An Evaluation of the EnKF vs. EnOI and the Assimilation of SMAP, SMOS and ESA CCI Soil Moisture Data over the Contiguous US
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data
2.1. Satellite Derived SSM
2.1.1. ESA CCI ACTIVE and PASSIVE SSM Product
2.1.2. SMAP Level-2 SSM
2.1.3. SMOS Level-2 SSM
2.2. In Situ Data
2.3. Atmospheric Forcing
3. Methods
3.1. Bias Correction of the ESA CCI ACTIVE and PASSIVE, SMAP-L2 and SMOS-L2 SSM Products
3.2. Modelling System
3.3. Data Assimilation Using the Ensemble Kalman Filter
3.4. Ensemble Optimal Interpolation (EnOI)
3.5. Model and Observation Errors
4. Experiments and Skill Metrics
5. Data Assimilation Results and Discussion
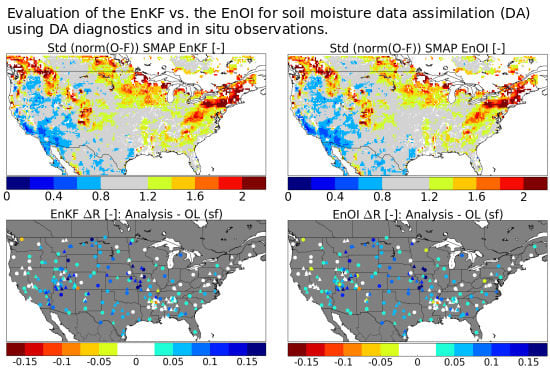
5.1. Filter Performance EnKF vs. EnOI Using Data Assimilation Diagnostics
5.2. EnKF vs. EnOI; Comparison with In Situ SM Data
5.2.1. Correlation Skill
5.2.2. Unbiased Root Mean Square Difference
5.3. Satellite Skill: Comparison between ESA CCI, SMAP and SMOS Using the EnOI
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loew, A. Impact of surface heterogeneity on surface soil moisture retrievals from passive microwave data at the regional scale: The Upper Danube case. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Corti, T.; Davin, E.L.; Hirschi, M.; Jaeger, E.B.; Lehner, I.; Orlowsky, B.; Teuling, A.J. Investigating Soil Moisture-Climate Interactions in a Changing Climate: A Review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2010, 99, 125–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, A.W.; Lettenmaier, D.P. An ensemble approach for attribution of hydrologic prediction uncertainty. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Luo, L.; Wood, E.F.; Schaake, J. The role of initial conditions and forcing uncertainties in seasonal hydrologic forecasting. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thober, S.; Kumar, R.; Sheffield, J.; Mai, J.; Schäfer, D.; Samaniego, L. Seasonal Soil Moisture Drought Prediction over Europe Using the North American Multi-Model Ensemble (NMME). J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 2329–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Sheffield, J.; Wood, E.F.; Lettenmaier, D.P. On the sources of global land surface hydrologic predictability. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 2781–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reichle, R.; McLaughlin, D.; Entekhabi, D. Variational data assimilation of microwave radiobrightness observations for land surface hydrology applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1708–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.V.; Reichle, R.H.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Koster, R.D.; Zhan, X.; Crow, W.T.; Eylander, J.B.; Houser, P.R. A land surface data assimilation framework using the land information system: Description and applications. Adv. Water Resour. 2008, 31, 1419–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, C.S.; Mahfouf, J.F.; Walker, J.P. An EKF assimilation of AMSR-E soil moisture into the ISBA land surface scheme. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lahoz, W.; Khattatov, B.; Ménard, R. Data Assimilation: Making Sense of Observations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 1–718. [Google Scholar]
- Lievens, H.; De Lannoy, G.J.M.; Al Bitar, A.; Drusch, M.; Dumedah, G.; Hendricks Franssen, H.J.; Kerr, Y.H.; Tomer, S.K.; Martens, B.; Merlin, O.; et al. Assimilation of SMOS Soil Moisture and Brightness Temperature Products Into a Land Surface Model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 180, 292–304. [Google Scholar]
- De Lannoy, G.J.; Reichle, R.H. Assimilation of SMOS brightness temperatures or soil moisture retrievals into a land surface model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 4895–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albergel, C.; Munier, S.; Jennifer Leroux, D.; Dewaele, H.; Fairbairn, D.; Lavinia Barbu, A.; Gelati, E.; Dorigo, W.; Faroux, S.; Meurey, C.; et al. Sequential assimilation of satellite-derived vegetation and soil moisture products using SURFEX-v8.0: LDAS-Monde assessment over the Euro-Mediterranean area. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 3889–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albergel, C.; Munier, S.; Bocher, A.; Bonan, B.; Zheng, Y.; Draper, C.; Leroux, D.J.; Calvet, J.C. LDAS-Monde sequential assimilation of satellite derived observations applied to the contiguous US: An ERA-5 driven reanalysis of the land surface variables. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsamo, G.; Agustì-Parareda, A.; Albergel, C.; Arduini, G.; Beljaars, A.; Bidlot, J.; Bousserez, N.; Boussetta, S.; Brown, A.; Buizza, R.; et al. Satellite and In Situ Observations for Advancing Global Earth Surface Modelling: A Review. Remote Sens. 2018, 12, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmugge, T.J.; Kustas, W.P.; Ritchie, J.C.; Jackson, T.J.; Rango, A. Remote sensing in hydrology. Adv. Water Resour. 2002, 25, 1367–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koster, R.D.; Liu, Q.; Mahanama, S.P.P.; Reichle, R.H. Improved Hydrological Simulation Using SMAP Data: Relative Impacts of Model Calibration and Data Assimilation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichle, R.H.; De Lannoy, G.J.M.; Liu, Q.; Koster, R.D.; Kimball, J.S.; Crow, W.T.; Ardizzone, J.V.; Chakraborty, P.; Collins, D.W.; Conaty, A.L.; et al. Global Assessment of the SMAP Level-4 Surface and Root-Zone Soil Moisture Product Using Assimilation Diagnostics. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 3217–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evensen, G. Sequential data assimilation with a nonlinear quasi-geostrophic model using Monte Carlo methods to forecast error statistics (part 1). J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 10143–10162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonan, B.; Albergel, C.; Zheng, Y.; Barbu, A.; Fairbairn, D.; Munier, S.; Calvet, J.C. An Ensemble Kalman Filter for the joint assimilation of surface soil moisture and leaf area index within LDAS-Monde: Application over the Euro-Mediterranean basin. HESSD HYMEX 2019, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Oke, P.R. Assimilation of surface velocity data into a primitive equation coastal ocean model. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evensen, G. The Ensemble Kalman Filter: Theoretical formulation and practical implementation. Ocean Dyn. 2003, 53, 343–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Reichle, R.H.; Bindlish, R.; Cosh, M.H.; Crow, W.T.; de Jeu, R.; De Lannoy, G.J.M.; Huffman, G.J.; Jackson, T.J. The Contributions of Precipitation and Soil Moisture Observations to the Skill of Soil Moisture Estimates in a Land Data Assimilation System. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 750–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maggioni, V.; Reichle, R.H.; Anagnostou, E.N. The Efficiency of Assimilating Satellite Soil Moisture Retrievals in a Land Data Assimilation System Using Different Rainfall Error Models. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelaro, R.; McCarty, W.; Suárez, M.J.; Todling, R.; Molod, A.; Takacs, L.; Randles, C.A.; Darmenov, A.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Reichle, R.; et al. The modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications, version 2 (MERRA-2). J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5419–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, K.E. The multi-institution North American Land Data Assimilation System (NLDAS): Utilizing multiple GCIP products and partners in a continental distributed hydrological modeling system. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D07S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desroziers, G.; Berre, L.; Chapnik, B.; Poli, P. Diagnosis of observation, background and analysis-error statistics in observation space. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 131, 3385–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Dorigo, W.A.; Parinussa, R.M.; De Jeu, R.A.; Wagner, W.; McCabe, M.F.; Evans, J.P.; Van Dijk, A.I. Trend-preserving blending of passive and active microwave soil moisture retrievals. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, W.A.; Gruber, A.; De Jeu, R.A.; Wagner, W.; Stacke, T.; Loew, A.; Albergel, C.; Brocca, L.; Chung, D.; Parinussa, R.M.; et al. Evaluation of the ESA CCI soil moisture product using ground-based observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 162, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, W.; Wagner, W.; Albergel, C.; Albrecht, F.; Balsamo, G.; Brocca, L.; Chung, D.; Ertl, M.; Forkel, M.; Gruber, A.; et al. ESA CCI Soil Moisture for improved Earth system understanding: State-of-the art and future directions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 203, 185–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, A.; Dorigo, W.A.; Crow, W.; Wagner, W. Triple Collocation-Based Merging of Satellite Soil Moisture Retrievals. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6780–6792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Lemoine, G.; Rott, H. A method for estimating soil moisture from ERS Scatterometer and soil data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 70, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartalis, Z.; Wagner, W.; Naeimi, V.; Hasenauer, S.; Scipal, K.; Bonekamp, H.; Figa, J.; Anderson, C. Initial soil moisture retrievals from the METOP-A Advanced Scatterometer (ASCAT). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naeimi, V.; Bartalis, Z.; Wagner, W. ASCAT Soil Moisture: An Assessment of the Data Quality and Consistency with the ERS Scatterometer Heritage. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owe, M.; de Jeu, R.; Holmes, T. Multisensor historical climatology of satellite-derived global land surface moisture. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loizu, J.; Massari, C.; Álvarez-Mozos, J.; Tarpanelli, A.; Brocca, L.; Casalí, J. On the assimilation set-up of ASCAT soil moisture data for improving streamflow catchment simulation. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 111, 86–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, C.S.; Reichle, R.H. Assimilation of passive and active microwave soil moisture retrievals—Draper—2012—Geophysical Research Letters—Wiley Online Library. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G.; O’Neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Crow, W.T.; Edelstein, W.N.; Entin, J.K.; Goodman, S.D.; Jackson, T.J.; Johnson, J.; et al. The Soil Moisture Active Passive {(SMAP)} Mission. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Wigneron, J.P.; Martinuzzi, J.M.; Font, J.; Berger, M. Soil moisture retrieval from space: The Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) mission. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Richaume, P.; Wigneron, J.P.; Ferrazzoli, P.; Mahmoodi, A.; Al Bitar, A.; Cabot, F.; Gruhier, C.; Juglea, S.E.; et al. The SMOS soil moisture retrieval algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1384–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Wigneron, J.P.; Delwart, S.; Cabot, F.; Boutin, J.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Font, J.; Reul, N.; Gruhier, C.; et al. The SMOS L: New tool for monitoring key elements ofthe global water cycle. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 666–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, W.A.; Wagner, W.; Hohensinn, R.; Hahn, S.; Paulik, C.; Xaver, A.; Gruber, A.; Drusch, M.; Mecklenburg, S.; Van Oevelen, P.; et al. The International Soil Moisture Network: A data hosting facility for global in situ soil moisture measurements. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1675–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, W.; Xaver, A.; Vreugdenhil, M.; Gruber, A.; Hegyiová, A.; Sanchis-Dufau, A.; Zamojski, D.; Cordes, C.; Wagner, W.; Drusch, M. Global Automated Quality Control of In Situ Soil Moisture Data from the International Soil Moisture Network. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, G.L.; Cosh, M.H.; Jackson, T.J. The USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service Soil Climate Analysis Network (SCAN). J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2007, 24, 2073–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, H.J.; Karl, T.R.; Palecki, M.A.; Baker, C.B.; Bell, J.E.; Leeper, R.D.; Easterling, D.R.; Lawrimore, J.H.; Meyers, T.P.; Helfert, M.R.; et al. U.S. climate reference network after one decade of operations status and assessment. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palecki, M.A.; Bell, J.E. U.S. Climate Reference Network Soil Moisture Observations with Triple Redundancy: Measurement Variability. Vadose Zone J. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zreda, M.; Desilets, D.; Ferré, T.P.; Scott, R.L. Measuring soil moisture content non-invasively at intermediate spatial scale using cosmic-ray neutrons. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zreda, M.; Shuttleworth, W.J.; Zeng, X.; Zweck, C.; Desilets, D.; Franz, T.; Rosolem, R. COSMOS: The cosmic-ray soil moisture observing system. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 4079–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, R.H.; De Lannoy, G.J.M.; Liu, Q.; Colliander, A.; Conaty, A.; Jackson, T.; Kimball, J.; Koster, R.D. Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) Project Assessment Report for the Beta-Release L4_SM Data Product; Technical Report NASA/TM-2015-104606; Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015.
- Reichle, R.H.; De Lannoy, G.J.M.; Liu, Q.; Ardizzone, J.V.; Colliander, A.; Conaty, A.; Crow, W.; Jackson, T.J.; Jones, L.A.; Kimball, J.S.; et al. Assessment of the SMAP Level-4 Surface and Root-Zone Soil Moisture Product Using In Situ Measurements. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 2621–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reichle, R.H.; Koster, R.D. Bias reduction in short records of satellite soil moisture. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drusch, M.; Wood, E.F.; Gao, H. Observation operators for the direct assimilation of TRMM microwave imager retrieved soil moisture. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brocca, L.; Hasenauer, S.; Lacava, T.; Melone, F.; Moramarco, T.; Wagner, W.; Dorigo, W.; Matgen, P.; Martínez-Fernández, J.; Llorens, P.; et al. Soil moisture estimation through ASCAT and AMSR-E sensors: An intercomparison and validation study across Europe. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3390–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.V.; Reichle, R.H.; Harrison, K.W.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Yatheendradas, S.; Santanello, J.A. A comparison of methods for a priori bias correction in soil moisture data assimilation. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolassa, J.; Reichle, R.; Liu, Q.; Cosh, M.; Bosch, D.; Caldwell, T.; Colliander, A.; Holifield Collins, C.; Jackson, T.; Livingston, S.; et al. Data Assimilation to Extract Soil Moisture Information from SMAP Observations. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, V.; Le Moigne, P.; Martin, E.; Faroux, S.; Alias, A.; Alkama, R.; Belamari, S.; Barbu, A.; Boone, A.; Bouyssel, F.; et al. The SURFEXv7.2 land and ocean surface platform for coupled or offline simulation of earth surface variables and fluxes. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 929–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noilhan, J.; Mahfouf, J.F. The ISBA land surface parameterisation scheme. Glob. Planet. Chang. 1996, 13, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvet, J.C.; Noilhan, J.; Roujean, J.L.; Bessemoulin, P.; Cabelguenne, M.; Olioso, A.; Wigneron, J.P. An interactive vegetation SVAT model tested against data from six contrasting sites. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1998, 92, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decharme, B.; Boone, A.; Delire, C.; Noilhan, J. Local evaluation of the Interaction between Soil Biosphere Atmosphere soil multilayer diffusion scheme using four pedotransfer functions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boone, A.; Masson, V.; Meyers, T.; Noilhan, J. The Influence of the Inclusion of Soil Freezing on Simulations by a Soil–Vegetation–Atmosphere Transfer Scheme. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 1544–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boone, A.; Etchevers, P. An Intercomparison of Three Snow Schemes of Varying Complexity Coupled to the Same Land Surface Model: Local-Scale Evaluation at an Alpine Site. J. Hydrometeorol. 2001, 2, 374–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faroux, S.; Kaptué Tchuenté, A.T.; Roujean, J.L.; Masson, V.; Martin, E.; Le Moigne, P. ECOCLIMAP-II/Europe: A twofold database of ecosystems and surface parameters at 1 km resolution based on satellite information for use in land surface, meteorological and climate models. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 563–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieder, W.R.; Boehnert, J.; Bonan, G.B.; Langseth, M. Regridded Harmonized World Soil Database v1.2. 2014. Available online: http://daac.ornl.gov (accessed on 25 February 2019).
- Noilhan, J.; Lacarrere, P. GCM grid-scale evaporation from mesoscale modeling. J. Clim. 1995, 8, 206–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakov, P.; Oke, P.R. Implications of the Form of the Ensemble Transformation in the Ensemble Square Root Filters. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 1042–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbairn, D.; Barbu, A.L.; Mahfouf, J.F.; Calvet, J.C.; Gelati, E. Comparing the ensemble and extended Kalman filters for in situ soil moisture assimilation with contrasting conditions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4811–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.V.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Mocko, D.; Reichle, R.; Liu, Y.; Arsenault, K.R.; Xia, Y.; Ek, M.; Riggs, G.; Livneh, B.; Cosh, M. Assimilation of Remotely Sensed Soil Moisture and Snow Depth Retrievals for Drought Estimation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 2446–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhan, X.; Zheng, Y.; Hain, C.R.; Liu, J.; Fang, L. Optimal ensemble size of ensemble Kalman filter in sequential soil moisture data assimilation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 6710–6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Counillon, F.; Bertino, L. Ensemble Optimal Interpolation: Multivariate properties in the Gulf of Mexico. Tellus Ser. A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2009, 61, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lannoy, G.J.M.; Reichle, R.H. Global Assimilation of Multiangle and Multipolarization SMOS Brightness Temperature Observations into the GEOS-5 Catchment Land Surface Model for Soil Moisture Estimation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 669–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto, C.; Marc, B.; Laurent, B.; Geir, E. Data assimilation in the geosciences: An overview of methods, issues, and perspectives. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2018, 9, e535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalstad, K.; Westermann, S.; Schuler, T.V.; Boike, J.; Bertino, L. Ensemble-based assimilation of fractional snow-covered area satellite retrievals to estimate the snow distribution at Arctic sites. Cryosphere 2018, 12, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahfouf, J.F.; Bergaoui, K.; Draper, C.; Bouyssel, F.; Taillefer, F.; Taseva, L. A comparison of two off-line soil analysis schemes for assimilation of screen level observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yaari, A.; Wigneron, J.P.; Kerr, Y.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, N.; O’Neill, P.E.; Jackson, T.J.; De Lannoy, G.J.; Al Bitar, A.; Mialon, A.; Richaume, P.; et al. Evaluating soil moisture retrievals from ESA’s SMOS and NASA’s SMAP brightness temperature datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 193, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lannoy, G.J.; Reichle, R.H.; Peng, J.; Kerr, Y.; Castro, R.; Kim, E.J.; Liu, Q. Converting between SMOS and SMAP Level-1 Brightness Temperature Observations over Nonfrozen Land. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sensi. Lett. 2015, 12, 1908–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrassi, A.; Hamdi, R.; Termonia, P.; Vannitsem, S. Short time augmented extended Kalman filter for soil analysis: A feasibility study. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2012, 13, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievens, H.; Reichle, R.H.; Liu, Q.; De Lannoy, G.J.; Dunbar, R.S.; Kim, S.B.; Das, N.N.; Cosh, M.; Walker, J.P.; Wagner, W. Joint Sentinel-1 and SMAP data assimilation to improve soil moisture estimates. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 6145–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Variable | Type | Std Dev | Cross-Corr with Perturbations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRECIP | SW | LW | |||
| PRECIP | M | 0.5 | 1 | −0.8 | 0.5 |
| SW | M | 0.3 | −0.8 | 1 | −0.5 |
| LW | A | 0.5 | −0.5 | 1 | |
| clay | Logit normal | - | - | - | |
| sand | Logit normal | - | - | - | |
| Exp. | Param. Pert. | Rel. Obs. Error | Satellite Data | Forcing | CPU Cost | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eOL_MERRA2 | 12 | yes | - | - | MERRA-2 | 12 |
| EnKF_MERRA2 | 12 | yes | SMAP | MERRA-2 | 24 | |
| EnOI_MERRA2 | 1 | yes | SMAP | MERRA-2 | 13 | |
| EnOI_MERRA2-Clim | 1 | no | SMAP | MERRA-2 | 2 | |
| eOL_NLDAS | 12 | yes | - | - | NLDAS-2 | 12 |
| EnKF_NLDAS | 12 | yes | SMAP | NLDAS-2 | 24 | |
| EnOI_NLDAS | 1 | yes | SMAP | NLDAS-2 | 13 | |
| EnOI_NLDAS-Clim | 1 | no | SMAP | NLDAS-2 | 2 | |
| Satellite skill experiments | ||||||
| EnOI_ESA_M | 1 | yes | ESA CCI | MERRA-2 | 13 | |
| EnOI_SMAP_M | 1 | yes | SMAP | MERRA-2 | 13 | |
| EnOI_SMOS_M | 1 | yes | SMOS | MERRA-2 | 13 | |
| EnOI_ESA_N | 1 | yes | ESA CCI | NLDAS-2 | 13 | |
| EnOI_SMAP_N | 1 | yes | SMAP | NLDAS-2 | 13 | |
| EnOI_SMOS_N | 1 | yes | SMOS | NLDAS-2 | 13 | |
| Exp. | SCAN a,b | USCRN c,d | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | CI | Ubrmsd | R | CI | Ubrmsd | ||
| sfzsm ( | |||||||
| eOL_MERRA | 0.62 | 0.057 | 0.66 | 0.052 | |||
| EnKF_MERRA2 | 0.67 | 0.053 | 0.70 | 0.049 | |||
| EnOI_MERRA2 | 0.66 | 0.054 | 0.70 | 0.049 | |||
| EnOI_MERRA2-Clim | 0.65 | 0.054 | 0.68 | 0.050 | |||
| eOL_NLDAS | 0.67 | 0.053 | 0.71 | 0.048 | |||
| EnKF_NLDAS | 0.69 | 0.052 | 0.73 | 0.047 | |||
| EnOI_NLDAS | 0.68 | 0.052 | 0.72 | 0.048 | |||
| EnOI_NLDAS Clim | 0.67 | 0.053 | 0.71 | 0.048 | |||
| rzsm | |||||||
| eOL_MERRA | 0.63 | 0.041 | 0.68 | 0.042 | |||
| EnKF_MERRA2 | 0.66 | 0.040 | 0.71 | 0.040 | |||
| EnOI_MERRA2 | 0.65 | 0.040 | 0.71 | 0.040 | |||
| EnOI_MERRA2-Clim | 0.65 | 0.040 | 0.70 | 0.041 | |||
| eOL_NLDAS | 0.67 | 0.041 | 0.75 | 0.041 | |||
| EnKF_NLDAS | 0.66 | 0.041 | 0.75 | 0.041 | |||
| EnOI_NLDAS | 0.65 | 0.041 | 0.75 | 0.041 | |||
| EnOI_NLDAS Clim | 0.67 | 0.041 | 0.75 | 0.041 | |||
| Exp. | SCAN a,b | USCRN c,d | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | CI | Ubrmsd | R | CI | Ubrmsd | ||
| sfzsm ( | |||||||
| eOL_MERRA | 0.63 | 0.061 | 0.64 | 0.054 | |||
| EnOI_SMAP | 0.68 | 0.057 | 0.70 | 0.050 | |||
| EnOI_SMOS | 0.66 | 0.058 | 0.68 | 0.051 | |||
| EnOI_ESA | 0.65 | 0.059 | 0.65 | 0.053 | |||
| rzsm ( | |||||||
| eOL_MERRA | 0.64 | 0.043 | 0.63 | 0.042 | |||
| EnOI_SMAP | 0.67 | 0.042 | 0.68 | 0.041 | |||
| EnOI_SMOS | 0.66 | 0.043 | 0.66 | 0.041 | |||
| EnOI_ESA | 0.67 | 0.042 | 0.64 | 0.042 | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blyverket, J.; Hamer, P.D.; Bertino, L.; Albergel, C.; Fairbairn, D.; Lahoz, W.A. An Evaluation of the EnKF vs. EnOI and the Assimilation of SMAP, SMOS and ESA CCI Soil Moisture Data over the Contiguous US. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11050478
Blyverket J, Hamer PD, Bertino L, Albergel C, Fairbairn D, Lahoz WA. An Evaluation of the EnKF vs. EnOI and the Assimilation of SMAP, SMOS and ESA CCI Soil Moisture Data over the Contiguous US. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(5):478. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11050478
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlyverket, Jostein, Paul D. Hamer, Laurent Bertino, Clément Albergel, David Fairbairn, and William A. Lahoz. 2019. "An Evaluation of the EnKF vs. EnOI and the Assimilation of SMAP, SMOS and ESA CCI Soil Moisture Data over the Contiguous US" Remote Sensing 11, no. 5: 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11050478
APA StyleBlyverket, J., Hamer, P. D., Bertino, L., Albergel, C., Fairbairn, D., & Lahoz, W. A. (2019). An Evaluation of the EnKF vs. EnOI and the Assimilation of SMAP, SMOS and ESA CCI Soil Moisture Data over the Contiguous US. Remote Sensing, 11(5), 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11050478