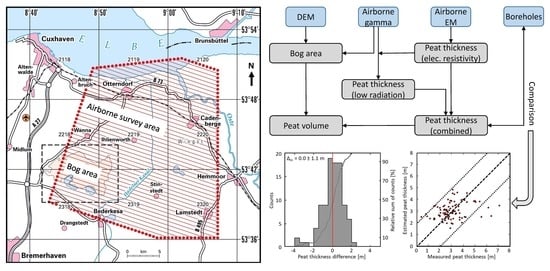
Airborne Electromagnetic and Radiometric Peat Thickness Mapping of a Bog in Northwest Germany (Ahlen-Falkenberger Moor)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area: Ahlen-Falkenberger Moor
2.2. Airborne Geophysical Data
2.2.1. Helicopter-Borne Survey
2.2.2. Data Processing
Position Data Processing
HEM Data Processing
HRD Data Processing
2.2.3. Peat Volume Estimation
HEM Analysis
HRD Analysis
Combined HEM and HRD Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Lateral Extent of the Bog
3.1.1. HEM Results
3.1.2. HRD Results
3.2. Vertical Extent of the Peat Within the Area of the Bog
3.2.1. HEM Results
3.2.2. HRD Results
3.3. Combined HEM and HRD Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Höper, H. Freisetzung von Treibhausgasen aus deutschen Mooren (Emission of greenhouse gases from German peatlands). TELMA 2007, 37, 85–116. [Google Scholar]
- Gatis, N.; Luscombe, D.J.; Carless, D.; Parry, L.E.; Fyfe, R.M.; Harrod, T.R.; Brazier, R.E.; Anderson, K. Mapping upland peat depth using airborne radiometric and lidar survey data. Geoderma 2019, 335, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, L.D.; Reeve, A. Investigating peatland stratigraphy and hydrogeology using integrated electrical geophysics. Geophysics 2002, 67, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comas, X.; Slater, L. Low-frequency electrical properties of peat. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, W12414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, L.E.; West, L.J.; Holden, J.; Chapman, P.J. Evaluating approaches for estimating peat depth. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2014, 119, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comas, X.; Terry, N.; Slater, L.; Warren, M.; Kolka, R.; Kristiyono, A.; Sudiana, N.; Nurjaman, D.; Darusman, T. Imaging tropical peatlands in Indonesia using ground-penetrating radar (GPR) and electrical resistivity imaging (ERI): Implications for carbon stock estimates and peat soil characterization. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 2995–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Airo, M.-L.; Hyvönen, E.; Lerssi, J.; Leväniemi, H.; Ruotsalainen, A. Tips and Tools for the Application of GTK’s Airborne Geophysical Data; Report of Investigation 215; Geological Survey of Finland: Espoo, Finland, 2014; pp. 1–35. Available online: http://tupa.gtk.fi/julkaisu/tutkimusraportti/tr_215.pdf (accessed on 4 October 2019).
- Minasny, B.; Berglund, Ö.; Connolly, J.; Hedley, C.; de Vriese, F.; Gimona, A.; Kempen, B.; Kidd, D.; Lilja, H.; Malone, B.; et al. Digital mapping of peatlands—A critical review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 196, 102178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamish, D. Peat mapping associations of airborne radiometric survey data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keaney, A.; McKinley, J.; Graham, C.; Robinson, M.; Ruffell, A. Spatial statistics to estimate peat thickness using airborne radiometric data. Spat. Stat. 2013, 5, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puranen, R.; Saavuori, H.; Sahala, L.; Suppala, I.; Makila, M.; Lerssi, J. Airborne electromagnetic mapping of surficial deposits in Finland. First Break 1999, 17, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamish, D.; Farr, G. Airborne geophysics: A novel approach to assist hydrogeological investigations at groundwater dependent wetlands. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrog. 2013, 46, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silvestri, S.; Christensen, C.W.; Lysdahl, A.O.K.; Anschütz, H.; Pfaffhuber, A.A.; Viezzoli, A. Peatland volume mapping over restive substrates with airborne electromagnetic technology. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 6459–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silvestri, S.; Knight, R.; Viezzoli, A.; Richardson, C.J.; Anshari, G.Z.; Dewar, N.; Flanagan, N.; Comas, X. Quantification of peat thickness and stored carbon at the landscape scale in tropical peatlands: A comparison of airborne geophysics and an empirical topographic method. J. Geophys. Res.-Earth 2019, 124, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneekloth, H. Das Ahlen-Falkenberger Moor-Eine moorgeologische Studie mit Beiträgen zur Altersfrage des Schwarz-/Weißtorfkontaktes und zur Stratigraphie des Küstenholozäns. Geol. Jb. (Hann. Ger.) 1970, 89, 63–96. [Google Scholar]
- Schneekloth, H. Die Moore Niedersachsen. 7. Teil: Bereich der Blätter Neumünster, Helgoland, Emden, und Lingen der Geologischen Karte der Bundesrepublik Deutschland (1:200.000); Niedersächsisches Institut für Landeskunde und Landesentwicklung an der Universität Göttingen und Schriften der Wirtschaftswissenschaftlichen Gesellschaft zum Studium Niedersachsens E.V.: Göttingen, Germany, 1981; Volume 96. [Google Scholar]
- Ahrendt, R. Die Entdeckung des Ahlenmoores. Aneignung einer Landschaft in der ersten Hälfte des 20. Jahrhunderts; Beiträge zur Geschichte und Kultur des Elbe-Weser-Raumes, Band 6; Verlag des Landschaftsverbandes der ehemaligen Herzogtümer Bremen und Verden: Stade, Germany, 2012; pp. 1–160. Available online: https://www.landschaftsverband-stade.de/ahlenmoorrolandahrendt1.html (accessed on 4 October 2019).
- Frank, S.; Tiemeyer, B.; Gelbrecht, J.; Freibauer, A. High soil solution carbon and nitrogen concentrations in a drained Atlantic bog are reduced to natural levels by 10 years of rewetting. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 2309–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- BKG. Digitales Geländemodel (DGM25); Bundesamt für Kartographie und Geodäsie: Frankfurt, Germany, 2012; Available online: https://www.geodatenzentrum.de (accessed on 1 February 2012).
- LBEG. Borehole Database of Lower Saxony (BDN); State Authority for Mining, Energy and Geology (LBEG): Hannover, Germany, 2019; Available online: http://nibis.lbeg.de/cardomap3/ (accessed on 4 February 2019).
- Caspers, G. Die Unterscheidung der Torfarten in der bodenkundlichen und geologischen Kartierung (Differentiating different types of peat in pedological and geological mapping). TELMA 2010, 40, 33–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BKG. Rasterdaten Topographische Karte 1:50000 (DTK50-V); Bundesamt für Kartographie und Geodäsie: Frankfurt, Germany, 2014; Available online: https://www.geodatenzentrum.de (accessed on 4 February 2014).
- Siemon, B.; Wiederhold, W.; Steuer, A.; Miensopust, M.P.; Voß, W.; Ibs-von Seht, M.; Meyer, U. Helicopter-borne electromagnetic surveys in Northern Germany. In Proceedings of the 23rd Salt Water Intrusion Meeting—SWIM 2014, Husum, Germany, 15–22 June 2014; pp. 375–378. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/25644189/Programme_and_Proceedings_SWIM_2014_23_rd_Salt_Water_Intrusion_Meeting (accessed on 4 October 2019).
- BGR. Helicopter-Borne Electromagnetics (HEM) Area 109 Hadelner Marsch; Technical Report, Resistivity Maps and Vertical Resistivity Sections; Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR): Hannover, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BGR. Raw Data on Helicopter-Borne Electromagnetics (HEM) Area 109 Hadelner Marsch; Raw and Processed Helicopter-Borne Electromagnetic Data; Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR): Hannover, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BGR. Helicopter-Borne Radiometrics (HRD) Area 109 Hadelner Marsch; Technical Report and Radiometric Maps; Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR): Hannover, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BGR. Raw Data on Helicopter-Borne Radiometrics (HRD) Area 109 Hadelner Marsch; Raw and Processed Radiometric Data; Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR): Hannover, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemon, B.; Voß, W.; Kerner, T.; Pielawa, J. Technischer Bericht Hubschraubergeophysik Hadelner Marsch Mai/Juni 2004 (Revision 2017); Archives No. 0134290; Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR): Hannover, Germany, 2017; pp. 1–144. Available online: https://www.bgr.bund.de/DE/Themen/GG_Geophysik/Aerogeophysik/Downloads/Technischer-Bericht-109-Hadelner-Marsch-Web.html?nn=1555598 (accessed on 4 October 2019).
- Siemon, B.; Kerner, T.; Krause, Y.; Noell, U. Airborne and ground geophysical investigation of the environment of abandoned salt mines along the Staßfurt-Egeln anticline, Germany. First Break 2012, 30, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemon, B.; Ibs-von Seht, M.; Pielawa, J. Ergänzung zum Technischer Bericht-Neuauswertung der Befliegung Hadelner Marsch 2004; Archives No. 0135485; Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR): Hannover, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–38. Available online: https://www.bgr.bund.de/DE/Themen/GG_Geophysik/Aerogeophysik/Downloads/Moorstudie.html?nn=1555598 (accessed on 4 October 2019).
- Oasis montaj™ Mapping and Processing System Version 9.5. Geosoft Inc. Available online: https://www.geosoft.com/products/oasis-montaj (accessed on 4 October 2019).
- Briggs, I.C. Machine contouring using minimum curvature. Geophysics 1974, 39, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, C.J. A FORTRAN IV program for interpolating irregularly spaced data using the difference equations for minimum curvature. Comput. Geosci. 1976, 1, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deus, N.; Elbracht, J.; Siemon, B. 3D-modeling of the salt-/fresh water interface in coastal aquifers of Lower Saxony (Germany) based on airborne electromagnetic measurements (HEM). In Proceedings of the AquaConSoil, 13th International UFZ-Deltares Conference on Sustainable Use and Management of Soil, Sediment and Water Resources, Copenhagen, Denmark, 9–12 June 2015; pp. 5–10. Available online: https://www.aquaconsoil.org/ACS_History/assets/aquaconsoil_proceedings_2015.pdf (accessed on 4 October 2019).
- Siemon, B. Levelling of frequency-domain helicopter-borne electromagnetic data. J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 67, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemon, B.; Steuer, A.; Ullmann, A.; Vasterling, M.; Voß, W. Application of frequency-domain helicopter-borne electromagnetics for groundwater exploration in urban areas. Phys. Chem. Earth 2011, 36, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.H.; Hohmann, G.W. Electromagnetic theory for geophysical applications. In Electromagnetic Methods in Applied Geophysics Vol. 1, Theory; Nabighian, M.N., Ed.; Society of Exploration Geophysics: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1988; pp. 130–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemon, B. Improved and new resistivity-depth profiles for helicopter electromagnetic data. J. Appl. Geophys. 2001, 46, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengpiel, K.-P. Approximate inversion of airborne EM data from a multi-layered ground. Geophys. Prospect. 1988, 36, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengpiel, K.-P.; Siemon, B. Advanced inversion methods for airborne electromagnetic exploration. Geophysics 2000, 65, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemon, B.; Auken, E.; Christiansen, A.V. Laterally constrained inversion of frequency-domain helicopter-borne electromagnetic data. J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 67, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemon, B.; van Baaren, E.; Dabekaussen, W.; Delsman, J.; Dubelaar, W.; Karaoulis, M.; Steuer, A. Automatic identification of fresh-saline groundwater interfaces from airborne electromagnetic data in Zeeland, The Netherlands. Near Surf. Geophys. 2019, 17, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siemon, B. Electromagnetic methods-frequency domain: Airborne techniques. In Groundwater Geophysics—A Tool for Hydrogeology, 1st ed.; Kirsch, R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 155–170. Available online: https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9783540884040 (accessed on 4 October 2019).
- IAEA. Guidelines for Radioelement Mapping Using Gamma Ray Spectrometry; IAEA-TECDOC-1363; International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Vienna, Austria, 2003; pp. 1–173. Available online: https://www-pub.iaea.org/mtcd/publications/pdf/te_1363_web.pdf (accessed on 4 October 2019).
- Reinsch, C.H. Smoothing by spline functions. Numer. Math. 1967, 10, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naudy, H.; Dreyer, H. Essai de filtrage non-linéaire appliqué aux profils aéromagnétiques. Geophys. Prospect. 1968, 16, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davisson, C.M. Interaction of gamma-radiation with matter. In Alpha-, Beta- and Gamma-ray Spectroscopy, 1st ed.; Siegbahn, K., Ed.; North-Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1968; Volume 1, pp. 37–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endrestøl, G. Principle and method for measurement of snow water equivalent by detection of natural gamma radiation. Hydrol. Sci. Bull. 1980, 25, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamish, D. Gamma ray attenuation in the soils of Northern Ireland, with special reference to peat. J. Environ. Radioactiv. 2013, 115, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, L.V. Adsorption problems in radioactivity. Philos. Mag. 1912, 23, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasty, R.L. Gamma-ray spectrometric methods in uranium exploration—theory and operational procedures. In Geophysics and Geochemistry in the Search for Metallic Ores; Economic Geology Report; Hood, P.J., Ed.; Geological Survey of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1979; Volume 31, pp. 147–161. [Google Scholar]


















© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siemon, B.; Ibs-von Seht, M.; Frank, S. Airborne Electromagnetic and Radiometric Peat Thickness Mapping of a Bog in Northwest Germany (Ahlen-Falkenberger Moor). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020203
Siemon B, Ibs-von Seht M, Frank S. Airborne Electromagnetic and Radiometric Peat Thickness Mapping of a Bog in Northwest Germany (Ahlen-Falkenberger Moor). Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(2):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020203
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiemon, Bernhard, Malte Ibs-von Seht, and Stefan Frank. 2020. "Airborne Electromagnetic and Radiometric Peat Thickness Mapping of a Bog in Northwest Germany (Ahlen-Falkenberger Moor)" Remote Sensing 12, no. 2: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020203
APA StyleSiemon, B., Ibs-von Seht, M., & Frank, S. (2020). Airborne Electromagnetic and Radiometric Peat Thickness Mapping of a Bog in Northwest Germany (Ahlen-Falkenberger Moor). Remote Sensing, 12(2), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020203