Evaluation of Six Satellite-Based Precipitation Products and Their Ability for Capturing Characteristics of Extreme Precipitation Events over a Climate Transition Area in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Reference Data
2.2.2. SPPs
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Statistical Analysis
2.3.2. Extreme Precipitation Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of the SPPs at Different Temporal Scales
3.1.1. Daily Temporal Scale
3.1.2. Monthly and Annual Temporal Scale
3.2. Evaluation of SPPs to Capture Extreme Precipitation Characteristics
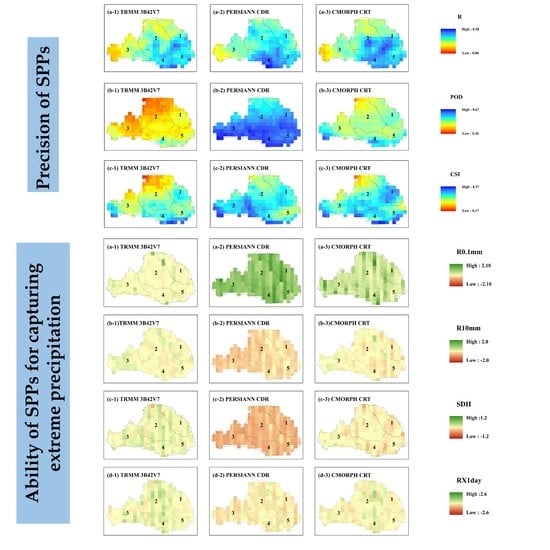
3.2.1. Identification Ability of SPPs for Extreme Precipitation
3.2.2. Spatial Analysis of the Capability of SPPs to Capture Extreme Precipitation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



References
- Bell, J.L.; Sloan, L.C.; Snyder, M.A. Regional Changes in Extreme Climatic Events: A Future Climate Scenario. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xia, J.; She, D. Spatiotemporal variation and statistical characteristic of extreme precipitation in the middle reaches of the Yellow River Basin during 1960–2013. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 135, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, D.; Shao, Q.; Xia, J.; Taylor, J.A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zou, L. Investigating the variation and non-stationarity in precipitation extremes based on the concept of event-based extreme precipitation. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, K.E.; Easterling, D.R.; Redmond, K.; Hubbard, K. Temporal variations of extreme precipitation events in the United States: 1895–2000. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Mishra, V.; Pai, D.S. Observed and projected urban extreme rainfall events in India. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 12621–12641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Dominguez, F.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Urban precipitation extremes: How reliable are regional climate models? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 419–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, D.; Hong, Y. Multi-scale evaluation of high-resolution multi-sensor blended global precipitation products over the Yangtze River. J. Hydrol. 2013, 500, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Liu, J.; Tuo, Y.; Chiogna, G.; Disse, M. Evaluation of eight high spatial resolution gridded precipitation products in Adige Basin (Italy) at multiple temporal and spatial scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 1536–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Javanmard, S.; Yatagai, A.; Nodzu, M.I.; Bodaghjamali, J.; Kawamoto, H. Comparing high-resolution gridded precipitation data with satellite rainfall estimates of TRMM_3B42 over Iran. Adv. Geosci. 2010, 25, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brunetti, M.; Maugeri, M.; Monti, F.; Nannia, T. Temperature and precipitation variability in Italy in the last two centuries from homogenised instrumental time series. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 345–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Gippel, C.J.; Shan, L.; Chen, S.; Yang, W. Uncertainty of Flood Forecasting Based on Radar Rainfall Data Assimilation. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 2710457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Borga, M. Improving Radar-Based Estimation of Rainfall over Complex Terrain. J. Appl. Meteor. 2002, 41, 1163–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Xiong, A.-Y. A conceptual model for constructing high-resolution gauge-satellite merged precipitation analyses. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Tang, G.; Ma, Y.; Huang, Q.; Han, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Guo, X. Remote Sensing Precipitation: Sensors, Retrievals, Validations, and Applications. In Observation and Measurement; Li, X., Vereecken, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 1–23. ISBN 978-3-662-47871-4. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J. The TRMM Multi-Satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA). In Satellite Rainfall Applications for Surface Hydrology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P.P. CMORPH: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.L.; Gao, X.G.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, H.V. Precipitation estimation from remotely sensed information using artificial neural networks. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Ushio, T.; Shige, S.; Kida, S.; Kachi, M.; Okamoto, K. Verification of High-Resolution Satellite-Based Rainfall Estimates around Japan Using a Gauge-Calibrated Ground-Radar Dataset. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 87, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The Global Precipitation Measurement Mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, F.J.; Miller, S.D. Toward improved characterization of remotely sensed precipitation regimes with MODIS/AMSR-E blended data techniques. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations—A new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Duan, Z.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, A.-X. Evaluation of Three Satellite Precipitation Products TRMM 3B42, CMORPH, and PERSIANN over a Subtropical Watershed in China. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 151239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H. Accuracy and spatio-temporal variation of high resolution satellite rainfall estimate over the Ganjiang River Basin. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2013, 56, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Zhang, K.; Hong, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xue, X.; Chen, S. Evaluation of the TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis and its applicability in supporting reservoir operation and water resources management in Hanjiang basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, S.; Chen, C.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, N.; Zaman, Q. Effects of temporal scales and space mismatches on the TRMM 3B42 v7 precipitation product in a remote mountainous area. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 4315–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Lu, J.; Pang, Z. Assessment of TRMM Satellite Precipitation Data and Its Impacts on the Water Balance of the Heihe River Basin. In Proceedings of the PIAGENG 2013: Intelligent Information, Control, and Communication Technology for Agricultural Engineering; Tan, H., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2013; Volume 8762, p. 87620R. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Wang, D. Evaluation of extreme precipitation based on satellite retrievals over China. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 12, 846–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xiong, A.; Wang, Y.; Xie, P. Performance of high-resolution satellite precipitation products over China. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirpa, F.A.; Gebremichael, M.; Hopson, T. Evaluation of High-Resolution Satellite Precipitation Products over Very Complex Terrain in Ethiopia. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghajarnia, N.; Liaghat, A.; Arasteh, P.D. Comparison and evaluation of high resolution precipitation estimation products in Urmia Basin-Iran. Atmos. Res. 2015, 158, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Ashouri, H.; Hsu, K.-L.; Sorooshian, S.; Duan, Q. Evaluation of the PERSIANN-CDR Daily Rainfall Estimates in Capturing the Behavior of Extreme Precipitation Events over China. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katiraie-Boroujerdy, P.-S.; Asanjan, A.A.; Hsu, K.-L.; Sorooshian, S. Intercomparison of PERSIANN-CDR and TRMM-3B42V7 precipitation estimates at monthly and daily time scales. Atmos. Res. 2017, 193, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faridzad, M.; Yang, T.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S.; Xiao, C. Rainfall frequency analysis for ungauged regions using remotely sensed precipitation information. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casse, C.; Gosset, M. Analysis of hydrological changes and flood increase in Niamey based on the PERSIANN-CDR satellite rainfall estimate and hydrological simulations over the 1983–2013 period. In Proceedings of the Changes in Flood Risk and Perception in Catchments and Cities; Rogger, M., Aksoy, H., Kooy, M., Schumann, A., Toth, E., Chen, Y., Estupina, V.B., Bloschl, G., Eds.; Copernicus Gesellschaft MBH: Gottingen, Germany, 2015; Volume 370, pp. 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Bao, A.; Liu, T.; Chen, S.; Ndayisaba, F. Evaluation of PERSIANN-CDR for Meteorological Drought Monitoring over China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Ma, Y.; Long, D.; Zhong, L.; Hong, Y. Evaluation of GPM Day-1 IMERG and TMPA Version-7 legacy products over Mainland China at multiple spatiotemporal scales. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Adler, R.F.; Kubota, T.; Ushio, T. Evaluation of GSMaP Precipitation Estimates over the Contiguous United States. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Ibrahim, A.L.; Duan, Z.; Cracknell, A.P.; Chaplot, V. Evaluation of Six High-Resolution Satellite and Ground-Based Precipitation Products over Malaysia. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1504–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Q.; Xuan, W.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.-P. Evaluation and hydrological application of precipitation estimates derived from PERSIANN-CDR, TRMM 3B42V7, and NCEP-CFSR over humid regions in China. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 3061–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pombo, S.; de Oliveira, R.P. Evaluation of extreme precipitation estimates from TRMM in Angola. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiraie-Boroujerdy, P.-S.; Ashouri, H.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S. Trends of precipitation extreme indices over a subtropical semi-arid area using PERSIANN-CDR. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 130, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.; Xu, Z.; Wu, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, F. Identification of Streamflow Response to Climate Change and Human Activities in the Wei River Basin, China. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 833–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Wang, Y.; Istanbulluoglu, E.; Bai, T.; Huang, Q.; Yang, D.; Huang, S. Impact of climate change and human activities on runoff in the Weihe River Basin, China. Quat. Int. 2015, 380–381, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xiong, A. Validation and comparison of a new gauge-based precipitation analysis over mainland China. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Yuan, H.; Liu, X.; Jiang, X. Evaluation of the latest satellite-gauge precipitation products and their hydrologic applications over the Huaihe River basin. J. Hydrol. 2016, 536, 302–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Yatagai, A. Evaluation of TRMM 3B42 product using a new gauge-based analysis of daily precipitation over China. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 2749–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Sun, W.; Yang, G.; Zhang, D. Hydrological Analysis Using Satellite Remote Sensing Big Data and CREST Model. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 9006–9016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, E.E.; Janowiak, J.E.; Kidd, C. Comparison of near-real-time precipitation estimates from satellite observations and numerical models. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, F.L.; Hsu, K.L.; Noto, L.V.; Sorooshian, S. Evaluation and comparison of satellite precipitation estimates with reference to a local area in the Mediterranean Sea. Atmos. Res. 2014, 138, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, Q.; Kang, S.; Aguilar, E.; Pepin, N.; Fluegel, W.-A.; Yan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J. Changes in daily climate extremes in China and their connection to the large scale atmospheric circulation during 1961–2003. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 36, 2399–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Mu, X.; Song, X.; Wu, D.; Cheng, A.; Qiu, B. Changes in extreme temperature and precipitation events in the Loess Plateau (China) during 1960–2013 under global warming. Atmos. Res. 2016, 168, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Lue, H.; Wang, J.; Sadeghi, A.M.; Zhu, Y. Evaluating the Applicability of Four Latest Satellite-Gauge Combined Precipitation Estimates for Extreme Precipitation and Streamflow Predictions over the Upper Yellow River Basins in China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Gochis, D.; Cheng, J.-T.; Hsu, K.-L.; Sorooshian, S. Evaluation of PERSIANN-CCS rainfall measurement using the NAME Event Rain Gauge Network. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Duan, Z. Assessment of GPM and TRMM Precipitation Products over Singapore. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, Q.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Mo, K.; Li, Z.; Tang, G. Multiscale Comparative Evaluation of the GPM IMERG v5 and TRMM 3B42 v7 Precipitation Products from 2015 to 2017 over a Climate Transition Area of China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raftery, A.E.; Gneiting, T.; Balabdaoui, F.; Polakowski, M. Using Bayesian model averaging to calibrate forecast ensembles. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 1155–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Hong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Tang, G.; Yao, Y.; Long, D.; Li, C.; Han, Z.; Liu, R. Performance of Optimally Merged Multisatellite Precipitation Products Using the Dynamic Bayesian Model Averaging Scheme Over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 814–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Levizzani, V.; Schellekens, J.; Miralles, D.G.; Martens, B.; de Roo, A. MSWEP: 3-hourly 0.25 degrees global gridded precipitation (1979–2015) by merging gauge, satellite, and reanalysis data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 589–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Dataset | Period | Resolution | Coverage | Category | Latency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRMM 3B42RT | 1998 to 2015 | 0.25°/3h | 60°N–60°S | PMW plus IR, Satellite-only | 9 hours |
| TRMM 3B42V7 | 1998 to 2015 | 0.25°/3h | 50°N–50°S | PMW plus IR, Satellite-gauge | 10–15 days after the end of each month |
| PERSIANN | 2000 to present | 0.25°/3h | 60°N–60°S | IR, Satellite-only | 2 days |
| PERSIANN CDR | 1983 to present | 0.25°/3h | 60°N–60°S | PMW plus IR, Satellite-gauge | about 6 months |
| CMORPH RAW | 1998 to present | 0.25°/3h | 60°N–60°S | PMW plus IR, Satellite-only | 18 hours |
| CMORPH CRT | 1998 to present | 0.25°/3h | 60°N–60°S | PMW plus IR, Satellite-gauge | about 5 months |
| Index | Descriptive Name | Definition | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| R0.1mm | Number of precipitation days | Annual count of days when RR ≥ 0.1 mm | day |
| R10mm | Number of moderate precipitation days | Annual count of days when RR ≥ 10 mm | day |
| R12mm | Number of erosion precipitation days | Annual count of days when RR ≥ 12 mm | day |
| R25mm | Number of heavy precipitation days | Annual count of days when RR ≥ 25 mm | day |
| PRCPTOT | Wet-day precipitation | Total precipitation on days when RR ≥1 mm | mm |
| SDII | Simple daily intensity index | Total rainfall divided by the number of wet days | mm/day |
| RX1day | Maximum 1-day precipitation | Maximum 1-day rainfall total | mm |
| RX5day | Maximum 5-day precipitation | Maximum 5-day rainfall total | mm |
| CWD | Consecutive wet days | Maximum number of consecutive wet days | day |
| CDD | Consecutive dry days | Maximum number of consecutive dry days | day |
| R95p | Very wet day | Total rainfall due to events exceeding the 95th percentile | mm |
| R99p | Extreme very wet day | Total rainfall due to events exceeding the 99th percentile | mm |
| Spatial Scale | Metric | TRMM 3B42RT | TRMM 3B42V7 | PERSIANN | PERSIANN CDR | CMORPH RAW | CMORPH CRT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | R | 0.81 | 0.94 | 0.17 | 0.89 | 0.78 | 0.87 |
| MAE (mm/d) | 0.76 | 0.41 | 1.39 | 0.49 | 0.71 | 0.57 | |
| RMSE (mm/d) | 1.16 | 0.66 | 1.94 | 0.85 | 1.20 | 0.90 | |
| Sub-basin | R | 0.85 | 0.94 | 0.14 | 0.90 | 0.81 | 0.89 |
| MAE (mm/d) | 0.66 | 0.36 | 1.34 | 0.44 | 0.63 | 0.48 | |
| RMSE (mm/d) | 0.99 | 0.67 | 1.85 | 0.77 | 1.07 | 0.80 | |
| Whole basin | R | 0.92 | 0.99 | 0.14 | 0.97 | 0.87 | 0.96 |
| MAE (mm/d) | 0.52 | 0.19 | 1.33 | 0.28 | 0.57 | 0.34 | |
| RMSE (mm/d) | 0.67 | 0.29 | 1.76 | 0.47 | 0.93 | 0.49 |
| Metric | TRMM 3B42RT | TRMM 3B42V7 | PERSIANN | PERSIANN CDR | CMORPH RAW | CMORPH CRT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 0.72 | 0.87 | 0.33 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.75 |
| MAE (mm/d) | 0.31 | 0.18 | 0.31 | 0.22 | 0.32 | 0.22 |
| RMSE (mm/d) | 0.39 | 0.22 | 0.43 | 0.29 | 0.41 | 0.28 |
| Metric | Reference Data | TRMM 3B42RT | TRMM 3B42V7 | PERSIANN | PERSIANN CDR | CMORPH RAW | CMORPH CRT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R0.1 mm(days) | 88.25 | 89.66 | 91.15 | 157.66 | 187.05 | 125.00 | 122.44 |
| R10 mm(days) | 18.28 | 21.98 | 18.89 | 11.05 | 12.22 | 13.07 | 17.37 |
| R12 mm(days) | 14.88 | 18.05 | 15.46 | 7.85 | 8.89 | 9.98 | 13.86 |
| R25 mm(days) | 4.53 | 5.49 | 5.29 | 1.07 | 2.01 | 1.92 | 3.84 |
| CWD(days) | 5.96 | 5.25 | 4.96 | 6.13 | 8.23 | 5.10 | 5.38 |
| CDD(days) | 38.47 | 52.18 | 51.22 | 22.02 | 40.42 | 56.70 | 54.96 |
| PRCPTOT | 577.80 | 666.30 | 604.62 | 496.77 | 545.58 | 452.88 | 557.01 |
| RX1day(mm) | 51.46 | 55.00 | 55.06 | 28.20 | 35.81 | 34.98 | 47.58 |
| RX5day(mm) | 175.26 | 190.51 | 190.33 | 103.32 | 121.72 | 121.30 | 163.49 |
| R95(mm) | 386.29 | 427.74 | 411.56 | 243.90 | 273.42 | 278.04 | 361.17 |
| R99(mm) | 149.99 | 162.94 | 162.88 | 87.62 | 104.47 | 103.31 | 139.79 |
| SDII(mm/day) | 8.57 | 9.54 | 9.29 | 5.16 | 5.17 | 6.61 | 8.07 |
| Mean Absolute Error | / | 15.53 | 8.58 | 40.68 | 31.73 | 35.07 | 10.51 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Xia, J.; She, D.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.; Zou, L. Evaluation of Six Satellite-Based Precipitation Products and Their Ability for Capturing Characteristics of Extreme Precipitation Events over a Climate Transition Area in China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121477
Liu J, Xia J, She D, Li L, Wang Q, Zou L. Evaluation of Six Satellite-Based Precipitation Products and Their Ability for Capturing Characteristics of Extreme Precipitation Events over a Climate Transition Area in China. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(12):1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121477
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jie, Jun Xia, Dunxian She, Lingcheng Li, Qiang Wang, and Lei Zou. 2019. "Evaluation of Six Satellite-Based Precipitation Products and Their Ability for Capturing Characteristics of Extreme Precipitation Events over a Climate Transition Area in China" Remote Sensing 11, no. 12: 1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121477
APA StyleLiu, J., Xia, J., She, D., Li, L., Wang, Q., & Zou, L. (2019). Evaluation of Six Satellite-Based Precipitation Products and Their Ability for Capturing Characteristics of Extreme Precipitation Events over a Climate Transition Area in China. Remote Sensing, 11(12), 1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121477