Trends in Remote Sensing Accuracy Assessment Approaches in the Context of Natural Resources
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Article Selection
2.2. Data Extraction and Analysis
3. Results
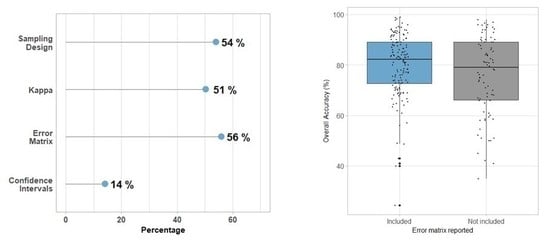
3.1. Characterization of How Map Accuracy is Being Reported
3.2. Sampling Designs for the Reference Data
3.3. Relationship between the Type and Number of Sampling Units with Accuracy
3.4. Relationship between Accuracy and Classification Characteristics (Number of Classes and Type of Satellite Data)
4. Discussion
4.1. Implications for Lack of Reproducibility and Transparency
4.2. Overall Trends in Features of the Accuracy Assessment: Error Matrix, Metrics, and Type of Validation Dataset
4.3. Other Aspects of Accuracy that are Relevant for Natural Resources Management: Reference Sample Size and Number of Classes
4.4. Limitations of the Review
5. Conclusions
- Probability sampling design (including a map showing the distribution of the reference data).
- An error matrix, that conveys proportional areas.
- The sampling unit including the number of units used in the assessment, their type (i.e., single pixels, pixel cluster, etc.); size, and in the case of field plots their shape and size.
- Clear reference of the source of validation/training data; and where applicable a protocol or a description of how the labels for the reference data was obtained.
- The accuracy metrics with an adequate interpretation and a measure of sampling variance (i.e., confidence intervals, standard error, or standard deviation)
- Report any limitations found within any of the elements of the assessment process, particularly any deviations from the sampling design.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foody, G.M. Status of land cover classification accuracy assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, P.C.; Dellepiane, S.G.; Schowengerdt, R.A. Quality assessment of image classification algorithms for land-cover mapping: A review and a proposal for a cost-based approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 1461–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, P.L.; Housman, I.W.; Perry, C.H.; Chastain, R.A.; Webb, J.B.; Finco, M.V. An accuracy assessment of forest disturbance mapping in the western Great Lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, P.; Foody, G.M.; Stehman, S.V.; Woodcock, C.E. Making better use of accuracy data in land change studies: Estimating accuracy and area and quantifying uncertainty using stratified estimation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M. Valuing map validation: The need for rigorous land cover map accuracy assessment in economic valuations of ecosystem services. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 111, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, M.J.; Roberts, H.M.; Bell, D.M.; Ohmann, J.L.; Davis, R.J. How sampling and scale limit accuracy assessment of vegetation maps: A comment on Loehle et al. (2015). For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 358, 361–364. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Weng, Q. A survey of image classification methods and techniques for improving classification performance. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 823–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, R.; Mountrakis, G.; Stehman, S.V. A meta-analysis of remote sensing research on supervised pixel-based land-cover image classification processes: General guidelines for practitioners and future research. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkinson, G.G. Results and implications of a study of fifteen years of satellite image classification experiments. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, S.S.; Mountrakis, G. Effect of classifier selection, reference sample size, reference class distribution and scene heterogeneity in per-pixel classification accuracy using 26 Landsat sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.H.; Stehman, S.V.; Wickham, J.D.; Yang, L.M. Effects of landscape characteristics on land-cover class accuracy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Z.; Quackenbush, L.J.; Stehman, S.V.; Zhang, L. Impact of training and validation sample selection on classification accuracy and accuracy assessment when using reference polygons in object-based classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 6914–6930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millard, K.; Richardson, M.; Millard, K.; Richardson, M. On the Importance of Training Data Sample Selection in Random Forest Image Classification: A Case Study in Peatland Ecosystem Mapping. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8489–8515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Lunetta, R.S. Comparison of support vector machine, neural network, and CART algorithms for the land-cover classification using limited training data points. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 70, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, L.-H.; Cheng, K.-S.; Hsiao, L.-H.; Cheng, K.-S. Assessing Uncertainty in LULC Classification Accuracy by Using Bootstrap Resampling. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.T.; Langille, J. Improving classification accuracy assessments with statistical bootstrap resampling techniques. GIScience Remote Sens. 2007, 44, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, M.B.; Keith, D.A.; Phinn, S.R.; Mason, T.J.; Elith, J. A comparison of resampling methods for remote sensing classification and accuracy assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 208, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehman, S.V.; Czaplewski, R.L. Design and Analysis for Thematic Map Accuracy Assessment - an application of satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 64, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehman, S.V. Basic probability sampling designs for thematic map accuracy assessment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 2423–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, P.; Foody, G.M.; Herold, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Woodcock, C.E.; Wulder, M.A. Good practices for estimating area and assessing accuracy of land change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, M.A.; Woodcock, C.; Gopal, S.; Muchoney, D.; Strahler, A.H.; Barker-Schaaf, C.; Oodcock, C.W.; Gopa, L.S.; Uchoney, D.M.; Ler, A.H.S.; et al. A note on procedures used for accuracy assessment in land cover maps derived from AVHRR data. Int J Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahler, A.H.; Boschetti, L.; Foody, G.M.; Friedl, M.A.; Hansen, M.C.; Herold, M.; Mayaux, P.; Morisette, J.T.; Stehman, S.V.; Woodcock, C.E. Global Land Cover Validation: Recommendations for Evaluation and Accuracy Assessment of Global Land Cover Maps; European Communities: Luxembourg, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Skidmore, A.K. Accuracy assessment of spatial information. In Spatial statistics for Remote Sensing; Stein, A., Van der Meer, F., Gorte, B., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 197–209. [Google Scholar]
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data: Principles and Practices, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; ISBN 9781420055122. [Google Scholar]
- Stehman, S.V. Sampling designs for accuracy assessment of land cover. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 5243–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricotta, C. On possible measures for evaluating the degree of uncertainty of fuzzy thematic maps. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 5573–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G. Impacts of Sample Design for Validation Data on the Accuracy of Feedforward Neural Network Classification. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M. Latent Class Modeling for Site- and Non-Site-Specific Classification Accuracy Assessment Without Ground Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 2827–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, B.M.; Patterson, D.A.; Redmond, R.L. Toward estimation of map accuracy without a probability test sample. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 2003, 10, 333–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M. Harshness in image classification accuracy assessment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3137–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castilla, G. We Must all Pay More Attention to Rigor in Accuracy Assessment: Additional Comment to “The Improvement of Land Cover Classification by Thermal Remote Sensing”. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8368–8390. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M. The impact of imperfect ground reference data on the accuracy of land cover change estimation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 3275–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; Franklin, S.E.; White, J.C.; Linke, J.; Magnussen, S. An accuracy assessment framework for large-area land cover classification products derived from medium-resolution satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 663–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G. A review of assessing the accuracy of classifications of remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 37, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, R.G.; Millones, M. Death to Kappa: Birth of quantity disagreement and allocation disagreement for accuracy assessment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 4407–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Frazier, P.; Kumar, L. Comparative assessment of the measures of thematic classification accuracy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 107, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.J.; Downie, A.-L.; Diesing, M. How good is my map? A tool for semi-automated thematic mapping and spatially explicit confidence assessment. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 108, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cripps, E.; O’Hagan, A.; Quaife, T. Quantifying uncertainty in remotely sensed land cover maps. Stoch. Environ. Res. RISK Assess. 2013, 27, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehman, S.V.; Wickham, J.D. Pixels, blocks of pixels, and polygons: Choosing a spatial unit for thematic accuracy assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3044–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehman, S.V. Practical Implications of Design-Based Sampling Inference for Thematic Map Accuracy Assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 72, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzon-Lopez, C.; Foody, G.; Bastin, L.; Rocchini, D.; Pal, M. The Sensitivity of Mapping Methods to Reference Data Quality: Training Supervised Image Classifications with Imperfect Reference Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2016, 5, 199. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Fehrmann, L.; Kukunda, C.B.; Nölke, N.; Schnell, S.; Seidel, D.; Magnussen, S.; Kleinn, C. A unified framework for land cover monitoring based on a discrete global sampling grid (GSG). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Gong, P. Google Earth as a virtual globe tool for Earth science applications at the global scale: Progress and perspectives. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 3966–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettorelli, N.; Wegmann, M.; Skidmore, A.; Mücher, S.; Dawson, T.P.; Fernandez, M.; Lucas, R.; Schaepman, M.E.; Wang, T.; O’Connor, B.; et al. Framing the concept of satellite remote sensing essential biodiversity variables: Challenges and future directions. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2016, 2, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coops, N.C.; Wulder, M.A. Breaking the Habit(at). Trends Ecol. Evol. 2019, 34, 585–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, R.A.; Byler, D.; Eastman, J.R.; Fleishman, E.; Geller, G.; Goetz, S.; Guild, L.; Hamilton, H.; Hansen, M.; Headley, R.; et al. Ten ways remote sensing can contribute to conservation. Conserv. Biol. 2015, 29, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radoux, J.; Bogaert, P.; Fasbender, D.; Defourny, P. Thematic accuracy assessment of geographic object-based image classification. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2011, 25, 895–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, C.; White, J.C.; Wulder, M.A. Optical remotely sensed time series data for land cover classification: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 116, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, S.; Pontius, R.G.; Rakshit, R. A review of accuracy assessment for object-based image analysis: From per-pixel to per-polygon approaches. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 141, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehman, S.V.; Foody, G.M. Key issues in rigorous accuracy assessment of land cover products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, A.M.; Langford, W.T.; Bekessy, S.A.; Jones, S.D. Are landscape ecologists addressing uncertainty in their remote sensing data? Landsc. Ecol. 2012, 27, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Hu, L.; Liu, S.; Yu, L.; Wang, X.; Zhu, P.; et al. Meta-discoveries from a synthesis of satellite-based land-cover mapping research. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 4573–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelfsema, C.M.; Phinn, S.R. Coral Reef Remote Sensing. In Coral Reef Remote Sensing; Goodman, J.A., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 375–401. ISBN 9789048192922. [Google Scholar]
- The World Bank Land Area (sq. km)|Data. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/ag.lnd.totl.k2 (accessed on 4 April 2019).
- Lesiv, M.; See, L.; Laso Bayas, J.; Sturn, T.; Schepaschenko, D.; Karner, M.; Moorthy, I.; McCallum, I.; Fritz, S.; Lesiv, M.; et al. Characterizing the Spatial and Temporal Availability of Very High Resolution Satellite Imagery in Google Earth and Microsoft Bing Maps as a Source of Reference Data. Land 2018, 7, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, R.; Mountrakis, G.; Stehman, S.V. Mapping per-pixel predicted accuracy of classified remote sensing images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comber, A.; Fisher, P.; Wadsworth, R. Comparing the consistency of expert land cover knowledge. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2005, 7, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janssen, F.L.L.; van der Wel, F.J.M. Accuracy assessment of satellite derived land cover data: A review. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1994, 60, 419–426. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Li, M.; Ma, X.; Cheng, L.; Du, P.; Liu, Y. A review of supervised object-based land-cover image classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 130, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andréfouët, S.; Kramer, P.; Torres-Pulliza, D.; Joyce, K.E.; Hochberg, E.J.; Garza-Pérez, R.; Mumby, P.J.; Riegl, B.; Yamano, H.; White, W.H.; et al. Multi-site evaluation of IKONOS data for classification of tropical coral reef environments. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 88, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Type of Reference Sampling Unit | Description | Percent of Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Pixel | Single pixel collected from higher or similar spatial resolution imagery | 35.2 |
| Pixel cluster | Group of pixels pixel collected from higher or similar spatial resolution imagery to match coarser resolution imagery | 11.3 |
| Polygons | Group of pixels, usually of irregular shape and number of pixels | 5.3 |
| Field plots | Data collected in the field, using an area-based sampling unit | 10.3 |
| GPS points | Point data collected using a GPS device | 22.3 |
| Map correlation | Direct comparison with a map regarded as more accurate | 2.7 |
| Unclear | Information on sampling unit was either absent, incomplete or contradictory. | 13 |
| Study Area Size Categories (n) * | Mean Overall Accuracy (± SD) | Median Number of Sampling Units (IQR) | Maximum Number of Sampling Units | Minimum Number of Sampling Units | Mean Number of Classes (± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landscape (n = 92) | 76.8 ± 14.8 | 250 (490) | 315869 | 29 | 24.6 ± 9.0 |
| Regional (n = 26) | 82.9 ± 13.4 | 404 (805) | 30000 | 33 | 19.5 ± 10.3 |
| Continental (n = 36) | 79.0 ± 12.0 | 1023 (2270) | 378878 | 86 | 18.0 ± 11.3 |
| Global (n = 10) | 80.6 ± 11.6 | 2858 (69765) | 30000000 | 102 | 18.4 ± 10.9 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morales-Barquero, L.; Lyons, M.B.; Phinn, S.R.; Roelfsema, C.M. Trends in Remote Sensing Accuracy Assessment Approaches in the Context of Natural Resources. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192305
Morales-Barquero L, Lyons MB, Phinn SR, Roelfsema CM. Trends in Remote Sensing Accuracy Assessment Approaches in the Context of Natural Resources. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(19):2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192305
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorales-Barquero, Lucia, Mitchell B. Lyons, Stuart R. Phinn, and Chris M. Roelfsema. 2019. "Trends in Remote Sensing Accuracy Assessment Approaches in the Context of Natural Resources" Remote Sensing 11, no. 19: 2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192305
APA StyleMorales-Barquero, L., Lyons, M. B., Phinn, S. R., & Roelfsema, C. M. (2019). Trends in Remote Sensing Accuracy Assessment Approaches in the Context of Natural Resources. Remote Sensing, 11(19), 2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192305