Application of GeoSHM System in Monitoring Extreme Wind Events at the Forth Road Bridge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. GeoSHM on the Forth Road Bridge
2.1. Overview of the Forth Road Bridge
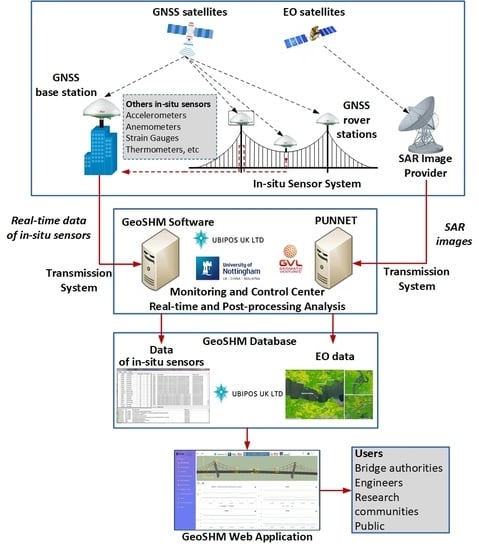
2.2. GeoSHM Sensor System on the Forth Road Bridge
3. Wind-Induced Effects on the Forth Road Bridge
4. Reponses of the Forth Road Bridge during Extreme Wind Events
4.1. Extreme Windstorms
4.2. Storm Ali
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Failure Knowledge Database. Available online: www.shipai.org/fkd/en/cfen/CD1000144.html (accessed on 17 May 2018).
- Liao, M.; Okazaki, T.A. Computational Study of the I-35W Bridge Collapse (CTS 09-20); Research Report for Centre for Transportation Studies; University of Minnesota: Minneapolis, MN, USA, October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- The Guardian. Available online: www.theguardian.com/cities/2019/feb/26/what-caused-the-genoa-morandi-bridge-collapse-and-the-end-of-an-italian-national-myth (accessed on 22 October 2019).
- New Civil Engineer. Available online: www.newcivilengineer.com/latest/fatal-taiwan-bridge-collapse-is-latest-example-of-maintenance-failings-07-10-2019 (accessed on 15 October 2019).
- New Civil Engineer. Available online: www.newcivilengineer.com/latest/work-begins-on-hammersmith-bridge-as-120m-repair-bill-announced-05-09-2019 (accessed on 15 October 2019).
- Meng, X. Real-time Deformation Monitoring of Bridges using GPS/Accelerometers. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK, May 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Nickitopoulou, A.; Protopsalti, K.; Stiros, S. Monitoring dynamic and quasi-static deformations of large flexible engineering structures with GPS: Accuracy, limitations and promises. Eng. Struct. 2006, 28, 1471–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.B.; Hurlebaus, S.; Kang, Y.J. Summary review of GPS technology for structural health monitoring. J. Struct. Eng. 2013, 139, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Guo, J.; Jiang, J. Time-frequency analysis of a suspension bridge based on GPS. J. Sound Vib. 2002, 245, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Dodson, A.; Roberts, G. Detecting bridge dynamics with GPS and triaxial accelerometers. Eng. Struct. 2007, 29, 3178–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.; Watson, T.; Coleman, R. Structural monitoring of cable-stayed bridges: Analysis of GPS versus modeled deflections. J. Surv. Eng. 2007, 133, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psimoulis, P.; Pytharouli, S.; Karambalis, D.; Stiros, S. Potential of global positioning system (GPS) to measure frequencies of oscillations of engineering structures. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 318, 606–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, G.W.; Brown, C.J.; Atkins, C.; Meng, X.; Colford, B.; Ogundipe, O. Deflection and frequency monitoring of the Forth Road Bridge, Scotland, by GPS. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Bridge Eng. 2012, 165, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Meng, X.; Shao, X.; Yan, B.; Yang, L. Identification of dynamic displacements and model frequencies of a medium-span suspension bridge using multimode GNSS processing. Eng. Struct. 2014, 81, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Nguyen, D.T.; Xie, Y.; Owen, J.S.; Psimoulis, P.; Ince, S.; Chen, Q.; Ye, J.; Bhatia, P. Design and implementation of a new system for large bridge monitoring—GeoSHM. Sensors 2018, 18, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Roberts, G.W.; Dodson, A.; Cosser, E.; Barnes, J.; Rizos, C. Impact of GPS satellite and pseudolite geometery on structural deformation monitoring: Analytical and empirical studies. J. Geod. 2004, 77, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijewski-Correa, T.; Kochly, M. Monitoring the wind-induced response of tall buildings: GPS performance and the issue of multipath effects. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2007, 95, 1176–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschas, F.; Stiros, S. Dynamic multipath in structural bridge monitoring: An experimental approach. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Meng, X.; Gao, C.; Pan, S.; Zhu, Z.; Xia, Y. Analysis of the carrier-phase multipath in GNSS triple-frequency observation combinations. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 2735–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, G.W.; Cosser, E.; Meng, X.; Dodson, A. High frequency deflection monitoring of bridges by GPS. J. Glob. Position. 2004, 3, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, Y.; Matui, M.; Panini, L.-C.; Ishibashi, R.; Yoshida, A. Measurement of wind-induced response of buildings using RTK-GPS. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2002, 90, 1783–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownjohn, J.W.M.; Stringer, M.; Tan, G.; Poh, Y.K.; Ge, L.; Pan, T.C. Experience with RTK-GPS system for monitoring wind and seismic effects on a tall building. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Structural Health Monitoring of Intelligent Infrastructure, Shenzhen, China, 16–18 November 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, J.S.; Nguyen, D.T.; Meng, X.; Xie, Y.; Psimoulis, P. The influence of uncertainty in wind field parameters on predicted buffeting response of bridges. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Wind Engineering, Beijing, China, 1–6 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Moschas, F.; Stiros, S. Measurement of the dynamic displacements and of the modal frequencies of a short-span pedestrian bridges using GPS and an accelerometer. Eng. Struct. 2011, 33, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, L.; Ambikairajah, E.; Rizos, C.; Tamura, Y.; Yoshida, A. Full-scale structural monitoring using an intergrated GPS and accelerometer system. GPS Solut. 2006, 10, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Lu, H.; Zhu, J. Operational model analysis of bridge structures using data from GNSS/accelerometer measurements. Sensors 2017, 17, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wang, J.; Han, H. Optimal GPS/accelerometer integration algorithm for monitoring the vertical structural dynamics. J. Appl. Geod. 2014, 8, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Wang, J.; Meng, X.; Lui, H. Analysis of the dynamic response of a long span bridge using GPS/accelerometer/anemometer under typhoon loading. Eng. Struct. 2016, 122, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.H.; Yu, L.; Tam, H.Y.; Ni, Y.Q.; Liu, S.; Chung, W.; Cheng, L. Fiber bragg grating sensor for structural health monitoring of Tsing Ma Bridge: Background and experimental observation. Eng. Struct. 2006, 28, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.L.; Xia, Y. Structural Health Monitoring of Long-Span Suspension Bridges; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, E.; Pederson, L. Structural monitoring of the Great Belt East Bridge. Strait Crossings 1994, 94, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Tao, T.; Li, A.; Zhang, Y. Structural health monitoring system for Sutong cable-stayed bridge. Smart Struct. Syst. 2016, 18, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laory, I.; Ali, N.B.; Trinh, T.N.; Smith, I.F.C. Measurement system configuration for damage identification of continuously monitored structures. J. Bridge Eng. 2012, 17, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dervilis, N.; Worden, K.; Crosss, E.J. On robust regression analysis as a means of exploring environmental and operational conditions of SHM data. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 347, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, E.J.; Koo, K.Y.; Brownjohn, J.M.W.; Worden, K. Long-term monitoring and data analysis of the Tamar Bridge. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 35, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Jiang, W.; Meng, X.; Jiang, P.; Wang, K.; Xie, Y.; Ge, Y. Vertical deformation monitoring of the suspension bridge tower using GNSS: A case study of the Forth Road Bridge in the UK. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, G.W.; Meng, X.; Psimoulis, P.; Brown, C.J. Time series analysis of rapid GNSS measurements for quasi-static and dynamic bridge monitoring. In Geodetic Time Series Analysis in Earth Sciences; Montillet, J.P., Bos, M., Eds.; Springer Geophysics: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 345–417. [Google Scholar]
- World Meteorological Organization. Guidelines for Converting Between Various Wind Averaging Periods in Tropical Cyclone Conditions; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ewins, D.J. Modal Testing: Theory, Practice and Application, 2nd ed.; Research Studies Press: Baldock, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 3 Centuries of Spanning the Forth. Available online: web.archive.org/web/20130606162211/http://www.transportscotland.gov.uk/files/documents/projects/forth-replacement/Forth_Bridge_Brochure_VisFinal.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2019).
- Owen, J.S.; Nguyen, D.T.; Meng, X.; Psimoulis, P.; Xie, Y. The application of rainfall radar to interpret non-stationary wind effects on the Forth Road Bridge. In Proceedings of the 13th UK Conference on Wind Engineering, Leeds, UK, 3–4 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Simiu, E.; Scanlan, R. Wind Effects on Structures: Fundamentals and Application to Design, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]























| Storm Name | Date of Impact | Maximum Gust |
|---|---|---|
| Storm Elon | 09 January 2015 | 113 mph (measured at Stornoway) |
| Storm Gertrude | 29 January 2016 | 76 mph (measured at Inverbervie) |
| Storm Ali | 19 September 2018 | 77 mph (measured at Inverbervie) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, X.; Nguyen, D.T.; Owen, J.S.; Xie, Y.; Psimoulis, P.; Ye, G. Application of GeoSHM System in Monitoring Extreme Wind Events at the Forth Road Bridge. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232799
Meng X, Nguyen DT, Owen JS, Xie Y, Psimoulis P, Ye G. Application of GeoSHM System in Monitoring Extreme Wind Events at the Forth Road Bridge. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(23):2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232799
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Xiaolin, Dinh Tung Nguyen, John S. Owen, Yilin Xie, Panagiotis Psimoulis, and George Ye. 2019. "Application of GeoSHM System in Monitoring Extreme Wind Events at the Forth Road Bridge" Remote Sensing 11, no. 23: 2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232799
APA StyleMeng, X., Nguyen, D. T., Owen, J. S., Xie, Y., Psimoulis, P., & Ye, G. (2019). Application of GeoSHM System in Monitoring Extreme Wind Events at the Forth Road Bridge. Remote Sensing, 11(23), 2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232799