Tidal Mixing Signatures in the Hong Kong Coastal Waters from Satellite-Derived Sea Surface Temperature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Tidal Mixing and Ocean Currents
2.2. Satellite-Based SST and In Situ Velocity Data
2.3. Tidal Analysis
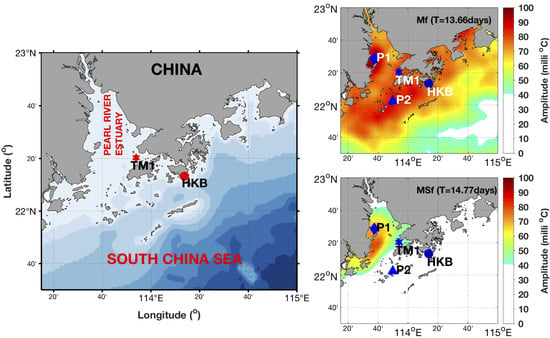
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, G. Nonlinear effect of tidal friction, II. Acta Oceanologica Sinica 1981, 6 (Suppl. 1), 105–122. [Google Scholar]
- Nugroho, D.; Koch-Larrouy, A.; Gaspar, P.; Lyard, F.; Reffray, G.; Tranchant, B. Modelling explicit tides in the Indonesian seas: An important process for surface sea water properties. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 131, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beardsley, R.C.; Duda, T.F.; Lynch, J.F.; Irish, J.D.; Ramp, S.R.; Chiu, C.-S.; Tang, T.Y.; Yang, Y.-J.; Fang, G. Barotropic tide in the northeast South China Sea. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2004, 29, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Guo, P.; Fang, W.-D. Internal tides in the northern South China Sea from 20-day in-situ mooring observations in 1998. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 14, 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.X.; Fang, G.H.; Susanto, R.D.; Adi, T.R.; Fan, B.; Setiawan, A.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.G.; Gao, X.M. Tidal elevation, current and energy flux in the area between the South China Sea and Java Sea. Ocean Sci. 2016, 12, 2831–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, M.H.; Peacock, T.; MacKinnon, J.A. The formation and fate of internal waves in the South China Sea. Nature 2015, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatayama, T.; Awaji, T.; Akitomo, K. Tidal currents in the Indonesian Seas and their effect on transport and mixing. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 12353–12373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Kwok, Y.-K.; Yu, K.; Zhu, Y. Numerical simulation of principal tidal constituents in the South China Sea, Gulf of Tonkin and Gulf of Thailand. Cont. Shelf Res. 1999, 19, 845–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Huang, Q.; Long, X. Three-dimensional numerical model study of the residual current in the South China, Sea. Oceanol. Acta. 2003, 26, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, T.; Gan, J.; Erofeeva, S.Y. Numerical study of the tidal and tidal dynamics in the South China Sea. Deep-Sea Res. Part I 2008, 55, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Counillo, F.; Zhu, J.; Bertno, L. An eddy resolving tidal-driven model of the South China Sea assimilating along-track SLA data using the EnOI. Ocean Sci. 2011, 7, 609–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, B.H.; Min, B.I.; Kim, K.O.; Yuk, J.H. Wavetide-surge coupled simulation for typhoon Maemi. China Ocean Eng. 2013, 27, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzega, P.; Bergé, M. Ocean tides in the Asian semi-enclosed seas from TOPEX/ POSEIDON. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 24867–24881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagi, T.; Takao, T.; Marimoto, A. Co-tidal and co-range charts in the South China Sea derived from satellite altimetry data. La Mer 1997, 35, 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Ffield, A.; Gordon, A.L. Tidal mixing signatures in the Indonesian seas. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1996, 26, 1924–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, D.; Woodworth, P. Sea Level Science: Understanding Tides, Surges, Tsunamis and Mean Sea-Level Changes; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, A.J.; Pineda, J. Tidal mixing modulation of sea surface temperature and diatom abundance in Southern California. Cont. Shelf Res. 2001, 21, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes-Vaz, R.A.; Lennon, G.W.; Samarasinghe, J.R. The negative role of turbulence in estuarine mass transport. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1989, 28, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.D.; Susanto, R.D. Tidal mixing signatures in the Indonesian seas from high-resolution sea surface temperature data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JPL MUR MEaSUREs Project, 2010, GHRSST Level-4 MUR Global Foundation Sea Surface Temperature Analysis Version 1, PO DAAC, CA, USA. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.5067/GHNMR-4FJ01 (accessed on 19 March 2016).
- Chin, T.M.; Vazquez, J.; Armstrong, E. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document: A Multi-Scale, High-Resolution Analysis of Global Sea Surface Temperature, Version 1.3; Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2013.
- Chin, T.M.; Vazquez-Cuervo, J.; Armstrong, E. Multi-scale high-resolution analysis of global sea surface temperature. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 200, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codiga, D.L. Unified Tidal Analysis and Prediction Using the UTide Matlab Functions; Technical Report 2011-01; Graduate School of Oceanography, University of Rhode Island: Narragansett, RI, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowicz, R.; Beardsley, B.; Lentz, S. Classical tidal harmonic analysis with errors in matlab using t-tide. Comput. Geosci. 2002, 28, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leffler, K.E.; Jay, D. Enhancing tidal harmonic analysis: Robust (hybrid L1/L2) solutions. Cont. Shelf Res. 2009, 29, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.H.; Brown, J.; Matthews, J.; Allen, G. Tidal straining, density currents and stirring control of estuarine stratification. Estuaries 1990, 13, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, B.B. Tidal Analysis and Prediction; NOAA special publication, NOS-COPS 3; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA): Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2007.
- MacMahan, J.; Kreeke, J.; Reniers, A.; Elgar, S.; Raubenheimer, B.; Thornton, E.; Weltmer, M.; Rynne, P.; Brown, J. Fortnightly tides and subtidal motions in a choked inlet. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 150, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Percival, D.B.; Walden, A.T. Spectral Analysis for Physical Applications: Multitaper and Conventional Univariate Techniques; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, D.J. Spectrum estimation and harmonic analysis. Proc. IEEE 1982, 70, 1055–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egbert, G.D.; Erofeeva, S.Y. Efficient inverse modeling of barotropic ocean tides. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, W.R. Tide-induced mixing in the Amazon frontal zone. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 2341–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetzel, Y.; Pattiaratchi, C.; Lowe, R. Intermittent dense water outflows under variable tidal forcing in Shark Bay, Western Australia. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 66, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetzel, Y.; Pattiaratchi, C.; Lowe, R.; Hofmeister, R. Wind and tidal mixing controls on stratification and dense water outflows in a large hypersaline bay. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 6034–6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Susanto, R.D.; Pan, J.; Devlin, A.T. Tidal Mixing Signatures in the Hong Kong Coastal Waters from Satellite-Derived Sea Surface Temperature. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11010005
Susanto RD, Pan J, Devlin AT. Tidal Mixing Signatures in the Hong Kong Coastal Waters from Satellite-Derived Sea Surface Temperature. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleSusanto, R. Dwi, Jiayi Pan, and Adam T. Devlin. 2019. "Tidal Mixing Signatures in the Hong Kong Coastal Waters from Satellite-Derived Sea Surface Temperature" Remote Sensing 11, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11010005
APA StyleSusanto, R. D., Pan, J., & Devlin, A. T. (2019). Tidal Mixing Signatures in the Hong Kong Coastal Waters from Satellite-Derived Sea Surface Temperature. Remote Sensing, 11(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11010005