Goaf Locating Based on InSAR and Probability Integration Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Principle
2.1. DInSAR Technology
2.2. Feature Points of PIM
2.3. Goaf Locating
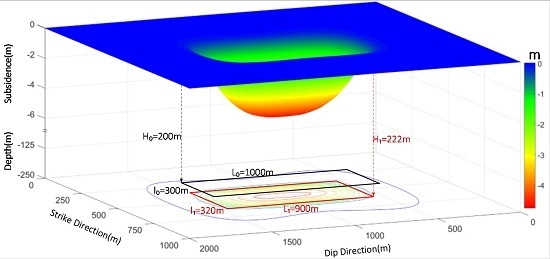
3. Simulation Experiment
3.1. Numerical Simulation
3.2. Simulated Goaf Locating
3.3. Accuracy Evaluation
4. Real Data Experiment
4.1. Study Area
4.2. DInSAR Data Processing
4.3. Goaf Location Process and Result
4.4. Precision Analysis
5. Discussion
5.1. Influence of DInSAR on the Location Result
5.2. Influence of Geological Structure on the Location Result
5.3. Influence of Subcritical Extraction on the Location Result
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, M.; Zeng, Y. Study on Geological Hazards Due to Mining Subsidence and Their Countermeasures in Mining Area. Jiangsu Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 18, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.Y.; Qiu, Y.X. Analysis of subsidence status formation mechanisms in shallow mining seam of ravine cutting area. J. Xi’an Univ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 32, 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.-B.; Deng, K.-Z.; Zou, Y.-F. Research Progress and Prospect of the Control Technology for Surface and Overlying Strata Subsidence. China Saf. Sci. J. 2005, 15, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.-D.; Wang, X.-X.; Li, T.-J. Geological Environmental Problems Induced by Coalfield Exploition and Control Countermeasures. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2007, 14, 351–354. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Suo, K.; Song, Z.; Zhang, G. Goal Mine Detection with Transient Electromagnetic Method and Magnetic Method. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2018, 66, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Deng, K.; Ju, C.; Zhu, C.; Xue, J. Land subsidence monitoring by D-InSAR technique. Min. Sci. Technol. (China) 2011, 21, 869–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Gao, X.; Yang, J.; Deng, K.; Yu, Y. Monitoring mining subsidence using a combination of phase-stacking and offset-tracking methods. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9166–9183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.F.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.J.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.J.; Chen, G.L. InSAR-Based Model Parameter Estimation of Probability Integral Method and Its Application for Predicting Mining-Induced Horizontal and Vertical Displacements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4818–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-F.; Yu, J.; Wu, J.-Q.; Wu, S.-L.; Li, X.-Q.; Zhang, J.-F.; Luo, Y.; Su, Y.-M. Application comparison of D-InSAR and PS-InSAR techniques in Suzhou land subsidence monitoring. J. Geol. 2010, 34, 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Solari, L.; Ciampalini, A.; Raspini, F.; Bianchini, S.; Zinno, I.; Bonano, M.; Manunta, M.; Moretti, S.; Casagli, N. Combined use of C-and X-Band SAR data for subsidence monitoring in an urban area. Geosciences 2017, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solari, L.; Del Soldato, M.; Bianchini, S.; Ciampalini, A.; Ezquerro, P.; Montalti, R.; Raspini, F.; Moretti, S. From ERS 1/2 to Sentinel-1: Subsidence monitoring in Italy in the last two decades. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-F.; Song, X.-G.; Shan, X.-J.; Qu, C.-Y.; Wang, C.-S.; Guo, L.-M.; Zhang, G.-F.; Liu, Y.-H. Deformation monitoring of Changbaishan Tianchi volcano using D-InSAR technique and error analysis. Chin. J. Geophys. 2010, 53, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar]
- Di Traglia, F.; Nolesini, T.; Solari, L.; Ciampalini, A.; Frodella, W.; Steri, D.; Allotta, B.; Rindi, A.; Marini, L.; Monni, N.; et al. Lava delta deformation as a proxy for submarine slope instability. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 488, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Engelhardt, H.; Kamb, B.; Frolich, R.M. Satellite radar interferometry for monitoring ice sheet motion: application to an Antarctic ice stream. Science 1993, 262, 1525–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.X. An Illegal Mining Detection Method Based on D-InSAR. Master’s Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Ge, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, L. An underground-mining detection system based on DInSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Du, S.; Liu, X.; Zhou, H. Integration of D-InSAR and GIS technology for identifying illegal underground mining in Yangquan District, Shanxi Province, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yi, H.; Feng, G.; Hu, J.; Wu, L.; Preusse, A.; Wang, Y.; Papst, M. Locating and defining underground goaf caused by coal mining from space-borne SAR interferometry. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 135, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.S.; Ma, W.; Zhong, W. Surface Subsidence Engineering; Society for Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration Littleton: Englewood, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, K.Z.; Tan, Z.X.; Jiang, Y. Subject of Deformation Monitoring and Subsidence Engineering; China University of Mining and Technology Press: Xuzhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.D.; Wei, G.; Yong, Q.; Xue, J.Q.; Chen, B.Q. A model for extracting large deformation mining subsidence using D-InSAR technique and probability integral method. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 1242–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Cheng, D.; Deng, K.; Chen, B.; Zhu, C. Subsidence monitoring using D-InSAR and probability integral prediction modelling in deep mining areas. Surv. Rev. 2015, 47, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yin, Z. Ground Subsidence Monitoring with D-InSAR in Qianyingzi Coal Mine. Available online: http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS201103039.htm (accessed on 2 April 2019).
- Buckland, J.; Huntley, J.; Turner, S. Unwrapping noisy phase maps by use of a minimum-cost-matching algorithm. Appl. Opt. 1995, 34, 5100–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Yang, L. Mining Subsidence; China University of Mining and Technology Press: Xuzhou, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Bureau, C.I.S. Regulations for Coal Pillar Setting and Coal Pressure Mining in Buildings, Water Bodies, Railways and Main Roadways; China Coal Industry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhao, B.; Guo, G.; Zha, J.; Bi, J. The influence of an abandoned goaf on surface subsidence in an adjacent working coal face: A prediction method. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2018, 77, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, A.H.M.; Ge, L.; Du, Z.; Wang, S.; Ma, C. Satellite radar interferometry for monitoring subsidence induced by longwall mining activity using Radarsat-2, Sentinel-1 and ALOS-2 data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 61, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Name of the Overlying Rock | Parameters of the Mohr–Coulomb Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk | Shear | Cohesion | Tension | Friction | |
| topsoil | 4.3 | 2.5 | 4.1 | 2.6 | 1.8 |
| fine—sandstone1 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 1.9 | 8.0 | 3.0 |
| siltstone1 | 8.6 | 6.6 | 1.7 | 4.4 | 2.6 |
| siltstone2 | 8.6 | 6.6 | 1.7 | 4.4 | 2.6 |
| fine—sandstone2 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 1.9 | 8.0 | 3.0 |
| medium-sandstone1 | 3.5 | 2.8 | 1.9 | 7.1 | 3.3 |
| medium—sandstone2 | 3.5 | 2.8 | 1.9 | 7.1 | 3.3 |
| coal seam | 8.3 | 2.4 | 3.2 | 3.1 | 2.7 |
| coal seam floor | 8.6 | 6.6 | 1.4 | 4.4 | 2.6 |
| Length | Width | Depth | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Real value | 1000 m | 300 m | 200 m |
| Calculated value | 900 m | 320 m | 222 m |
| Absolute boundary error | m | 10 m | 22 m |
| Relative boundary error | % | 3.30% | 11.00% |
| Interferograms Pairs | Spatial Baseline | Time Baseline |
|---|---|---|
| 20151013–20151106 | 47.1835 m | 24 d |
| 20151106–20151130 | 3.8988 m | 24 d |
| 20151130–20151224 | 13.3323 m | 24 d |
| 20151224–20160117 | −43.7693 m | 24 d |
| 20160117–20160305 | −37.7825 m | 48 d |
| Northwest | Southeast | Southwest | Northeast | Depth | Average Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute error (m) | 22.58 | 23.45 | 74.58 | 4.52 | 67.12 | 38.45 |
| Relative error | 15.90% | 16.51% | 20.25% | 1.23% | 9.07% | 12.59% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, S.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, D.; Xia, Y. Goaf Locating Based on InSAR and Probability Integration Method. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11070812
Du S, Wang Y, Zheng M, Zhou D, Xia Y. Goaf Locating Based on InSAR and Probability Integration Method. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(7):812. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11070812
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Sen, Yunjia Wang, Meinan Zheng, Dawei Zhou, and Yuanping Xia. 2019. "Goaf Locating Based on InSAR and Probability Integration Method" Remote Sensing 11, no. 7: 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11070812
APA StyleDu, S., Wang, Y., Zheng, M., Zhou, D., & Xia, Y. (2019). Goaf Locating Based on InSAR and Probability Integration Method. Remote Sensing, 11(7), 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11070812