Validation of Preliminary Results of Thermal Tropopause Derived from FY-3C GNOS Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. RO Data
2.2. Radiosonde Data
2.3. Tropopause Determination Method
2.4. Algorithm Introduction
2.5. Binning Method
3. Results
3.1. Temperature Comparison with COSMIC Data
3.2. Tropopause Parameters Comparison with COSMIC Data
3.3. Tropopause Parameters Comparison with Radiosonde Data
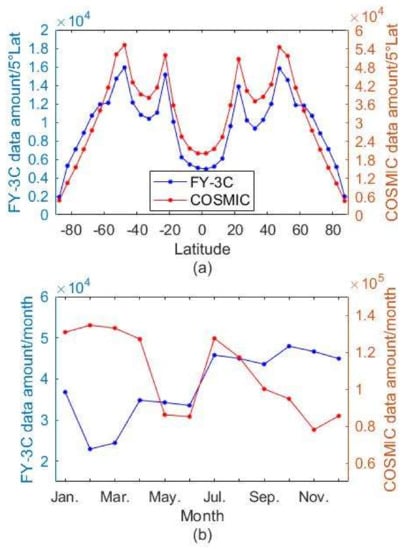
3.4. FY-3C Global Tropopause Patterns
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holton, J.R.; Haynes, P.H.; Mcintyre, M.E.; Douglass, A.R.; Pfister, L. Stratosphere-troposphere exchange. Rev. Geophys. 1995, 33, 403–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randel, W.J.; Wu, F.; Vömel, H.; Nedoluha, G.E.; Forster, P. Decreases in stratospheric water vapor after 2001: Links to changes in the tropical tropopause and the Brewer-Dobson circulation. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Randel, W.J.; Wu, F.; Oltmans, S.J.; Rosenlof, K.; Nedoluha, G. Interannual changes of stratospheric water vapor and correlations with tropical tropopause temperatures. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 61, 2133–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fueglistaler, S.; Dessler, A.E.; Dunkerton, T.J.; Folkins, I.; Fu, Q.; Mote, P. Tropical tropopause layer. Rev. Geophys. 2009, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santer, B.D.; Wehne, M.F.; Wigley, T.M.L.; Sausen, R.; Meehl, G.A.; Taylor, K.E.; Ammann, C.; Arblaster, J.; Washington, W.M.; Boyle, J.S.; et al. Contributions of anthropogenic and natural forcing to recent tropopause height changes. Science 2003, 301, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, D.J.; DeWeaver, E.T. Tropopause height and zonal wind response to global warming in the IPCC scenario integrations. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinbrecht, W.; Claude, H.; Köhler, U.; Hoinka, K.P. Correlations between Tropopause Height and Total Ozone: Implications for Long-Term Changes. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 19183–19192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sausen, R.; Santer, B.D. Use of changes in tropopause height to detect human influences on climate. Meteorol. Z. 2003, 12, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birner, T.; Sankey, D.; Shepherd, T.G. The tropopause inversion layer in models and analyses. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sturaro, G. A closer look at the climatological discontinuities present in the NCEP/NCAR reanalysis temperature due to the introduction of satellite data. Clim. Dyn. 2003, 21, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterl, A. On the (in-)homogeneity of reanalysis products. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 3866–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, R.; Steiner, A.K.; Kirchengast, G.; Rieckh, T. Characterization of thermal structure and conditions for overshooting of tropical and extratropical cyclones with GPS radio occultation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5181–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravindra Babu, S.; Venkat Ratnam, S.; Basha, G.; Krishnamurthy, B.V.; Venkateswararao, B. Effect of tropical cyclones on the tropical tropopause parameters observed using COSMIC GPS RO data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 10239–10249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishida, M.; Shimizu, A.; Tsuda, T.; Rocken, C.; Ware, R.H. Seasonal and longitudinal variations in the tropical tropopause observed with the GPS occultation technique (GPS/MET). J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2000, 78, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randel, W.J.; Wu, F.; Rivera, R.W. Thermal variability of the tropical tropopause region derived from GPS/MET observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Wickert, J.; Beyerle, G.; Reigber, C. Tropical tropopause parameters derived from GPS radio occultation measurements with CHAMP. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, T.; Heise, S.; Wickert, J.; Beyerle, G.; Reigber, C. Gps radio occultation with champ and sac-c: Global monitoring of thermal tropopause parameters. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 1473–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Wickert, J.; Beyerle, G.; Heise, S. Global tropopause height trends estimated from GPS radio occultation data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Son, S.W. Tropical Cold-Point Tropopause: Climatology, Seasonal Cycle, and Intraseasonal Variability Derived from COSMIC GPS Radio Occultation Measurements. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 5343–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.W.; Tandon, N.F.; Polvani, L.M. The fin-scale structure of the global tropopause derived from COSMIC GPS radio occultation measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieckh, T.; Scherllin-Pirscher, B.; Ladstädter, F.; Foelsche, U. Characteristics of tropopause parameters as observed with GPS radio occultation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 4693–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yuan, Y.B.; Chai, Y.J.; Liou, Y.A.; Ou, J.M.; Zhong, S.M. Characteristics of the global thermal tropopause derived from multiple radio occultation measurements. Atmos. Res. 2017, 185, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Sun, Y.Q.; Du, Q.F.; Bai, W.H.; Wang, D.W.; Cai, Y.R.; Wu, D.; Yu, Q.L. GNOS—Radio Occultation Sounder on Board of Chinese FY3 Satellites. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS 2014), Quebec, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 4982–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Q.; Bai, W.H.; Liu, C.L.; Liu, Y.; Du, Q.F.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, G.L.; Liao, M.; Yang, Z.D.; Zhang, X.X.; et al. The FengYun-3C radio occultation sounder GNOS: A review of the mission and its early results and science applications. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5797–5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.H.; Sun, Y.Q.; Du, Q.F.; Yang, G.L.; Yang, Z.D.; Zhang, P.; Bi, Y.M.; Wang, X.Y.; Cheng, C.; Han, Y. An introduction to the FY3 GNOS instrument and mountain-top tests. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 1817–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Q.F.; Sun, Y.Q.; Bai, W.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, D.W.; Meng, X.G.; Cai, Y.R.; Liu, C.L.; Wu, D.; Wu, C.J.; et al. The Next Generation GNOS Instrument for FY-3 Meteorological Satellites. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS 2016), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Z.; Zhu, G.-W.; Bai, W.-H.; Liu, C.; Sun, Y.-Q.; Du, Q.-F.; Wang, X.-Y.; Meng, X.-G.; Yang, G.-L.; Yang, Z.-D.; et al. For the first time fengyun3 C satellite-global navigation satellite system occultation sounder achieved spaceborne Bei Dou system radio occultation. Acta Phys. Sin. 2015, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.H.; Liu, C.L.; Meng, X.G.; Sun, Y.Q.; Kirchengast, G.; Du, Q.F.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, G.L.; Liao, M.; Yang, Z.D.; et al. Evaluation of atmospheric profiles derived from single- and zero-difference excess phase processing of BeiDou radio occultation data from the FY-3C GNOS mission. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scherllin-Pirscher, B.; Steiner, A.K.; Kirchengast, G.; Schwärz, M.; Leroy, S.S. The power of vertical geolocation of atmospheric profiles from GNSS radio occultation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 1595–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewis, H.W. A robust method for tropopause altitude identification using GPS radio occultation data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, T.; Wickert, J.; Haser, A. Variability of the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere observed with GPS radio occultation bending angles and temperatures. Adv. Space Res. 2010, 46, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randel, W.J.; Seidel, D.J. Interannual variability of the tropical tropopause derived from radiosonde data and NCEP reanalyses. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 15509–15523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Highwood, E.J.; Hoskins, B.J. The tropical tropopause. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 124, 1579–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zängl, G.; Hoinka, K.P. The Tropopause in the Polar Regions. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 3117–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomikawa, Y.; Nishimura, Y.; Yamanouchi, T. Characteristics of tropopause and tropopause inversion layer in the polar region. Sola 2009, 5, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladstädter, F.; Steiner, A.K.; Schwärz, M.; Kirchengast, G. Climate intercomparison of GPS radio occultation, RS90/92 radiosondes and GRUAN from 2002 to 2013. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 1819–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]













| Station Name | Organization | Location | Time Span | Data Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAR | GRUAN | 71.4N, 155.6W | 2014.1–2017.12 | 1815 |
| GRA | GRUAN | 39.0N, 27.4W | 2017.1–2017.12 | 477 |
| LIN | GRUAN | 52.2N, 15.2E | 2014.1–2017.12 | 4310 |
| NYA | GRUAN | 78.9N, 13.8E | 2014.1–2017.12 | 1219 |
| SGP | GRUAN | 36.4N, 96.2W | 2014.1–2017.12 | 3578 |
| SOD | GRUAN | 67.2N, 26.7E | 2014.1–2017.12 | 1318 |
| USM00072402 | IGRA | 37.9N, 75.5W | 2016.1–2017.12 | 1498 |
| FMM00091413 | IGRA | 9.5N, 138.1E | 2016.1–2017.12 | 1445 |
| RMM00091376 | IGRA | 7.1N, 171.4E | 2016.1–2017.12 | 1453 |
| Station | Location | Collocate Pairs | TPH AMD | TPH MD | TPT AMD | TPT MD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAR | 71.4N, 155.6W | 36 | 0.42 km | 0.27 km | 2.01 K | –1.43 K |
| GRA | 39.0N, 27.4W | 15 | 0.17 km | 0.05 km | 1.17 K | –0.22 K |
| LIN | 52.2N, 15.2E | 151 | 0.35 km | 0.07 km | 2.13 K | –0.32 K |
| NYA | 78.9N, 13.8E | 84 | 0.36 km | 0.21 km | 1.91 K | –0.85 K |
| SGP | 36.4N, 96.2W | 48 | 0.69 km | 0.40 km | 2.42 K | –1.70 K |
| SOD | 67.2N, 26.7E | 49 | 0.40 km | 0.20 km | 1.99 K | –0.20 K |
| USM | 37.9N, 75.5W | 46 | 0.41 km | 0.15 km | 2.15 K | 0.08 K |
| FMM | 9.5N, 138.1E | 27 | 0.22 km | 0.05 km | 1.16 K | –0.13 K |
| RMM | 7.1N, 171.4E | 18 | 0.28 km | 0.02 km | 1.51 K |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Bai, W.; Xia, J.; Tan, G.; Cheng, C.; Du, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhao, D.; Tian, Y.; et al. Validation of Preliminary Results of Thermal Tropopause Derived from FY-3C GNOS Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11091139
Liu Z, Sun Y, Bai W, Xia J, Tan G, Cheng C, Du Q, Wang X, Zhao D, Tian Y, et al. Validation of Preliminary Results of Thermal Tropopause Derived from FY-3C GNOS Data. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(9):1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11091139
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ziyan, Yueqiang Sun, Weihua Bai, Junming Xia, Guangyuan Tan, Cheng Cheng, Qifei Du, Xianyi Wang, Danyang Zhao, Yusen Tian, and et al. 2019. "Validation of Preliminary Results of Thermal Tropopause Derived from FY-3C GNOS Data" Remote Sensing 11, no. 9: 1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11091139
APA StyleLiu, Z., Sun, Y., Bai, W., Xia, J., Tan, G., Cheng, C., Du, Q., Wang, X., Zhao, D., Tian, Y., Meng, X., Liu, C., Cai, Y., & Wang, D. (2019). Validation of Preliminary Results of Thermal Tropopause Derived from FY-3C GNOS Data. Remote Sensing, 11(9), 1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11091139