Automatic Shadow Detection in Urban Very-High-Resolution Images Using Existing 3D Models for Free Training
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Related Work
- Shadows have low radiance due to obstruction of direct sunlight.
- Radiance received from shadow areas decreases from short (blue-violet) to long (red) wavelength due to scattering effects.
- In urban canyons, reflection effects of surroundings cannot be ignored in the shadow area.
- Radiance received from shadow areas is material-dependent.
1.3. Contribution of Our Study
- We provide a fully automatic, effective, and robust approach of shadow detection in VHR images using existing 3D city models for shadow reconstruction to provide free-training samples. The reconstructed shadow image is used label VHR images for providing free training, meaning that training samples are generated by a computer and free from manual labor.
- We conduct a comparative study on how machine learning methods are affected by mislabeling effects introduced by free-training samples and their ability to detect complicated shadows.
2. Study Area and Data Preparation
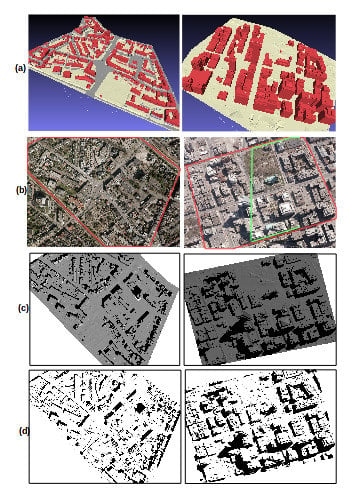
2.1. 3D model Generation
2.2. VHR Image Description
3. Shadow Detection
3.1. Shadow Reconstruction Using an Existing 3D Model
3.1.1. Ray Tracing
3.1.2. KD Tree
3.2. Adaptive Erosion Filtering
3.3. Classifications from Automatically Selected Samples
3.3.1. QDA Classification with Decision Fusion
3.3.2. Support Vector Machine
3.3.3. K Nearest Neighbors
3.3.4. Random Forest
3.4. Evaluation of Classification
4. Experiments and Comparisons
4.1. Feasibility of Shadow Reconstruction for Free-Training Samples
4.2. Method Comparison for Classification from Free-Training Samples
4.2.1. Shadow Classification Results for Amersfoort
4.2.2. Shadow Classification Results for Toronto
4.2.3. Mislabeling Simulation on Toronto Dataset
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haala, N.; Kada, M. An update on automatic 3D building reconstruction. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosselman, G.; Dijkman, S. 3D building model reconstruction from point clouds and ground plans. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2001, 34, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Hirschmuller, H. Stereo processing by semiglobal matching and mutual information. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 30, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartley, R.; Zisserman, A. Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zlatanova, S.; Holweg, D. 3D Geo-information in emergency response: A framework. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on Mobile Mapping Technology, Kunming, China, 29–31 March 2004; pp. 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ok, A.O. Automated detection of buildings from single VHR multispectral images using shadow information and graph cuts. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 86, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeline, K.; Chen, M.; Briottet, X.; Pang, S.; Paparoditis, N. Shadow detection in very high spatial resolution aerial images: A comparative study. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 80, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, L.; Melgani, F.; Mercier, G. A complete processing chain for shadow detection and reconstruction in VHR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3440–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, V.J. A comparative study on shadow compensation of color aerial images in invariant color models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.L.; Lin, Y.R.; Huang, Y.H. Efficient shadow detection of color aerial images based on successive thresholding scheme. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. Automatica 1975, 11, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbel, E.; Hel-Or, H. Shadow removal using intensity surfaces and texture anchor points. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 1202–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Dai, Q.; Hoiem, D. Paired regions for shadow detection and removal. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 2956–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; She, R.; Xiao, D.; Ma, K.L. Fast Shadow Removal Using Adaptive Multi-Scale Illumination Transfer; Computer Graphics Forum; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; Volume 32, pp. 207–218. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, A.; Lischinski, D.; Weiss, Y. A closed-form solution to natural image matting. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 30, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolt, G.; Shimoni, M.; Ahlberg, J. A shadow detection method for remote sensing images using VHR hyperspectral and LIDAR data. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011; pp. 4423–4426. [Google Scholar]
- Gorte, B.; van der Sande, C. Reducing false alarm rates during change detection by modeling relief, shade and shadow of multi-temporal imagery. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, 40, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yan, L.; Yuan, Q.; Ma, Z. An Automatic Shadow Detection Method for VHR Remote Sensing Orthoimagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elberink, S.O.; Stoter, J.; Ledoux, H.; Commandeur, T. Generation and dissemination of a national virtual 3D city and landscape model for the Netherlands. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2013, 79, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, S.C.; Whitman, D.; Shyu, M.L.; Yan, J.; Zhang, C. A progressive morphological filter for removing nonground measurements from airborne LIDAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soetaert, K.; Petzoldt, T. Inverse modelling, sensitivity and monte carlo analysis in R using package FME. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicodemus, F.E. Directional reflectance and emissivity of an opaque surface. App. Opt. 1965, 4, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, R. Cascaded Shadow Maps; Developer Documentation; NVIDIA Corp.: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer, M.; Scherzer, D.; Purgathofer, W. Light Space Perspective Shadow Maps; Rendering Techniques; The Eurographics Association: Norköping, Sweden, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Whitted, T. An improved illumination model for shaded display. ACM SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. ACM 1979, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wald, I.; Havran, V. On building fast kd-trees for ray tracing, and on doing that in O (N log N). In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Symposium on Interactive Ray Tracing, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–20 September 2006; pp. 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Theodoridis, S.; Koutroumbas, K. Pattern recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2008, 19, 376. [Google Scholar]
- Fauvel, M.; Chanussot, J.; Benediktsson, J.A. Decision fusion for the classification of urban remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2828–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Gorte, B. Shadow detection from VHR aerial images in urban area by using 3D city models and a decision fusion approach. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, 42, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromiley, P.; Thacker, N.; Bouhova-Thacker, E. Shannon Entropy, Renyi Entropy, and Information; Statistics and Information Series; The University of Manchester: Manchester, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Frénay, B.; Verleysen, M. Classification in the presence of label noise: A survey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2014, 25, 845–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, S.; Yugami, N. An average-case analysis of the k-nearest neighbor classifier for noisy domains. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Nagoya, Japan, 23–29 August 1997; pp. 238–245. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, X.; Heaton, J.S.; Zheng, S.; Charlet, D.A.; Liu, H. Applying tree-based ensemble algorithms to the classification of ecological zones using multi-temporal multi-source remote-sensing data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 1823–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gislason, P.O.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Sveinsson, J.R. Random forests for land cover classification. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briem, G.J.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Sveinsson, J.R. Multiple classifiers applied to multisource remote sensing data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2291–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M. Random forest classifier for remote sensing classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Classification and Regression Trees; Routledge: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dare, P.M. Shadow analysis in high-resolution satellite imagery of urban areas. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2005, 71, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfanidis, S.J. Introduction to Signal Processing; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]











| Method | OA % | KC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QDA Fusion | 89.92 | 95.80 | 93.45 | 0.87 |
| SVM | 84.66 | 98.88 | 92.08 | 0.84 |
| KNN | 95.61 | 95.65 | 95.72 | 0.91 |
| RF | 93.92 | 96.12 | 95.38 | 0.92 |
| Tsai’s RGB | 99.12 | 70.88 | 80.51 | 0.62 |
| Tsai’s ratio | 82.34 | 91.46 | 88.18 | 0.76 |
| Adeline’s | 90.95 | 97.53 | 94.20 | 0.88 |
| Methods | OA % | KC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QDA Fusion | 94.99 | 88.82 | 95.16 | 0.88 |
| SVM | 94.20 | 93.98 | 96.69 | 0.92 |
| KNN | 97.69 | 88.63 | 95.85 | 0.90 |
| RF | 97.34 | 91.05 | 96.59 | 0.92 |
| Tsai’s RGB | 98.50 | 83.41 | 92.87 | 0.85 |
| Tsai’s ratio | 95.60 | 82.75 | 93.20 | 0.84 |
| Adeline’s | 80.48 | 92.81 | 92.55 | 0.81 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, K.; Lindenbergh, R.; Gorte, B. Automatic Shadow Detection in Urban Very-High-Resolution Images Using Existing 3D Models for Free Training. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11010072
Zhou K, Lindenbergh R, Gorte B. Automatic Shadow Detection in Urban Very-High-Resolution Images Using Existing 3D Models for Free Training. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(1):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11010072
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Kaixuan, Roderik Lindenbergh, and Ben Gorte. 2019. "Automatic Shadow Detection in Urban Very-High-Resolution Images Using Existing 3D Models for Free Training" Remote Sensing 11, no. 1: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11010072
APA StyleZhou, K., Lindenbergh, R., & Gorte, B. (2019). Automatic Shadow Detection in Urban Very-High-Resolution Images Using Existing 3D Models for Free Training. Remote Sensing, 11(1), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11010072