Regional Daily ET Estimates Based on the Gap-Filling Method of Surface Conductance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
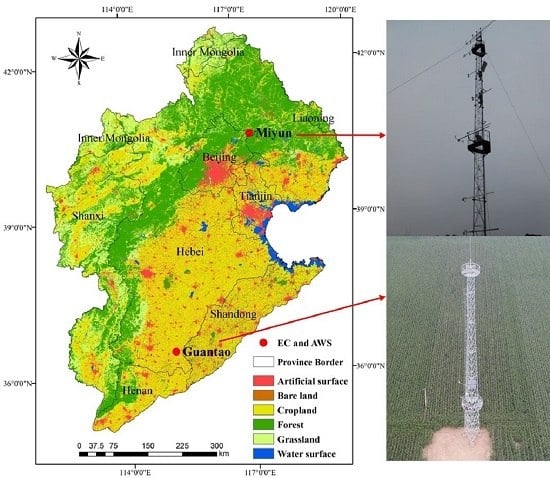
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Site Measurements
2.3. Remote Sensing Data
3. Methodology
3.1. Surface Conductance Model
3.1.1. Canopy Conductance
3.1.2. Surface Conductance
3.2. Gap-Filling Method
3.3. Evaluation Index
4. Results
4.1. Estimation of Surface Conductance
4.2. Comparison between Different Methods with EC Measurements
4.3. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.; Molden, D.J.; Makin, I.W. Remote sensing for irrigated agriculture: Examples from research and possible applications. Agric. Water Manag. 2000, 46, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B. A biophysical process-based estimate of global land surface evaporation using satellite and ancillary data. In Observing Land from Space: Science, Customers and Technology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2000; pp. 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Islam, S.; Guo, W.; Jutla, A.S.; Senarath, S.U.; Ramsay, B.H.; Eltahir, E. A satellite-based daily actual evapotranspiration estimation algorithm over south florida. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2009, 67, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldocchi, D.; Falge, E.; Gu, L.; Olson, R.; Hollinger, D.; Running, S.; Anthoni, P.; Bernhofer, C.; Davis, K.; Evans, R. Fluxnet: A new tool to study the temporal and spatial variability of ecosystem–scale carbon dioxide, water vapor, and energy flux densities. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 82, 2415–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotzge, J.A.; Crawford, K.C. Examination of the surface energy budget: A comparison of eddy correlation and bowen ratio measurement systems. J. Hydrometeorol. 2003, 4, 160–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutsaert, W. Use of pan evaporation to estimate terrestrial evaporation trends: The case of the tibetan plateau. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 3054–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleissl, J.; Gomez, J.; Hong, S.-H.; Hendrickx, J.; Rahn, T.; Defoor, W. Large aperture scintillometer intercomparison study. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2008, 128, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Xu, Z.W.; Wang, W.; Jia, Z.; Zhu, M.; Bai, J.; Wang, J. A comparison of eddy-covariance and large aperture scintillometer measurements with respect to the energy balance closure problem. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1291–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelle, H.; Durner, W.; Iden, S.C.; Fank, J. Simultaneous estimation of soil hydraulic and root distribution parameters from lysimeter data by inverse modeling. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 19, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, F.; Durner, W.; Fank, J.; Gebler, S.; Pütz, T.; Hannes, M.; Wollschläger, U. Estimating precipitation and actual evapotranspiration from precision lysimeter measurements. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 19, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z. The surface energy balance system (sebs) for estimation of turbulent heat fluxes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteith, J.L. Evaporation and environment. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1965, 19, 205–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Penman, H.L. Natural evaporation from open water, bare soil and grass. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1948, 193, 120–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleugh, H.A.; Leuning, R.; Mu, Q.; Running, S.W. Regional evaporation estimates from flux tower and modis satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuning, R.; Zhang, Y.; Rajaud, A.; Cleugh, H.; Tu, K. A simple surface conductance model to estimate regional evaporation using modis leaf area index and the penman-monteith equation. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Heinsch, F.A.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Development of a global evapotranspiration algorithm based on modis and global meteorology data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 111, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a modis global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; McCabe, M.; Wood, E.; Su, Z.; Prueger, J. Modeling evapotranspiration during smacex: Comparing two approaches for local-and regional-scale prediction. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 910–922. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Wood, E.; McCabe, M.; Su, Z. Evaluation of remotely sensed evapotranspiration over the ceop eop-1 reference sites. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2007, 85, 439–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.; Pelgrum, H.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Moreno, J.; Roerink, G.; Van der Wal, T. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (sebal).: Part 2: Validation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.; Holtslag, A. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (sebal). 1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Singh, V.P.; Li, Z.L. How sensitive is sebal to changes in input variables, domain size and satellite sensor? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.M.; Kustas, W.P.; Humes, K.S. Source approach for estimating soil and vegetation energy fluxes in observations of directional radiometric surface temperature. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 77, 263–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.T.; Anderson, M.C.; Zaitchik, B.; Hain, C.R.; Crow, W.T.; Ozdogan, M.; Chun, J.A.; Evans, J. Comparison of prognostic and diagnostic surface flux modeling approaches over the nile river basin. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 386–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.; Norman, J.; Diak, G.; Kustas, W.; Mecikalski, J. A two-source time-integrated model for estimating surface fluxes using thermal infrared remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 60, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Norman, J.M.; Mecikalski, J.R.; Otkin, J.A.; Kustas, W.P. A climatological study of evapotranspiration and moisture stress across the continental united states based on thermal remote sensing: 1. Model formulation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Allen, R.G.; Morse, A.; Kustas, W.P. Use of landsat thermal imagery in monitoring evapotranspiration and managing water resources. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Kustas, W.P.; Alfieri, J.G.; Gao, F.; Hain, C.; Prueger, J.H.; Evett, S.; Colaizzi, P.; Howell, T.; Chávez, J.L. Mapping daily evapotranspiration at landsat spatial scales during the bearex’08 field campaign. Adv. Water Resour. 2012, 50, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Norman, J.; Mecikalski, J.R.; Torn, R.D.; Kustas, W.P.; Basara, J.B. A multi-scale remote sensing model for disaggregating regional fluxes to micrometeorological scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 343–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.; Anderson, M.; Kustas, W.; French, A.; Mecikalski, J.; Torn, R.; Diak, G.; Schmugge, T.; Tanner, B. Remote sensing of surface energy fluxes at 101-m pixel resolutions. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmens, K.A.; Anderson, M.C.; Kustas, W.P.; Gao, F.; Alfieri, J.G.; McKee, L.; Prueger, J.H.; Hain, C.R.; Cammalleri, C.; Yang, Y. Monitoring daily evapotranspiration over two california vineyards using landsat 8 in a multi-sensor data fusion approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Xiong, J.; Yan, N. Etwatch: Models and methods. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 15, 224–230. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Zhu, W.; Yan, N.; Feng, X.; Xing, Q.; Zhuang, Q. An improved method for deriving daily evapotranspiration estimates from satellite estimates on cloud-free days. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.-F.; Xiong, J.; Yan, N.-N.; Yang, L.-D.; Du, X. Etwatch for monitoring regional evapotranspiration with remote sensing. Adv. Water Sci. 2008, 19, 671–678. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; Wu, B.; Liu, S.; Yan, N.; Wu, F. Etwatch: Calibration methods. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 15, 240–254. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Liu, S.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, M. Validation of remotely sensed evapotranspiration over the hai river basin, China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S. Narrowband to broadband conversions of land surface albedo i: Algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 213–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, M.C.M.; Ackerman, S.; Strabala, K.; Menzel, P.; Frey, R.; Moeller, C.; Gumley, L.; Baum, B.; Schaaf, C.; Riggs, G. Discriminating clear-sky from cloud with modis algorithm theoretical basis document (mod35). ATBD Ref. ATBD-MOD-06 Ver. 1997, 4, 115. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Jönsson, P.; Tamura, M.; Gu, Z.; Matsushita, B.; Eklundh, L. A simple method for reconstructing a high-quality ndvi time-series data set based on the savitzky–golay filter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wu, B.; Yan, N. A method for deriving the boundary layer mixing height from modis atmospheric profile data. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1346–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Liu, S.; Zhu, W.; Yan, N.; Xing, Q.; Tan, S. An improved approach for estimating daily net radiation over the heihe river basin. Sensors 2017, 17, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Liu, S.; Zhu, W.; Yu, M.; Yan, N.; Xing, Q. A method to estimate sunshine duration using cloud classification data from a geostationary meteorological satellite (fy-2d) over the heihe river basin. Sensors 2016, 16, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Yan, N.; Xiong, J.; Bastiaanssen, W.; Zhu, W.; Stein, A. Validation of etwatch using field measurements at diverse landscapes: A case study in hai basin of china. J. Hydrol. 2012, 436, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, K.; Ma, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X. A revised surface resistance parameterisation for estimating latent heat flux from remotely sensed data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 17, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Xu, D.; Cai, J.; Li, F. Evapotranspiraton estimation based on scaling up from leaf stomatal conductance to canopy conductance. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Q.; Wu, B.; Yan, N.; Zhu, W.; Xing, Q. A method for sensible heat flux model parameterization based on radiometric surface temperature and environmental factors without involving the parameter kb−1. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 47, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noilhan, J.; Planton, S. A simple parameterization of land surface processes for meteorological models. Mon. Weather Rev. 1989, 117, 536–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, P.; Mintz, Y.; Sud, Y.E.A.; Dalcher, A. A simple biosphere model (sib) for use within general circulation models. J. Atmos. Sci. 1986, 43, 505–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, P. The interpretation of the variations in leaf water potential and stomatal conductance found in canopies in the field. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 1976, 273, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Jia, L. Monitoring of evapotranspiration in a semi-arid inland river basin by combining microwave and optical remote sensing observations. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 3056–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, N.; Barrie, I.; Ayles, M. The meteorological office rainfall and evaporation calculation system: Morecs, (July 1981). Hydrol. Memos 1981, 45, 27–306. [Google Scholar]
- Lambers, H.; Pons, T.; Chapin, F.S. Plant Physiological Ecology, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Dudhia, J. Coupling an advanced land surface–hydrology model with the penn state–ncar mm5 modeling system. Part i: Model implementation and sensitivity. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, R.E. Modeling evapotranspiration for three-dimensional global climate models. Clim. Process. Clim. Sensit. 1984, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghilain, N.; Arboleda, A.; Gellens-Meulenberghs, F. Evapotranspiration modelling at large scale using near-real time msg seviri derived data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, C.; Wang, S. Predicting forest evapotranspiration by coupling carbon and water cycling based on a critical stomatal conductance model. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 4469–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yebra, M.; Van Dijk, A.; Leuning, R.; Huete, A.; Guerschman, J.P. Evaluation of optical remote sensing to estimate actual evapotranspiration and canopy conductance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration: Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 56; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.L.; Su, Z.B.; Ma, Y.M.; Yang, K.; Wen, J.; Zhang, Y. An improvement of roughness height parameterization of the surface energy balance system (sebs) over the tibetan plateau. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchet, R. Evapotranspiration Reelle, Evapotranspiration Potentielle, et Production Agricole. Ann. Agron. 1963, 14, 743–824. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, J.B.; Tu, K.P.; Baldocchi, D.D. Global estimates of the land–atmosphere water flux based on monthly avhrr and islscp-ii data, validated at 16 fluxnet sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 901–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuttleworth, W.; Gurney, R.; Hsu, A.; Ormsby, J. Fife: The Variation in Energy Partition at Surface Flux Sites; IAHS Publications: Wallingford, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Sugita, M.; Brutsaert, W. Daily evaporation over a region from lower boundary layer profiles measured with radiosondes. Water Resour. Res. 1991, 27, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Station | Land Cover | Measurements | Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guantao | Winter wheat Summer maize | EC | January–December 2016 |
| AWS | |||
| Miyun | Orchard Summer maize | EC | January–December 2016 |
| AWS | January–Auguat 2016 |
| Underlying Surface | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Deciduous broad-leaf forest | 1/100 | 0.025 | 30 |
| Evergreen needle-leaf forest | 1/150 | 0.025 | 30 |
| Evergreen broad-leaf forest | 1/150 | 0.025 | 30 |
| Cropland | 1/40 | 0.023 | 100 |
| Grassland | 1/40 | 0.0155 | 100 |
| Wetland | 1/150 | 0.0155 | 100 |
| Bare soil | 1/50 | -- | -- |
| Sites | Original Method | Enhanced Method | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily | Guantao | 0.68 | 0.90 | −0.42 | −22.1% | 0.75 | 0.79 | −0.26 | −12.5% |
| Miyun | 0.79 | 0.80 | −0.07 | −4.2% | 0.88 | 0.62 | −0.05 | −3.3% | |
| Monthly Averaged | Guantao | 0.96 | 0.29 | −0.38 | −22.5% | 0.97 | 0.27 | −0.27 | −14.6% |
| Miyun | 0.97 | 0.26 | −0.06 | −3.1% | 0.98 | 0.23 | −0.05 | −2.8% | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Wu, B.; Yan, N.; Tan, S. Regional Daily ET Estimates Based on the Gap-Filling Method of Surface Conductance. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040554
Xu J, Wu B, Yan N, Tan S. Regional Daily ET Estimates Based on the Gap-Filling Method of Surface Conductance. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(4):554. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040554
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jiaming, Bingfang Wu, Nana Yan, and Shen Tan. 2018. "Regional Daily ET Estimates Based on the Gap-Filling Method of Surface Conductance" Remote Sensing 10, no. 4: 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040554
APA StyleXu, J., Wu, B., Yan, N., & Tan, S. (2018). Regional Daily ET Estimates Based on the Gap-Filling Method of Surface Conductance. Remote Sensing, 10(4), 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040554