Troposphere Water Vapour Tomography: A Horizontal Parameterised Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Principle of the Proposed Parameterised Approach for Tropospheric Tomography
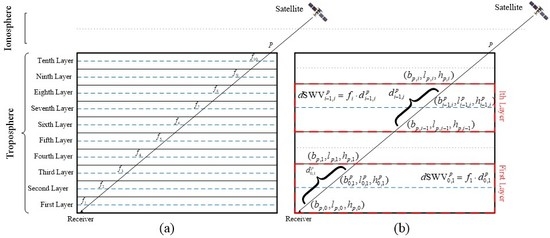
2.1. Estimation of Slant Water Vapor (SWV) Value
2.2. Horizontal Parameterised Approach for Tropospheric Tomography
2.3. Prior Constraint
3. The Weights Strategy for Proposed Tomography Approach
3.1. Selection of the Weights for the Same Type of Equation
3.2. Determination of the Weights for Different Types of Equations
- (1)
- Set the initial value of unit weight variance for different equations as the same, for example 1 is selected in our study.
- (2)
- Conduct adjustment using the least squares method for Equation (10) and obtain the posteriori residuals of observation equation and priori equation ( and ).
- (3)
- (4)
- Decide whether the unit weight variances and are equal or not. In our study, the homogeneity test is used on the principle that the estimated variance components are statistically equal [25,28]. In Figure 2, represents the case when the calculated posteriori unit weight variances are not equal while refers to the opposite case.
- (5)
- Adjust and update the weight matrices according to the formula below and repeat Steps (2) to (4) until the relationship between the calculated and in Step (4) satisfies the termination criteria for statistical equality.where is the number of iterations, and is an arbitrary constant which takes the value of .
4. Validation of the Horizontal Parameterised Approach
4.1. Processing Strategy
4.2. Evaluation of the Proposed Tomographic Model
4.2.1. Internal Accuracy Validation
4.2.2. External Accuracy Validation
4.3. Comparison with the Traditional Tomographic Method
4.3.1. Uniformity of the Height System
- (1)
- Converting geopotential to geopotential height [33]:where represents geopotential while represents geopotential height. is the local gravitational acceleration with a constant value of 9.80665 m/s2.
- (2)
- Converting geopotential height to geoid height according to the formulae below [33,34,35]:where is the ellipsoid height. represents the normal gravitational acceleration on the surface of the ellipsoid of revolution while is an effective radius of the Earth for latitude . is the normal gravitational acceleration on the surface of the ellipsoid for latitude 45° (9.80665 m/s2); and and can be calculated from [33]:
- (3)
- Converting geoid height to quasi-geoid height using the official Earth Gravitational Model 2008 (EGM 2008) derived from the U.S. National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency EGM Development Team [36]:where represents the quasi-geoid height. and are the geoid and height anomaly, respectively, which are both derived from EGM 2008.
- (4)
4.3.2. Integrated Water Vapour (IWV) Comparison
4.3.3. Water Vapour Profile Comparison
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braun, J.; Rocken, C.; Meertens, C.; Ware, R. Development of a water vapor tomography system using low cost L1 GPS receivers. Proc. Ninth Anrruai ARM Sci. Team Meet. 1999, 2226, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, A.; Ruffini, G.; Rius, A. 4D tropospheric tomography using GPS slant wet delays. Ann. Geophys. 2000, 18, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seko, H.; Shimada, S.; Nakamura, H.; Kato, T. 3-d distribution of water vapor estimated from tropospheric delay of GPS data in a mesoscale precipitation system of the Baiu front. Earth Planets Space 2000, 52, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, D.; MacMillan, D.S.; Gipson, J.M. Tropospheric delay ray tracing applied in VLBI analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2014, 119, 9156–9170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hofmeister, A.; Böhm, J. Application of ray-traced tropospheric slant delays to geodetic VLBI analysis. J. Geodesy 2017, 91, 945–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirahara, K. Local GPS tropospheric tomography. Earth Planets Space 2000, 52, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Troller, M.; Bürki, B.; Cocard, M.; Geiger, A.; Kahle, H.G. 3-D refractivity field from GPS double difference tomography. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 29, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skone, S.; Hoyle, V. Troposphere modeling in a regional GPS network. J. Glob. Position. Syst. 2005, 4, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, T.; Gradinarsky, L. Water vapor tomography using GPS phase observations: Simulation results. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2927–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, M.; Raabe, A. Preconditions to ground based GPS water vapour tomography. Ann. Geophys. 2007, 25, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perler, D.; Geiger, A.; Hurter, F. 4D GPS water vapor tomography: New parameterised approaches. J. Geodesy 2011, 85, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenot, H.; Walpersdorf, A.; Reverdy, M.; Van Baelen, J.; Ducrocq, V.; Champollion, C.; Giroux, P. A GPS network for tropospheric tomography in the framework of the Mediterranean hydrometeorological observatory Cévennes-Vivarais (southeastern France). Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 553–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, Y.; Zhao, Q. A novel, optimized approach of voxel division for water vapor tomography. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2016, 129, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Cai, C.; Liu, Z. GNSS troposphere tomography based on two-step reconstructions using GPS observations and COSMIC profiles. Ann. Geophys. 2013, 31, 1805–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alshawaf, F. Constructing Water Vapor Maps by Fusing InSAR, GNSS and WRF Data. Ph.D. Dissertation, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Karlsruhe, Baden-Württemberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Heublein, M.; Zhu, X.X.; Alshawaf, F.; Mayer, M.; Bamler, R.; Hinz, S. Compressive sensing for neutrospheric water vapor tomography using GNSS and InSAR observations. Geosci. Remote Sens. Symp. (IGARSS) 2015, 5268–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benevides, P.; Nico, G.; Catalao, J.; Miranda, P. Merging SAR interferometry and GPS tomography for high-resolution mapping of 3D tropospheric water vapour. Geosci. Remote Sens. Symp. (IGARSS) 2015, 3607–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Ye, S.R.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Xia, P.F. Near real-time water vapor tomography using ground-based GPS and meteorological data: Long-term experiment in Hong Kong. Ann. Geophys. 2014, 32, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, Y.B.; Zhao, Q.Z.; Zhang, B. A method to improve the utilization of GNSS observation for water vapor tomography. Ann. Geophys. 2016, 34, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bender, M.; Dick, G.; Ge, M.; Deng, Z.; Wickert, J.; Kahle, H.G.; Tetzlaff, G. Development of a GNSS water vapour tomography system using algebraic reconstruction techniques. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 1704–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bevis, M.; Businger, S.; Herring, T.A.; Rocken, C.; Anthes, R.A.; Ware, R.H. GPS meteorology: Remote sensing of atmospheric water vapor using the Global Positioning System. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 15787–15801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, P.H. GPS real-time estimation of precipitable water vapor-Hong Kong experiences. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2007, 36, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Herring, T.A.; King, R.W.; McClusky, S.C. Documentation of the GAMIT GPS Analysis Software Release 10.4; Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Böhm, J.; Niell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Schuh, H. Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Yang, F.; Shi, J.; Xu, C. An optimal weighting method of global positioning system (GPS) troposphere tomography. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 5880–5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafarend, E.; Kleusberg, A.; Schaffrin, B. An introduction to the variance-covariance component estimation of Helmert type. Z. Vermess. 1980, 105, 161–180. [Google Scholar]
- Mikhail, E.; Ackerman, F. Observation and Least Square; University Press of America: New York, NY, USA, 1976; pp. 110–115. [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett, M.S. Properties of sufficiency and statistical tests. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1937, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocken, C.; Hove, T.V.; Johnson, J.; Solheim, F.; Ware, R.; Bevis, M.; Businger, S. GPS/STORM-GPS sensing of atmospheric water vapor for meteorology. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1995, 12, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niell, A.E. Comparison of measurements of atmospheric wet delay by radiosonde, water vapor radiometer, GPS, and VLBI. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2001, 18, 830–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, B.; Joerg, S. Analysis of water vapor over nigeria using radiosonde and satellite data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2012, 51, 1855–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, G. Reconstruction of 3D Wet Refractivity Fields in the Lower Atmosphere along Bended GNSS Signal Paths. Ph.D. Thesis, TU Wien, Department for Geodesy and Geoinformation, Vienna, Austria, 2017. Available online: http://amalthea.hg.tuwien.ac.at/~members/Moeller/Thesis_Gregor_Moeller_final_version.pdf (accessed on 9 September 2017).
- Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Wu, S.; Fan, S.; Cheng, Y. Water vapor weighted mean temperature and its impact on the determination of precipitable water vapor and its linear trend. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 2849–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dousa, J.; Elias, M. An improved model for calculating tropospheric wet delay. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 4389–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zus, F.; Dick, G.; Douša, J.; Heise, S.; Wickert, J. The rapid and precise computation of GPS slant total delays and mapping factors utilizing a numerical weather model. Radio Sci. 2014, 49, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavlis, N.K.; Holmes, S.A.; Kenyon, S.C.; Factor, J.K. The development and evaluation of the Earth Gravitational Model 2008 (EGM2008). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2012, 117, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, S.; Bengtsson, L.; Gendt, G. On the determination of atmospheric water vapor from GPS measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 1999–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Dai, A. Global estimates of water vapor weighted mean temperature of the atmosphere for gps applications. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, 2927–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartier, P.M.; Keller, C.P. Multivariate interpolation to incorporate thematic surface data using inverse distance weighting (IDW). Comput. Geosci. 1996, 22, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, Z. Voxel-optimized regional water vapor tomography and comparison with radiosonde and numerical weather model. J. Geodesy 2014, 88, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhao, Q. Maximally using gps observation for water vapor tomography. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 7185–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Number | Longitude (°E) | Latitude (°N) | Number | Longitude (°E) | Latitude (°N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 113.875 | 22.250 | 7 | 114.125 | 22.375 |
| 2 | 114.000 | 22.250 | 8 | 114.250 | 22.375 |
| 3 | 114.125 | 22.250 | 9 | 113.875 | 22.500 |
| 4 | 114.250 | 22.250 | 10 | 114.000 | 22.500 |
| 5 | 113.875 | 22.375 | 11 | 114.125 | 22.500 |
| 6 | 114.000 | 22.375 | 12 | 114.250 | 22.500 |
| Statistical Result | Root Mean Square (RMS) | Bias |
|---|---|---|
| Scheme 1 vs. Radiosonde | 5.1 | −3.9 |
| Scheme 2 vs. Radiosonde | 3.2 | −0.8 |
| Scheme 1 vs. ECMWF | 6.3 | −5.9 |
| Scheme 2 vs. ECMWF | 3.3 | −1.7 |
| Statistical Result | RMS | Bias |
|---|---|---|
| Scheme 1 vs. Radiosonde | 1.33 | 0.38 |
| Scheme 2 vs. Radiosonde | 0.88 | 0.06 |
| Scheme 1 vs. ECMWF | 1.59 | 0.40 |
| Scheme 2 vs. ECMWF | 0.92 | −0.08 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Q.; Yao, Y.; Yao, W. Troposphere Water Vapour Tomography: A Horizontal Parameterised Approach. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10081241
Zhao Q, Yao Y, Yao W. Troposphere Water Vapour Tomography: A Horizontal Parameterised Approach. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(8):1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10081241
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Qingzhi, Yibin Yao, and Wanqiang Yao. 2018. "Troposphere Water Vapour Tomography: A Horizontal Parameterised Approach" Remote Sensing 10, no. 8: 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10081241
APA StyleZhao, Q., Yao, Y., & Yao, W. (2018). Troposphere Water Vapour Tomography: A Horizontal Parameterised Approach. Remote Sensing, 10(8), 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10081241