Inherent Optical Properties in Lake Taihu Derived from VIIRS Satellite Observations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. In Situ Data and VIIRS-SNPP Data
2.1. In Situ Measurements of Rrs(λ), aph(λ), and adg(λ)
2.2. VIIRS-SNPP Satellite Observations
3. The NIR-Based IOP Algorithm in Lake Taihu and Its Performance
3.1. The NIR-Based IOP Algorithm
3.2. Performance of the NIR-Based IOP Algorithm in Lake Taihu
4. IOPs from VIIRS-SNPP Observations between 2012–2018
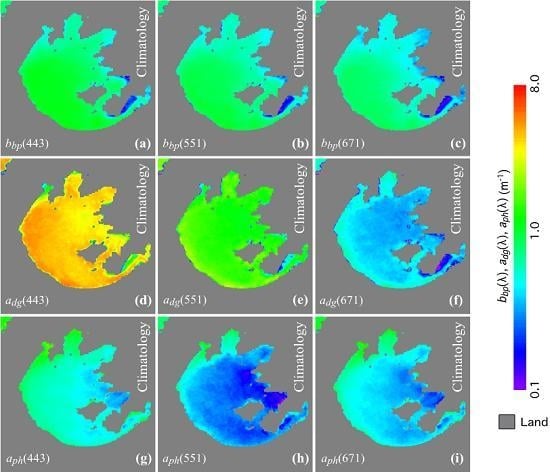
4.1. Climatology IOPs between 2012 and 2018
4.2. Seasonal Variability of IOPs in Lake Taihu
4.3. Time Series of IOPs in Lake Taihu between 2012 and 2018
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
A NIR-Based IOP Algorithm for VIIRS-SNPP in Lake Taihu
Step 1: Compute bbp(λ) and at(λ) from the VIIRS-SNPP nLw(λ)
Step 2: Decompose at(λ) into adg(λ) and aph(λ)
References
- Guo, L. Ecology—Doing battle with the green monster of Taihu Lake. Science 2007, 317, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W.; Tang, J.W. Water property monitoring and assessment for China’s inland Lake Taihu from MODIS-Aqua measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.Q.; Zhu, G.W.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.L.; Li, W.; Paerl, H.W.; Carmichael, W.W. A drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: Linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Son, S.; Harding, L.W. Retrieval of diffuse attenuation coefficient in the Chesapeake Bay and turbid ocean regions for satellite ocean color applications. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Wang, M. Diffuse attenuation coefficient of the photosynthetically available radiation K-d(PAR) for global open ocean and coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.M.; Lee, Z.P.; Ma, R.H.; Yu, K.; Li, D.Q.; Shang, S.L. Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) observations of cyanobacteria blooms in Taihu Lake, China. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M. Deriving total suspended matter concentration from the near-infrared-based inherent optical properties over turbid waters: A case study in Lake Taihu. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Troy, A. Mapping the concentrations of total suspended matter in Lake Tailm, China, using Landsat-5 TM data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.Q.; Xu, P.Z.; Wu, Q.L.; Luo, L.C.; Zhang, Y.L. Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.Y.; Zhu, G.W.; Zhao, L.L.; Yao, X.; Zhang, Y.L.; Gao, G.; Qin, B.Q. Influence of algal bloom degradation on nutrient release at the sediment-water interface in Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 1803–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B.Q.; Zhu, G.W.; Gao, G. Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Qin, B.Q.; Liu, M.L. Temporal—Spatial variations of chlorophyll a and primary production in Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu, China from 1995 to 2003. J. Plankton Res. 2007, 29, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Yin, Y.; Liu, X.H.; Shi, Z.Q.; Feng, L.Q.; Liu, M.L.; Zhu, G.W.; Gong, Z.J.; Qin, B.Q. Spatial-seasonal dynamics of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in Lake Taihu, a large eutrophic, shallow lake in China. Org. Geochem. 2011, 42, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Li, J.S.; Feng, S.; Zhao, Q.H.; Liu, M.L.; Qin, B.Q. A study of absorption characteristics of chromophoric dissolved organic matter and particles in Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 2007, 592, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; van Dijk, M.A.; Liu, M.L.; Zhu, G.W.; Qin, B.Q. The contribution of phytoplankton degradation to chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in eutrophic shallow lakes: Field and experimental evidence. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4685–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Qin, B.Q. Variations in spectral slope in lake taihu, a large subtropical shallow lake in China. J. Great Lakes Res. 2007, 33, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.H.; Pan, D.L.; Duan, H.T.; Song, Q.J. Absorption and scattering properties of water body in Taihu Lake, China: Backscattering. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 2321–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Shen, Q.; Chen, D. A bio-optical model based method of estimating total suspended matter of Lake Taihu from near-infrared remote sensing reflectance. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 145, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garver, S.A.; Siegel, D.A. Inherent optical property inversion of ocean color spectra and its biogeochemical interpretation.1. Time series from the Sargasso Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1997, 102, 18607–18625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Brown, O.B.; Evans, R.H.; Brown, J.W.; Smith, R.C.; Baker, K.S.; Clark, D.K. A semianalytic radiance model of ocean color. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1988, 93, 10909–10924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.P.; Carder, K.L.; Arnone, R.A. Deriving inherent optical properties from water color: A multiband quasi-analytical algorithm for optically deep waters. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 5755–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werdell, P.J.; Franz, B.A.; Bailey, S.W.; Feldman, G.C.; Boss, E.; Brando, V.E.; Dowell, M.; Hirata, T.; Lavender, S.J.; Lee, Z.P.; et al. Generalized ocean color inversion model for retrieving marine inherent optical properties. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 2019–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.M.; Lee, Z.P.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Carder, K.L.; Walsh, J.J. Ocean color reveals phase shift between marine plants and yellow substance. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.A.; Maritorena, S.; Nelson, N.B.; Hansell, D.A.; Lorenzi-Kayser, M. Global distribution and dynamics of colored dissolved and detrital organic materials. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2002, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maritorena, S.; Siegel, D.A.; Peterson, A.R. Optimization of a semianalytical ocean color model for global-scale applications. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 2705–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Salama, M.S.; Zhou, Y.X.; Li, J.F.; Su, Z.B.; Kuang, D.B. Remote-sensing reflectance characteristics of highly turbid estuarine waters—A comparative experiment of the Yangtze River and the Yellow River. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 2639–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. An assessment of the black ocean pixel assumption for MODIS SWIR bands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Ocean reflectance spectra at the red, near-infrared, and shortwave infrared from highly turbid waters: A study in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and East China Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doron, M.; Belanger, S.; Doxaran, D.; Babin, M. Spectral variations in the near-infrared ocean reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1617–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddick, K.G.; De Cauwer, V.; Park, Y.J.; Moore, G. Seaborne measurements of near infrared water-leaving reflectance: The similarity spectrum for turbid waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hale, G.M.; Querry, M.R. Optical constants of water in the 200 nm to 200 μm wavelength region. Appl. Opt. 1973, 12, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, L.H.; Labrie, D.; Chylek, P. Refractive-indexes of water and ice in the 0.65- to 2.5-μM spectral range. Appl. Opt. 1993, 32, 3531–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roesler, C.S.; Perry, M.J.; Carder, K.L. Modeling in situ phytoplankton absorption from total absorption-spectra in productive inland marine waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1989, 34, 1510–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Schalles, J.F.; Hladik, C.M. Remote chlorophyll-a retrieval in turbid, productive estuaries: Chesapeake Bay case study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.H.; Yin, Y.; Wang, M.Z.; Qin, B.Q. A simple optical model to estimate diffuse attenuation coefficient of photosynthetically active radiation in an extremely turbid lake from surface reflectance. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 20482–20493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.L.; McKee, B.A. Using MODIS Terra 250 m imagery to map concentrations of total suspended matter in coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tang, J.W.; Dong, Q.; Song, Q.T.; Ding, J. Retrieval of total suspended matter concentration in the Yellow and East China Seas from MODIS imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C. A novel ocean color index to detect floating algae in the global oceans. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2118–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Green macroalgae blooms in the Yellow Sea during the spring and summer of 2008. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, C.F.; Li, Y.M.; Zha, Y.; Sun, D.Y.; Yin, B. Validation of a quasi-analytical algorithm for highly turbid eutrophic water of Meiliang Bay in Taihu Lake, China. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2492–2500. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.Z.; Lyu, H.; Wang, Y.N.; Jin, Q.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.M.; Fu, Q.H. An improved approach to retrieve IOPs based on a quasi-analytical algorithm (QAA) for turbid eutrophic inland water. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 5177–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Characterization of particle backscattering of global highly turbid waters from VIIRS ocean color observations. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 9255–9275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. A blended inherent optical property algorithm for global satellite ocean color observations. Limnol. Oceanogr.: Methods 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Characterization of suspended particle size distribution in global highly turbid waters from VIIRS measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2019, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Feng, L.Q.; Li, J.S.; Luo, L.C.; Yin, Y.; Liu, M.L.; Li, Y.L. Seasonal-spatial variation and remote sensing of phytoplankton absorption in Lake Taihu, a large eutrophic and shallow lake in China. J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 1023–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldberg, M.D.; Kilcoyne, H.; Cikanek, H.; Mehta, A. Joint Polar Satellite System: The United States next generation civilian polar-orbiting environmental satellite system. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 13463–13475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomonson, V.V.; Barnes, W.L.; Maymon, P.W.; Montgomery, H.E.; Ostrow, H. MODIS—Advanced facility instrument for studies of the Earth as a system. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1989, 27, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Wang, M. Retrieval of water-leaving radiance and aerosol optical-thickness over the oceans with SeaWiFS—A preliminary algorithm. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W. The NIR-SWIR combined atmospheric correction approach for MODIS ocean color data processing. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 15722–15733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M. Remote sensing of the ocean contributions from ultraviolet to near-infrared using the shortwave infrared bands: Simulations. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Tan, L.; Jiang, L.; Son, S.; Shi, W.; Rausch, K.; Voss, K. Impacts of VIIRS SDR performance on ocean color products. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 10347–10360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Son, S.; Shi, W. Evaluation of MODIS SWIR and NIR-SWIR atmospheric correction algorithms using SeaBASS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.; Cannizzaro, J.P.; English, D.C.; Hu, C. Validation of VIIRS and MODIS reflectance data in coastal and oceanic waters: An assessment of methods. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 220, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Son, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W. Remote sensing of water optical property for China’s inland Lake Taihu using the SWIR atmospheric correction with 1640 and 2130 nm bands. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 2505–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.T.; Ma, R.H.; Xu, X.F.; Kong, F.X.; Zhang, S.X.; Kong, W.J.; Hao, J.Y.; Shang, L.L. Two-Decade Reconstruction of Algal Blooms in China’s Lake Taihu. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3522–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milliman, J.D.; Shen, H.T.; Yang, Z.S.; Meade, R.H. Transport and deposition of river sediment in the Changjiang estuary and adjacent continental-shelf. Cont. Shelf Res. 1985, 4, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| IOP | Coefficient of Determination R2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Bands | 410 nm | 443 nm | 486 nm | 551 nm | 671 nm | |
| at(λ) | 0.772 | 0.760 | 0.810 | 0.784 | 0.745 | |
| adg(λ) | 0.681 | 0.656 | 0.662 | 0.523 | ||
| aph(λ) | 0.487 | 0.398 | 0.594 | 0.474 | 0.439 | 0.537 |
| IOP. | IOP Ratio of Derived/In Situ (Mean ± STD). | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Bands | 410 nm | 443 nm | 486 nm | 551 nm | 671 nm | |
| at(λ) | 0.970 ± 0.233 | 0.975 ± 0.265 | 0.953 ± 0.238 | 0.905 ± 0.202 | 0.897 ± 0.186 | 1.118 + 0.276 |
| adg(λ) | .948 ± 0.298 | ± 0.273 | 1.001 ± 0.296 | 0.956 ± 0.297 | 0.943 ± 0.292 | 0.910 ± 0.331 |
| aph(λ) | 1.196 ± 0.728 | 1.272 ± 0.718 | 0.932 ± 0.641 | 0.967 ± 0.753 | 1.126 ± 0.891 | 1.683 ± 0.640 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, W.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y. Inherent Optical Properties in Lake Taihu Derived from VIIRS Satellite Observations. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121426
Shi W, Wang M, Zhang Y. Inherent Optical Properties in Lake Taihu Derived from VIIRS Satellite Observations. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(12):1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121426
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Wei, Menghua Wang, and Yunlin Zhang. 2019. "Inherent Optical Properties in Lake Taihu Derived from VIIRS Satellite Observations" Remote Sensing 11, no. 12: 1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121426
APA StyleShi, W., Wang, M., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Inherent Optical Properties in Lake Taihu Derived from VIIRS Satellite Observations. Remote Sensing, 11(12), 1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121426