An Object Similarity-Based Thresholding Method for Urban Area Mapping from Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite Day/Night Band (VIIRS DNB) Data
Abstract
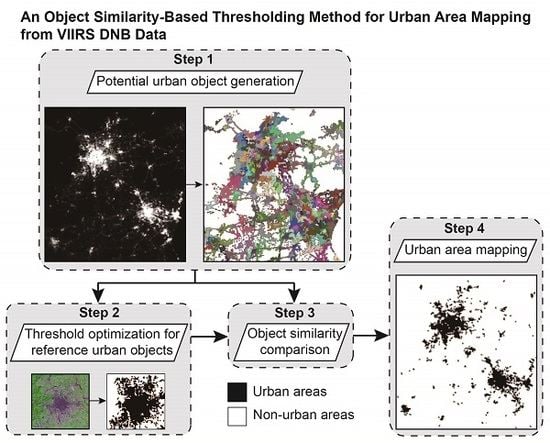
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Preprocessing
3. Methods
3.1. Potential Urban Object Generation
3.2. Threshold Optimization for Reference Urban Objects
3.3. Object Similarity Comparison
3.4. Urban Area Mapping
3.5. Validation
4. Results
4.1. Potential Urban Objects
4.2. Estimation of Thresholds for Potential Urban Objects
4.3. Urban Area Mapping Results
4.4. Accuracy Assessments
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2014 Revision, Highlights; Department of Economic and Social Affairs, UN: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Goudie, A. The Human Impact on the Natural Environment, 3rd ed.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Small, C. Global analysis of urban population distributions and the physical environment. In Proceedings of the Open Meeting of the Human Dimension of Global Environmental Change Research Community, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 6–8 October 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global change and the ecology of cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myint, S.W.; Gober, P.; Brazel, A.; Grossman-Clarke, S.; Weng, Q. Per-pixel vs. Object-based classification of urban land cover extraction using high spatial resolution imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 115, 1145–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R.; Landry, S.; Yu, Q. Object-based urban detailed land cover classification with high spatial resolution IKONOS imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 3285–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Weng, Q. Urban classification using full spectral information of Landsat ETM+ imagery in Marion County, Indiana. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2005, 71, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Friedl, M.A.; McIver, D.K.; Woodcock, C.E. Mapping urban areas by fusing multiple sources of coarse resolution remotely sensed data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, M.A.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Tan, B.; Schneider, A.; Ramankutty, N.; Sibley, A.; Huang, X. MODIS Collection 5 global land cover: Algorithm refinements and characterization of new datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontemps, S.; Defourny, P.; Bogaert, E.V.; Arino, O.; Kalogirou, V.; Perez, J.R. GlobCover 2009-Products Description and Validation Report; Université Catholique de Louvain (UCL): Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium; European Space Agency (ESA): Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tateishi, R.; Hoan, N.T.; Kobayashi, T.; Alsaaideh, B.; Tana, G.; Phong, D.X. Production of global land cover data-GLCNMO2008. J. Geogr. Geol. 2014, 6, 99–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.; Baugh, K.; Hobson, V.; Kihn, E.; Kroehl, H.; Davis, E.; Cocero, D. Satellite inventory of human settlements using nocturnal radiation emissions: A contribution for the global toolchest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 1997, 3, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Tuttle, B.T.; Sutton, P.S.; Baugh, K.E.; Howard, A.T.; Milesi, C.; Bhaduri, B.L.; Nemani, R. Global distribution and density of constructed impervious surfaces. Sensors 2007, 7, 1962–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Yang, X.; Gao, B.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Application of DMSP/OLS nighttime light images: A meta-analysis and a systematic literature review. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6844–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Smith, S.J.; Elvidge, C.D.; Zhao, K.; Thomson, A.; Imhoff, M. A cluster-based method to map urban area from DMSP/OLS nightlights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Smith, S.J.; Zhao, K.; Imhoff, M.; Thomson, A.; Bondlamberty, B.; Asrar, G.R.; Zhang, X.; He, C.; Elvidge, C.D. A global map of urban extent from nightlights. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 054011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y. Urban mapping using dmsp/ols stable night-time light: A review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K. Mapping urban structure and spatial connectivity with VIIRS and OLS night light imagery. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2013 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Sao Paulo, Brazil, 21–23 April 2013; pp. 230–233. [Google Scholar]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.-C. Why VIIRS data are superior to DMSP for mapping nighttime lights. In Proceedings of the 35th Asia-Pacific Advanced Network, Honolulu, HI, USA, 13–18 January 2013; pp. 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.D.; Straka, W.; Mills, S.P.; Elvidge, C.D.; Lee, T.F.; Solbrig, J.; Walther, A.; Heidinger, A.K.; Weiss, S.C. Illuminating the capabilities of the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (NPP) Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) Day/Night Band. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6717–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Bai, Y. Quantitative analysis of VIIRS DNB nightlight point source for light power estimation and stability monitoring. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11915–11935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Huang, C.; Yu, B.; Yin, B.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J. Evaluation of NPP-VIIRS night-time light composite data for extracting built-up urban areas. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaturapitpornchai, R.; Kasetkasem, T.; Kumazawa, I.; Rakwatin, P.; Chanwimaluang, T. A level-based method for urban mapping using NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2015 6th International Conference of Information and Communication Technology for Embedded Systems (IC-ICTES), Hua-Hin, Thailand, 22–24 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Weng, Q.; Weng, A. A comparative study of NPP-VIIRS and DMSP-OLS nighttime light imagery for derivation of urban demographic metrics. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2014 Third International Workshop on Earth Observation and Remote Sensing Applications (EORSA), Changsha, China, 11–14 June 2014; pp. 335–339. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X. Mapping Regional Land Cover and Land Use Change Using MODIS Time Series; Boston University: Boston, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.C.; Tateishi, R.; Hara, K.; Gharechelou, S.; Iizuka, K. Global mapping of urban built-up areas of year 2014 by combining MODIS multispectral data with VIIRS nighttime light data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2016, 9, 1004–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Haynie, S.; Xu, T. Diverse relationships between Suomi-NPP VIIRS night-time light and multi-scale socioeconomic activity. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Shao, X.; Cao, C.; Fu, X.; Yan, L. Comparison between the Suomi-NPP Day-Night Band and DMSP-OLS for correlating socio-economic variables at the provincial level in China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Li, C. Potential of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light imagery for modeling the regional economy of China. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3057–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yin, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, J. Evaluating the ability of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data to estimate the gross domestic product and the electric power consumption of China at multiple scales: A comparison with DMSP-OLS data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1705–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, S.; Takeuchi, W.; Hatoyama, K.; Mazurov, Y. Socio-economic impact of Trans-Siberian railway after the collapse of Soviet Union by integrated spatial data analysis. In Proceedings of the 8th IGRSM International Conference and Exhibition on Remote Sensing & GIS (IGRSM 2016), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–14 April 2016; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, M.L.; Melaas, E.K.; Malik, A. Using VIIRS Day/Night Band to measure electricity supply reliability: Preliminary results from Maharashtra, India. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Aegerter, C.; Xu, X.; Szykman, J.J. Potential application of VIIRS Day/Night Band for monitoring nighttime surface PM2.5 air quality from space. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, P.; Takeuchi, W. Analysis of air quality and nighttime light for Indian urban regions. In Proceedings of the 8th IGRSM International Conference and Exhibition on Remote Sensing & GIS (IGRSM 2016), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–14 April 2016; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Shi, H.; Yu, H.; Yang, P. Inversion of nighttime PM2.5 mass concentration in Beijing based on the VIIRS Day-Night Band. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Lu, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. Mapping impervious surface distribution with integration of SNNP VIIRS-DNB and MODIS NDVI data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12459–12477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.S.; Zhang, J.; Hyer, E.J.; Miller, S.D.; Reid, J.S. Preliminary investigations toward nighttime aerosol optical depth retrievals from the VIIRS Day/Night Band. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Li, W. Evaluation of NPP-VIIRS nighttime night data for mapping global fossil fuel combustion CO2 emissions: A comparison with DMSP-OLS nighttime light data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Shi, K.; Wu, J. Estimating house vacancy rate in metropolitan areas using NPP-VIIRS nighttime light composite data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 2188–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Zhizhin, M.; Baugh, K.; Hsu, F.-C. Automatic boat identification system for VIIRS low light imaging data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 3020–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Shuai, G.; Liu, H. Support vector data description model to map urban extent from National Polar-Orbiting Partnership Satellite–Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite nightlights and normalized difference vegetation index. J. App. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 026012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Weng, Q. Updating urban extents with nighttime light imagery by using an object-based thresholding method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, M.; Yeh, E.T.; Gong, P.; Elvidge, C.; Baugh, K. Validation of urban boundaries derived from global night-time satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Tian, H.; Zhou, G.; Ge, H. Regional mapping of human settlements in southeastern China with multisensor remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3668–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.H.; Song, S. Rural–urban migration and urbanization in China: Evidence from time-series and cross-section analyses. China Econ. Rev. 2003, 14, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Huang, J.; Rozelle, S.; Uchida, E. Growth, population and industrialization, and urban land expansion of China. J. Urban Econ. 2008, 63, 96–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. Analysis on the difference of the developing level of the regional urbanization in China. Popul. J. 2002, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, C.; Wang, Z. The study on comprehensive evaluation and urbanization division at county level in China. Geog. Res. 2012, 31, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, S.; Chen, Y. Spatio-temporal change of urban–rural equalized development patterns in China and its driving factors. J. Rural Stud. 2013, 32, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The State Council of China. Notice on Adjusting the Classification Standards of Urban Sizes. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2014-11/20/content_9225.htm (accessed on 7 February 2018).
- Homer, C.; Dewitz, J.; Yang, L.; Jin, S.; Danielson, P.; Xian, G.; Coulston, J.; Herold, N.; Wickham, J.; Megown, K. Completion of the 2011 National Land Cover Database for the conterminous United States–Representing a decade of land cover change information. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2015, 81, 345–354. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, A.; Woodcock, C.E. Compact, dispersed, fragmented, extensive? A comparison of urban growth in twenty-five global cities using remotely sensed data, pattern metrics and census information. Urban Stud. 2008, 45, 659–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook 2014; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Neubert, M.; Herold, H.; Meinel, G. Assessing image segmentation quality–concepts, methods and application. In Object-Based Image Analysis; Blaschke, T., Lang, S., Hay, G.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 769–784. [Google Scholar]
- Blaschke, T. Object based image analysis for remote sensing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, P.; Wang, X. A new segmentation method for very high resolution imagery using spectral and morphological information. ISPRS J. Photogram. Remote Sens. 2015, 101, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J. A survey on evaluation methods for image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 1996, 29, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baatz, M.; Schäpe, A. Multiresolution segmentation: An optimization approach for high quality multi-scale image segmentation. In Angewandte Geographische Informationsverarbeitung XII, 1st ed.; Strobl, J., Blaschke, T., Griesebner, G., Eds.; Herbert Wichmann Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Mahalanobis, P.C. On the generalised distance in statistics. Proc. Nat. Inst. Sci. 1936, 2, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Elmore, K.L.; Richman, M.B. Euclidean distance as a similarity metric for principal component analysis. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.W.; Lin, C.; Forsman, A.; Avdic, A.; Åkerblom, L. An Euclidean similarity measure approach for hotel rating data analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing and Big Data Analysis, Chengdu, China, 28–30 April 2017; pp. 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, S.; Nie, F.; Zhang, C. Learning a mahalanobis distance metric for data clustering and classification. Pattern Recognit. 2008, 41, 3600–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, P.M.; Hirzer, M.; Köstinger, M.; Beleznai, C.; Bischof, H. Mahalanobis distance learning for person re-identification. In Person Re-Identification; Springer: London, UK, 2014; pp. 247–267. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Chen, J.; Imura, H.; Higashi, O. A SVM-based method to extract urban areas from DMSP-OLS and SPOT VGT data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2205–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Test | Reference Urban Objects | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Training | 256 | 152 | 214 | 29 |
| Validation | 462 | 209 | 260 | 39 | |
| 2 | Training | 368 | 117 | 202 | 32 |
| Validation | 350 | 244 | 272 | 36 | |
| 3 | Training | 285 | 84 | 226 | 35 |
| Validation | 433 | 277 | 248 | 33 | |
| 4 | Training | 357 | 146 | 262 | 32 |
| Validation | 361 | 215 | 212 | 36 | |
| 5 | Training | 239 | 223 | 220 | 17 |
| Validation | 479 | 138 | 254 | 51 |
| City Group | City | City-Optimized Method | Logistic Regression Method | Object Similarity-Based Method | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ED | MD | ||||||||||
| OA (%) | Kappa | OA (%) | Kappa | OA (%) | Kappa | OA (%) | Kappa | ||||
| 1 | Beijing | 81.26 | 0.62 | 73.97 ± 1.244 | 0.47 ± 0.027 | 76.46 ± 0.731 | 0.52 ± 0.015 | 76.33 ± 0.403 | 0.52 ± 0.007 | ||
| Hong Kong | 91.41 | 0.69 | 73.41 ± 2.542 | 0.40 ± 0.030 | 80.17 ± 0.330 | 0.50 ± 0.006 | 77.22 ± 2.685 | 0.43 ± 0.036 | |||
| Nanjing | 89.82 | 0.72 | 83.64 ± 0.415 | 0.56 ± 0.011 | 87.17 ± 0.882 | 0.64 ± 0.022 | 86.81 ± 1.449 | 0.64 ± 0.034 | |||
| Shenyang | 83.57 | 0.66 | 76.52 ± 0.523 | 0.51 ± 0.003 | 78.34 ± 0.658 | 0.54 ± 0.011 | 78.75 ± 1.416 | 0.55 ± 0.033 | |||
| Wuhan | 89.77 | 0.70 | 79.90 ± 2.129 | 0.50 ± 0.021 | 83.14 ± 1.943 | 0.56 ± 0.036 | 80.48 ± 2.221 | 0.51 ± 0.039 | |||
| Xi’an | 85.96 | 0.70 | 80.13 ± 0.706 | 0.58 ± 0.012 | 83.44 ± 0.161 | 0.64 ± 0.003 | 82.44 ± 1.969 | 0.63 ± 0.04 | |||
| Chengdu | 88.65 | 0.73 | 75.08 ± 2.763 | 0.49 ± 0.036 | 81.16 ± 1.861 | 0.58 ± 0.028 | 74.87 ± 5.019 | 0.48 ± 0.082 | |||
| Chongqing | 84.38 | 0.63 | 74.00 ± 1.847 | 0.44 ± 0.028 | 79.95 ± 1.481 | 0.53 ± 0.030 | 78.06 ± 3.205 | 0.52 ± 0.045 | |||
| Tianjin | 88.30 | 0.63 | 81.79 ± 1.360 | 0.50 ± 0.020 | 86.01 ± 1.161 | 0.58 ± 0.018 | 86.18 ± 0.947 | 0.58 ± 0.015 | |||
| Guangzhou & Foshan | 75.69 | 0.49 | 67.44 ± 2.002 | 0.36 ± 0.020 | 70.85 ± 2.908 | 0.42 ± 0.044 | 67.44 ± 5.231 | 0.37 ± 0.079 | |||
| 2 | Changchun | 84.29 | 0.67 | 75.11 ± 2.120 | 0.50 ± 0.035 | 76.14 ± 3.347 | 0.53 ± 0.052 | 77.55 ± 5.629 | 0.55 ± 0.100 | ||
| Hangzhou | 83.69 | 0.63 | 77.73 ± 0.829 | 0.52 ± 0.006 | 79.64 ± 0.910 | 0.54 ± 0.006 | 78.48 ± 2.108 | 0.53 ± 0.016 | |||
| Harbin | 91.59 | 0.70 | 86.72 ± 1.182 | 0.58 ± 0.022 | 90.71 ± 0.218 | 0.67 ± 0.008 | 91.15 ± 0.282 | 0.70 ± 0.010 | |||
| Jinan | 91.09 | 0.74 | 85.14 ± 0.274 | 0.56 ± 0.031 | 87.98 ± 1.775 | 0.64 ± 0.043 | 87.36 ± 0.539 | 0.60 ± 0.013 | |||
| Suzhou | 83.39 | 0.67 | 78.87 ± 0.469 | 0.58 ± 0.009 | 80.77 ± 0.456 | 0.62 ± 0.009 | 80.38 ± 0.563 | 0.61 ± 0.011 | |||
| Xuzhou | 87.53 | 0.66 | 81.09 ± 0.832 | 0.49 ± 0.024 | 85.66 ± 0.639 | 0.57 ± 0.012 | 85.48 ± 0.317 | 0.55 ± 0.016 | |||
| Zhengzhou | 86.43 | 0.65 | 78.88 ± 1.137 | 0.50 ± 0.012 | 82.58 ± 1.197 | 0.57 ± 0.023 | 82.05 ± 2.852 | 0.56 ± 0.059 | |||
| 3 | Changde | 94.29 | 0.78 | 83.83 ± 0.437 | 0.38 ± 0.052 | 90.40 ± 2.756 | 0.64 ± 0.049 | 92.22 ± 1.551 | 0.69 ± 0.059 | ||
| Fuzhou | 89.08 | 0.74 | 83.58 ± 0.370 | 0.60 ± 0.019 | 87.02 ± 1.908 | 0.68 ± 0.054 | 86.34 ± 0.909 | 0.66 ± 0.025 | |||
| Guiyang | 92.38 | 0.69 | 90.10 ± 0.365 | 0.58 ± 0.029 | 91.99 ± 0.424 | 0.63 ± 0.030 | 91.51 ± 0.177 | 0.60 ± 0.011 | |||
| Haikou | 90.16 | 0.65 | 82.98 ± 1.864 | 0.46 ± 0.027 | 87.63 ± 1.107 | 0.57 ± 0.017 | 87.72 ± 0.847 | 0.57 ± 0.027 | |||
| Hefei | 90.83 | 0.73 | 86.68 ± 0.156 | 0.65 ± 0.004 | 89.71 ± 0.871 | 0.71 ± 0.020 | 89.57 ± 0.555 | 0.71 ± 0.015 | |||
| Hohhot | 86.22 | 0.70 | 75.52 ± 2.595 | 0.49 ± 0.027 | 84.20 ± 0.990 | 0.64 ± 0.035 | 82.84 ± 0.726 | 0.61 ± 0.032 | |||
| Kunming | 91.06 | 0.77 | 84.17 ± 0.566 | 0.62 ± 0.016 | 87.94 ± 0.226 | 0.70 ± 0.006 | 89.11 ± 0.204 | 0.73 ± 0.005 | |||
| Lanzhou | 91.82 | 0.79 | 86.60 ± 0.358 | 0.67 ± 0.010 | 88.94 ± 0.500 | 0.70 ± 0.008 | 88.02 ± 2.079 | 0.68 ± 0.058 | |||
| Nanchang | 88.81 | 0.73 | 85.32 ± 0.914 | 0.63 ± 0.039 | 84.07 ± 3.017 | 0.56 ± 0.111 | 85.51 ± 0.379 | 0.62 ± 0.022 | |||
| Nanning | 87.49 | 0.67 | 80.80 ± 2.114 | 0.53 ± 0.021 | 85.49 ± 1.301 | 0.63 ± 0.039 | 85.37 ± 2.559 | 0.63 ± 0.090 | |||
| Nanyang | 85.76 | 0.66 | 75.22 ± 1.011 | 0.43 ± 0.006 | 82.62 ± 2.220 | 0.56 ± 0.067 | 82.26 ± 1.914 | 0.58 ± 0.028 | |||
| Shijiazhuang | 82.86 | 0.63 | 76.43 ± 0.394 | 0.46 ± 0.007 | 78.41 ± 0.989 | 0.48 ± 0.032 | 80.49 ± 1.650 | 0.54 ± 0.050 | |||
| Urumqi | 91.60 | 0.77 | 86.21 ± 0.778 | 0.62 ± 0.014 | 88.66 ± 0.645 | 0.66 ± 0.023 | 88.11 ± 0.725 | 0.65 ± 0.034 | |||
| Wenzhou | 90.19 | 0.69 | 84.31 ± 0.834 | 0.53 ± 0.002 | 87.36 ± 1.175 | 0.60 ± 0.016 | 88.14 ± 0.157 | 0.60 ± 0.012 | |||
| Xiamen | 89.87 | 0.70 | 79.02 ± 2.878 | 0.50 ± 0.044 | 80.47 ± 4.066 | 0.53 ± 0.064 | 79.79 ± 7.477 | 0.53 ± 0.128 | |||
| Xining | 93.45 | 0.78 | 89.03 ± 0.211 | 0.60 ± 0.016 | 89.44 ± 0.756 | 0.59 ± 0.003 | 91.33 ± 0.847 | 0.65 ± 0.044 | |||
| Yichang | 92.90 | 0.69 | 84.89 ± 2.150 | 0.47 ± 0.034 | 91.18 ± 0.431 | 0.65 ± 0.002 | 90.77 ± 1.004 | 0.62 ± 0.043 | |||
| Yinchuan | 89.74 | 0.72 | 78.83 ± 1.372 | 0.49 ± 0.008 | 85.71 ± 0.834 | 0.62 ± 0.002 | 88.34 ± 0.398 | 0.69 ± 0.014 | |||
| 4 | Bengbu | 90.27 | 0.66 | 86.38 ± 0.410 | 0.53 ± 0.038 | 89.06 ± 1.280 | 0.60 ± 0.052 | 89.83 ± 0.920 | 0.62 ± 0.052 | ||
| Chaoyang | 87.18 | 0.64 | 77.41 ± 1.532 | 0.36 ± 0.067 | 83.49 ± 1.471 | 0.43 ± 0.078 | 82.85 ± 3.157 | 0.40 ± 0.135 | |||
| Chengde | 92.22 | 0.60 | 88.71 ± 0.104 | 0.47 ± 0.010 | 92.16 ± 0.502 | 0.54 ± 0.049 | 91.96 ± 1.535 | 0.47 ± 0.171 | |||
| Hengyang | 89.05 | 0.67 | 77.66 ± 1.039 | 0.36 ± 0.047 | 85.87 ± 0.297 | 0.50 ± 0.069 | 86.15 ± 0.537 | 0.50 ± 0.068 | |||
| Jingdezhen | 94.13 | 0.74 | 90.66 ± 0.356 | 0.48 ± 0.035 | 91.85 ± 0.477 | 0.53 ± 0.038 | 91.98 ± 0.210 | 0.54 ± 0.014 | |||
| Lhasa | 87.70 | 0.60 | 82.01 ± 0.940 | 0.56 ± 0.017 | 83.86 ± 1.666 | 0.56 ± 0.032 | 85.78 ± 0.939 | 0.59 ± 0.018 | |||
| Linfen | 78.33 | 0.55 | 75.14 ± 0.594 | 0.46 ± 0.023 | 75.84 ± 0.785 | 0.47 ± 0.020 | 73.47 ± 1.375 | 0.41 ± 0.041 | |||
| Mudanjiang | 93.75 | 0.72 | 90.17 ± 0.185 | 0.58 ± 0.006 | 92.07 ± 0.770 | 0.59 ± 0.037 | 92.52 ± 0.696 | 0.63 ± 0.049 | |||
| Xingtai | 80.39 | 0.58 | 69.42 ± 0.735 | 0.30 ± 0.012 | 73.68 ± 6.937 | 0.35 ± 0.227 | 71.87 ± 9.671 | 0.29 ± 0.328 | |||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, W.; Li, P. An Object Similarity-Based Thresholding Method for Urban Area Mapping from Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite Day/Night Band (VIIRS DNB) Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020263
Ma W, Li P. An Object Similarity-Based Thresholding Method for Urban Area Mapping from Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite Day/Night Band (VIIRS DNB) Data. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(2):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020263
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Wenting, and Peijun Li. 2018. "An Object Similarity-Based Thresholding Method for Urban Area Mapping from Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite Day/Night Band (VIIRS DNB) Data" Remote Sensing 10, no. 2: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020263
APA StyleMa, W., & Li, P. (2018). An Object Similarity-Based Thresholding Method for Urban Area Mapping from Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite Day/Night Band (VIIRS DNB) Data. Remote Sensing, 10(2), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020263