Delineating Spatial Patterns in Human Settlements Using VIIRS Nighttime Light Data: A Watershed-Based Partition Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. VIIRS Nighttime Light Data
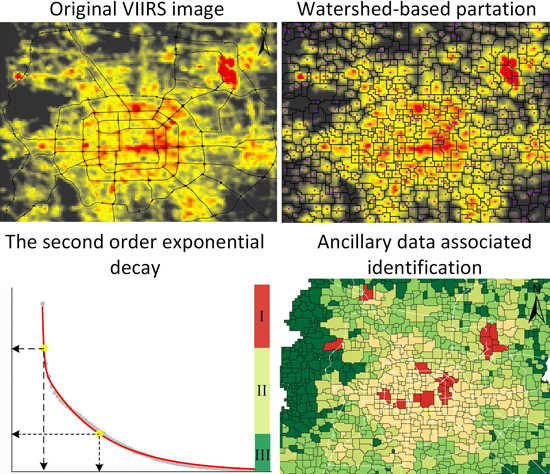
2.2. Ancillary Data
2.3. Watershed-Based Partition of VIIRS Images
2.4. The Second Order Exponential Decay Model
2.5. Further Identification Based on the Bivariate Relationship
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparisons of Different Types of Nighttime Lighting Areas
3.2. City-Level Characteristics of Nightlight Partitions
3.3. Regional-Level Patterns of Human Settlement
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Region | Type | Residential | Financial | Shopping | Transportation | Agricultural |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U01 | I | 1.14 +++ | 1.27 +++ | 1.49 +++ | 0.80 −−− | 0.14 −−− |
| III-II | 0.19 −−− | 0.31 −−− | 0.31 −−− | 1.45 +++ | 4.52 +++ | |
| U02 | I | 1.22 +++ | 1.32 +++ | 1.37 +++ | 1.12 +++ | 0.33 −−− |
| III-II | 0.22 −−− | 0.78 −−− | 0.49 −−− | 0.77 −−− | 5.27 +++ | |
| U03 | I | 0.88 −−− | 1.27 +++ | 1.33 +++ | 1.12 +++ | 0.11 −−− |
| III-II | 0.26 −−− | 0.41 −−− | 0.31 −−− | 0.33 −−− | 5.62 +++ | |
| U04 | I | 1.22 +++ | 1.07 +++ | 1.27 +++ | 1.10 +++ | 0.13 −−− |
| III-II | 0.23 −−− | 0.89 −−− | 0.61 − | 0.43 −−− | 4.03 +++ | |
| U05 | I | 1.30 +++ | 1.01 | 0.81 −−− | 0.95 −−− | 0.41 −− |
| III-II | 0.23 −−− | 1.03 | 0.63 −−− | 0.87 −−− | 3.42 +++ | |
| U06 | I | 1.00 | 1.19 +++ | 1.11 + | 1.20 +++ | 0.16 −− |
| III-II | 0.52 −−− | 0.66 −−− | 0.45 −−− | 0.48 −−− | 3.51 +++ | |
| U07 | I | 1.27 +++ | 1.07 +++ | 0.60 −−− | 1.06 +++ | 0.00 −−− |
| III-II | 0.31 −−− | 0.77 −−− | 1.10 + | 0.81 −−− | 8.02 +++ | |
| U08 | I | 1.11 +++ | 1.06 +++ | 1.41 +++ | 0.81 −−− | 0.30 −−− |
| III-II | 0.39 −−− | 0.78 −−− | 0.36 −−− | 0.80 −−− | 3.85 +++ | |
| U09 | I | 0.95 | 1.32 +++ | 1.53 +++ | 0.89 −−− | 0.00 |
| III-II | 0.31 −−− | 0.74 −−− | 0.47 −−− | 1.13 +++ | 8.23 +++ | |
| U10 | I | 1.15 +++ | 1.19 +++ | 1.27 +++ | 0.96 −−− | 0.26 −−− |
| III-II | 0.12 −−− | 0.40 −−− | 0.44 −−− | 0.83 −−− | 1.93 + |
References
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global change and the ecology of cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, M. The effects of urban patterns on ecosystem function. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2005, 28, 168–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudie, A.S. The Human Impact on the Natural Environment: Past, Present, And Future; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jenerette, G.D.; Harlan, S.L.; Brazel, A.; Jones, N.; Larsen, L.; Stefanov, W.L. Regional relationships between surface temperature, vegetation, and human settlement in a rapidly urbanizing ecosystem. Landsc. Ecol. 2007, 22, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauleit, S.; Ennos, R.; Golding, Y. Modeling the environmental impacts of urban land use and land cover change—A study in Merseyside, UK. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2005, 71, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milesi, C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Nemani, R.R.; Running, S.W. Assessing the impact of urban land development on net primary productivity in the southeastern United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Elvidge, C.; Sutton, P.C.; Baugh, K.E.; Powell, R.; Anderson, S. Shedding light on the global distribution of economic activity. Open Geogr. J. 2010, 3, 148–161. [Google Scholar]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Kihn, E.A.; Kroehl, H.W.; Davis, E.R.; Davis, C.W. Relation between satellite observed visible-near infrared emissions, population, economic activity and electric power consumption. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, Y. Characterizing spatio-temporal dynamics of urbanization in China using time series of DMSP/OLS night light data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7708–7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Elvidge, C.D. Mapping decadal change in anthropogenic night light. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 7, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.M.; Smith, L.C. Advances in using multitemporal night-time lights satellite imagery to detect, estimate, and monitor socioeconomic dynamics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 176–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Seto, K.C. Mapping urbanization dynamics at regional and global scales using multi-temporal DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2320–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Kihn, E.A.; Kroehl, H.W.; Davis, E.R. Mapping city lights with nighttime data from the DMSP Operational Linescan System. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1997, 63, 727–734. [Google Scholar]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Cinzano, P.; Pettit, D.; Arvesen, J.; Sutton, P.; Small, C.; Nemani, R.; Longcore, T.; Rich, C.; Safran, J. The Nightsat mission concept. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 2645–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Yang, X.; Gao, B.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Application of DMSP/OLS nighttime light images: A meta-analysis and a systematic literature review. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6844–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, J.; Imura, H.; Higashi, O. A SVM-based method to extract urban areas from DMSP-OLS and SPOT VGT data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2205–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, M.; Yeh, E.T.; Gong, P.; Elvidge, C.; Baugh, K. Validation of urban boundaries derived from global night-time satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Schaaf, C.; Seto, K.C. The vegetation adjusted NTL urban index: A new approach to reduce saturation and increase variation in nighttime luminosity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillger, D.; Kopp, T.; Lee, T.; Lindsey, D.; Seaman, C.; Miller, S.; Solbrig, J.; Kidder, S.; Bachmeier, S.; Jasmin, T. First-light imagery from Suomi NPP VIIRS. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.-C. Why VIIRS data are superior to DMSP for mapping nighttime lights. Proc. Asia-Pac. Adv. Netw. 2013, 35, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N. The impact of seasonal changes on observed nighttime brightness from 2014 to 2015 monthly VIIRS DNB composites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 193, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchi, F.; Cinzano, P.; Duriscoe, D.; Kyba, C.C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Portnov, B.A.; Rybnikova, N.A.; Furgoni, R. The new world atlas of artificial night sky brightness. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Tao, P.; Haynie, S.; Fan, J. Responses of Suomi-NPP VIIRS-derived nighttime lights to socioeconomic activity in China’s cities. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K. Mapping urban structure and spatial connectivity with VIIRS and OLS night light imagery. In Proceedings of the 2013 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Sao Paulo, Brazil, 21–23 April 2013; pp. 230–233. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Li, C. Potential of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light imagery for modeling the regional economy of China. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3057–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie., Y.; Weng, Q.; Weng, A.; Xie., Y.; Weng, Q.; Weng, A. A comparative study of NPP-VIIRS and DSMP-OLS nighttime light imagery for derivation of urban demographic metrics. In Proceedings of the 2014 Third International Workshop on Earth Observation and Remote Sensing Applications (EORSA), Changsha, China, 11–14 June 2014; pp. 335–339. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Haynie, S.; Xu, T. Diverse relationships between Suomi-NPP VIIRS night-time light and multi-scale socioeconomic activity. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Huang, C.; Yu, B.; Yin, B.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J. Evaluation of NPP-VIIRS night-time light composite data for extracting built-up urban areas. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.C.; Tateishi, R.; Hara, K.; Gharechelou, S.; Iizuka, K. Global mapping of urban built-up areas of year 2014 by combining MODIS multispectral data with VIIRS nighttime light data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2016, 9, 1004–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Weng, Q. Updating urban extents with nighttime light imagery by using an object-based thresholding method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Smith, S.J.; Elvidge, C.D.; Zhao, K.; Thomson, A.; Imhoff, M. A cluster-based method to map urban area from DMSP/OLS nightlights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Tian, H.; Zhou, G.; Ge, H. Regional mapping of human settlements in southeastern China with multisensor remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3668–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, M.L.; Lawrence, W.T.; Stutzer, D.C.; Elvidge, C.D. A technique for using composite DMSP/OLS “city lights” satellite data to map urban area. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, C.; Yue, H. Urban land extraction using VIIRS nighttime light data: An Evaluation of Three Popular Methods. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, C.; Haynie, S.; Pei, T.; Xu, T. Night-time light derived estimation of spatio-temporal characteristics of urbanization dynamics using DMSP/OLS satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N.; Kark, S.; Crandall, D. Where have all the people gone? Enhancing global conservation using night lights and social media. Ecol. Appl. 2015, 25, 2153–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sui, Z.; Kang, C.; Gao, Y. Uncovering patterns of inter-urban trip and spatial interaction from social media check-in data. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roick, O.; Heuser, S. Location based social networks-definition, current state of the art and research Agenda. Trans. GIS 2013, 17, 763–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.D.; Hawkins, J.D.; Kent, J.; Turk, F.J.; Lee, T.F.; Kuciauskas, A.P.; Richardson, K.; Wade, R.; Hoffman, C. NexSat: Previewing NPOESS/VIIRS imagery capabilities. Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 87, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, T.; Marconcini, M.; Felbier, A.; Roth, A.; Heldens, W.; Huber, M.; Schwinger, M.; Taubenböck, H.; Müller, A.; Dech, S. Urban footprint processor-fully automated processing chain generating settlement masks from global data of the TanDEM-X mission. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1617–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, D.; Huang, Z.; Shi, L.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y. Inferring spatial interaction patterns from sequential snapshots of spatial distributions. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2018, 32, 783–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Song, W.; Liu, H.; Wu, Q.; Shi, K.; Wu, J. A new approach for detecting urban centers and their spatial structure with nighttime light remote sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6305–6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Nordhaus, W.D. Using luminosity data as a proxy for economic statistics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8589–8594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, S.; Câmara, G.; Monteiro, A.M.V.; Quintanilha, J.A.; Elvidge, C.D. Estimating population and energy consumption in Brazilian Amazonia using DMSP night-time satellite data. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2005, 29, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Shao, X.; Cao, C.; Fu, X.; Yan, L. Comparison between the Suomi-NPP Day-Night Band and DMSP-OLS for correlating socio-economic variables at the provincial level in China. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Xu, T. Nighttime light derived assessment of regional inequality of socioeconomic development in China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1242–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Type | Residential | Financial | Shopping | Transportation | Agricultural | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | High | 0.74 −−− | 1.24 +++ | 1.50 +++ | 0.89 −− | 0.06 −−− |
| II-I | High-medium | 1.04 +++ | 1.04 +++ | 0.88 −−− | 0.87 −−− | 0.11 −−− |
| II-II | Medium | 1.18 +++ | 0.81 −−− | 0.97 | 1.09 ++ | 1.26 +++ |
| III-I | Medium-low | 0.82 −−− | 0.67 −−− | 1.14 | 2.16 +++ | 6.59 +++ |
| III-II | Low | 0.65 −−− | 0.90 | 0.93 | 0.76 − | 14.35 +++ |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, T.; Yin, Z.; Zhou, A. Delineating Spatial Patterns in Human Settlements Using VIIRS Nighttime Light Data: A Watershed-Based Partition Approach. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030465
Ma T, Yin Z, Zhou A. Delineating Spatial Patterns in Human Settlements Using VIIRS Nighttime Light Data: A Watershed-Based Partition Approach. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(3):465. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030465
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Ting, Zhan Yin, and Alicia Zhou. 2018. "Delineating Spatial Patterns in Human Settlements Using VIIRS Nighttime Light Data: A Watershed-Based Partition Approach" Remote Sensing 10, no. 3: 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030465
APA StyleMa, T., Yin, Z., & Zhou, A. (2018). Delineating Spatial Patterns in Human Settlements Using VIIRS Nighttime Light Data: A Watershed-Based Partition Approach. Remote Sensing, 10(3), 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030465