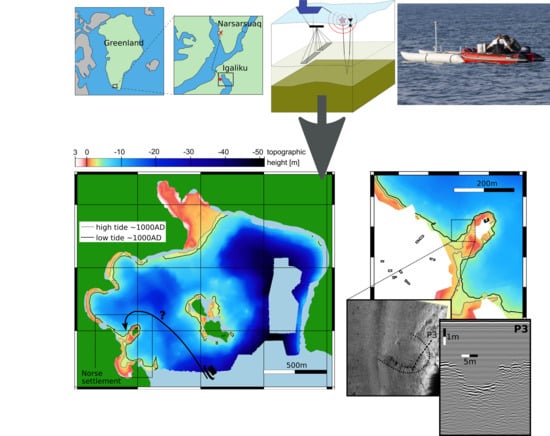
Investigating the Norse Harbour of Igaliku (Southern Greenland) Using an Integrated System of Side-Scan Sonar and High-Resolution Reflection Seismics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The identification of potential landing and mooring places used by the Norse until the early 15th century and a discussion concerning the accessibility of the coastal areas of Garðar for ships of the Norse period;
- An assessment of the impact of local sea level rise on the area of fertile land and homefields available in the inner Igaliku fjord based on a new bathymetric map.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Marine Acquisition System
- Bandpass filtering using a Butterworth filter with a low cut at 2 kHz to 3 kHz and high cut from 6 kHz to 7 kHz;
- Deconvolution using a fixed filter operator, derived from the Wiener predictive error deconvolution of the complete direct wave signal in deeper water, which is convolved with the full seismic trace;
- Trace normalization by the first quantile of each trace;
- Migration of the data using a post-stack Fresnel-volume migration approach after [25] using a water velocity of 1480 m/s;
- Geometrical spreading correction using a linear time-gain function;
- Skeletonising of traces by leaving only the local amplitude maxima, giving each sample as the maximum in a window of 7 samples.
2.2. Tide Gauge
2.3. Side-Scan Sonar Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Bathymetric Map
3.2. Seismics
3.3. Side Scan Sonar
4. Discussion
4.1. Implications of the Local Bathymetry and Sea Level Rise on the Norse Settlement Area
4.2. Harbour Infrastructure and Function
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frei, K.M.; Coutu, A.N.; Smiarowski, K.; Harrison, R.; Madsen, C.K.; Arneborg, J.; Frei, R.; Guðmundsson, G.; Sindbæk, S.; Woollett, J.; et al. Was it for walrus? Viking Age settlement and medieval walrus ivory trade in Iceland and Greenland. World Archaeol. 2015, 47, 439–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Þorláksson, H.; Gunnarsson, G.; Agnarsdóttir, A.; Bjarnarson, H.; Kjartanson, H.S. Líftaug Landsins–Saga Íslenskrar Utanlandsverslunar; Forlagið bókabuð: Reykjavík, Iceland, 2017; pp. 900–2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mehler, N.; Gardiner, M.; Dugmore, A.; Coolen, J. The elusive Norse harbours of the North Atlantic: Why they were abandoned, and why they are so hard to find. In Häfen im 1. Millennium AD. Bauliche Konzepte, Herrschaftliche Und Religiöse Einflüsse. RGZM Tagungen 22 (Interdisziplinäre Forschungen Zu den Häfen von Der Römischen Kaiserzeit Bis Zum Mittelalter in Europa 1); Schmidts, T.H., Vučetić, M., Eds.; Verlag des Römisch-Germanischen Zentralmuseums: Mainz, Germany, 2015; pp. 313–321. [Google Scholar]
- Arneborg, J. Norse Greenland—research into abandonment, in Medieval Archaeology in Scandinavia and Beyond. In History, Trends and Tomorrow, Proceedings of Conference to Celebrate 40 Years of Medieval Archaeology at Aarhus University; Kristiansen, M.S., Roesdahl, E., Eds.; Aarhus University Press: Aarhus, Denmark, 2015; pp. 257–273. [Google Scholar]
- Dugmore, A.; Keller, C.; McGovern, T.H. Norse Greenland Settlement: Reflections on Climate Change, Trade, and the Contrasting Fates of Human Settlements in the North Atlantic Islands. Arct. Anthropol. 2007, 44, 12–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, N.; Kuijpers, A. The Norse in Greenland and late Holocene sea-level change. Polar Rec. 2008, 44, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westerdahl, C. Die Maritime Kulturlandschaft. Schiffe, Schiffahrtswege, Häfen-Überlegungen zu einem Forschungsansatz. In Deutsches Schiffahrtsarchiv; Ernst Kabel Verlag: Hamburg, Germany, 1986; Volume 9, pp. 7–58. [Google Scholar]
- Westerdahl, C. The maritime cultural landscape. In The Oxford Handbook of Maritime Archaeology; Ford, B., Catsambis, A., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 733–762. [Google Scholar]
- von Carnap-Bornheim, C.; Kalmring, S. DFG-Schwerpunktprogramm 1630 “Häfen von der Römischen Kaiserzeit bis zum Mittelalter. Zur Archäologie und Geschichte regionaler und überregionaler Verkehrssysteme”. In Jahresbericht Zentrum für Baltische und Skandinavische Archäologie; Eriksen, B.V., Sonnenschein, I., Eds.; Stiftung Schleswig-Holsteinische Landesmuseen Schloss Gottorf: Schleswig, Germany, 2011; pp. 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Arneborg, J. Saga Trails; National Museum of Denmark: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Funder, S.; Hansen, L. The Greenland ice sheet—A model for its culmination and decay during and after the last glacial maximum. Bull. Geol. Soc. Den. 1996, 42, 137–152. [Google Scholar]
- Rasch, M.; Nielsen, N. Coastal morpho-stratigraphy and Holocene relative sea level changes at Tuapaat, southeastern Disko Island, central West Greenland. Polar Res. 1995, 14, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.; Bendixen, M.; Kroon, A.; Hede, M.U.; Clemmensen, L.B.; Weβling, R.; Elberling, B. Sea-level proxies in Holocene raised beach ridge deposits (Greenland) revealed by ground-penetrating radar. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weidick, A. Neoglacial change of ice cover and the related response of the Earth’s crust in West Greenland. Rapp. Grønlands Geol. Undersøgelse 1993, 159, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Rasch, M.; Jensen, J.F. Ancient Eskimo dwelling sites and Holocene relative sea-level changes in southern Disko Bugt, central West Greenland. Polar Res. 1997, 16, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandgren, P.; Fredskild, B. Magnetic measurements recording Late Holocene man-induced erosion in S. Greenland. Boreas 1991, 20, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijpers, A.; Abrahamsen, N.; Hoffmann, G.; Hühnerbach, V.; Konradi, P.; Kunzendorf, H.; Mikkelsen, N.; Thiede, J.; Weinrebe, W.; Rv Poseidon, S.S.P. Climate change and the Viking-age fjord environment of the Eastern Settlement, South Greenland. Geol. Greenl. Surv. Bull. 1999, 183, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Arneborg, J.; Heinemeier, J.; Lynnerup, N.; Nielsen, H.L.; Rud, N.; Sveinbjörnsdóttir, Á. C-14 dating and the disappearance of Norsemen from Greenland. Europhys. News 2002, 33, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilken, D.; Wunderlich, T.; Hollmann, H.; Schwardt, M.; Rabbel, W.; Mohr, C.; Schulte-Kortnack, D.; Nakoinz, O.; Enzmann, J.; Jürgens, F.; et al. Imaging a medieval shipwreck with the new PingPong 3D marine reflection seismic system. Archaeol. Prospect. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.; Woelz, S.; Kalmring, S. High-Resolution 3D Marine Seismic Investigation of HedebyHarbour, Germany. Naut. Archaeol. 2013, 42, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plets, R.M.K.; Dix, J.K.; Adams, J.R.; Bull, J.M.; Henstock, T.J.; Gutowski, M.; Best, A.I. The use of a high-resolution 3D Chirp sub-bottom profiler for the reconstruction of the shallow water archaeological site of the Grace Dieu (1439), River Hamble, UK. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2009, 36, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westley, K.; Mcneary, R. Archaeological Applications of Low-Cost Integrated Sidescan Sonar/Single-Beam Echosounder Systems in Irish Inland Waterways. J. Archaeol. Prospect. 2017, 24, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, R.; Breen, C.; Forsythe, W. Integrated Geophysical Surveys of the French Frigate La Surveillante (1797), Bantry Bay, Co. Cork, Ireland. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2002, 29, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grøn, O.; Boldreel, L.O. Sub-bottom profiling for large-scale maritime archaeological survey. In Proceedings of the 2013 MTS/IEEE OCEANS, Bergen, Norway, 10–14 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Buske, S.; Gutjahr, S.; Sick, C. Fresnel volume migration of single-component seismic data. Geophysics 2009, 74, WCA47–WCA55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrenbom, C.J.; Bennike, O.; Björck, S.; Lambeck, K. Holocene relative sea-level changes in the Qaqortoq area, southern Greenland. Boreas 2006, 35, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, P. The Handbook of Sidescan Sonar; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; p. 319. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, R.; Dean, M.; Lawrence, M.; Liscoe, S.; Boland, D. Backscatter responses and resolution considerations in archaeological side-scan sonar surveys: A control experiment. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2005, 32, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilken, D.; Feldens, P.; Wunderlich, T.; Heinrich, C. Application of 2D Fourier filtering for elimination of stripe noise in side-scan sonar mosaics. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2012, 32, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGovern, T.H. Cows, Harp Seals, and Churchbells: Adaptation and Extinction in Norse Greenland. Hum. Ecol. 1980, 8, 245–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, J. The Decline of the Norse Settlements in Greenland. Arct. Anthropol. 1986, 23, 109–135. [Google Scholar]
- Dugmore, A.J.; McGovern, T.H.; Vésteinsson, O.; Arneborg, J.; Streeter, R.; Keller, C. Cultural adaptation, compounding vulnerabilities and conjunctures in Norse Greenland. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3658–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milliman, J.D.; Syvitski, J.P.M. Geomorphic/Tectonic Control of Sediment Discharge to the Ocean: The Importance of Small Mountaineous Rivers. J. Geol. 1991, 100, 525–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGovern, T.H. Farmpact 06, Computer Program in Excel. Available from Hunter Bioarchaeology Lab 695 Park Ave. NYC. 2012. Available online: http://www.nabohome.org/products/models/farmpact/farmpact.html (accessed on 7 January 2019).
- Buckland, P.C.; Edwards, K.J.; Panagiotakopulu, E.; Edward Schofield, J. Palaeoecological and historical evidence for manuring and irrigation at Garðar (Igaliku), Norse Eastern Settlement, Greenland. Holocene 2009, 19, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, K.J.; Schofield, J.E. Investigation of proposed Norse irrigation channels and dams at Garðar/Igaliku, Greenland. Water Hist. 2013, 5, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chritiansen, D. Veien Handel og kommunikation i Nordatlanten. In Rapport om Prøveundersøgelser på den Formodede Atlanthavn, Sandhavn ved Maakkarneq, Nanortalik kommune, Sommeren 2001; SILA Feltrapport 3: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Halldórsson, Ó. Grænland í Miðaldaritum; Sögufélag: Reykjavík, Iceland, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, C. The Eastern Settlement Reconsidered. Some Analyses of Norse Medieval Greenland. Ph.D. Thesis, Oslo university, Oslo, Norway, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Guðmundsson, G. Greenland and the Wider World. J. North Atl. Spec. 2009, 2, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, K., Translator; The Vinland Sagas; Penguin books: London, UK, 2008.
- Richter, M. Die Diözese am Ende der Welt. Die Geschichte des Grönlandbistums Garðar; Münchner Nordistische Studien 28 (München 2017); Herbert Utz Verlag: Munich, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nørlund, P. Norse ruins at Garðar. The episcopal seat of mediaeval Greenland. Medd. om Grønland 1929, 76, 1–171. [Google Scholar]
- Molaug, P.B. Oslo havn før 1624. Viking 75; Norwegian Archaeological Society: Oslo, Norway, 2012; pp. 211–237. [Google Scholar]
- Herteig, A. Details from the Bergen medieval waterfront. In Proceedings of the Conference on Waterfront Archaeology in Northern European Towns; Herteig, A., Ed.; Historisk museum Bergen: Bergen, Norway, 1985; pp. 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Sognnes, K. King Øystein´s harbour at Agdenes, Norway. In Proceedings of the Conference on Waterfront Archaeology in Northern European Towns; Herteig, A., Ed.; Historisk museum Bergen: Bergen, Norway, 1985; pp. 59–65. [Google Scholar]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wilken, D.; Wunderlich, T.; Feldens, P.; Coolen, J.; Preston, J.; Mehler, N. Investigating the Norse Harbour of Igaliku (Southern Greenland) Using an Integrated System of Side-Scan Sonar and High-Resolution Reflection Seismics. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1889. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11161889
Wilken D, Wunderlich T, Feldens P, Coolen J, Preston J, Mehler N. Investigating the Norse Harbour of Igaliku (Southern Greenland) Using an Integrated System of Side-Scan Sonar and High-Resolution Reflection Seismics. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(16):1889. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11161889
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilken, Dennis, Tina Wunderlich, Peter Feldens, Joris Coolen, John Preston, and Natascha Mehler. 2019. "Investigating the Norse Harbour of Igaliku (Southern Greenland) Using an Integrated System of Side-Scan Sonar and High-Resolution Reflection Seismics" Remote Sensing 11, no. 16: 1889. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11161889
APA StyleWilken, D., Wunderlich, T., Feldens, P., Coolen, J., Preston, J., & Mehler, N. (2019). Investigating the Norse Harbour of Igaliku (Southern Greenland) Using an Integrated System of Side-Scan Sonar and High-Resolution Reflection Seismics. Remote Sensing, 11(16), 1889. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11161889