Photometric Normalization of Chang’e-4 Visible and Near-Infrared Imaging Spectrometer Datasets: A Combined Study of In-Situ and Laboratory Spectral Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. VNIS Instrument
2.2. Photometric Models
2.2.1. Lommel–Seeliger Model
2.2.2. Hapke Radiative Transfer Model
2.3. CE-4 VNIS Datasets
2.4. Laboratorial Spectral Measurements by a VNIS Replica
3. Results
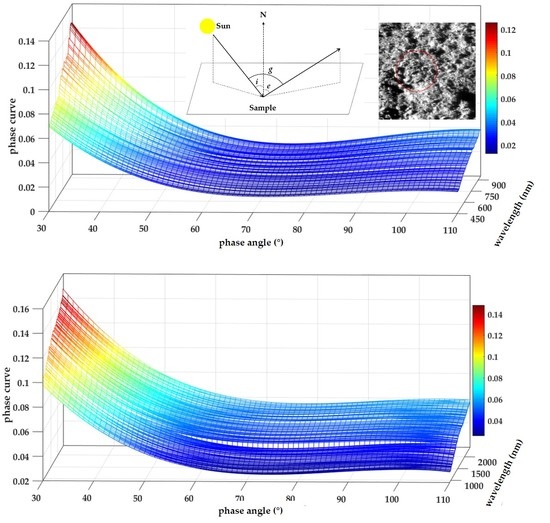
3.1. Phase Functions of the LS Model and Initial Photometric Normalization of CE-4 Datasets
3.2. Laboratory Spectral Measurements of Lunar Regolith Analog
4. Discussion
4.1. Evaluation of the Shadow Effects
4.2. Improvement and Validation of Photometric Models
4.3. Comparison of the Spectral and Mineralogical Properties of the CE-4 and CE-3 Lunar Soils
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- From in-situ and laboratory measurements, the shadows caused by surface roughness have significant impacts on the reflectance spectra acquired during lunar in-situ VNIS observations and proper corrections for shadows were introduced.
- (2)
- We produced empirical wavelength-dependent phase functions of Lommel–Seeliger model from CE-4 VNIS datasets. Values of phase functions exhibit declining trends with the increase in phase angles and an opposition effect and phase reddening effect were observed. This is the first time that empirical phase functions have been derived for wavelengths from 450 to 2395 nm using in-situ visible and near-infrared spectral datasets.
- (3)
- Photometric corrections of CE-4 and laboratory VNIS spectra were conducted using the Lommel–Seeliger and Hapke radiative transfer models to determine the most suitable phase functions. Then, the validations of different phase functions conducted by comparing photometric-normalized spectra of the same target suggest that their discrepancies at 1500 nm are 3.7% using the Lommel–Seeliger model and 7.4% using the Hapke radiative transfer model (with parameters b = −0.17, c = 0.70).
- (4)
- Generally, photometrically normalized spectra exhibit smaller spectral slopes, lower FeO contents and thus a larger OMAT than that of spectra without correction. In addition, the band centers of the 1 and 2 μm absorption of spectra after photometric normalization exhibit a more concentrated distribution, indicating the compositional homogeneity of soils at the CE-4 landing site after Yutu-2 traveling ~448 m.
- (5)
- We prefer the phase functions derived from the LS model to apply to the photometric normalization of VNIS datasets and these empirical phase functions will contribute to the detection of, and accurate interpretation of, relative quantitative mineralogy along the traverse route of the Yutu-2 rover in the Von Kármán crater.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, Y.; Zou, Y.; Ping, J.; Xue, C.; Yan, J.; Ning, Y. The scientific objectives and payloads of Chang’E-4 mission. Planet. Space Sci. 2018, 162, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, D.; Liu, B.; Ren, X.; Liu, J.; He, Z.; Zuo, W.; Zeng, X.; Xu, R.; Tan, X. Chang’E-4 initial spectroscopic identification of lunar far-side mantle-derived materials. Nature 2019, 569, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, S.; Di, K.; Yue, Z.; Liu, Z.; He, Z.; Xu, R.; Lin, H.; Liu, B.; Peng, M.; Wan, W. Lunar deep materials observed by Chang’e-4 rover. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2019, 528, 115829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ma, P.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, M.H.; Jiang, T.; Lucey, P.G.; Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Xu, R. Mineral Abundances Inferred From In Situ Reflectance Measurements of Chang’E-4 Landing Site in South Pole-Aitken Basin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 9439–9447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; He, Z.; Yang, W.; Lin, Y.; Xu, R.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, M.-H.; Chang, R.; Zhang, J.; Li, C. Olivine-norite rock detected by the lunar rover Yutu-2 likely crystallized from the SPA impact melt pool. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 7, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Ling, Z.; Qiao, L.; He, Z.; Xu, R.; Sun, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Fu, X.; Liu, C. Mineralogy of Chang’e-4 landing site: Preliminary results of visible and near-infrared imaging spectrometer. Inf. Sci. 2020, 63, 1–140903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, H.; Robinson, M.; Hapke, B.; Denevi, B.; Boyd, A. Resolved Hapke parameter maps of the Moon. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2014, 119, 1775–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkuratov, Y.G.; Grynko, Y.S. Light scattering by media composed of semitransparent particles of different shapes in ray optics approximation: Consequences for spectroscopy, photometry, and polarimetry of planetary regoliths. Icarus 2005, 173, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapke, B. Bidirectional reflectance spectroscopy: 1. Theory. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1981, 86, 3039–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, S.; Sunshine, J.; Staid, M.; Boardman, J.; Pieters, C.; Guasqui, P.; Malaret, E.; McLaughlin, S.; Yokota, Y.; Li, J.-Y. A visible and near-infrared photometric correction for Moon Mineralogy Mapper (M3). Icarus 2013, 222, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapke, B. Theory of Reflectance and Emittance Spectroscopy; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, J.K.; Buratti, B.J.; Hill, K. Multispectral photometry of the Moon and absolute calibration of the Clementine UV/Vis camera. Icarus 1999, 141, 205–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnaert, M. The reciprocity principle in lunar photometry. Astrophys. J. 1941, 93, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, M.; Buratti, B.; Nettles, J.; Staid, M.; Sunshine, J.; Pieters, C.; Besse, S.; Boardman, J. A photometric function for analysis of lunar images in the visual and infrared based on Moon Mineralogy Mapper observations. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2011, 116, E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkuratov, Y.; Starukhina, L.; Hoffmann, H.; Arnold, G. A model of spectral albedo of particulate surfaces: Implications for optical properties of the Moon. Icarus 1999, 137, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbarin, M.B. Planetary Photometry: The Lommel-Seeliger Law. J. R. Astron. Soc. Can. 2005, 99, 92. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, H.; Boyd, A.; Robinson, M.; Denevi, B.; Hapke, B.; McEwen, A.; Speyerer, E. Photometric normalization of LROC WAC global color mosaic. epsc 2011, 2011, 636. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Qin, Q.; Zhang, N.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Jiang, H. Research on photometric calibration and reflectance calculation of CE-1 IIS data. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2011, 31, 1985–1990. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Besse, S.; Li, J.-Y.; Combe, J.-P.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wang, C. Photometric correction and in-flight calibration of Chang’E-1 Interference Imaging Spectrometer (IIM) data. Icarus 2013, 222, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ling, Z.; Zhang, W.; Ren, X.; Li, C.; Liu, J. Photometric modeling of the Moon using Lommel-Seeliger function and Chang’E-1 IIM data. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 4588–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Xu, R.; Yang, W.; Lin, Y.; Wei, Y.; Hu, S.; He, Z.; Qiao, L.; Wan, W. In situ photometric experiment of lunar regolith with visible and near-infrared imaging spectrometer onboard the Yutu-2 lunar rover. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2020, 125, e2019JE006076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapke, B. Bidirectional reflectance spectroscopy: 4. The extinction coefficient and the opposition effect. Icarus 1986, 67, 264–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hapke, B. Space weathering from Mercury to the asteroid belt. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2001, 106, 10039–10073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfenstein, P.; Veverka, J.; Hillier, J. The lunar opposition effect: A test of alternative models. Icarus 1997, 128, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfenstein, P.; Veverka, J.; Thomas, P.C. Uranus satellites: Hapke parameters from Voyager disk-integrated photometry. Icarus 1988, 74, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingue, D.; Hapke, B. Fitting theoretical photometric functions to asteroid phase curves. Icarus 1989, 78, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinness, E.A.; Arvidson, R.E.; Clark, I.H.; Shepard, M.K. Optical scattering properties of terrestrial varnished basalts compared with rocks and soils at the Viking Lander sites. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 1997, 102, 28687–28703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warell, J. Properties of the Hermean regolith: IV. Photometric parameters of Mercury and the Moon contrasted with Hapke modelling. Icarus 2004, 167, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-Y.; A’Hearn, M.F.; Belton, M.J.; Crockett, C.J.; Farnham, T.L.; Lisse, C.M.; McFadden, L.A.; Meech, K.J.; Sunshine, J.M.; Thomas, P.C. Deep Impact photometry of comet 9P/Tempel 1. Icarus 2007, 187, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, J.; Schmidt, F.; Ceamanos, X.; Pinet, P.; Douté, S.; Daydou, Y. Surface reflectance of Mars observed by CRISM/MRO: 2. Estimation of surface photometric properties in Gusev Crater and Meridiani Planum. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2013, 118, 534–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lin, H.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wei, Y.; Hu, S.; Yang, W.; Xu, R.; He, Z.; Zou, Y. The Effects of Viewing Geometry on the Spectral Analysis of Lunar Regolith as Inferred by in situ Spectrophotometric Measurements of Chang’E-4. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreslavsky, M.; Shkuratov, Y.G. Photometric anomalies of the lunar surface: Results from Clementine data. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Jolliff, B.L.; Wang, A.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Sun, L.; Chen, J.; Xiao, L. Correlated compositional and mineralogical investigations at the Chang′ e-3 landing site. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Jin, W.; Lucey, P.G.; Zhu, M.H.; Kaydash, V.G.; Shkuratov, Y.G.; Di, K.; Wan, W. In situ optical measurements of Chang’E-3 landing site in Mare Imbrium: 1. Mineral abundances inferred from spectral reflectance. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 6945–6950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, B.; Hicks, M.; Nettles, J.; Staid, M.; Pieters, C.; Sunshine, J.; Boardman, J.; Stone, T. A wavelength-dependent visible and infrared spectrophotometric function for the Moon based on ROLO data. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2011, 116, E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, Y.; Matsunaga, T.; Ohtake, M.; Haruyama, J.; Nakamura, R.; Yamamoto, S.; Ogawa, Y.; Morota, T.; Honda, C.; Saiki, K. Lunar photometric properties at wavelengths 0.5–1.6 μm acquired by SELENE Spectral Profiler and their dependency on local albedo and latitudinal zones. Icarus 2011, 215, 639–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shkuratov, Y.G.; Lucey, P.G.; Kaydash, V.G.; Zhu, M.H.; Xue, B.; Di, K. In situ optical measurements of Chang’E-3 landing site in Mare Imbrium: 2. Photometric properties of the regolith. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 8312–8319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, S.; Hu, S.; Yang, W.; Wan, W.; Xu, R. Photometric properties of lunar regolith revealed by the Yutu-2 rover. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 638, A35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.-P.; Wang, B.-Y.; Lü, G.; Li, C.-L.; Yuan, L.-Y.; Xu, R.; Liu, B.; Chen, K.; Wang, J.-Y. Operating principles and detection characteristics of the Visible and Near-Infrared Imaging Spectrometer in the Chang’e-3. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 14, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Xu, R.; Lv, G.; Yuan, L.; He, Z.; Wang, J. The scientific information model of Chang’e-4 visible and near-IR imaging spectrometer (VNIS) and in-flight verification. Sensors 2019, 19, 2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Yu, G.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W. Design of Chang’E-4 lunar farside soft-landing mission. J. Deep Space Explor. 2017, 4, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Li, C.; Xu, R.; Lv, G.; Yuan, L.; Wang, J. Spectrometers based on acousto-optic tunable filters for in-situ lunar surface measurement. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2019, 13, 027502. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, L. Radiative transfer modeling for quantifying lunar surface minerals, particle size, and submicroscopic metallic Fe. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2011, 116, E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henyey, L.G.; Greenstein, J.L. Diffuse radiation in the galaxy. Astrophys. J. 1941, 93, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, C.-L.; Zhang, G.-L.; Xu, R.; Liu, J.-J.; Ren, X.; Tan, X.; Zhang, X.-X.; Zuo, W.; Wen, W.-B. Data processing and preliminary results of the Chang’e-3 VIS/NIR Imaging Spectrometer in-situ analysis. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 14, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemelin, M.; Lucey, P.G.; Miljković, K.; Gaddis, L.R.; Hare, T.; Ohtake, M. The compositions of the lunar crust and upper mantle: Spectral analysis of the inner rings of lunar impact basins. Planet. Space Sci. 2019, 165, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Ling, Z.; Fu, X.; Li, B. Geological characterization of the Chang’e-4 landing area on the lunar farside. Icarus 2019, 333, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Qiao, L.; Liu, C.; Cao, H.; Bi, X.; Lu, X.; Zhang, J.; Fu, X.; Li, B.; Liu, J. Composition, mineralogy and chronology of mare basalts and non-mare materials in Von Kármán crater: Landing site of the Chang’E-4 mission. Planet. Space Sci. 2019, 179, 104741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, S.E.; Grynko, Y.; Pommerol, A.; Keller, H.; Thomas, N.; Roush, T. Laboratory observations and simulations of phase reddening. Icarus 2014, 239, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustard, J.F.; Pieters, C.M. Photometric phase functions of common geologic minerals and applications to quantitative analysis of mineral mixture reflectance spectra. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1989, 94, 13619–13634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, P.G. Model near-infrared optical constants of olivine and pyroxene as a function of iron content. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 1998, 103, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, C.M.; Taylor, L.A.; Noble, S.K.; Keller, L.P.; Hapke, B.; Morris, R.V.; Allen, C.C.; McKAY, D.S.; Wentworth, S. Space weathering on airless bodies: Resolving a mystery with lunar samples. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2000, 35, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, P.G.; Blewett, D.T.; Taylor, G.J.; Hawke, B.R. Imaging of lunar surface maturity. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2000, 105, 20377–20386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Blewett, D.T.; Cloutis, E.A.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, J. Submicroscopic metallic iron in lunar soils estimated from the in situ spectra of the Chang’E-3 mission. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 3485–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, S.; Yue, Z.; Kaichang, D.; Cai, Z.; Liu, Z.; Niu, S. Absolute model age of lunar Finsen crater and geologic implications. Icarus 2020, 354, 114046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, M.; Hiesinger, H.; van der Bogert, C.; Orgel, C.; Pasckert, J.; Head, J. Geologic History of the Northern Portion of the South Pole-Aitken Basin on the Moon. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2018, 123, 2585–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Zhu, P.; Fang, G.; Xiao, Z.; Zou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, N.; Yuan, Y.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, X. A young multilayered terrane of the northern Mare Imbrium revealed by Chang’E-3 mission. Science 2015, 347, 1226–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, S.; Yue, Z.; Di, K.; Wan, W.; Liu, Z.; Liu, B.; Peng, M.; Wang, Y.; He, Z.; Xu, R. In situ spectral measurements of space weathering by Chang’e-4 rover. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2020, 535, 116117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.-H.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, J.; Ling, Z.-C.; Li, B. The subsurface structure and stratigraphy of the Chang’E-4 landing site: Orbital evidence from small craters on the Von Kármán crater floor. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 20, 008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Huang, J.; Qiao, L.; Xiao, Z.; Huang, Q.; Wang, J.; He, Q.; Xiao, L. Geologic characteristics of the Chang’E-3 exploration region. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2014, 57, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloutis, E.A.; Gaffey, M.J. Pyroxene spectroscopy revisited: Spectral-compositional correlations and relationship to geothermometry. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 1991, 96, 22809–22826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty Iii, D.; Pieters, C. The character of south pole-Aitken basin: Patterns of surface and subsurface composition. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2018, 123, 729–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Observation | i (°) | e (°) | g (°) | Observation | i (°) | e (°) | g (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0068 | 76.543 | 48.273 | 79.376 | 0079 | 57.272 | 44.414 | 91.082 |
| 0069 | 75.946 | 48.273 | 78.433 | 0080 | 57.873 | 44.414 | 92.113 |
| 0070 | 71.319 | 48.273 | 71.432 | 0081 | 58.289 | 44.414 | 92.814 |
| 0071 | 70.102 | 48.273 | 69.544 | 0082 | 58.741 | 44.414 | 93.568 |
| 0072 | 69.576 | 48.273 | 68.722 | 0083 | 59.239 | 44.414 | 94.386 |
| 0073 | 68.867 | 48.273 | 67.607 | 0084 | 63.498 | 44.414 | 100.990 |
| 0074 | 68.299 | 48.273 | 66.708 | 0085 | 64.127 | 44.414 | 101.916 |
| 0075 | 63.709 | 48.273 | 59.185 | 0086 | 64.640 | 44.414 | 102.664 |
| 0076 | 62.823 | 48.273 | 57.672 | 0087 | 65.227 | 44.414 | 103.512 |
| 0077 | 62.015 | 48.273 | 56.269 | 0088 | 65.812 | 44.414 | 104.349 |
| 0078 | 61.149 | 48.273 | 54.737 | 0089 | 66.370 | 44.414 | 105.139 |
| 0090 | 77.113 | 44.414 | 111.614 |
| Mineral (wt.%) | Ol | Opx | Cpx | Pl |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Finsen ejecta | 7 ± 3 | 25 ± 4 | 13 ± 4 | 55 ± 4 |
| Lunar regolith analog | 7 | 25 | 13 | 55 |
| Observation | Azimuth Angle (°) | i (°) | e (°) | g (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement 1 | 150 | 60 | 45 | 103 |
| Measurement 2 | 140 | 60 | 45 | 97 |
| Measurement 3 | 130 | 60 | 45 | 76 |
| Measurement 4 | 120 | 60 | 45 | 63 |
| Measurement 5 | 110 | 60 | 45 | 56 |
| Measurement 6 | 100 | 60 | 45 | 49 |
| Measurement 7 | 90 | 60 | 45 | 42 |
| Measurement 8 | 80 | 60 | 45 | 35 |
| Measurement 9 | 70 | 60 | 45 | 28 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, X.; Ling, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Cao, H.; Liu, C.; Qiao, L.; Fu, X.; He, Z.; Xu, R.; et al. Photometric Normalization of Chang’e-4 Visible and Near-Infrared Imaging Spectrometer Datasets: A Combined Study of In-Situ and Laboratory Spectral Measurements. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193211
Qi X, Ling Z, Zhang J, Chen J, Cao H, Liu C, Qiao L, Fu X, He Z, Xu R, et al. Photometric Normalization of Chang’e-4 Visible and Near-Infrared Imaging Spectrometer Datasets: A Combined Study of In-Situ and Laboratory Spectral Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(19):3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193211
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Xiaobin, Zongcheng Ling, Jiang Zhang, Jian Chen, Haijun Cao, Changqing Liu, Le Qiao, Xiaohui Fu, Zhiping He, Rui Xu, and et al. 2020. "Photometric Normalization of Chang’e-4 Visible and Near-Infrared Imaging Spectrometer Datasets: A Combined Study of In-Situ and Laboratory Spectral Measurements" Remote Sensing 12, no. 19: 3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193211
APA StyleQi, X., Ling, Z., Zhang, J., Chen, J., Cao, H., Liu, C., Qiao, L., Fu, X., He, Z., Xu, R., Liu, J., & Zou, Y. (2020). Photometric Normalization of Chang’e-4 Visible and Near-Infrared Imaging Spectrometer Datasets: A Combined Study of In-Situ and Laboratory Spectral Measurements. Remote Sensing, 12(19), 3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193211