Remote Sensing Image Classification Based on Stacked Denoising Autoencoder
Abstract
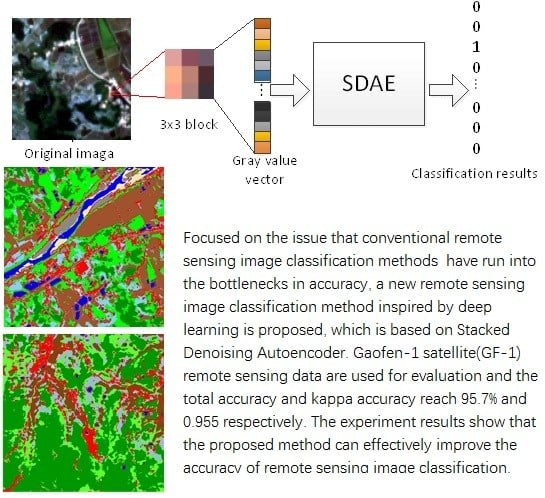
:1. Introduction
2. Stacked Denoising Autoencoder Model
2.1. Denoising Autoencoder
2.2. BP Neural Network
3. Remote Sensing Image Classification Method Based on SDAE
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Experimental Data
4.2. Evaluation Index for Classification Accuracy
4.3. Results and Discussion
- The impact of the amount of hidden layers in the network and the neural units per layer on remote sensing image classification results;
- The impact of the denoising process on classification ability of the model;
- Comparison with SVM and the conventional artificial neural network.
4.3.1. The Impact of the Amount of Hidden Layer and the Neurons per Layer
4.3.2. The Impact of Denoising Pre-Training on Classification Ability of the Model
4.3.3. Comparison with Conventional Remote Sensing Images Classification Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, K.; Li, Q.Z.; Tian, Y.C.; Wu, B.F. A Review of Classification Methods of Remote Sensing Imagery. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2011, 31, 2618–2623. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Han, D.; Rico-Ramirez, M.A.; Bray, M.; Islam, T. Selection of classification techniques for land use/land cover change investigation. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 50, 1250–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Ban, Y.F. Multi-temporal RADARSAT-2 polarimetric SAR data for urban land cover classification using an object based support vector machine and a rule-based approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazi, Y.; Melgani, F. Toward an optimal SVM classification system for hyperspectral remotesensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 3374–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Singh, D.; Yamaguchi, Y. Land cover classification of PALSAR images by knowledge based decision tree classifier and supervised classifiers based on SAR observables. Prog. Electromagn. Res. B 2011, 30, 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.; Yuan, X.P.; He, D.M. An application of vegetation classification in Northwest Yunnan with remote sensing expert classifier. J. Yunnan Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2003, 25, 553–557. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E.; Osindero, S. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput. 2006, 18, 1527–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengio, Y. Learning Deep Architectures for AI; Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning; Now Publishers Inc.: Hanover, MA, USA, 2009; Volume 2, pp. 1–127. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Hinton, G.E. Learning to detect roads in high resolution aerial images. In Proceedings of the 2010 European Conference Computer Vision, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; pp. 210–223. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Yu, L.; Tian, S.W.; Wang, Z.; Long, Y.U.; Tian, S.; Qian, Y.; Ding, J.; Yang, L. Water body extraction method based on stacked autoencoder. J. Comput. Appl. 2015, 35, 2706–2709. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Deng, C.; Huang, G.B.; Zhao, B. Compressed-domain ship detection on spaceborne optical image using deep neural network and extreme learning machine. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 1174–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Xia, G.S.; Hu, J.W. Transferring deep convolutional neural networks for the scene classification of high-resolution remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14680–14707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Längkvist, M.; Kiselev, A.; Alirezaie, M.; Loutfi, A. Classification and segmentation of satellite orthoimagery using convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y.Q. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4806–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Lu, H.; Mou, L. Learning a transferable change rule from a Recurrent Neural Network for Land Cover Change Detection. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Nakadai, K.; Okuno, H.G.; Ogata, T. Audio-visual speech recognition using deep learning. Appl. Intell. 2015, 42, 722–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, P.; Larochelle, H.; Lajoie, I.; Bengio, Y.; Manzagol, P.A. Stacked denoising autoencoders: Learning useful representations in a deep network with a local denoising criterion. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 3371–3408. [Google Scholar]
- Baldi, P. Autoencoders, unsupervised learning, and deep architecture. In Proceedings of the ICML Workshop on Unsupervised and Transfer, Bellevue, WA, USA, 2 July 2011; Volume 27, pp. 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagation errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Area | Class | SDAE | SVM | BP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flatland area | OA/% | 95.7 | 94.1 | 92.4 |
| KAPPA | 0.955 | 0.936 | 0.921 | |
| mountainous area | OA/% | 96.2 | 94.2 | 93.7 |
| KAPPA | 0.958 | 0.937 | 0.936 | |
| Computation Time/s | 51.2 | 47.1 | 58.4 |
| Class | Classification Result | Total | Accuracy/% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest | Water | Grass | RS | BL | SD | ARC | Crop | |||
| Forest | 720 | 0 | 16 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 740 | 97.3 |
| Water | 0 | 452 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 556 | 99.1 |
| Grass | 4 | 2 | 686 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 8 | 4 | 710 | 96.4 |
| RS | 2 | 18 | 0 | 450 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 4 | 484 | 93.0 |
| BL | 0 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 742 | 2 | 8 | 0 | 758 | 97.9 |
| SD | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 412 | 24 | 2 | 440 | 93.6 |
| ARC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 4 | 44 | 482 | 12 | 550 | 88.6 |
| Crop | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 646 | 662 | 97.6 |
| Total | 728 | 478 | 704 | 462 | 754 | 460 | 546 | 668 | 4800 | 100 |
| Class | Classification Result | Total | Accuracy/% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest | Water | Grass | RS | BL | SD | ARC | Crop | |||
| Forest | 2287 | 8 | 45 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 2352 | 97.2 |
| Water | 0 | 31 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 32 | 96.9 |
| Grass | 14 | 0 | 826 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 8 | 4 | 856 | 96.6 |
| RS | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| BL | 3 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 588 | 0 | 9 | 3 | 611 | 96.2 |
| SD | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| ARC | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 10 | 23 | 408 | 6 | 452 | 90.3 |
| Crop | 1 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 477 | 497 | 96.0 |
| Total | 2305 | 41 | 888 | 3 | 616 | 23 | 433 | 491 | 4800 | 100 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, P.; Shi, W.; Zhang, X. Remote Sensing Image Classification Based on Stacked Denoising Autoencoder. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010016
Liang P, Shi W, Zhang X. Remote Sensing Image Classification Based on Stacked Denoising Autoencoder. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Peng, Wenzhong Shi, and Xiaokang Zhang. 2018. "Remote Sensing Image Classification Based on Stacked Denoising Autoencoder" Remote Sensing 10, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010016
APA StyleLiang, P., Shi, W., & Zhang, X. (2018). Remote Sensing Image Classification Based on Stacked Denoising Autoencoder. Remote Sensing, 10(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010016