Validation of the SMOS Level 1C Brightness Temperature and Level 2 Soil Moisture Data over the West and Southwest of Iran
Abstract
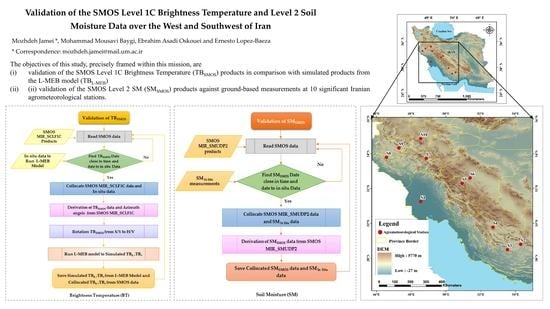
:1. Introduction
- (i)
- Validation of the SMOS Level 1C Brightness Temperature data products in comparison with the simulated brightness temperature data using of a radiative transfer model (L-MEB model) [52].
- (ii)
- Validation of the SMOS Level 2 Soil Moisture data products through a comparison with ground-based in situ soil moisture measurements at agrometeorological stations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Ground-Based In Situ Measurements
2.3. SMOS Satellite and Products
2.4. The SMOS Level 2 SM Algorithm
2.4.1. L-MEB Radiative Transfer Model Formulation
2.4.2. Bare Soil Radiometric Modeling
2.4.3. Low Vegetation Radiometric Modeling
2.5. Validation of SMOS Brightness Temperature and Soil Moisture Data
2.5.1. Validation of TBSMOS Data
2.5.2. Validation Algorithm for SMSMOS Data
2.6. Evaluation Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Validation Results for the SMOS Brightness Temperature
3.2. Validation Results for SMOS Soil Moisture
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Martinuzzi, J.-M.; Font, J.; Berger, M. Soil moisture retrieval from space: The Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) mission. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Moramarco, T.; Melone, F.; Wagner, W.; Hasenauer, S.; Hahn, S. Assimilation of surface-and root-zone ASCAT soil moisture products into rainfall–runoff modeling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 2542–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharssi, I.; Bovis, K.; Macpherson, B.; Jones, C. Operational assimilation of ASCAT surface soil wetness at the Met Office. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2729–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berthet, L.; Andréassian, V.; Perrin, C.; Javelle, P. How crucial is it to account for the antecedent moisture conditions in flood forecasting? Comparison of event-based and continuous approaches on 178 catchments. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Yaari, A.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Kerr, Y.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, N.; O’Neill, P.; Jackson, T.; De Lannoy, G.; Al Bitar, A.; Mialon, A.; Richaume, P. Evaluating soil moisture retrievals from ESA’s SMOS and NASA’s SMAP brightness temperature datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 193, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bircher, S.; Skou, N.; Kerr, Y.H.; Member, S. Validation of SMOS L1C and L2 Products and Important Parameters of the Retrieval Algorithm in the Skjern River Catchment, Western Denmark. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 2969–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brocca, L.; Ciabatta, L.; Massari, C.; Camici, S.; Tarpanelli, A.J.W. Soil moisture for hydrological applications: Open questions and new opportunities. Water 2017, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Pathe, C.; Doubkova, M.; Sabel, D.; Bartsch, A.; Hasenauer, S.; Blöschl, G.; Scipal, K.; Martínez-Fernández, J.; Löw, A. Temporal stability of soil moisture and radar backscatter observed by the Advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar (ASAR). Sensors 2008, 8, 1174–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djamai, N.; Magagi, R.; Goita, K.; Merlin, O.; Kerr, Y.; Walker, A. Disaggregation of SMOS soil moisture over the Canadian Prairies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dall’Amico, J.T. Multiscale Analysis of Soil Moisture Using Satellite and Aircraft Microwave Remote Sensing, in Situ Measurements and Numerical Modelling. Ph.D. Thesis, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, Munich, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dari, J.; Morbidelli, R.; Saltalippi, C.; Massari, C.; Brocca, L. Spatial-temporal variability of soil moisture: A strategy to optimize monitoring at the catchment scale with varying topography and land use. EGUGA 2018, 20, 7632. [Google Scholar]
- Santi, E.; Dabboor, M.; Pettinato, S.; Paloscia, S. Combining machine learning and compact polarimetry for estimating soil moisture from C-band SAR data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G.; Neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Crow, W.T.; Edelstein, W.N.; Entin, J.K.; Goodman, S.D.; Jackson, T.J.; Johnson, J. The soil moisture active passive (SMAP) mission. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yaari, A.; Wigneron, J.; Kerr, Y.; De Jeu, R.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, N.; Van Der Schalie, R.; Al Bitar, A.; Mialon, A.; Richaume, P.; Dolman, A. Testing regression equations to derive long-term global soil moisture datasets from passive microwave observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Delwart, S.; Cabot, F.O.; Boutin, J.; Escorihuela, M.-J.; Font, J.; Reul, N.; Gruhier, C. The SMOS mission: New tool for monitoring key elements ofthe global water cycle. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 666–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parinussa, R.M.; Holmes, T.R.; Wanders, N.; Dorigo, W.A.; de Jeu, R.A. A preliminary study toward consistent soil moisture from AMSR2. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 932–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, M.S.; Walker, J.P.; Rüdiger, C.; Parinussa, R.M.; Koike, T.; Kerr, Y.H. A comparison of SMOS and AMSR2 soil moisture using representative sites of the OzNet monitoring network. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 195, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Hahn, S.; Kidd, R.; Melzer, T.; Bartalis, Z.; Hasenauer, S.; Figa-Saldaña, J.; De Rosnay, P.; Jann, A.; Schneider, S. The ASCAT soil moisture product: A review of its specifications, validation results, and emerging applications. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 5–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bousbih, S.; Zribi, M.; Lili-Chabaane, Z.; Baghdadi, N.; El Hajj, M.; Gao, Q.; Mougenot, B. Potential of Sentinel-1 radar data for the assessment of soil and cereal cover parameters. Sensors 2017, 17, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Q.; Zribi, M.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Baghdadi, N.; Segui, P.Q. Irrigation mapping using Sentinel-1 time series at field scale. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Neill, P.E.; Chan, S.; Njoku, E.G.; Jackson, T.; Bindlish, R. Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document Level 2 & 3 Soil Moisture (Passive) Data Products; Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–82. [Google Scholar]
- Das, N.N.; Entekhabi, D.; Dunbar, R.S.; Chaubell, M.J.; Colliander, A.; Yueh, S.; Jagdhuber, T.; Chen, F.; Crow, W.; O’Neill, P.E. The SMAP and copernicus sentinel 1A/B microwave active-passive high resolution surface soil moisture product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Richaume, P.; Wigneron, J.P.; Ferrazzoli, P.; Mahmoodi, A.; Al Bitar, A.; Cabot, F.; Gruhier, C.; Juglea, S.E. The SMOS soil moisture retrieval algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1384–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yaari, A.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Ducharne, A.; Kerr, Y.; De Rosnay, P.; De Jeu, R.; Govind, A.; Al Bitar, A.; Albergel, C.; Munoz-Sabater, J. Global-scale evaluation of two satellite-based passive microwave soil moisture datasets (SMOS and AMSR-E) with respect to Land Data Assimilation System estimates. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 149, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Yaari, A.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Ducharne, A.; Kerr, Y.; Wagner, W.; De Lannoy, G.; Reichle, R.; Al Bitar, A.; Dorigo, W.; Richaume, P. Global-scale comparison of passive (SMOS) and active (ASCAT) satellite based microwave soil moisture retrievals with soil moisture simulations (MERRA-Land). Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Al-Yaari, A.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, N.; Parrens, M.; Molero, B.; Leroux, D.; Bircher, S.; Mahmoodi, A.; Mialon, A.; Richaume, P. Overview of SMOS performance in terms of global soil moisture monitoring after six years in operation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 40–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, D.J.; Kerr, Y.H.; Richaume, P.; Fieuzal, R. Spatial distribution and possible sources of SMOS errors at the global scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 133, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albergel, C.; De Rosnay, P.; Gruhier, C.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Hasenauer, S.; Isaksen, L.; Kerr, Y.; Wagner, W. Evaluation of remotely sensed and modelled soil moisture products using global ground-based in situ observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Bitar, A.; Mialon, A.; Kerr, Y.H.; Cabot, F.; Richaume, P.; Jacquette, E.; Quesney, A.; Mahmoodi, A.; Tarot, S.; Parrens, M.; et al. The global SMOS Level 3 daily soil moisture and brightness temperature maps. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2017, 9, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Champagne, C.; Rowlandson, T.; Berg, A.; Burns, T.; L’Heureux, J.; Tetlock, E.; Adams, J.R.; McNairn, H.; Toth, B.; Itenfisu, D. Satellite surface soil moisture from SMOS and Aquarius: Assessment for applications in agricultural landscapes. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 45, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djamai, N.; Magagi, R.; Goïta, K.; Hosseini, M.; Cosh, M.H.; Berg, A.; Toth, B. Evaluation of SMOS soil moisture products over the CanEx-SM10 area. J. Hydrol. 2015, 520, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Bitar, A.; Leroux, D.; Kerr, Y.H.; Merlin, O.; Richaume, P.; Sahoo, A.; Wood, E.F. Evaluation of SMOS soil moisture products over continental US using the SCAN/SNOTEL network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1572–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, T.J.; Bindlish, R.; Cosh, M.H.; Zhao, T.; Starks, P.J.; Bosch, D.D.; Seyfried, M.; Moran, M.S.; Goodrich, D.C.; Kerr, Y.H. validation of soil moisture and ocean salinity (SMOS) soil moisture over watershed networks in the US. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1530–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leroux, D.J.; Kerr, Y.H.; Al Bitar, A.; Bindlish, R.; Jackson, T.J.; Berthelot, B.; Portet, G. Comparison between SMOS, VUA, ASCAT, and ECMWF soil moisture products over four watersheds in US. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1562–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, W.; Brocca, L.; Naeimi, V.; Reichle, R.; Draper, C.; De Jeu, R.; Ryu, D.; Su, C.H.; Western, A.; Calvet, J.C.; et al. Clarifications on the “comparison between SMOS, VUA, ASCAT, and ECMWF Soil Moisture Products over Four Watersheds in U.S.”. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1901–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, V.A.; Hornbuckle, B.K.; Cosh, M.H. A five-year evaluation of SMOS Level 2 soil moisture in the corn belt of the United States. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 4664–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Xu, J.; Zeng, J.; Chen, K.-S.; Bai, X.; Lu, H.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, T. Soil moisture mapping from satellites: An intercomparison of SMAP, SMOS, FY3B, AMSR2, and ESA CCI over two dense network regions at different spatial scales. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dall’Amico, J.T.; Schlenz, F.; Loew, A.; Mauser, W. First Results of SMOS Soil Moisture Validation in the Upper Danube Catchment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hajj, M.; Baghdadi, N.; Zribi, M.; Rodríguez-Fernández, N.; Wigneron, J.P.; Al-Yaari, A.; Al Bitar, A.; Albergel, C.; Calvet, J.-C. Evaluation of SMOS, SMAP, ASCAT and sentinel-1 soil moisture products at sites in Southwestern France. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Zamora, A.; Sanchez, N.; Gumuzzio, A.; Piles, M.; Olmedo, E.; Martínez-Fernández, J. Validation of SMOS L2 and L3 soil moisture products over the Duero basin at different spatial scales. ISPRS Arch. 2015, 40, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montzka, C.; Bogena, H.R.; Weihermüller, L.; Jonard, F.; Bouzinac, C.; Kainulainen, J.; Balling, J.E.; Loew, A.; Amico, J.T.; Rouhe, E.; et al. brightness temperature and soil moisture validation at different scales during the SMOS validation campaign in the rur and erft catchments, Germany. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 1728–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierdicca, N.; Pulvirenti, L.; Fascetti, F.; Crapolicchio, R.; Talone, M. Analysis of two years of ASCAT-and SMOS-derived soil moisture estimates over Europe and North Africa. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 46, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, N.; Martínez-fernández, J.; Scaini, A.; Pérez-gutiérrez, C. Validation of the SMOS L2 Soil Moisture Data in the REMEDHUS Network (Spain). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1602–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigneron, J.-P.; Schwank, M.; Baeza, E.L.; Kerr, Y.; Novello, N.; Millan, C.; Moisy, C.; Richaume, P.; Mialon, A.; Al Bitar, A. First evaluation of the simultaneous SMOS and ELBARA-II observations in the Mediterranean region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louvet, S.; Pellarin, T.; al Bitar, A.; Cappelaere, B.; Galle, S.; Grippa, M.; Gruhier, C.; Kerr, Y.; Lebel, T.; Mialon, A.; et al. SMOS soil moisture product evaluation over West-Africa from local to regional scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.-H.; Ryu, D.; Young, R.I.; Western, A.W.; Wagner, W. Inter-comparison of microwave satellite soil moisture retrievals over the Murrumbidgee Basin, Southeast Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, K.; Qin, J.; Cui, Q.; Lu, H.; La, Z.; Han, M.; Tang, W. Evaluation of SMAP, SMOS, and AMSR2 soil moisture retrievals against observations from two networks on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 5780–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yang, K.; Qin, J.; Chen, Y.; Tang, W.; Lu, H.; Yang, Z.-L. The scale-dependence of SMOS soil moisture accuracy and its improvement through land data assimilation in the central Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anam, R.; Chishtie, F.; Ghuffar, S.; Qazi, W.; Shahid, I. Inter-comparison of SMOS and AMSR-E soil moisture products during flood years (2010–2011) over Pakistan. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 50, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, H.; Jiang, L.; Du, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, G.; Lu, Z.; Wang, J. Evaluation and analysis of AMSR-2, SMOS, and SMAP soil moisture products in the Genhe area of China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 8650–8666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; He, C.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, Y. Evaluation of the SMOS and SMAP soil moisture products under different vegetation types against two sparse in situ networks over arid mountainous watersheds, Northwest China. Sci. Chin. Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigneron, J.-P.; Kerr, Y.; Waldteufel, P.; Saleh, K.; Escorihuela, M.-J.; Richaume, P.; Ferrazzoli, P.; De Rosnay, P.; Gurney, R.; Calvet, J.-C. L-band Microwave Emission of the Biosphere (L-MEB) Model: Description and calibration against experimental data sets over crop fields. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 107, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamei, M. Validation of SMOS Satellite Data to Estimate Soil Moisture (A Case Study: West and South-West of Iran). Ph.D. Thesis, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dorigo, W.; Wagner, W.; Hohensinn, R.; Hahn, S.; Paulik, C.; Xaver, A.; Gruber, A.; Drusch, M.; Mecklenburg, S.; Oevelen, P.v. The international soil moisture network: A data hosting facility for global in situ soil moisture measurements. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1675–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerr, Y.; Waldteufel, P.; Richaume, P.; Wigneron, J.; Ferrazzoli, P.; Gurney, R. SMOS Level 2 Processor for Soil Moisture—Algorithm Theoretical Based Document (ATBD); Technical Report SO-TN-ESL-SM-GS-0001; CESBIO: Toulouse, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Yaari, A.M. Global-Scale Evaluation of a Hydrological Variable Measured from Space: SMOS Satellite Remote Sensing Soil Moisture Products. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris VI, Paris, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wigneron, J.-P.; Jackson, T.; O’Neill, P.; De Lannoy, G.; de Rosnay, P.; Walker, J.; Ferrazzoli, P.; Mironov, V.; Bircher, S.; Grant, J. Modelling the passive microwave signature from land surfaces: A review of recent results and application to the L-band SMOS & SMAP soil moisture retrieval algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 238–262. [Google Scholar]
- Wigneron, J.-P.; Chanzy, A.; De Rosnay, P.; Rudiger, C.; Calvet, J.-C. Estimating the effective soil temperature at L-band as a function of soil properties. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigneron, J.-P.; Chanzy, A.; Kerr, Y.H.; Lawrence, H.; Shi, J.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Mironov, V.; Mialon, A.; Demontoux, F.; De Rosnay, P. Evaluating an improved parameterization of the soil emission in L-MEB. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1177–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.P.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Van de Griend, A.A.; Guglielmetti, M.; Saleh, K.; Schwank, M. Calibration of L-MEB for soil moisture retrieval over forests. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS 2007, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 2248–2251. [Google Scholar]
- Montzka, C.; Grant, J.P.; Moradkhani, H.; Franssen, H.-J.H.; Weihermüller, L.; Drusch, M.; Vereecken, H. Estimation of radiative transfer parameters from L-band passive microwave brightness temperatures using advanced data assimilation. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing Active and Passive-Volume III: From Theory to Applications; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Yumpu. Available online: https://www.yumpu.com/en/document/read/36615690/rwapi-and-xy2hv-transformation-cesbio (accessed on 20 July 2020).
- Gebregiorgis, M.F.; Savage, M.J. Field, laboratory and estimated soil-water content limits. Water SA 2006, 32, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, K.E. Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 7183–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascaro, G.; Ko, A.; Vivoni, E.R. Closing the loop of satellite soil moisture estimation via scale invariance of hydrologic simulations. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Station Code | Station Name | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | Altitude (m.a.s.l) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Ahvaz | 31°18′0″ N | 48°36′0″ E | 12 |
| S2 | Darab | 28°48′0″ N | 54°17′60″ E | 1098 |
| S3 | Jahrom | 28°30′0″ N | 53°30′0″ E | 1082 |
| S4 | Zarqan | 29°48′0″ N | 52°42′0″ E | 1596 |
| S5 | Farokhshahr | 32°17′60″ N | 50°53′60″ E | 2085 |
| S6 | Najafabad | 32°36′0″ N | 51°23′60″ E | 1636 |
| S7 | Silakhur | 33°42′0″ N | 48°53′60″ E | 1497 |
| S8 | Sarableh | 33°47′60″ N | 46°36′0″ E | 1045 |
| S9 | Sararud | 34°17′60″ N | 47°17′60″ E | 1362 |
| S10 | Ekbatan | 34°53′60″ N | 48°36′0″ E | 1730 |
| Station Code | Station Name | Station Type | SM Type | Texture | Cover Type | Soil Bulk Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Ahvaz | Automatic | Volumetric | Silty-Clay | Desert | 1.3 |
| S2 | Darab | Automatic | Volumetric | Clay-Loam | Grassland | 1.6 |
| S3 | Jahrom | Automatic | Volumetric | Clay-Loam | Grassland | 1.4 |
| S4 | Zarqan | Traditional | Gravimetric | Clay-Loam | Grassland | 1.6 |
| S5 | Farokhshahr | Automatic | Volumetric | Silt | Grassland | 1.4 |
| S6 | Najafabad | Automatic | Volumetric | Sandy-Clay-Loam | Grassland | 1.5 |
| S7 | Silakhur | Automatic | Volumetric | Silt-Loam | Grassland | 1.2 |
| S8 | Sarableh | Traditional | Gravimetric | Sandy-Clay-Loam | Grassland | 1.6 |
| S9 | Sararud | Traditional | Gravimetric | Clay-Loam | Grassland | 1.3 |
| S10 | Ekbatan | Traditional | Gravimetric | Sandy- Clay | Grassland | 1.4 |
| Station Code | Station Name | RMSE (K) | cRMSE (K) | Bias (K) | R | Standard Deviation (K) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TBH SMOS | TBH L-MEB | ||||||
| S1 | Ahvaz | 9.61 | 9.35 | 1.42 | 0.81 | 16 | 12 |
| S2 | Darab | 9.17 | 9.1 | 0.10 | 0.76 | 15 | 11 |
| S3 | Jahrom | 10.39 | 10.33 | 1.16 | 0.79 | 18 | 15 |
| S4 | Zarqan | 11.95 | 11.73 | 3.83 | 0.79 | 17 | 10 |
| S5 | Farokhshahr | 12.32 | 11.45 | −2.16 | 0.61 | 15 | 11 |
| S6 | Najafabad | 9.95 | 9.76 | −2.02 | 0.81 | 18 | 15 |
| S7 | Silakhur | 10.85 | 10.76 | 1.46 | 0.69 | 16 | 11 |
| S8 | Sarableh | 11.31 | 11.08 | 2.40 | 0.80 | 16 | 19 |
| S9 | Sararud | 11.25 | 10.55 | 4.07 | 0.83 | 23 | 21 |
| S10 | Ekbatan | 12.88 | 11.94 | 6.08 | 0.70 | 17 | 12 |
| Station Code | Station Name | RMSE (K) | cRMSE (K) | Bias (K) | R | Standard Deviation (K) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TBV SMOS | TBV L-MEB | ||||||
| S1 | Ahvaz | 9.68 | 9.66 | 0.35 | 0.84 | 19 | 16 |
| S2 | Darab | 9.54 | 9.5 | 0.08 | 0.78 | 16 | 13 |
| S3 | Jahrom | 11.45 | 11.4 | 0.07 | 0.74 | 17 | 15 |
| S4 | Zarqan | 10.73 | 10.17 | 3.58 | 0.8 | 18 | 15 |
| S5 | Farokhshahr | 12.66 | 11.16 | 5.45 | 0.72 | 20 | 14 |
| S6 | Najafabad | 9.71 | 9.73 | -2.68 | 0.82 | 18 | 16 |
| S7 | Silakhur | 11.36 | 10.99 | -2.98 | 0.65 | 16 | 9 |
| S8 | Sarableh | 12.63 | 12.38 | 2.65 | 0.83 | 21 | 24 |
| S9 | Sararud | 11.9 | 10.36 | 6.11 | 0.8 | 20 | 23 |
| S10 | Ekbatan | 12.91 | 11.76 | 7.45 | 0.75 | 20 | 14 |
| Station Code | Station Name | RMSE (m3 m−3) | cRMSE (m3 m−3) | BIAS (m3 m−3) | R | Standard Deviation (m3 m−3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SM SMOS | SM in Situ | ||||||
| S1 | Ahvaz | 0.046 | 0.039 | −0.026 | 0.83 | 0.050 | 0.026 |
| S2 | Darab | 0.048 | 0.046 | 0.016 | 0.79 | 0.047 | 0.019 |
| S3 | Jahrom | 0.050 | 0.048 | 0.017 | 0.77 | 0.048 | 0.028 |
| S4 | Zarqan | 0.059 | 0.050 | −0.031 | 0.80 | 0.059 | 0.070 |
| S5 | Farokhshahr | 0.066 | 0.060 | −0.032 | 0.67 | 0.058 | 0.040 |
| S6 | Najafabad | 0.049 | 0.040 | 0.029 | 0.75 | 0.039 | 0.024 |
| S7 | Silakhur | 0.053 | 0.044 | 0.040 | 0.65 | 0.042 | 0.016 |
| S8 | Sarableh | 0.079 | 0.046 | −0.095 | 0.82 | 0.069 | 0.088 |
| S9 | Sararud | 0.070 | 0.059 | −0.072 | 0.84 | 0.068 | 0.098 |
| S10 | Ekbatan | 0.066 | 0.056 | −0.061 | 0.77 | 0.055 | 0.027 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jamei, M.; Mousavi Baygi, M.; Oskouei, E.A.; Lopez-Baeza, E. Validation of the SMOS Level 1C Brightness Temperature and Level 2 Soil Moisture Data over the West and Southwest of Iran. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12172819
Jamei M, Mousavi Baygi M, Oskouei EA, Lopez-Baeza E. Validation of the SMOS Level 1C Brightness Temperature and Level 2 Soil Moisture Data over the West and Southwest of Iran. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(17):2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12172819
Chicago/Turabian StyleJamei, Mozhdeh, Mohammad Mousavi Baygi, Ebrahim Asadi Oskouei, and Ernesto Lopez-Baeza. 2020. "Validation of the SMOS Level 1C Brightness Temperature and Level 2 Soil Moisture Data over the West and Southwest of Iran" Remote Sensing 12, no. 17: 2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12172819
APA StyleJamei, M., Mousavi Baygi, M., Oskouei, E. A., & Lopez-Baeza, E. (2020). Validation of the SMOS Level 1C Brightness Temperature and Level 2 Soil Moisture Data over the West and Southwest of Iran. Remote Sensing, 12(17), 2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12172819