Monitoring Water Quality of Valle de Bravo Reservoir, Mexico, Using Entire Lifespan of MERIS Data and Machine Learning Approaches
Abstract
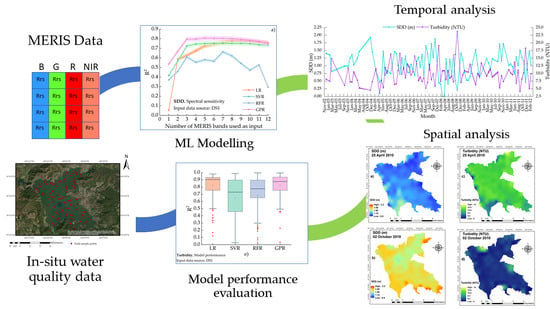
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Materials
3.1. Field Campaigns
3.2. MERIS Satellite Data
4. Methods
4.1. Linear Regression (LR)
4.2. Random Forest Regression (RFR)
4.3. Support Vector Regression (SVR)
4.4. Gaussian Processes Regression (GPR)
4.5. Hyperparameter Tuning
4.6. Model Evaluation
5. Results
5.1. In-Situ Measurements
5.2. Spectral Sensitivity
5.3. Model Performance
5.4. Processing Efficiency
5.5. SDD and Turbidity Maps
5.6. Multitemporal Anaylsis of MERIS Imagery
6. Discussion
6.1. Performance of Machine Learning Algorithms
6.2. Dynamics of Water Quality Parameters and Its Influencing Factors
6.3. Water Quality Status in the Reservoir
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MEA. Ecosystems and Human Well Being: Synthesis; Millennium Ecosystem Assessment: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, J.C.; Zimba, P.V.; Everitt, J.H. Remote sensing techniques to assess water quality. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Preisendorfer, R.W. Secchi disk science: Visual optics of natural waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1986, 31, 909–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luhtala, H.; Tolvanen, H. Optimizing the Use of Secchi Depth as a Proxy for Euphotic Depth in Coastal Waters: An Empirical Study from the Baltic Sea. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2013, 2, 1153–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E. A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, K.-S.; Lei, T.-C. Reservoir Trophic State evaluation using Landsat TM Images. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37, 1321–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathrop, R. Landsat Thematic Mapper monitoring of turbid inland water quality. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1992, 58, 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, F.A.; Ansari, A.A. Eutrophication: An ecological vision. Bot. Rev. 2005, 71, 449–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Water Quality and Health—Review of Turbidity: INFORMATION for Regulators and Water Suppliers; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dekker, A.G.; Peters, S.W.M. The use of the Thematic Mapper for the analysis of eutrophic lakes: A case study in the Netherlands. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odermatt, D.; Heege, T.; Nieke, J.; Kneubühler, M.; Itten, K. Water quality monitoring for lake constance with a physically based algorithm for MERIS data. Sensors 2008, 8, 4582–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthews, M.W. Eutrophication and cyanobacterial blooms in South African inland waters: 10 years of MERIS observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 155, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.; Burian, S.J.; Dennison, P.E.; Williams, G. Spatiotemporal Variability of Lake Water Quality in the Context of Remote Sensing Models. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giardino, C.; Candiani, G.; Zilioli, E. Detecting Chlorophyll-a in Lake Garda using TOA MERIS radiances. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2005, 71, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzer, S.; Brockmann, C.; Moore, G. Using MERIS full resolution data to monitor coastal waters—A case of study from Himmerfjärden, a fjord-like bay in the northwestern Baltic Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2284–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, M.W. A current review of empirical procedures of remote sensing in inland and near-coastal transitional waters. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 6855–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, R. Diseño de modelos de calidad del agua mediante el uso de percepción remota. In Master and Doctoral Program in Engineering; National Autonomous University of Mexico: Mexico City, Mexico, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer, B.A.; Schaeffer, K.G.; Keith, D.; Lunetta, R.S.; Conmy, R.; Gould, R.W. Barriers to adopting satellite remote sensing for water quality management. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 7534–7544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, S.N.; Pavelsky, T.M.; Jensen, D.; Simard, M.; Ross, M.R. Research Trends in the Use of Remote Sensing for Inland Water Quality Science: Moving Towards Multidisciplinary Applications. Water 2020, 12, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odermatt, D.; Giardino, C.; Heege, T. Chlorophyll retrieval with MERIS Case-2-Regional in perialpine lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giardino, C.; Oggioni, A.; Bresciani, M.; Yan, H. Remote sensing of suspended particulate matter in Himalayan lakes. Mt. Res. Dev. 2010, 30, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, J.; Roelfsema, C.; Chollett, I.; Harborne, A.; Heron, S.; Weeks, S.; Skirving, W.; Strong, A.; Eakin, C.; Christensen, T.; et al. Remote Sensing of Coral Reefs for Monitoring and Management: A Review. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giardino, C.; Brando, V.; Gege, P.; Pinnel, N.; Hochberg, E.; Knaeps, E.; Reusen, I.; Doerffer, R.; Bresciani, M.; Braga, F.; et al. Imaging Spectrometry of Inland and Coastal Waters: State of the Art, Achievements and Perspectives. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 40, 401–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, C.; Hu, C.; Cannizzaro, J.; English, D.; Muller-Karger, F.; Lee, Z. Evaluation of chlorophyll-a remote sensing algorithms for an optically complex estuary. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Han, X.; Chen, X.; Qi, L. Long-term distribution patterns of chlorophyll-a concentration in China’s largest freshwater lake: MERIS full-resolution observations with a practical approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 7, 275–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kallio, K.; Koponen, S.; Ylöstalo, P.; Kervinen, M.; Pyhälahti, T.; Attila, J. Validation of MERIS spectral inversion processors using reflectance, IOP and water quality measurements in boreal lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezonik, P.; Menken, K.D.; Bauer, M. Landsat-based remote sensing of lake water quality characteristics, including chlorophyll and colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM). Lake Reserv. Manag. 2005, 21, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, G.; Du, C. Landsat-Based Long-Term Monitoring of Total Suspended Matter Concentration Pattern Change in the Wet Season for Dongting Lake, China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 13975–13999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noori, R.K.; Karbassi, A.R.; Moghaddamnia, A.; Han, D.; Zokaei-Ashtiani, M.H.; Farokhnia, A.; Ghafari Gousheh, M. Assessment of input variables determination on the SVM model performance using PCA, Gamma test, and forward selection techniques for monthly stream flow prediction. J. Hydrol. 2011, 401, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountrakis, G.; Im, J.; Ogole, C. Support vector machines in remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V.; Golowich, S.E.; Smola, A. Support vector method for function approximation, regression estimation and signal processing. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Mozer, M.C., Jordan, M.I., Petsche, T., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997; pp. 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, D.; Ding, C.; Jiang, J.L. Multivariable integration method for estimating sea surface salinity in coastal waters from in situ data and remotely sensed data using random forest algorithm. Comput. Geosci. 2015, 75, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Galiano, V.; Mendes, M.P.; Garcia-Soldado, M.J.; Chica-Olmo, M.; Ribeiro, L. Predictive modeling of groundwater nitrate pollution using random forest and multisource variables related to intrinsic and specific vulnerability: A case study in an agricultural setting (southern Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476–477, 189–206. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, C.E.; Williams, C.K.I. Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Verrelst, J.; Rivera, J.P.; Moreno, J.; Camps-Valls, G. Gaussian processes uncertainty estimates in experimental Sentinel-2 LAI and leaf chlorophyll content retrieval. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 86, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blix, K.; Pálffy, K.R.; Tóth, V.; Eltoft, T. Remote Sensing of Water Quality Parameters over Lake Balaton by Using Sentinel-3 OLCI. Water 2018, 10, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasolli, L.; Melgani, F.; Blanzieri, E. Gaussian Process Regression for Estimating Chlorophyll Concentration in Subsurface Waters from Remote Sensing Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrelst, J.; Muñoz, J.; Alonso, L.; Rivera, J.P.; Camps-Valls, G.; Moreno, J. Machine learning regression algorithms for biophysical parameter retrieval: Opportunities for Sentinel-2 and -3. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Im, J.; Ha, H.K.; Choi, J.-K.; Ha, S. Machine learning approaches to coastal water quality monitoring using GOCI satellite data. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2014, 51, 158–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipomex. Diagnostico en Materia de Turismo Valle de Bravo; Ayuntamiento Constitucional de Valle de Bravo: Municipio de Valle de Bravo, Estado de México, México, 2014; Available online: https://www.ipomex.org.mx/recursos/ipo/files_ipo/2014/8/8/2ed859f540454faa56eba99a59eedb19.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Olvera-Viascan, V. Estudio de la Eutroficacion del Embalse Valle de Bravo, Mexico. Master’s Thesis, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico, Mexico City, Mexico, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Olvera-Viascan, V.; Bravo-Inclan, L.; Sanchez-Chavez, J. Aquatic ecology management assessment in Valle de Bravo reservoir and its watershed. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 1998, 1, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, P.R.; Nandini, S.; Sarma, S.S.S.; Valderrama, E.R.; Cuesta, I.; Hurtado, M.D. Seasonal variations of zooplankton abundance in the freshwater reservoir Valle de Bravo. Hydrobiologia 2002, 467, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandini, S.; Merino-Ibarra, M.; Sarma, S.S.S. Seasonal changes in the zooplankton abundances of the reservoir Valle de Bravo (State of Mexico, Mexico). Lake Reserv. Manag. 2008, 24, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Figueroa-Sanchez, M.A.; Nandini, S.; Sarma, S.S.S. Zooplankton communitiy structure in the presence of low levels of cyanotoxins: A case study in a high altitude tropical reservoir (Valle de Bravo, Mexico). J. Limnol. 2014, 73, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CNN. La Ciudad de México, en Crisis de Agua, in Expansión in Alliance with CNN. 2010. Available online: https://expansion.mx (accessed on 18 October 2018).
- Fondo para la Comunicación y la Educación Ambiental A.C. Recorte en el Suministro de Agua del Sistema Cutzamala. 2009. Available online: https://agua.org.mx (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Escolero, Ó.; Martínez, S.; Kralisch, S.; Perevochtchikova, M. Vulnerabilidad de las Fuentes de Abastecimiento de Agua Potable de la Ciudad de México en el Contexto de Cambio Climático; Centro Virtual de Cambio Climático de la Ciudad de México-UNAM: Ciudad de México, México, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez, P.; Olvera, V.; Pulido, M.; Duran, A. Presence of Vibrio cholerae in a fresh water Reservoir of Valle de Bravo (México State, México). Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 1998, 83, 647–650. [Google Scholar]
- Merino-Ibarra, M.; Monroy-Ríos, E.; Vilaclara, G.; Castillo, F.S.; Gallegos, M.E.; Ramírez-Zierold, J. Physical and chemical limnology of a wind-swept tropical highland reservoir. Aquat. Ecol. 2008, 42, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaytan-Herrera, M.L.; Martinez-Almeida, V.; Oliva-Martinez, M.G.; Duran-Diaz, Á.; Ramirez-Garcia, P. Temporal variation of phytoplankton from the tropical reservoir Valle de Bravo, Mexico. J. Environ. Biol. 2011, 32, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Zierold, J.A.; Merino-Ibarra, M.; Monroy-Ríos, E.; Olson, M.; Castillo, F.S.; Gallegos, M.E.; Vilaclara, G. Changing water, phosphorus and nitrogen budgets for Valle de Bravo reservoir, water supply for Mexico City Metropolitan Area. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2010, 26, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobierno de México. Sistema Cutzamala, la Llave de Agua del Valle de México. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/temas/archivo/articulos/agua?page=123&post=articulos&query%5Btopics%5D=agua (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Santer, R.; Zagolski, F.; Gilson, M. ICOL—Improve Contrast between Ocean and Land; MERIS: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Schiller, R.D.H. The MERIS Case 2 water algorithm. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 517–535. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B. Remote-sensing assessment of regional inland lake water clarity in northeast China. Limnology 2009, 10, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonansea, M.; Ledesma, M.; Rodriguez, C.; Pinotti, L. Using new remote sensing satellites for assessing water quality in a reservoir. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2018, 64, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Härmä, P.; Vepsäläinen, J.; Hannonen, T.; Pyhälahti, T.; Kämäri, J.; Kallio, K.; Eloheimo, K.; Koponen, S. Detection of water quality using simulated satellite data and semi-empirical algorithms in Finland. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 268, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloiber, S.M.; Brezonik, P.L.; Olmanson, L.G.; Bauer, M.E. A procedure for regional lake water clarity assessment using Landsat multispectral data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 82, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaba, S.P.; Badewien, T.H.; Braun, A.; Schulz, A.-C.; Zielinski, O. Using ocean colour remote sensing products to estimate turbidity at the Wadden Sea time series station Spiekeroog. J. Eur. Opt. Soc.-Rapid 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toming, K.; Kutser, T.; Uiboupin, R.; Arikas, A.; Vahter, K.; Paavel, B. Mapping Water Quality Parameters with Sentinel-3 Ocean and Land Colour Instrument imagery in the Baltic Sea. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alikas, K.; Kratzer, S. Improved retrieval of Secchi depth for optically-complex waters using remote sensing data. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 77, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruescas, A.B.; Hieronymi, M.; Mateo-Garcia, G.; Koponen, S.; Kallio, K.; Camps-Valls, G. Machine Learning Regression Approaches for Colored Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) Retrieval with S2-MSI and S3-OLCI Simulated Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maier, P.M.; Keller, S. Application of Different Simulated Spectral Data and Machine Learning to Estimate the Chlorophyll a Concentration of Several Inland Waters. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th Workshop on Hyperspectral Imaging and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 24–26 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- James, G.; Witten, D.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. An Introduction to Statistical Learning with Applications in R; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. In Machine Learning; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Berlin, Germany, 2001; Volume 45, pp. 5–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Batur, E.; Maktav, D. Assessment of Surface Water Quality by Using Satellite Images Fusion Based on PCA Method in the Lake Gala, Turkey. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 2983–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-J.; Chang, C.-C. LIBSVM: A Library for Support Vector Machines. 2001. Available online: https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/papers/libsvm.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Blix, K.; Camps-Valls, G.; Jenssen, R. Gaussian Process Sensitivity Analysis for Oceanic Chlorophyll Estimation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 1265–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candiani, G.; Giardino, C.; Brando, V.E. Adjacency effects and bio-optical model regionalisation: MERIS data to assess lake water quality in the subalpine ecoregion. In Proceedings of the Envisat Symposium, Montreux, Switzerland, 23–27 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Brando, V.E.; Dekker, A.G. Satellite hyperspectral remote sensing for estimating estuarine and coastal water quality. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1378–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnero-Bravo, V.; Merino-Ibarra, M.; Ruiz-Fernández, A.C.; Sanchez-Cabeza, J.A.; Sanchez-Cabeza, B. Sedimentary record of water column trophic conditions and sediment carbon fluxes in a tropical water reservoir (Valle de Bravo, Mexico). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4680–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokoletsky, L.G. MERIS Retrieval of Water Quality Components in the Turbid Albemarle-Pamlico Sound Estuary, USA. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 684–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CONAGUA. Diagnóstico para el manejo integral de las subcuencas Tuxpan, El Bosque, Ixtapan del Oro, Valle de Bravo, Colorines-Chilesdo y Villa Victoria pertenecientes al Sistema Cutzamala. World Bank Group 2015, 104, 36–51. [Google Scholar]
- ProValle. El Valor del monitoreo. In Boletín del Patronato ProValle A.C; Municipio de Valle de Bravo: Estado de México, México, 2013.
- OECD. Eutrofication of Waters: Monitoring, Assessment and Control; Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development: Paris, France, 1982; p. 154. [Google Scholar]














| Product Name | Acquisition | Field Campaign |
|---|---|---|
| MER_FRS_1PPBCM20100427_171020_000000172089_00012_42651_0001 | 27 April 2010 | 25 April 2010 |
| MER_FRS_1PPBCM20101003_171308_000000142093_00284_44927_0001 | 3 October 2010 | 2 October 2010 |
| Method | Hyperparameter | GridSearch Values | SDD Result | Turb. Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR | - | - | - | - |
| RFR | n_estimators | 1, 10, 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000, 1500, 2000 | 1 | 10 |
| min_samples_leaf | 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, 10 | 1 | 1 | |
| min_samples_split | 2, 5, 10, 50, 100 | 10 | 2 | |
| bootstrap | True, False | True | True | |
| max_depth | 2, 4, 10, 20, 50, 100, None | 50 | 20 | |
| SVR | C | 0.0001, 0.001, 0.005, 0.0075, 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, 10, 15, 20, 50, 100, 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| gamma | 0.0001, 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 5, 10, 100, 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | |
| GRP | alpha | 0.0001, 0.001, 0.0045, 0.0055, 0.0080, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10 | 0.0045 | 1 |
| n_restarts_optimizer | 0, 1, 2, 4, 8, 10, 12, 16, 20, 32, 64 | 2 | 0 |
| SDD | ||||||||
| Model | LR | SVR | RFR | GPR | ||||
| Dataset | DS1 | DS2 | DS1 | DS2 | DS1 | DS2 | DS1 | DS2 |
| R2 | 0.78 | 0.65 | 0.75 | 0.57 | 0.66 | 0.59 | 0.81 | 0.67 |
| RMSE (m) | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.24 | 0.2 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.2 |
| Turbidity | ||||||||
| Model | LR | SVR | RFR | GPR | ||||
| Dataset | DS1 | DS2 | DS1 | DS2 | DS1 | DS2 | DS1 | DS2 |
| R2 | 0.84 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.28 | 0.78 | 0.76 | 0.86 | 0.78 |
| RMSE (NTU) | 1.12 | 1.64 | 1.58 | 2.55 | 1.24 | 1.36 | 0.95 | 1.35 |
| Model | SDD | Turbidity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Band Combination | R2 | RMSE | Band Combination | R2 | RMSE | |
| LR | b1, b3, b4, b5, b6, b7, b8, b9, b10 | 0.78 | 0.15 | b1, b2, b3, b4, b5, b6, b7, b8 | 0.84 | 1.12 |
| RFR | b1, b2, b4, b5, b6, b8, b10 | 0.66 | 0.20 | b2, b5, b8, b9, b10, b13 | 0.78 | 1.24 |
| SVR | b3, b4, b5, b6, b8 | 0.75 | 0.17 | All Bands | 0.67 | 1.58 |
| GPR | b4, b5, b6, b7, b8 | 0.81 | 0.15 | b2, b5, b12, b13, b14 | 0.86 | 0.95 |
| SDD | ||||||||
| Model | LR | SVR | RFR | GPR | ||||
| Dataset | DS1 | DS2 | DS1 | DS2 | DS1 | DS2 | DS1 | DS2 |
| R2 | 0.74 | 0.41 | 0.69 | 0.39 | 0.25 | 0.16 | 0.76 | 0.58 |
| RMSE (m) | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.16 | 0.21 |
| Turbidity | ||||||||
| Model | LR | SVR | RFR | GPR | ||||
| Dataset | DS1 | DS2 | DS1 | DS2 | DS1 | DS2 | DS1 | DS2 |
| R2 | 0.82 | 0.63 | 0.64 | 0.15 | 0.68 | 0.28 | 0.83 | 0.75 |
| RMSE (NTU) | 1.11 | 1.69 | 1.54 | 2.50 | 1.41 | 2.20 | 1.10 | 1.36 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arias-Rodriguez, L.F.; Duan, Z.; Sepúlveda, R.; Martinez-Martinez, S.I.; Disse, M. Monitoring Water Quality of Valle de Bravo Reservoir, Mexico, Using Entire Lifespan of MERIS Data and Machine Learning Approaches. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101586
Arias-Rodriguez LF, Duan Z, Sepúlveda R, Martinez-Martinez SI, Disse M. Monitoring Water Quality of Valle de Bravo Reservoir, Mexico, Using Entire Lifespan of MERIS Data and Machine Learning Approaches. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(10):1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101586
Chicago/Turabian StyleArias-Rodriguez, Leonardo F., Zheng Duan, Rodrigo Sepúlveda, Sergio I. Martinez-Martinez, and Markus Disse. 2020. "Monitoring Water Quality of Valle de Bravo Reservoir, Mexico, Using Entire Lifespan of MERIS Data and Machine Learning Approaches" Remote Sensing 12, no. 10: 1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101586
APA StyleArias-Rodriguez, L. F., Duan, Z., Sepúlveda, R., Martinez-Martinez, S. I., & Disse, M. (2020). Monitoring Water Quality of Valle de Bravo Reservoir, Mexico, Using Entire Lifespan of MERIS Data and Machine Learning Approaches. Remote Sensing, 12(10), 1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12101586