Unsupervised Nonlinear Hyperspectral Unmixing Based on Bilinear Mixture Models via Geometric Projection and Constrained Nonnegative Matrix Factorization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The negative effect of collinearity in BMM-based nonlinear unmixing methods can be addressed. To be specific, this goal is reached by adopting a distance measure to project pixels onto their approximate linear mixture components based on the geometric characteristics of the BMMs. This procedure reduces effectively the virtual endmembers’ impact on nonlinear unmixing, which is a remarkable advantage compared with other relevant unmixing methods.
- The issue of local minima in standard NMF can be well alleviated, and highly mixed nonlinear hyperspectral data can be unmixed accurately. To be specific, the procedure of geometric projection facilitates the direct use of NMF in nonlinear unmixing, and the incorporation of a minimum endmember distance constraint into the NMF framework enables the accurate estimation of endmembers and abundances when pixels are highly mixed.
- A general unsupervised nonlinear unmixing strategy is built which is simultaneously suitable for unmixing under the assumptions of three BMMs including the FM, GBM, and PPNM.
2. Related Works
2.1. Mixture Models
2.2. NMF
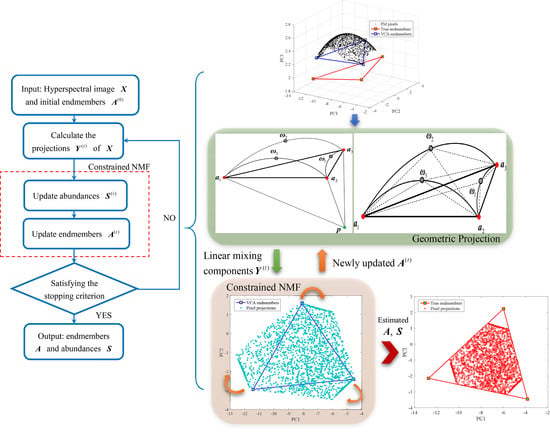
3. Proposed Algorithm for Unsupervised Nonlinear Spectral Unmixing
3.1. Motivation for the Proposed Algorithm
3.2. Nonlinear Hyperplanes and Geometric Projection
3.3. BMM-Based Constrained NMF
| Algorithm 1: BMM-based constrained NMF (BCNMF) |
| Input: Hyperspectral data and initial endmember matrix obtained by VCA. |
| Output: Abundance matrix and endmember matrix . |
| Step 1. Set , initialize and with Equations (10) and (11). while stopping conditions are not met, do Step 2. Update endmembers and abundances in the constrained NMF framework (2a) Update with Equation (16) [48,57,68]. (2b) Update with Equation (17) [48,57,68]. Step 3. Calculate pixels’ projections (3a) Calculate r nonlinear midpoints with Equation (5) [58]. (3b) Update pixels’ projections using Equation (11). Step 4. . |
| End |
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Experiments with Synthetic Data
4.1.1. Robustness to the Collinearity and the Number of Endmembers
4.1.2. Noise Robustness Analysis
4.1.3. Analysis of Sensitivity to the Degree of Mixing
4.1.4. Complexity and Convergence Analysis
4.1.5. Parameter Sensitivity Analysis
4.2. Experiments with Virtual Orchard and Real Hyperspectral Images
5. Discussion
5.1. Unmixing Accuracy Improvement by Addressing the Collinearity
5.2. Improvement of Endmember Extraction for Highly Mixed Nonlinear Data
5.3. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keshava, N.; Mustard, J.F. Spectral unmixing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2002, 19, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A.; Dobigeon, N.; Parente, M.; Du, Q.; Gader, P.; Chanussot, J. Hyperspectral unmixing overview: Geometrical, statistical, and sparse regression-based approaches. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 354–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, M.E. N-FINDR: An algorithm for fast autonomous spectral end-member determination in hyperspectral data. In Proceedings of the SPIE’s International Symposium on Optical Science, Engineering, and Instrumentation, San-Diego, CA, USA, 9–14 July 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Nascimento, J.M.; Dias, J.M. Vertex component analysis: A fast algorithm to unmix hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L. Orthogonal bases approach for the decomposition of mixed pixels in hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 219–223. [Google Scholar]
- Heinz, D.C.; Chang, C.I. Fully constrained least squares linear spectral mixture analysis method for material quantification in hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, Q. Geometric method of fully constrained least squares linear spectral mixture analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 3558–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.H.; Chi, C.Y.; Huang, Y.M.; Ma, W.K. A convex analysis based minimum-volume enclosing simplex algorithm for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 57, 4418–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Cin, C.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Chan, T.H. A fast hyperplane-based minimum-volume enclosing simplex algorithm for blind hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 1946–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Agathos, A.; Zaharie, D.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A.; Li, X. Minimum volume simplex analysis: A fast algorithm for linear hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 5067–5082. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, L.; Qi, H. Endmember extraction from highly mixed data using minimum volume constrained nonnegative matrix factorization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Guo, S.; Sun, W. Minimum distance constrained nonnegative matrix factorization for the endmember extraction of hyperspectral images. In Proceedings of the SPIE’s Conference on Remote Sensing and GIS Data Processing and Applications, Wuhan, China, 4 November 2007; Volume 6790, pp. 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.D.; Seung, H.S. Learning the parts of objects by nonnegative matrix factorization. Nature 1999, 401, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schachtner, R.; Pöppel, G.; Tomé, A.M.; Lang, E.W. Minimum determinant constraint for non-negative matrix factorization. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Independent Component Analysis and Signal Separation, Paraty, Brazil, 15–18 March 2009; pp. 106–113. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Du, B.; Zhang, L. An endmember dissimilarity constrained non-negative matrix factorization method for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 554–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xia, W.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L. An approach based on constrained nonnegative matrix factorization to unmix hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Qian, Y. Constrained nonnegative matrix factorization for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Yao, Y.; Cheng, S.; Jiao, L. Geometric nonnegative matrix factorization (GNMF) for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 2696–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Qian, Y.; Gao, Y. Region-based structure preserving nonnegative matrix factorization for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 1575–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Jia, S.; Zhou, J.; Robles-Kelly, A. Hyperspectral unmixing via L1/2 sparsity-constrained nonnegative matrix factorization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4282–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Yan, P.; Li, X. Manifold regularized sparse NMF for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 2815–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qian, Y.; Tang, Y. Hypergraph-regularized sparse NMF for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L. Sparsity-regularized robust non-negative matrix factorization for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 4267–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Fu, M.; Lu, X. Substance dependence constrained sparse NMF for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2975–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A.; Liu, L. Robust collaborative nonnegative matrix factorization for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 6076–6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobigeon, N.; Tourneret, J.Y.; Richard, C.; Bermudez, J.C.; McLaughlin, S.; Hero, A.O. Nonlinear unmixing of hyperspectral images: Models and algorithms. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2014, 31, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heylen, R.; Parente, M.; Gader, P. A review of nonlinear hyperspectral unmixing methods. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1844–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustard, J.F.; Pieters, C.M. Quantitative abundance estimates from bidirectional reflectance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1987, 92, E617–E626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapke, B. Bidirection reflectance spectroscopy. I. theory. J. Geophys. Res. 1981, 86, 3039–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Hu, B.; Miller, J.; Li, M. Comparative study between a new nonlinear model and common linear model for analysing laboratory simulated-forest hyperspectral data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 2951–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halimi, A.; Altmann, Y.; Dobigeon, N.; Tourneret, J.Y. Nonlinear unmixing of hyperspectral images using a generalized bilinear model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4153–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altmann, Y.; Halimi, A.; Dobigeon, N.; Tourneret, J.Y. Supervised nonlinear spectral unmixing using a postnonlinear mixing model for hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 3017–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Somers, B.; Tits, L.; Coppin, P. Quantifying nonlinear spectral mixing in vegetated areas: Computer simulation model validation and first results. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobigeon, N.; Tits, L.; Somers, B.; Altmann, Y.; Coppin, P. A comparison of nonlinear mixing models for vegetated areas using simulated and real hyperspectral data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1869–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinoni, A.; Gamba, P. A novel approach for efficient p-linear hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2015, 9, 1156–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halimi, A.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Dobigeon, N.; Buller, G.S.; McLaughlin, S. Fast hyperspectral unmixing in presence of nonlinearity or mismodeling effects. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2017, 3, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heylen, R.; Scheunders, P. A multilinear mixing model for nonlinear spectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoya, N.; Chanussot, J.; Iwasaki, A. Nonlinear unmixing of hyperspectral data using semi-nonnegative matrix factorization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, B.; Xia, W. Constrained least squares algorithms for nonlinear unmixing of hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1287–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ma, Y.; Huang, J.; Mei, X.; Liu, C.; Ma, J. GBM-based unmixing of hyperspectral data using bound projected optimal gradient method. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Richard, C.; Honeine, P. Nonlinear estimation of material abundances in hyperspectral images with l1-norm spatial regularization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 2654–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Q.; Nasrabadi, N.M.; Tran, T.D. Abundance estimation for bilinear mixture models via joint sparse and low-rank representation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 4404–4423. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Huang, B.; Zhao, L. Hopfield neural network approach for supervised nonlinear spectral unmixing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadwater, J.; Chellappa, R.; Banerjee, A.; Burlina, P. Kernel fully constrained least squares abundance estimates. In Proceedings of the IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007; pp. 4041–4044. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Richard, C.; Honeine, P. Nonlinear unmixing of hyperspectral data based on a linear mixture/nonlinear-fluctuation model. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heylen, R.; Scheunders, P. A distance geometric framework for nonlinear hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1879–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, Y.; Dobigeon, N.; Tourneret, J.Y. Unsupervised post-nonlinear unmixing of hyperspectral images using a Hamiltonian Monte Carlo algorithm. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 2663–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eches, O.; Guillaume, M. A bilinear-bilinear nonnegative matrix factorization method for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Gao, L.; Plaza, A.; Marinoni, A.; Yang, B.; Zhong, L.; Gamba, P.; Zhang, B. A new algorithm for bilinear spectral unmixing of hyperspectral images using particle swarm optimization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 5776–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, B.; Cools, K.; Delalieux, S.; Stuckens, J.; Van der Zande, D.; Verstraeten, W.W.; Coppin, P. Nonlinear hyperspectral image analysis for tree cover estimates in orchards. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Jia, X.; Somers, B.; Wu, J.; Coppin, P. A quantitative analysis of virtual endmembers’ increased impact on the collinearity effect in spectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2945–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X. Two-step constrained nonlinear spectral mixture analysis method for mitigating the collinearity effect. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2873–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meer, F.D.; Jia, X.P. Collinearity and orthogonality of endmembers in linear spectral unmixing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 18, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Févotte, C.; Dobigeon, N. Nonlinear hyperspectral unmixing with robust nonnegative matrix factorization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 4810–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Cui, J.; Zhao, L. Blind nonlinear hyperspectral unmixing based on constrained kernel nonnegative matrix factorization. Signal Image Video Process. 2014, 8, 1555–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, L. Nonlinear hyperspectral unmxing based on constrained multiple kernel NMF. In Proceedings of the SPIE’s Satellite Data Compression, Communications, and Processing, Baltimore, MD, USA, 22 May 2014; Volume 9124, pp. N1–N6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, F.; Honeine, P. Biobjective nonnegative matrix factorization linear versus kernel-based models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4012–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, B.; Wu, Z. Nonlinear hyperspectral unmixing based on geometric characteristics of bilinear mixture models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 694–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W. Introduction to the Theory of Simplex: Research on High. Dimensional Extension of Triangle; Hunan Normal University Press: Changsha, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ungar, A. Barycentric Calculus in Euclidean and Hyperbolic Geometry: A Comparative Introduction; World Scientific: Singapore, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Honeine, P.; Richard, C. Geometric unmixing of large hyperspectral images: A barycentric coordinate approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 50, 2185–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heylen, R.; Burazerović, D.; Scheunders, P. Fully constrained least squares spectral unmixing by simplex projection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4112–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farin, G.; Hoschek, J.; Kim, M.S. Handbook of Computer Aided Geometric Design; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Strang, G. Linear Algebra and Its Applications, 4th ed.; Thomson: Belmont, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, S.; Vandenberghe, L. Convex Optimization; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, I.H. Geometric Linear Algebra; World Scientific: Singapore, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Wang, B.; Wu, Z.; Lu, Q. Bilinear mixture models based unsupervised nonlinear unmixing using constrained nonnegative matrix factorization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 582–585. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.J. Projected gradient methods for non-negative matrix factorization. Neural Comput. 2007, 19, 2756–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iordache, M.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A. Sparse unmixing of hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2014–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuckens, J.; Somers, B.; Delalieux, S.; Verstraeten, W.W.; Coppin, P. The impact of common assumptions on canopy radiative transfer simulations: A case study in citrus orchards. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2009, 110, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethel, J.S.; Lee, C.; Landgrebe, D.A. Geometric registration and classification of hyperspectral airborne pushbroom data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2000, 33, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Nascimento, J.M. Hyperspectral subspace identification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 2435–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



















| Number of Endmembers | True Endmembers | True and Virtual Endmembers |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 5.1 | 5191.6 |
| 5 | 19.5 | 113,198.5 |
| 7 | 21.2 | 253,791.4 |
| 9 | 21.9 | 882,106.4 |
| Models | Number of Endmembers | FCLS [6] | FanNMF [48] | GBMsemiNMF [38] | PPNMGDA [32] | MLM [37] | DNSPU [46] | RNMF [54] | Bio-KNMF [57] | BCNMF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | FM | 3 | 0.0611 ± 0.0000 | 0.0110 ± 0.0000 | 0.0322 ± 0.0001 | 0.0297 ± 0.0001 | 0.1042 ± 0.0001 | 0.0689 ± 0.0006 | 0.0492 ± 0.0005 | 0.0731 ± 0.0000 | 0.0340 ± 0.0340 |
| 5 | 0.1132 ± 0.0000 | 0.0774 ± 0.0000 | 0.0987 ± 0.0001 | 0.0186 ± 0.0003 | 0.0888 ± 0.0001 | 0.1710 ± 0.0126 | 0.1081 ± 0.0000 | 0.1056 ± 0.0000 | 0.0265 ± 0.0265 | ||
| 7 | 0.1317 ± 0.0000 | 0.0927 ± 0.0000 | 0.1161 ± 0.0000 | 0.0223 ± 0.0008 | 0.1352 ± 0.0000 | 0.1719 ± 0.0081 | 0.1236 ± 0.0001 | 0.1255 ± 0.0000 | 0.0194 ± 0.0194 | ||
| 9 | 0.1325 ± 0.0000 | 0.0973 ± 0.0000 | 0.1169 ± 0.0001 | 0.0225 ± 0.0011 | 0.1285 ± 0.0000 | 0.1615 ± 0.0136 | 0.1263 ± 0.0002 | 0.1285 ± 0.0000 | 0.0162 ± 0.0162 | ||
| GBM | 3 | 0.0345 ± 0.0000 | 0.0359 ± 0.0001 | 0.0210 ± 0.0001 | 0.0192 ± 0.0000 | 0.0535 ± 0.0001 | 0.0529 ± 0.0007 | 0.0298 ± 0.0005 | 0.0418 ± 0.0000 | 0.0214 ± 0.0000 | |
| 5 | 0.0662 ± 0.0000 | 0.0573 ± 0.0000 | 0.0587 ± 0.0001 | 0.0139 ± 0.0002 | 0.0472 ± 0.0001 | 0.2003 ± 0.0070 | 0.0636 ± 0.0000 | 0.0598 ± 0.0001 | 0.0179 ± 0.0000 | ||
| 7 | 0.0789 ± 0.0000 | 0.0637 ± 0.0000 | 0.0717 ± 0.0001 | 0.0160 ± 0.0003 | 0.0732 ± 0.0001 | 0.1613 ± 0.0072 | 0.0755 ± 0.0001 | 0.0754 ± 0.0000 | 0.0149 ± 0.0001 | ||
| 9 | 0.0806 ± 0.0000 | 0.0660 ± 0.0001 | 0.0735 ± 0.0001 | 0.0158 ± 0.0005 | 0.0742 ± 0.0001 | 0.1631 ± 0.0115 | 0.0779 ± 0.0001 | 0.0783 ± 0.0000 | 0.0132 ± 0.0001 | ||
| PPNM | 3 | 0.0594 ± 0.0000 | 0.0725 ± 0.0000 | 0.0484 ± 0.0001 | 0.0029 ± 0.0011 | 0.0547 ± 0.0001 | 0.0932 ± 0.0004 | 0.0730 ± 0.0001 | 0.0525 ± 0.0000 | 0.0112 ± 0.0000 | |
| 5 | 0.0768 ± 0.0000 | 0.0691 ± 0.0000 | 0.0652 ± 0.0001 | 0.0081 ± 0.0007 | 0.0495 ± 0.0001 | 0.1975 ± 0.0099 | 0.0795 ± 0.0000 | 0.0673 ± 0.0000 | 0.0146 ± 0.0001 | ||
| 7 | 0.0786 ± 0.0000 | 0.0739 ± 0.0000 | 0.0696 ± 0.0000 | 0.0146 ± 0.0006 | 0.0621 ± 0.0001 | 0.1829 ± 0.0175 | 0.0800 ± 0.0001 | 0.0705 ± 0.0000 | 0.0123 ± 0.0001 | ||
| 9 | 0.0727 ± 0.0000 | 0.0681 ± 0.0000 | 0.0656 ± 0.0000 | 0.0156 ± 0.0005 | 0.0613 ± 0.0001 | 0.1660 ± 0.0166 | 0.0734 ± 0.0000 | 0.0674 ± 0.0000 | 0.0121 ± 0.0001 | ||
| Models | Number of Endmembers | VCA [4] | Fan-NMF [48] | DNSPU [46] | RNMF [54] | Bio-KNMF [57] | BCNMF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSAD | FM | 3 | 8.8265 ± 0.3536 | 5.2502 ± 0.3473 | 9.0515 ± 0.0190 | 5.0690 ± 0.2925 | 6.8671 ± 0.3421 | 2.0462 ± 0.2358 |
| 5 | 5.6533 ± 0.7541 | 5.7124 ± 0.6451 | 7.7206 ± 0.4463 | 5.1270 ± 1.0004 | 6.9426 ± 0.6995 | 1.1358 ± 0.0226 | ||
| 7 | 5.0358 ± 0.7853 | 5.2417 ± 0.4250 | 6.6328 ± 0.6447 | 4.6294 ± 0.4233 | 5.8363 ± 0.3533 | 1.4401 ± 0.4295 | ||
| 9 | 6.7803 ± 0.4831 | 6.7997 ± 0.3673 | 8.4783 ± 0.8827 | 6.5700 ± 0.6705 | 7.0620 ± 0.3964 | 2.1292 ± 0.6556 | ||
| GBM | 3 | 8.0771 ± 0.1951 | 5.1468 ± 0.2066 | 9.1713 ± 0.3667 | 4.9098 ± 0.4338 | 6.6004 ± 0.0406 | 1.6405 ± 0.1271 | |
| 5 | 5.0001 ± 0.3321 | 5.3684 ± 0.2490 | 7.0954 ± 0.8766 | 4.2958 ± 0.3425 | 5.8363 ± 0.2128 | 1.0418 ± 0.0545 | ||
| 7 | 4.4557 ± 0.6821 | 4.4152 ± 0.6657 | 6.5340 ± 0.3408 | 4.2153 ± 1.1267 | 4.8520 ± 0.0995 | 0.9470 ± 0.0655 | ||
| 9 | 6.5236 ± 0.2947 | 6.5768 ± 0.2435 | 7.3865 ± 0.3825 | 6.2732 ± 0.3615 | 6.3688 ± 0.3057 | 2.3192 ± 0.0915 | ||
| PPNM | 3 | 6.8858 ± 0.2760 | 4.4980 ± 0.8266 | 8.3913 ± 0.3780 | 4.6595 ± 0.2908 | 6.3666 ± 0.6336 | 1.1441 ± 0.3204 | |
| 5 | 4.7601 ± 0.6423 | 4.7758 ± 0.4575 | 6.9357 ± 0.5677 | 4.1588 ± 0.4930 | 5.1088 ± 0.3059 | 1.0886 ± 0.3378 | ||
| 7 | 4.9075 ± 0.4970 | 5.2785 ± 0.4148 | 9.4223 ± 0.2541 | 4.6159 ± 0.4678 | 5.5037 ± 0.0872 | 1.7113 ± 0.2294 | ||
| 9 | 6.1033 ± 0.3987 | 6.5077 ± 0.2628 | 7.6376 ± 0.2784 | 5.8120 ± 0.3507 | 6.2541 ± 0.3128 | 1.6238 ± 0.1240 | ||
| Models | Number of Endmembers | FCLS (VCA) [6] | FanNMF [48] | GBMsemiNMF (VCA) [38] | PPNMGDA (VCA) [32] | MLM (VCA) [37] | DNSPU [46] | RNMF [54] | Bio-KNMF [57] | BCNMF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | FM | 3 | 0.0982 ± 0.0042 | 0.0623 ± 0.0019 | 0.1023 ± 0.0038 | 0.0957 ± 0.0089 | 0.1398 ± 0.0071 | 0.0725 ± 0.0005 | 0.0814 ± 0.0038 | 0.0949 ± 0.0038 | 0.0407 ± 0.0034 |
| 5 | 0.1294 ± 0.0271 | 0.1051 ± 0.0110 | 0.1188 ± 0.0307 | 0.0862 ± 0.0314 | 0.1191 ± 0.0220 | 0.1922 ± 0.0092 | 0.4016 ± 1.0598 | 0.1305 ± 0.0307 | 0.0168 ± 0.0002 | ||
| 7 | 0.1391 ± 0.0256 | 0.1202 ± 0.0154 | 0.1259 ± 0.0236 | 0.0864 ± 0.0232 | 0.1319 ± 0.0164 | 0.1719 ± 0.0118 | 0.4827 ± 0.9507 | 0.1571 ± 0.0236 | 0.0137 ± 0.0039 | ||
| 9 | 0.1342 ± 0.0190 | 0.1333 ± 0.0167 | 0.1262 ± 0.0183 | 0.1175 ± 0.0185 | 0.1350 ± 0.0145 | 0.1515 ± 0.0078 | 0.3043 ± 0.5374 | 0.1407 ± 0.0183 | 0.0140 ± 0.0096 | ||
| GBM | 3 | 0.0984 ± 0.0026 | 0.0691 ± 0.0016 | 0.0956 ± 0.0052 | 0.0856 ± 0.0043 | 0.1032 ± 0.0065 | 0.0688 ± 0.0026 | 0.0824 ± 0.0022 | 0.0955 ± 0.0052 | 0.0353 ± 0.0021 | |
| 5 | 0.1097 ± 0.0332 | 0.1007 ± 0.0323 | 0.1033 ± 0.0347 | 0.0802 ± 0.0223 | 0.0873 ± 0.0179 | 0.1963 ± 0.0056 | 0.1700 ± 0.1802 | 0.0972 ± 0.0347 | 0.0166 ± 0.0007 | ||
| 7 | 0.0988 ± 0.0142 | 0.0940 ± 0.0119 | 0.0922 ± 0.0136 | 0.0719 ± 0.0134 | 0.0966 ± 0.0116 | 0.1667 ± 0.0122 | 0.0980 ± 0.0151 | 0.0967 ± 0.0136 | 0.0144 ± 0.0006 | ||
| 9 | 0.1405 ± 0.0124 | 0.1315 ± 0.0110 | 0.1333 ± 0.0130 | 0.1246 ± 0.0115 | 0.1389 ± 0.0090 | 0.1578 ± 0.0074 | 0.1440 ± 0.0192 | 0.1287 ± 0.0130 | 0.0165 ± 0.0320 | ||
| PPNM | 3 | 0.1328 ± 0.0281 | 0.1122 ± 0.0215 | 0.1372 ± 0.0385 | 0.1018 ± 0.0102 | 0.1029 ± 0.0107 | 0.1457 ± 0.0013 | 0.1164 ± 0.0184 | 0.1169 ± 0.0385 | 0.0402 ± 0.0060 | |
| 5 | 0.1393 ± 0.0180 | 0.1269 ± 0.0156 | 0.1289 ± 0.0197 | 0.0794 ± 0.0145 | 0.0881 ± 0.0184 | 0.2021 ± 0.0088 | 0.1352 ± 0.0170 | 0.1282 ± 0.0197 | 0.0290 ± 0.0029 | ||
| 7 | 0.1300 ± 0.0078 | 0.1246 ± 0.0080 | 0.1225 ± 0.0085 | 0.0806 ± 0.0091 | 0.0964 ± 0.0070 | 0.1798 ± 0.0116 | 0.1278 ± 0.0078 | 0.1302 ± 0.0085 | 0.0265 ± 0.0024 | ||
| 9 | 0.1317 ± 0.0132 | 0.1331 ± 0.0107 | 0.1289 ± 0.0125 | 0.1059 ± 0.0130 | 0.1194 ± 0.0125 | 0.1579 ± 0.0085 | 0.1341 ± 0.0139 | 0.1338 ± 0.0125 | 0.0183 ± 0.0010 | ||
| Models | SNR | VCA [4] | Fan-NMF [48] | DNSPU [46] | RNMF [54] | Bio-KNMF [57] | BCNMF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSAD | FM | 60 dB | 5.1928 ± 0.8362 | 5.1790 ± 0.6528 | 7.0513 ± 0.1545 | 4.3165 ± 0.3696 | 6.0327 ± 0.1460 | 0.9740 ± 0.5282 |
| 50 dB | 5.3686 ± 0.8261 | 5.6142 ± 0.6142 | 6.8207 ± 0.0189 | 4.8229 ± 0.6007 | 6.2430 ± 0.2802 | 1.0818 ± 0.8847 | ||
| 40 dB | 5.6533 ± 0.7541 | 5.7124 ± 0.6451 | 7.7206 ± 0.4463 | 5.1270 ± 1.0004 | 6.9426 ± 0.6995 | 1.1358 ± 0.0226 | ||
| 30 dB | 5.9726 ± 0.8138 | 5.4218 ± 0.6051 | 8.0765 ± 0.4096 | 5.2381 ± 1.2090 | 6.4824 ± 0.7723 | 1.3058 ± 0.1420 | ||
| 20 dB | 6.5694 ± 1.2014 | 6.1931 ± 0.9105 | 11.7315 ± 1.5761 | 5.3623 ± 1.3975 | 6.3718 ± 0.5830 | 2.4998 ± 0.4998 | ||
| GBM | 60 dB | 5.4980 ± 0.5312 | 5.7940 ± 0.5142 | 6.8903 ± 0.0024 | 4.7873 ± 0.7274 | 6.4455 ± 0.1232 | 0.9570 ± 0.2143 | |
| 50 dB | 5.1095 ± 0.8606 | 5.1122 ± 0.8300 | 6.8639 ± 0.5065 | 4.4089 ± 1.0767 | 5.8294 ± 0.5911 | 0.7909 ± 0.0658 | ||
| 40 dB | 5.0001 ± 0.3321 | 5.3684 ± 0.2490 | 7.0954 ± 0.8766 | 4.2958 ± 0.3425 | 5.8363 ± 0.2128 | 1.0418 ± 0.0545 | ||
| 30 dB | 5.5078 ± 0.9006 | 5.7078 ± 0.7290 | 9.1409 ± 0.6889 | 4.7647 ± 0.8881 | 5.9193 ± 0.6545 | 0.7008 ± 0.2155 | ||
| 20 dB | 5.9762 ± 0.8217 | 6.0560 ± 0.6121 | 12.3400 ± 1.3026 | 4.6946 ± 1.0708 | 6.8835 ± 0.7300 | 3.2856 ± 0.5320 | ||
| PPNM | 60 dB | 4.0249 ± 0.8929 | 4.3834 ± 0.3254 | 8.3420 ± 0.0742 | 3.6025 ± 0.5287 | 5.0740 ± 0.1237 | 1.5931 ± 0.2954 | |
| 50 dB | 4.8456 ± 0.5121 | 5.1456 ± 0.3779 | 9.0909 ± 0.0072 | 4.3166 ± 0.5222 | 6.1868 ± 0.4230 | 2.0639 ± 0.1513 | ||
| 40 dB | 4.7601 ± 0.6423 | 4.7758 ± 0.4575 | 6.9357 ± 0.5677 | 4.1588 ± 0.4930 | 5.1088 ± 0.3059 | 1.0886 ± 0.3378 | ||
| 30 dB | 4.1925 ± 0.5707 | 4.9437 ± 0.4154 | 10.8538 ± 1.2705 | 3.7890 ± 0.4622 | 5.8690 ± 0.4303 | 1.8610 ± 0.2670 | ||
| 20 dB | 6.5477 ± 1.1170 | 6.2704 ± 0.7471 | 12.9161 ± 0.8390 | 5.0067 ± 1.2445 | 6.8309 ± 1.1485 | 3.2091 ± 1.1020 | ||
| Models | SNR | FCLS (VCA) [6] | Fan-NMF [48] | GBM-semiNMF (VCA) [38] | PPNMGDA (VCA) [32] | MLM (VCA) [37] | DNSPU [46] | RNMF [54] | Bio-KNMF [57] | BCNMF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | FM | 60 dB | 0.1415 ± 0.0371 | 0.1184 ± 0.0329 | 0.1346 ± 0.0460 | 0.0899 ± 0.0342 | 0.1185 ± 0.0280 | 0.1874 ± 0.0086 | 0.1591 ± 0.0932 | 0.1293 ± 0.0460 | 0.0164 ± 0.0037 |
| 50 dB | 0.1455 ± 0.0461 | 0.1180 ± 0.0293 | 0.1413 ± 0.0618 | 0.0872 ± 0.0359 | 0.1171 ± 0.0246 | 0.2146 ± 0.0006 | 0.1541 ± 0.1233 | 0.1308 ± 0.0618 | 0.0172 ± 0.0096 | ||
| 40 dB | 0.1294 ± 0.0271 | 0.1051 ± 0.0110 | 0.1188 ± 0.0307 | 0.0862 ± 0.0314 | 0.1191 ± 0.0220 | 0.1922 ± 0.0092 | 0.4016 ± 1.0598 | 0.1305 ± 0.0307 | 0.0168 ± 0.0002 | ||
| 30 dB | 0.1346 ± 0.0238 | 0.1095 ± 0.0165 | 0.1242 ± 0.0258 | 0.0880 ± 0.0141 | 0.1124 ± 0.0120 | 0.1851 ± 0.0076 | 0.4072 ± 0.6097 | 0.1430 ± 0.0258 | 0.0235 ± 0.0011 | ||
| 20 dB | 0.1393 ± 0.0316 | 0.1152 ± 0.0230 | 0.1305 ± 0.0314 | 0.1237 ± 0.0258 | 0.1367 ± 0.0205 | 0.1881 ± 0.0096 | 0.3870 ± 0.4029 | 0.1369 ± 0.0314 | 0.0527 ± 0.0093 | ||
| GBM | 60 dB | 0.1007 ± 0.0113 | 0.0918 ± 0.0092 | 0.0941 ± 0.0130 | 0.0743 ± 0.0089 | 0.0877 ± 0.0113 | 0.1797 ± 0.0007 | 0.2201 ± 0.5056 | 0.1089 ± 0.0130 | 0.0170 ± 0.0041 | |
| 50 dB | 0.1190 ± 0.0268 | 0.1015 ± 0.0124 | 0.1147 ± 0.0364 | 0.0811 ± 0.0284 | 0.0963 ± 0.0199 | 0.2028 ± 0.0131 | 0.1566 ± 0.1563 | 0.1151 ± 0.0364 | 0.0167 ± 0.0004 | ||
| 40 dB | 0.1097 ± 0.0332 | 0.1007 ± 0.0323 | 0.1033 ± 0.0347 | 0.0802 ± 0.0223 | 0.0873 ± 0.0179 | 0.1963 ± 0.0056 | 0.1700 ± 0.1802 | 0.0972 ± 0.0347 | 0.0166 ± 0.0007 | ||
| 30 dB | 0.1268 ± 0.0563 | 0.1150 ± 0.0507 | 0.1232 ± 0.0656 | 0.0846 ± 0.0326 | 0.0943 ± 0.0285 | 0.1896 ± 0.0102 | 0.1679 ± 0.1234 | 0.1360 ± 0.0656 | 0.0224 ± 0.0009 | ||
| 20 dB | 0.1103 ± 0.0244 | 0.1000 ± 0.0182 | 0.1051 ± 0.0248 | 0.1082 ± 0.0225 | 0.1174 ± 0.0229 | 0.1881 ± 0.0096 | 0.2124 ± 0.3105 | 0.1317 ± 0.0248 | 0.0587 ± 0.0092 | ||
| PPNM | 60 dB | 0.1235 ± 0.0158 | 0.1163 ± 0.0109 | 0.1097 ± 0.0163 | 0.0676 ± 0.0138 | 0.0804 ± 0.0111 | 0.2035 ± 0.0049 | 0.1205 ± 0.0145 | 0.1290 ± 0.0163 | 0.0278 ± 0.0030 | |
| 50 dB | 0.1185 ± 0.0171 | 0.1101 ± 0.0108 | 0.1065 ± 0.0199 | 0.0713 ± 0.0134 | 0.0854 ± 0.0118 | 0.2146 ± 0.0001 | 0.1160 ± 0.0158 | 0.1192 ± 0.0199 | 0.0227 ± 0.0033 | ||
| 40 dB | 0.1393 ± 0.0180 | 0.1269 ± 0.0156 | 0.1289 ± 0.0197 | 0.0794 ± 0.0145 | 0.0881 ± 0.0184 | 0.2021 ± 0.0088 | 0.1352 ± 0.0170 | 0.1282 ± 0.0197 | 0.0290 ± 0.0029 | ||
| 30 dB | 0.1220 ± 0.0183 | 0.1124 ± 0.0142 | 0.1083 ± 0.0217 | 0.0700 ± 0.0141 | 0.0800 ± 0.0137 | 0.2260 ± 0.0189 | 0.1202 ± 0.0183 | 0.1253 ± 0.0217 | 0.0338 ± 0.0018 | ||
| 20 dB | 0.1583 ± 0.0327 | 0.1448 ± 0.0238 | 0.1439 ± 0.0308 | 0.1402 ± 0.0379 | 0.1463 ± 0.0292 | 0.1961 ± 0.0083 | 0.1501 ± 0.0287 | 0.1535 ± 0.0308 | 0.0681 ± 0.0127 | ||
| Models | Max Abundance | VCA [4] | Fan-NMF [48] | DNSPU [46] | RNMF [54] | Bio-KNMF [57] | BCNMF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSAD | FM | 0.7 | 7.7840 ± 1.0534 | 6.9663 ± 1.1162 | 7.5963 ± 0.2214 | 7.2176 ± 1.1828 | 7.4572 ± 0.1805 | 1.1660 ± 0.5538 |
| 0.8 | 5.6533 ± 0.7541 | 5.7124 ± 0.6451 | 7.7206 ± 0.4463 | 5.1270 ± 1.0004 | 6.9426 ± 0.6995 | 1.1358 ± 0.0226 | ||
| 0.9 | 4.3791 ± 0.8241 | 4.8034 ± 0.7321 | 5.1020 ± 0.5421 | 3.8174 ± 0.4699 | 5.7547 ± 0.3975 | 0.9011 ± 0.0733 | ||
| 1 | 4.7055 ± 1.0148 | 5.1588 ± 0.9478 | 7.6675 ± 0.4714 | 4.1536 ± 0.5129 | 5.7145 ± 0.1970 | 1.0095 ± 0.1880 | ||
| GBM | 0.7 | 7.7015 ± 0.5855 | 7.0277 ± 0.8111 | 8.8795 ± 1.1814 | 7.0326 ± 0.8482 | 7.7303 ± 0.3737 | 0.9683 ± 1.7619 | |
| 0.8 | 5.0001 ± 0.3321 | 5.3684 ± 0.2490 | 7.0954 ± 0.8766 | 4.2958 ± 0.3425 | 5.8363 ± 0.2128 | 1.0418 ± 0.0545 | ||
| 0.9 | 4.2771 ± 1.0941 | 4.7508 ± 0.7525 | 8.4035 ± 0.0505 | 3.5803 ± 1.1407 | 5.6849 ± 0.6202 | 0.7750 ± 0.5719 | ||
| 1 | 2.6242 ± 0.1061 | 3.9734 ± 0.1708 | 4.0788 ± 0.5298 | 2.4895 ± 0.0869 | 4.9445 ± 0.1268 | 0.9758 ± 0.1239 | ||
| PPNM | 0.7 | 7.4006 ± 0.7382 | 6.8323 ± 0.7830 | 7.7807 ± 0.1733 | 6.5748 ± 0.7546 | 7.1743 ± 0.1597 | 1.1779 ± 0.3369 | |
| 0.8 | 4.7601 ± 0.6423 | 4.7758 ± 0.4575 | 6.9357 ± 0.5677 | 4.1588 ± 0.4930 | 5.1088 ± 0.3059 | 1.0886 ± 0.3378 | ||
| 0.9 | 3.4342 ± 0.5611 | 3.9414 ± 0.5186 | 9.0882 ± 1.2471 | 3.2336 ± 0.4365 | 5.6435 ± 0.4376 | 1.5625 ± 0.1865 | ||
| 1 | 3.4667 ± 0.6525 | 4.1188 ± 0.4211 | 7.1567 ± 0.4224 | 3.1905 ± 0.5277 | 5.3384 ± 0.6197 | 1.3672 ± 0.1360 | ||
| Models | Max Abundance | FCLS (VCA) [6] | Fan-NMF [48] | GBM-semiNMF (VCA) [38] | PPNMGDA (VCA) [32] | MLM (VCA) [37] | DNSPU [46] | RNMF [54] | Bio-KNMF [57] | BCNMF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | FM | 0.7 | 0.1724 ± 0.0358 | 0.1396 ± 0.0304 | 0.1691 ± 0.0474 | 0.1306 ± 0.0405 | 0.1567 ± 0.0384 | 0.1808 ± 0.0078 | 0.3704 ± 0.3597 | 0.1580 ± 0.0474 | 0.0169 ± 0.0367 |
| 0.8 | 0.1294 ± 0.0271 | 0.1051 ± 0.0110 | 0.1188 ± 0.0307 | 0.0862 ± 0.0314 | 0.1191 ± 0.0220 | 0.1922 ± 0.0092 | 0.4016 ± 1.0598 | 0.1305 ± 0.0307 | 0.0168 ± 0.0002 | ||
| 0.9 | 0.1271 ± 0.0396 | 0.1071 ± 0.0314 | 0.1204 ± 0.0458 | 0.0724 ± 0.0321 | 0.1056 ± 0.0265 | 0.1850 ± 0.0180 | 0.1637 ± 0.2366 | 0.1193 ± 0.0458 | 0.0168 ± 0.0008 | ||
| 1 | 0.1457 ± 0.0496 | 0.1273 ± 0.0408 | 0.1408 ± 0.0603 | 0.0913 ± 0.0378 | 0.1201 ± 0.0288 | 0.1903 ± 0.0119 | 0.5205 ± 0.9566 | 0.1245 ± 0.0603 | 0.0171 ± 0.0028 | ||
| GBM | 0.7 | 0.1443 ± 0.0291 | 0.1210 ± 0.0248 | 0.1351 ± 0.0312 | 0.1161 ± 0.0278 | 0.1247 ± 0.0312 | 0.2083 ± 0.0099 | 0.4591 ± 0.8457 | 0.1299 ± 0.0312 | 0.0176 ± 0.0213 | |
| 0.8 | 0.1097 ± 0.0332 | 0.1007 ± 0.0323 | 0.1033 ± 0.0347 | 0.0802 ± 0.0223 | 0.0873 ± 0.0179 | 0.1963 ± 0.0056 | 0.1700 ± 0.1802 | 0.0972 ± 0.0347 | 0.0166 ± 0.0007 | ||
| 0.9 | 0.1043 ± 0.0277 | 0.0918 ± 0.0219 | 0.0987 ± 0.0306 | 0.0700 ± 0.0229 | 0.0834 ± 0.0195 | 0.1866 ± 0.0025 | 0.6296 ± 1.5157 | 0.1132 ± 0.0306 | 0.0167 ± 0.0049 | ||
| 1 | 0.0813 ± 0.0069 | 0.0764 ± 0.0058 | 0.0733 ± 0.0061 | 0.0413 ± 0.0031 | 0.0552 ± 0.0025 | 0.1930 ± 0.0075 | 0.0771 ± 0.0061 | 0.0908 ± 0.0061 | 0.0178 ± 0.0009 | ||
| PPNM | 0.7 | 0.1607 ± 0.0265 | 0.1418 ± 0.0196 | 0.1451 ± 0.0308 | 0.1172 ± 0.0277 | 0.1229 ± 0.0266 | 0.2025 ± 0.0079 | 0.1545 ± 0.0240 | 0.1515 ± 0.0308 | 0.0274 ± 0.0055 | |
| 0.8 | 0.1393 ± 0.0180 | 0.1269 ± 0.0156 | 0.1289 ± 0.0197 | 0.0794 ± 0.0145 | 0.0881 ± 0.0184 | 0.2021 ± 0.0088 | 0.1352 ± 0.0170 | 0.1282 ± 0.0197 | 0.0290 ± 0.0029 | ||
| 0.9 | 0.1095 ± 0.0171 | 0.1055 ± 0.0156 | 0.0940 ± 0.0154 | 0.0558 ± 0.0180 | 0.0783 ± 0.0149 | 0.2342 ± 0.0040 | 0.1080 ± 0.0161 | 0.1151 ± 0.0154 | 0.0253 ± 0.0019 | ||
| 1 | 0.1230 ± 0.0263 | 0.1187 ± 0.0205 | 0.1044 ± 0.0316 | 0.0594 ± 0.0260 | 0.0719 ± 0.0204 | 0.1964 ± 0.0112 | 0.1204 ± 0.0252 | 0.1337 ± 0.0316 | 0.0235 ± 0.0022 | ||
| Models | Number of Pixels | FCLS [6] | FanNMF [48] | GBM-semiNMF [38] | PPNMGDA [32] | MLM [37] | DNSPU [46] | RNMF [54] | Bio-KNMF [57] | BCNMF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FM | 1000 | 0.1239 | 4.1152 | 1.2758 | 53.5966 | 15.7729 | 1.5195 | 3.4219 | 148.6391 | 1.2356 |
| 2000 | 0.2273 | 5.2855 | 2.6185 | 99.8770 | 30.9716 | 5.9325 | 6.6961 | 291.4074 | 2.0923 | |
| 3000 | 0.3489 | 9.1838 | 4.1724 | 135.5260 | 45.9855 | 12.1312 | 9.7336 | 431.4345 | 2.8586 | |
| 4000 | 0.4403 | 17.1908 | 5.9542 | 161.9464 | 64.2482 | 25.9203 | 13.3124 | 639.6334 | 3.8118 | |
| GBM | 1000 | 0.1200 | 2.3792 | 1.2907 | 41.7358 | 16.5592 | 1.6612 | 2.9935 | 154.0707 | 1.2892 |
| 2000 | 0.2000 | 4.9185 | 2.7440 | 90.5012 | 33.4882 | 5.8882 | 6.9182 | 300.5740 | 2.3254 | |
| 3000 | 0.3958 | 9.6656 | 4.7533 | 88.6577 | 48.5171 | 13.1536 | 11.5889 | 448.1540 | 3.3518 | |
| 4000 | 0.3981 | 16.7353 | 5.7010 | 138.8427 | 63.7448 | 24.6258 | 13.0360 | 632.6619 | 3.7500 | |
| PPNM | 1000 | 0.1049 | 1.9698 | 1.2424 | 63.5584 | 17.0303 | 1.3595 | 3.4627 | 149.3477 | 1.1292 |
| 2000 | 0.1993 | 6.8100 | 2.6413 | 71.1788 | 34.0535 | 5.8834 | 6.7921 | 297.3334 | 2.0101 | |
| 3000 | 0.3547 | 7.6955 | 4.2586 | 151.1831 | 46.1141 | 12.2787 | 9.6034 | 456.6310 | 2.7770 | |
| 4000 | 0.3929 | 11.3194 | 5.5825 | 277.9795 | 85.2519 | 26.2875 | 11.1857 | 579.5540 | 3.6767 |
| Scene | Virtual Citrus Orchard |
|---|---|
| Illumination sources | A directional light (direct light) and a skymap (diffuse light) |
| Sensor platforms | Full-range (350–2500 nm) analytic spectral devices Fieldspec JR spectroradiometer with a 25 foreoptic; sensor noise, drift, etc., are ignored; number of bands: 216; spectral resolution: 10 nm; 20 × 20 pixels; spatial resolution: 2 m |
| Material optical properties | Description of photons’ interactions: bidirectional scattering distribution function (BSDF) model Ground covers’ spectrum: Tree (a calibrated citrus tree in [70]); Weed (Lolium sp); Soil (dry Luvisol) |
| Geometry descriptions | Leaves, branches and trunk are modeled as triangular meshes Row spacing: 4.5 m; tree spacing: 2 m; tree height: 3 m; row azimuth: 7.3° |
| Dataset | Virtual Orchard | AVIRIS | HYDICE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSAD | RMSE | (dB) | ||
| VCA-FCLS [4,6] | 7.0874 | 0.3494 | 28.4243 | 23.5525 |
| Fan-NMF [48] | 7.5851 | 0.3459 | 23.2673 | 20.0746 |
| GBM-semiNMF [38] | 7.0874 (VCA [4]) | 0.3203 | 25.8111 | 28.6362 |
| PPNMGDA [32] | 7.0874 (VCA [4]) | 0.2726 | 16.1437 | 17.5868 |
| MLM [37] | 7.0874 (VCA [4]) | 0.2763 | 17.9693 | 19.6737 |
| DNSPU [46] | 7.5817 | 0.2886 | 21.6336 | 18.9756 |
| RNMF [54] | 8.3689 | 0.3491 | 28.4953 | 27.0158 |
| Bio-KNMF [57] | 7.7868 | 0.3480 | 29.3000 | 30.7360 |
| BCNMF (FM) | 7.0289 | 0.2681 | 13.5714 | 23.1293 |
| BCNMF (GBM) | 7.0289 | 0.2681 | 13.5714 | 23.1293 |
| BCNMF (PPNM) | 6.7619 | 0.2027 | 17.5071 | 19.5446 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, B.; Wang, B.; Wu, Z. Unsupervised Nonlinear Hyperspectral Unmixing Based on Bilinear Mixture Models via Geometric Projection and Constrained Nonnegative Matrix Factorization. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050801
Yang B, Wang B, Wu Z. Unsupervised Nonlinear Hyperspectral Unmixing Based on Bilinear Mixture Models via Geometric Projection and Constrained Nonnegative Matrix Factorization. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(5):801. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050801
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Bin, Bin Wang, and Zongmin Wu. 2018. "Unsupervised Nonlinear Hyperspectral Unmixing Based on Bilinear Mixture Models via Geometric Projection and Constrained Nonnegative Matrix Factorization" Remote Sensing 10, no. 5: 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050801
APA StyleYang, B., Wang, B., & Wu, Z. (2018). Unsupervised Nonlinear Hyperspectral Unmixing Based on Bilinear Mixture Models via Geometric Projection and Constrained Nonnegative Matrix Factorization. Remote Sensing, 10(5), 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050801