Fleming, K.; Tregoning, P.; Hinz, C.; Veneklaas, E.J. Tropical cyclones and the ecohydrology of Australia’s recent continental-scale drought. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L03404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, M.J.; Tregoning, P.; Ramillien, G.; Tweed, S.O.; Fakes, A. Basin-scale, integrated observations of the early 21st century multiyear drought in southeast Australia. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Velicogna, I.; Famiglietti, J.S. Satellite-based estimates of groundwater depletion in India. Nature 2009, 460, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, D.; Longuevergne, L.; Scanlon, B.R. Global analysis of approaches for deriving total water storage changes from grace satellites. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 2574–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richey, A.S.; Thomas, B.F.; Lo, M.H.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Swenson, S.; Rodell, M. Uncertainty in global groundwater storage estimates in a total groundwater stress framework. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 5198–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, A.Y. Predicting groundwater level changes using grace data. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 5900–5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Tregoning, P.; Renzullo, L.J.; van Dijk, A.I.; Walker, J.P.; Pauwels, V.; Allgeyer, S. Improved water balance component estimates through joint assimilation of grace water storage and smos soil moisture retrievals. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 1820–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Huete, A.; Restrepo-Coupe, N.; Ma, X.; Devadas, R.; Caprarelli, G. Spatial partitioning and temporal evolution of Australia’s total water storage under extreme hydroclimatic impacts. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 183, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Donohue, R.J.; McVicar, T.R.; Roderick, M.L.; Beck, H.E. Long-term CO2 fertilization increases vegetation productivity but has little effect on hydrological partitioning in tropical rainforests. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 2125–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N.J.; Thomas, D.S. World Atlas of Desertification; Edward Arnold: London, UK, 1992; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Modaihsh, A.S.; Horton, R.; Kirkham, D. Soil water evaporation suppression by sand mulches. Soil Sci. 1985, 139, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, H. Changes of groundwater resources in recent 50 years and their impact on ecological environment in Hexi corridor. J. Nat. Resour. 2002, 17, 691–697. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.Z.; Wang, X.S.; Edmunds, W.M. The characteristics of ground-water resources and their changes under the impacts of human activity in the arid northwest China—A case study of the shiyang river basin. J. Arid Environ. 2005, 61, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Fan, S.; Zhou, L.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, K.; Feng, J. The temporal change of driving factors during the course of land desertification in arid region of north China: The case of minqin county. Environ. Geol. 2006, 51, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, J.; Kubota, J.; Chen, L. Effects of land-use changes on hydrological processes in the middle basin of the Heihe river, northwest China. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 1370–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, K.J.; Prince, S.; Malherbe, J.; Small, J.; Frost, P.; VanZyl, D. Can human-induced land degradation be distinguished from the effects of rainfall variability? A case study in south Africa. J. Arid Environ. 2007, 68, 271–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Tao, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, C. The impact of climate change and anthropogenic activities on alpine grassland over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 189, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.-S.; Zheng, C. Analysis of groundwater-lake interaction by distributed temperature sensing in Badain Jaran Desert, northwest China. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Wang, N.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Chen, L.; Ma, N. New observational and experimental evidence for the recharge mechanism of the lake group in the Alxa Desert, north-central China. J. Arid Environ. 2016, 124, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, B.X.; Zhou, Y.; Hao, C.; Wan, L. Groundwater contributions in water-salt balances of the lakes in the Badain Jaran Desert, China. J. Arid Land 2016, 8, 694–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Jiao, J.J.; Wang, X.; Liu, K. Temporal 222Rn distributions to reveal groundwater discharge into desert lakes: Implication of water balance in the Badain Jaran Desert, China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 534, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.S.; Li, L.; Wang, J.Y.; Barry, D.; Sheng, X.F.; Gu, W.Z.; Zhao, X.; Chen, L. Water resources: Groundwater maintains dune landscape. Nature 2004, 432, 459–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarihani, A.A.; Callow, J.N.; Johansen, K.; Gouweleeuw, B. Evaluation of multiple satellite altimetry data for studying inland water bodies and river floods. J. Hydrol. 2013, 505, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z. A study on life cycle of desert tourist area—A case study of Badain Jaran Desert. Econ. Geogr. 2011, 31, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Normile, D. Getting at the roots of killer dust storms. Science 2007, 317, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, W. Anthropogenic salinisation of inland waters. Hydrobiologia 2001, 466, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, K.A.; Jobbágy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. Effects of afforestation on water yield: A global synthesis with implications for policy. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomer, R.J.; Trabucco, A.; Bossio, D.A.; Verchot, L.V. Climate change mitigation: A spatial analysis of global land suitability for clean development mechanism afforestation and reforestation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2008, 126, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, B.P.; Sorice, M.G.; Young, M.H. Dryland ecohydrology in the anthropocene: Taking stock of human–ecological interactions. Geogr. Compass 2011, 5, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Wang, N.; Xie, Z.; Ma, X.; Huete, A. Water Loss Due to Increasing Planted Vegetation over the Badain Jaran Desert, China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010134
Zhang X, Wang N, Xie Z, Ma X, Huete A. Water Loss Due to Increasing Planted Vegetation over the Badain Jaran Desert, China. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(1):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010134
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xunhe, Nai’ang Wang, Zunyi Xie, Xuanlong Ma, and Alfredo Huete. 2018. "Water Loss Due to Increasing Planted Vegetation over the Badain Jaran Desert, China" Remote Sensing 10, no. 1: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010134
APA StyleZhang, X., Wang, N., Xie, Z., Ma, X., & Huete, A. (2018). Water Loss Due to Increasing Planted Vegetation over the Badain Jaran Desert, China. Remote Sensing, 10(1), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010134