A Unified Model for Multi-Frequency PPP Ambiguity Resolution and Test Results with Galileo and BeiDou Triple-Frequency Observations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Uncombined PPP Float Ambiguity Model
2.2. FCB Estimation Strategy
2.3. Uncombined PPP AR at the User End
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Data and Processing Strategy
3.2. FCB Residual Distributions
3.3. FCB Time Series
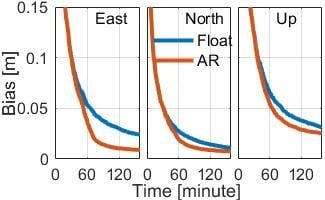
3.4. Triple-Frequency PPP AR
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kouba, J.; Héroux, P. Precise Point Positioning Using IGS Orbit and Clock Products. GPS Solut. 2001, 5, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumberge, J.F.; Heflin, M.B.; Jefferson, D.C.; Watkins, M.M.; Webb, F.H. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, C.; Gao, Y.; Pan, L.; Zhu, J. Precise point positioning with quad-constellations: GPS, BeiDou, GLONASS and Galileo. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 56, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabor, M.J.; Nerem, R.S. GPS carrier phase AR using satellite-satellite single difference. In Proceedings of the 12th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GPS 1999), Nashville, TN, USA, 14–17 September 1999; pp. 1569–1578. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Shen, X. A new method for carrier-phase-based precise point positioning. Navigation 2002, 49, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsigianni, G.; Loyer, S.; Perosanz, F.; Mercier, F.; Zajdel, R.; Sośnica, K. Improving Galileo orbit determination using zero-difference ambiguity fixing in a Multi-GNSS processing. Adv. Space Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Gendt, G.; Rothacher, M.a.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Resolution of GPS carrier-phase ambiguities in precise point positioning (PPP) with daily observations. J. Geod. 2008, 82, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Ren, X.; Zuo, X.; Pan, Y. Generating GPS satellite fractional cycle bias for ambiguity-fixed precise point positioning. GPS Solut. 2015, 20, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Sui, L.; Heck, B.; Zeng, T.; Tian, Y. Estimating satellite phase fractional cycle biases based on Kalman filter. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, P.; Lahaye, F.; Héroux, P.; Bisnath, S. Precise point positioning with ambiguity resolution using the decoupled clock model. In Proceedings of the 21st International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2008), Savannah, Georgia, 16–19 September 2008; pp. 1315–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Laurichesse, D.; Mercier, F.; Berthias, J.-P.; Broca, P.; Cerri, L. Integer ambiguity resolution on undifferenced GPS phase measurements and its application to PPP and satellite precise orbit determination. Navigation 2009, 56, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Gao, Y. A comparison of three PPP integer ambiguity resolution methods. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Khodabandeh, A. Review and principles of PPP-RTK methods. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 217–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Meng, X.; Dodson, A.H.; Teferle, F.N. Integer ambiguity resolution in precise point positioning: Method comparison. J. Geod. 2010, 84, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Shi, C. Rapid initialization of real-time PPP by resolving undifferenced GPS and GLONASS ambiguities simultaneously. J. Geod. 2016, 91, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Song, W.; Lou, Y.; Shi, C.; Yao, Y.; Guo, H.; Chen, M.; Wu, J. Improved method to estimate undifferenced satellite fractional cycle biases using network observations to support PPP ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, S.; Song, W.; Lou, Y.; Gu, S. Rapid PPP ambiguity resolution using GPS+ GLONASS observations. J. Geod. 2017, 91, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Guo, F. Ambiguity resolved precise point positioning with GPS and BeiDou. J. Geod. 2017, 91, 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, S.; Song, W.; Lou, Y.; Chen, D. Integrating GPS and BDS to shorten the initialization time for ambiguity-fixed PPP. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegedor, J.; Liu, X.; Jong, K.; Goode, M.; Øvstedal, O.; Vigen, E. Estimation of Galileo Uncalibrated Hardware Delays for Ambiguity-Fixed Precise Point Positioning. Navigation 2016, 63, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Li, P.; Sui, L.; Heck, B.; Schuh, H. Estimating and assessing Galileo satellite fractional cycle bias for PPP ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut. 2019, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X.; Wickert, J. Multi-GNSS phase delay estimation and PPP ambiguity resolution: GPS, BDS, GLONASS, Galileo. J. Geod. 2017, 92, 579–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Prange, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Perosanz, F.; Romero, I.; Noll, C.; Sturze, A.; Weber, G.; et al. The multi-GNSS experiment (MGEX) of the international GNSS service (IGS)—Achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 1671–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönemann, E.; Becker, M.; Springer, T. A new approach for GNSS analysis in a multi-GNSS and multi-signal environment. J. Geod. Sci. 2011, 1, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Shi, C.; Lou, Y.; Liu, J. Ionospheric effects in uncalibrated phase delay estimation and ambiguity-fixed PPP based on raw observable model. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Zheng, F.; Gu, S.; Wang, C.; Guo, H.; Feng, Y. Multi-GNSS precise point positioning with raw single-frequency and dual-frequency measurement models. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Dong, D.; Wang, J.; Qu, W.; Wu, B. A simplified and unified model of multi-GNSS precise point positioning. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Gu, S.; Shi, C.; Rizos, C. A reference station-based GNSS computing mode to support unified precise point positioning and real-time kinematic services. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 945–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odijk, D.; Zhang, B.; Khodabandeh, A.; Odolinski, R.; Teunissen, P.J.G. On the estimability of parameters in undifferenced, uncombined GNSS network and PPP-RTK user models by means of S system theory. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 15–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, R.; Zhang, H.; Ge, M.; Huang, G. A real-time ionospheric model based on GNSS Precise Point Positioning. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 52, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ou, J.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Z. Extraction of line-of-sight ionospheric observables from GPS data using precise point positioning. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 1919–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, N. Multi-GNSS triple-frequency differential code bias (DCB) determination with precise point positioning (PPP). J. Geod. 2018, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Fan, L.; Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Gu, S.; Zhong, S.; Song, W. An enhanced algorithm to estimate BDS satellite’s differential code biases. J. Geod. 2015, 90, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehentner, N.; Mayer-Gürr, T. Precise orbit determination based on raw GPS measurements. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Timing group delay and differential code bias corrections for BeiDou positioning. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Ge, M.; Schuh, H. Three-frequency BDS precise point positioning ambiguity resolution based on raw observables. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Zhang, H.; Wickert, J. A method for improving uncalibrated phase delay estimation and ambiguity-fixing in real-time precise point positioning. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Lou, Y.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. BeiDou phase bias estimation and its application in precise point positioning with triple-frequency observable. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanninger, L.; Beer, S. BeiDou satellite-induced code pseudorange variations: Diagnosis and therapy. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Z.; Montenbruck, O.; Tan, B. Determination of differential code biases with multi-GNSS observations. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leick, A.; Rapoport, L.; Tatarnikov, D. GPS Satellite Surveying; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hadas, T.; Krypiak-Gregorczyk, A.; Hernández-Pajares, M.; Kaplon, J.; Paziewski, J.; Wielgosz, P.; Garcia-Rigo, A.; Kazmierski, K.; Sosnica, K.; Kwasniak, D.; et al. Impact and Implementation of Higher-Order Ionospheric Effects on Precise GNSS Applications: Higher-Order Ionospheric Effects in GNSS. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 9420–9436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dach, R.; Lutz, S.; Walser, P.; Fridez, P. Bernese GNSS Software Version 5.2; University of Bern, Bern Open Publishing: Bern, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Jonge, P.J.; Tiberius, C.C.J.M. Performance of the LAMBDA method for fast GPS ambiguity resolution. Navigation 1997, 44, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, G.; Dettmering, D.; Gebhard, H. Networked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol (NTRIP). In Proceedings of the A Window on the future on Geodesy, Sapporo, Japan, 30 June–11 July 2003; pp. 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Joosten, P.; Tiberius, C.C.J.M. Geometry-free ambiguity success rates in case of partial fixing. In Proceedings of the 1999 National Technical Meeting of The Institute of Navigation, San Diego, CA, USA, 25–27 January 1999; pp. 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Zhang, X. Precise point positioning with partial ambiguity fixing. Sensors 2015, 15, 13627–13643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, X.; Guo, F.; Liu, J. GPS inter-frequency clock bias estimation for both uncombined and ionospheric-free combined triple-frequency precise point positioning. J. Geod. 2018, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Wu, G.; Tao, X.; Bian, L.; Wang, X. BDS satellite-induced code multipath: Mitigation and assessment in new-generation IOV satellites. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 60, 2672–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlemann, M.; Gendt, G.; Ramatschi, M.; Deng, Z. GFZ Global Multi-GNSS Network and Data Processing Results. In IAG 150 Years; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 673–679. [Google Scholar]
- Prange, L.; Orliac, E.; Dach, R.; Arnold, D.; Beutler, G.; Schaer, S.; Jäggi, A. CODE’s five-system orbit and clock solution—The challenges of multi-GNSS data analysis. J. Geod. 2017, 91, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmierski, K.; Hadas, T.; Sośnica, K. Weighting of Multi-GNSS Observations in Real-Time Precise Point Positioning. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Bock, Y. Triple-frequency GPS precise point positioning with rapid ambiguity resolution. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| GNSS | Coefficients | Wavelength [meter] | Ionospheric Delay [cycle] | Noise [cycle] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPS | (4, −3, 0) | 0.114 | 0.150 | 5.0 |
| (1, −1, 0) | 0.862 | −0.283 | 1.414 | |
| (1, 0, −1) | 0.751 | −0.339 | 1.414 | |
| Galileo | (4, −3, 0) | 0.108 | −0.017 | 5.0 |
| (1, −1, 0) | 0.751 | −0.339 | 1.414 | |
| (1, 0, −1) | 0.814 | −0.305 | 1.414 | |
| BDS | (4, −3, 0) | 0.114 | 0.120 | 5.0 |
| (1, −1, 0) | 0.847 | −0.293 | 1.414 | |
| (1, 0, −1) | 1.025 | −0.231 | 1.414 |
| System | No. | Solution | East | North | Up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDS | 804 | float | 3.70 | 1.83 | 6.12 |
| AR | 1.88 | 1.13 | 4.31 | ||
| Improv. | 49.2% | 38.3% | 29.6% | ||
| Galileo | 5805 | float | 2.15 | 1.00 | 2.99 |
| AR | 0.86 | 0.71 | 2.36 | ||
| Improv. | 60.0% | 29.0% | 21.1% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, G.; Li, P.; Gao, Y.; Heck, B. A Unified Model for Multi-Frequency PPP Ambiguity Resolution and Test Results with Galileo and BeiDou Triple-Frequency Observations. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11020116
Xiao G, Li P, Gao Y, Heck B. A Unified Model for Multi-Frequency PPP Ambiguity Resolution and Test Results with Galileo and BeiDou Triple-Frequency Observations. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(2):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11020116
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Guorui, Pan Li, Yang Gao, and Bernhard Heck. 2019. "A Unified Model for Multi-Frequency PPP Ambiguity Resolution and Test Results with Galileo and BeiDou Triple-Frequency Observations" Remote Sensing 11, no. 2: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11020116
APA StyleXiao, G., Li, P., Gao, Y., & Heck, B. (2019). A Unified Model for Multi-Frequency PPP Ambiguity Resolution and Test Results with Galileo and BeiDou Triple-Frequency Observations. Remote Sensing, 11(2), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11020116