Spatio-Temporal Analysis and Uncertainty of Fractional Vegetation Cover Change over Northern China during 2001–2012 Based on Multiple Vegetation Data Sets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sets
2.2.1. GLASS MODIS-FVC Product
2.2.2. GEOV1 FVC Product
2.2.3. TRAGL FVC Product
2.2.4. Li FVC Product
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Inter-Annual Change Trend of FVC
2.3.2. Multi-Data FVC Retrieval and Uncertainty Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Results of Single FVC Data Sets
3.1.1. Spatial Patterns of Each Single FVC Data Set
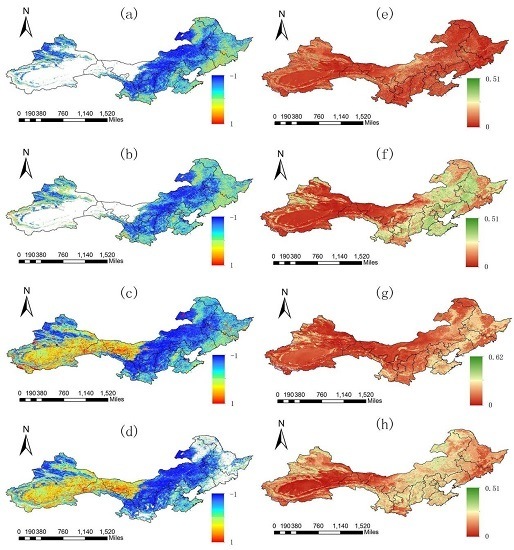
3.1.2. Variation Trends of Each FVC Data Set
3.2. Analysis of Multi-Source FVC Data Set
3.2.1. Data Set Evaluation
3.2.2. Change Trends of Multi-Source FVC Data Sets
3.2.3. Results of Multi-Data FVC and Uncertainty Analysis
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, S. Why Large-Scale Afforestation Efforts in China Have Failed To Solve the Desertification Problem. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 1826–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.R.; Halweil, B. China’s water shortage could shake world food security. World Watch 1998, 11, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhai, P.; Chao, Q.; Zou, X. Progress in China’s climate change study in the 20th century. J. Geogr. Sci. 2004, 14, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Shao, Q.; Peng, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, W.; An, G.; Yong, B. Spatial and temporal characteristics of changes in precipitation during 1957–2007 in the Haihe River basin, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2011, 25, 881–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonan, G.B. Forests and climate change: Forcings, feedbacks, and the climate benefits of forests. Science 2008, 320, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Liang, S.; Yuan, W. Observational evidence for impacts of vegetation change on local surface climate over northern China using the Granger causality test. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2015, 120, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.G.; Canadell, J.G.; Randerson, J.T.; Jackson, R.B.; Hungate, B.A.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Ban-Weiss, G.A.; Bonan, G.B.; Caldeira, K.; Cao, L.; et al. Biophysical considerations in forestry for climate protection. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Yan, C.; Tsunekawa, A.; Song, X.; Li, S.; Xie, J. Assessing vegetation dynamics in the Three-North Shelter Forest region of China using AVHRR NDVI data. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Rothstein, D.; Qi, J.; Liu, S. Methodology for an Integrative Assessment of China’s Ecological Restoration Programs. In An Integrated Assessment of China's Ecological Restoration Programs; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, E.; Xu, J.; Rozelle, S. Grain for Green: Cost-Effectiveness and Sustainability of China’s Conservation Set-Aside Program. Land Econ. 2005, 81, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, D.; Harvey, C.; Resosudarmo, P.; Sinclair, K.; Kurz, D.; McNair, M.; Crist, S.; Shpritz, L.; Fitton, L.; Saffouri, R.; et al. Environmental and economic costs of soil erosion and conservation benefits. Science 1995, 267, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacinthe, P.A.; Lal, R. A mass balance approach to assess carbon dioxide evolution during erosional events. Land Degrad. Dev. 2001, 12, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, B.; Li, X.; Wu, W.B. Retrieval and analysis of vegetation cover in the Three-North Regions of China based on MODIS data. Chin. J. Ecol. 2009, 28, 1712–1718. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.S.; Bo, Z.H. The Comparison Study on Forestry Ecological Projects in the World. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2002, 22, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Li, X.; Wang, J. Advanced Remote Sensing: Terrestrial Information Extraction and Applications; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; p. 800. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, K.; Liang, S.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Yao, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, S.; et al. Global Land Surface Fractional Vegetation Cover Estimation Using General Regression Neural Networks From MODIS Surface Reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 4787–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Liang, S.; Wei, X.; Li, Q.; Du, X.; Jiang, B.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y. Fractional Forest Cover Changes in Northeast China From 1982 to 2011 and Its Relationship With Climatic Variations. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jia, K.; Liang, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. Comparison of Four Machine Learning Methods for Generating the GLASS Fractional Vegetation Cover Product from MODIS Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Yu, D.-Y.; Sun, Z.-P.; Zhan, J.-G.; Liu, X.-X.; Luo, Q. Vegetation changes in the agricultural-pastoral areas of northern China from 2001 to 2013. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, T.; Guo, J.; Qu, J.; An, P. Vegetation change based on SPOT-VGT data from 1998 to 2007, northern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2009, 60, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Feng, Q.; Guo, J.; Shang, Z.; Liang, T. Spatio-temporal Changes of NDVI and Climatic Factors of Grassland in Northern China from 2000 to 2012. J. Desert Res. 2015, 35, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Jia, K.; Wei, X.; Yao, Y.; Sun, J.; Mou, L. Fractional vegetation cover estimation in northern China and its change analysis. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2015, 27, 112–117. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Motesharrei, S.; Song, X.P.; Kalnay, E.; Ying, Q.; Li, S.; Ma, Z. Inconsistent estimates of forest cover change in China between 2000 and 2013 from multiple datasets: Differences in parameters, spatial resolution, and definitions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Fang, J.; Tang, Z.; Zhu, B. Climatic control of primary forest structure and DBH–height allometry in Northeast China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 234, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baret, F.; Weiss, M.; Lacaze, R.; Camacho, F.; Makhmara, H.; Pacholcyzk, P.; Smets, B. GEOV1: LAI and FAPAR essential climate variables and FCOVER global time series capitalizing over existing products. Part1: Principles of development and production. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 137, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Wang, T.; Liang, S.; Sun, R. Estimating the Fractional Vegetation Cover from GLASS Leaf Area Index Product. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, F.; Cernicharo, J.; Lacaze, R.; Baret, F.; Weiss, M. GEOV1: LAI, FAPAR essential climate variables and FCOVER global time series capitalizing over existing products. Part 2: Validation and intercomparison with reference products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 137, 310–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Liang, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, P.; Yin, X.; Zhang, L.; Song, J. Use of General Regression Neural Networks for Generating the GLASS Leaf Area Index Product From Time-Series MODIS Surface Reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, G.; Ignatov, A. The derivation of the green vegetation fraction from NOAA/AVHRR data for use in numerical weather prediction models. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J. Spatial and temporal dynamics of vegetation in the San Pedro River basin area. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 105, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forthofer, R.N.; Lehnen, R.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1981; pp. 146–163. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Tan, K.; Zhao, S.; Fang, J. Changing climate affects vegetation growth in the arid region of the northwestern China. J. Arid Environ. 2011, 75, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H.; Marofi, S. Changes of Pan Evaporation in the West of Iran. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 25, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H. Exact distribution of the Mann–Kendall trend test statistic for persistent data. J. Hydrol. 2009, 365, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaagus, J. Climatic changes in Estonia during the second half of the 20th century in relationship with changes in large-scale atmospheric circulation. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2005, 83, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H.; Hosseinzadeh Talaee, P. Analysis of trends in temperature data in arid and semi-arid regions of Iran. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2011, 79, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.; Derksen, C.; Wang, L. A multi-data set analysis of variability and change in Arctic spring snow cover extent, 1967–2008. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J. Features of Weather/Climate over China in 2001. Meteorol. Mon. 2002, 29, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Fan, X. Some Extreme Events of Weather, Climate and Related Phenomena in 2009. Clim. Environ. Res. 2010, 15, 322–336. [Google Scholar]








| Product Name | Sensor | Available Time | Temporal Resolution | Spatial Coverage | Spatial Resolution | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLASS-MODIS | MODIS | 2001–now | 8 days | Global | 500 m | [16] |
| GEOV1 | SPOT VGT | 2001–now | 10 days | Global | 1 km | [25] |
| TRAGL | MOIDS | 2001–2012 | 8 days | Global | 1 km | [26] |
| Li | MODIS | 2001–2012 | 8 days | Northern China | 0.011° | [16] |
| Region | GLASS FVC | GEOV1 FVC | TRAGL FVC | Li FVC | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern china | 0.0020 | 0.0048 | 0.0016 | 0.0019 | 0.0026 |
| Northeast china | 0.0017 | 0.0072 | 0.0021 | 0.0010 | 0.0030 |
| Northwest china | 0.0012 | 0.0016 | 0.0008 | 0.0013 | 0.0012 |
| North China | 0.0040 | 0.0084 | 0.0029 | 0.0041 | 0.0049 |
| Regions | Significantly Increased | No Significant Change | Significantly Decreased |
|---|---|---|---|
| Northern china | 33.03% | 50.16% | 16.81% |
| Northeast china | 44.88% | 50.12% | 5.00% |
| Northwest china | 23.34% | 51.86% | 24.80% |
| North China | 56.05% | 35.59% | 8.36% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Jia, K.; Liang, S.; Liu, M.; Wei, X.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D. Spatio-Temporal Analysis and Uncertainty of Fractional Vegetation Cover Change over Northern China during 2001–2012 Based on Multiple Vegetation Data Sets. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040549
Yang L, Jia K, Liang S, Liu M, Wei X, Yao Y, Zhang X, Liu D. Spatio-Temporal Analysis and Uncertainty of Fractional Vegetation Cover Change over Northern China during 2001–2012 Based on Multiple Vegetation Data Sets. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(4):549. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040549
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Linqing, Kun Jia, Shunlin Liang, Meng Liu, Xiangqin Wei, Yunjun Yao, Xiaotong Zhang, and Duanyang Liu. 2018. "Spatio-Temporal Analysis and Uncertainty of Fractional Vegetation Cover Change over Northern China during 2001–2012 Based on Multiple Vegetation Data Sets" Remote Sensing 10, no. 4: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040549
APA StyleYang, L., Jia, K., Liang, S., Liu, M., Wei, X., Yao, Y., Zhang, X., & Liu, D. (2018). Spatio-Temporal Analysis and Uncertainty of Fractional Vegetation Cover Change over Northern China during 2001–2012 Based on Multiple Vegetation Data Sets. Remote Sensing, 10(4), 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040549