Understanding Land Subsidence Along the Coastal Areas of Guangdong, China, by Analyzing Multi-Track MTInSAR Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting and Datasets
2.1. Geological Setting
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. SAR Datasets and Landsat Datasets
2.2.2. In Situ Datasets
3. Methodology
4. Validation of InSAR Results
5. Results
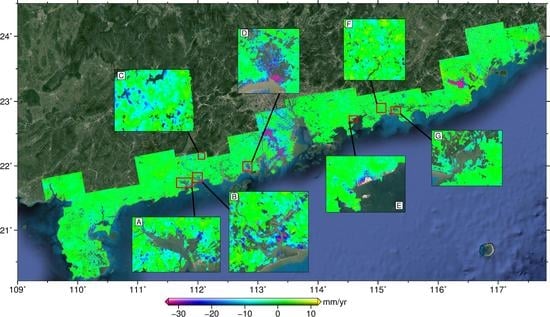
5.1. Subsidence in the Leizhou Peninsula
5.2. Subsidence in the Pearl River Delta
5.3. Subsidence in the Chaoshan Plain
5.4. Subsidence in Other Coastal Areas
6. Discussion
6.1. A positive Correlation between Sedimentary Thickness and Subsidence
6.2. Quantitative Correlation between Subsidence and Land-Use Class
6.3. Causes of Subsidence in Guangdong Province
6.3.1. Subsidence Probably Caused by Groundwater Exploitation for Freshwater Aquaculture Use
6.3.2. Subsidence Probably Caused by Groundwater Exploitation for Agricultural and Residential Use
6.3.3. Subsidence Caused by Land Reclamation
6.3.4. Subsidence Caused by Other Reasons
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marks, R. Robert Marks on the Pearl River Delta. Environ. Hist. 2004, 9, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, Y.-M. The further integration of the Pearl River Delta: A new beginning of reform. Environ. Urban. Asia 2010, 1, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Yang, C.; Yuan, Z.; Xiong, S.; Diana, J. Environmental impact of aquaculture and countermeasures to aquaculture pollution in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2007, 14, 452–462. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Feng, G.; Peng, X.; Li, Z. Subsidence Evolution of the Leizhou Peninsula, China, Based on InSAR Observation from 1992 to 2010. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Lin, H.; Cheng, S. Monitoring and assessing reclamation settlement in coastal areas with advanced InSAR techniques: Macao city (China) case study. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 3565–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G. Analysis of regional subsidence of Zhanjiang city. West China Explor. Eng. 2009, 12, 108–110. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Feng, W.; Wang, C.; Hu, Z.; Tu, W.; Li, H.J.R.S. Resolving surface displacements in Shenzhen of China from time series InSAR. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, P.; Lin, H.; Wang, W.; Shi, G. Distributed Scatterer InSAR Reveals Surface Motion of the Ancient Chaoshan Residence Cluster in the Lianjiang Plain, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, G.; Xu, B.; Yu, Y.; Li, Z.; Du, Y.; Zhu, J. Deriving spatio-temporal development of ground subsidence due to subway construction and operation in delta regions with PS-InSAR data: A case study in Guangzhou, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Wright, T.J.; Yu, Y.; Lin, H.; Jiang, L.; Li, C.; Qiu, G. InSAR reveals coastal subsidence in the Pearl River Delta, China. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 191, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.; Lin, H.; Jiang, L.; Chen, F.; Cheng, S. A study of ground deformation in the Guangzhou urban area with persistent scatterer interferometry. Sensors 2009, 9, 503–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.; Lu, Q.; Pan, X. Coastal use accelerated the regional sea-level rise. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 82, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poitevin, C.; Wöppelmann, G.; Raucoules, D.; Le Cozannet, G.; Marcos, M.; Testut, L. Vertical land motion and relative sea level changes along the coastline of Brest (France) from combined space-borne geodetic methods. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 222, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zheng, X.; Xu, H.; Ying, Y.; Hou, Y.; Xie, X.; Wang, S. Relative sea-level rising and its control strategy in coastal regions of China in the 21st century. Sci. China 2003, 46, 2562–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattacceca, J.C.; Vallet-Coulomb, C.; Mayer, A.; Claude, C.; Radakovitch, O.; Conchetto, E.; Hamelin, B. Isotopic and geochemical characterization of salinization in the shallow aquifers of a reclaimed subsiding zone: The southern Venice Lagoon coastland. J. Hydrol. 2009, 378, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Y.; Liu, X. Analysis of permafrost region coherence variation in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau with a high-resolution TerraSAR-X image. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. A New Algorithm for Processing Interferometric Data-Stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.; Segall, P.; Kampes, B. A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, X.; Lu, Z. Modeling PSInSAR time series without phase unwrapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, M.; Wang, C.; Xie, R.; Zhang, X.; Hu, J.; Du, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Dai, W.; Kuang, C. Monitoring the land subsidence with persistent scatterer interferometry in Nansha District, Guangdong, China. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 2947–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Feng, G.; Li, Z.; Peng, X.; Zhu, J.; Ren, Z. Effects of External Digital Elevation Model Inaccuracy on StaMPS-PS Processing: A Case Study in Shenzhen, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Feng, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Xie, R. Coastal subsidence monitoring associated with land reclamation using the point target based SBAS-INSAR method: A case study of shenzhen, China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abidin, H.Z.; Andreas, H.; Gumilar, I.; Fukuda, Y.; Pohan, Y.E.; Deguchi, T. Land subsidence of Jakarta (Indonesia) and its relation with urban development. Nat. Hazards 2011, 59, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Amelung, F.; Abidin, H.; Hong, S.-H. Sinking cities in Indonesia: ALOS PALSAR detects rapid subsidence due to groundwater and gas extraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Amelung, F. Land subsidence in central Mexico detected by ALOS InSAR time-series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Quiroz, P.; Doin, M.-P.; Tupin, F.; Briole, P.; Nicolas, J.-M. Time series analysis of Mexico City subsidence constrained by radar interferometry. J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 69, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erban, L.E.; Gorelick, S.M.; Zebker, H.A. Groundwater extraction, land subsidence, and sea-level rise in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 084010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.A. Review: Advances in delta-subsidence research using satellite methods. Hydrogeol. J. 2016, 24, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mialhe, F.; Gunnell, Y.; Mering, C.; Gaillard, J.-C.; Coloma, J.G.; Dabbadie, L. The development of aquaculture on the northern coast of Manila Bay (Philippines): An analysis of long-term land-use changes and their causes. J. Land Use Sci. 2016, 11, 236–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-H.; Bürgmann, R.; Hu, J.-C. Fifteen years of surface deformation in Western Taiwan: Insight from SAR interferometry. Tectonophysics 2016, 692, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, H.; Huang, C.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhi, B.; Zhao, X. The controlling factors of environment geology in the Pearl River Delta Economic Zone and an analysis of existing problems. Geol. China 2012, 39, 539–549. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.H.; Wang, R.; Zhu, C.Q. Research on spatial distribution law of gray clays of Zhanjiang Formation. Rock Soil Mech. 2013, 34, 331–338. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.S.; Chen, W.B.; Pan, H.; Zhang, Z.Z. Geological Age of Quaternary Series in Lianjiang Plain. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2012, 42, 154–161. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.L.; Hui-Long, X.U.; Peng, W.U.; Ye-Biao, W.U.; Qiu, X.L.; Zhan, W.H. Late Quaternary sedimentological characteristics and sedimentary environment evolution in sea area between Nan’ao and Chenghai, eastern Guangdong. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2007, 26, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.H.; Zheng, Z.; Wu, C.Y. Sedimentary Facies and Paleoenvironmental Evolution of the Late Quaternary in the Chao Shan Plain, East Guangdong. Actaentiarum Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 1997, 36, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, M.; Liang, C. Optimal schemes of groundwater exploitation for prevention of seawater intrusion in the Leizhou Peninsula in southern China. Environ. Geol. 2003, 43, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistical Bureau of Guangdong Province. Statistical Yearbook of Guangdong. Available online: http://stats.gd.gov.cn/gdtjnj/ (accessed on 17 November 2015).
- Irons, J.R.; Dwyer, J.L.; Barsi, J.A. The next Landsat satellite: The Landsat data continuity mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, D.P.; Wulder, M.A.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.; Allen, R.G.; Anderson, M.C.; Helder, D.; Irons, J.R.; Johnson, D.M.; Kennedy, R. Landsat-8: Science and product vision for terrestrial global change research. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Kang, Y.; Zhu, C. Ground subsidence in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from 1992 to 2014 revealed by multiple sar stacks. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samsonov, S. Topographic correction for ALOS PALSAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3020–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.; Ding, X.; Jung, H.-S.; Feng, G.; Lee, C.-W. Mapping ground surface deformation using temporarily coherent point SAR interferometry: Application to Los Angeles Basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, X.; Lu, Z.; Jung, H.-S.; Hu, J.; Feng, G. A novel multitemporal InSAR model for joint estimation of deformation rates and orbital errors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 3529–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Q. A ground crack longitudinally penetrating the holocene sand dyke in Gangzi, Leizhou Peninsula is discovered. Quat. Sci. 2008, 28, 712–720. [Google Scholar]
- Blaschke, T. Object based image analysis for remote sensing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Biging, G.S.; Yuan, C.; Hu, T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, X. The first all-season sample set for mapping global land cover with Landsat-8 data. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Earth System Science Data Center. National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China. Available online: http://www.geodata.cn (accessed on 1 February 2018).
- Casu, F.; Manzo, M.; Lanari, R. A quantitative assessment of the SBAS algorithm performance for surface deformation retrieval from DInSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.; Ferretti, A.; Minati, F.; Falco, S.; Trillo, F.; Colombo, D.; Novali, F.; Malvarosa, F.; Mammone, C.; Vecchioli, F. Analysis of surface deformations over the whole Italian territory by interferometric processing of ERS, Envisat and COSMO-SkyMed radar data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 250–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Yang, C. Deformation of Linfen-Yuncheng Basin (China) and its mechanisms revealed by Π-RATE InSAR technique. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 218, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagliani, A.; Mosconi, A.; Marzorati, D.; Cremonesi, A.; Ferretti, A.; Colombo, D.; Novali, F.; Tamburini, A. Use of satellite radar data for surface deformation monitoring: A wrap-up after 10 years of experimentation. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Florence, Italy, 20–22 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bonì, R.; Herrera, G.; Meisina, C.; Notti, D.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Zucca, F.; González, P.J.; Palano, M.; Tomás, R.; Fernández, J. Twenty-year advanced DInSAR analysis of severe land subsidence: The Alto Guadalentín Basin (Spain) case study. Eng. Geol. 2015, 198, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FAO. National Aquaculture Sector Overview. China. In National Aquaculture Sector Overview Fact Sheets; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, D.E.; Yu, F.D.; Yang, Y.X.; Xu, M.; Wei, H.; Luo, D.; Mu, X.D.; Hu, Y.C. Tilapia fisheries in Guangdong Province, China: Socio-economic benefits, and threats on native ecosystems and economics. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2019, 26, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.W.; Amelung, F.; Ferretti, A.; Bianchi, M.; Novali, F. Permanent scatterer InSAR reveals seasonal and long-term aquifer-system response to groundwater pumping and artificial recharge. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Horst, T.; Rutten, M.M.; van de Giesen, N.C.; Hanssen, R.F. Monitoring land subsidence in Yangon, Myanmar using Sentinel-1 persistent scatterer interferometry and assessment of driving mechanisms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, L. Environmental and geological problems caused by over-exploitation of groundwater and its prevention of Guangdong Province. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control 2007, 18, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Carrera-Hernández, J.; Gaskin, S. The Basin of Mexico aquifer system: Regional groundwater level dynamics and database development. Hydrogeol. J. 2007, 15, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzaghi, K. Erdbaumechanik auf Bodenphysikalischer Grundlage; Franz Deuticke: Wien, Austria, 1925. [Google Scholar]
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]












| Track_Frame | Polarization | Heading (°) | Incidence Angle (°) | Scenes | Time Span (yyyymmdd) | Master Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 452 | HH | −10.5 | 38.7 | 18 | 20070713–20110308 | 20091018 |
| 453_450 | HH | −10.6 | 38.7 | 5 | 20070614–20090201 | 20081217 |
| 453_460 | HH | −10.6 | 38.7 | 5 | 20070730–20090201 | 20081217 |
| 454 | HH | −10.5 | 38.7 | 13 | 20061229–20101009 | 20080101 |
| 455 | HH | −10.5 | 38.7 | 7 | 20070115–20090120 | 20080118 |
| 456 | HH | −10.5 | 38.7 | 15 | 20070201–20101228 | 20071220 |
| 457 | HH | −10.6 | 38.7 | 8 | 20070706–20100714 | 20091011 |
| 458 | HH | −10.6 | 38.7 | 14 | 20061205–20091213 | 20070723 |
| 459 | HH | −10.6 | 38.7 | 22 | 20061222–20110102 | 20090211 |
| 460_430 | HH | −10.6 | 38.7 | 21 | 20070711–20110119 | 20090716 |
| 460_440 | HH | −10.6 | 38.7 | 12 | 20070711–20110119 | 20080111 |
| 461 | HH | −10.6 | 38.7 | 19 | 20070125–20110205 | 20090802 |
| 462 | HH | −10.6 | 38.7 | 7 | 20061227–20101122 | 20080214 |
| 463 | HH | −10.6 | 38.7 | 8 | 20070113–20080718 | 20071016 |
| 464 | HH | −10.6 | 38.7 | 15 | 20070130–20101226 | 20090622 |
| 465 | HH | −10.6 | 38.7 | 9 | 20070216–20090106 | 20080104 |
| 466_410 | HH | −10.6 | 38.7 | 9 | 20070305–20100729 | 20080723 |
| 466_400 | HH | −10.7 | 38.7 | 13 | 20070305–20110129 | 20091211 |
| 467_390 | HH | −10.6 | 38.7 | 11 | 20061220–20100630 | 20071223 |
| 467_400 | HH | −10.6 | 38.7 | 11 | 20061220–20100630 | 20071223 |
| 467_410 | HH | −10.6 | 38.7 | 11 | 20061220–20100630 | 20071223 |
| Acquisition Time (yyyymmdd) | Cloud Content (%) | Path | Row |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20131023 | 0.03 | 119 | 42 |
| 20131023 | 0.11 | 119 | 43 |
| 20130407 | 0.02 | 120 | 43 |
| 20131201 | 0.08 | 120 | 44 |
| 20131005 | 0.02 | 121 | 44 |
| 20141015 | 0.17 | 122 | 44 |
| 20131231 | 0.86 | 122 | 45 |
| 20150416 | 0.72 | 123 | 45 |
| 20141013 | 0.37 | 124 | 45 |
| 20131026 | 0.27 | 124 | 46 |
| Adjacent Tracks | Mean | Std | Adjacent Tracks | Mean | Std |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T452-T453_450 | −0.8 | 3.1 | T460_430-T461 | 0.2 | 2.4 |
| T452-T453_460 | −0.9 | 3.1 | T460_440-T461 | 1.8 | 4.3 |
| T453_450-T454 | −1.0 | 4.0 | T461-T462 | 0.1 | 2.8 |
| T453_460-T454 | −0.4 | 3.9 | T462-T463 | −0.06 | 3.1 |
| T454-T455 | 0.4 | 2.2 | T463-T464 | 0.5 | 4.2 |
| T455-T456 | 0.03 | 2.4 | T464-T465 | −0.02 | 2.4 |
| T456-T457 | −1.0 | 2.6 | T465-T466 | −0.1 | 3.3 |
| T457-T458 | 0.3 | 2.2 | T466-T467_390 | −1.5 | 4.0 |
| T458-T459 | 0.4 | 2.0 | T466-T467_400 | −0.2 | 3.4 |
| T459-T460_440 | 0.8 | 3.6 | T466-T467_410 | −0.02 | 3.1 |
| Subsidence Rate (mm/yr) | Land-Use Class | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aquaculture (%) | Agriculture (%) | Forest (%) | Urban (%) | |
| (0, 5] | 14.0 | 44.3 | 13.4 | 28.3 |
| (5, 10] | 26.3 | 34.5 | 6.3 | 32.9 |
| (10, 20] | 35.4 | 25.6 | 1.4 | 37.6 |
| >20 | 40.8 | 21.5 | 0.6 | 37.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, Y.; Feng, G.; Liu, L.; Fu, H.; Peng, X.; Wen, D. Understanding Land Subsidence Along the Coastal Areas of Guangdong, China, by Analyzing Multi-Track MTInSAR Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020299
Du Y, Feng G, Liu L, Fu H, Peng X, Wen D. Understanding Land Subsidence Along the Coastal Areas of Guangdong, China, by Analyzing Multi-Track MTInSAR Data. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(2):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020299
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Yanan, Guangcai Feng, Lin Liu, Haiqiang Fu, Xing Peng, and Debao Wen. 2020. "Understanding Land Subsidence Along the Coastal Areas of Guangdong, China, by Analyzing Multi-Track MTInSAR Data" Remote Sensing 12, no. 2: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020299
APA StyleDu, Y., Feng, G., Liu, L., Fu, H., Peng, X., & Wen, D. (2020). Understanding Land Subsidence Along the Coastal Areas of Guangdong, China, by Analyzing Multi-Track MTInSAR Data. Remote Sensing, 12(2), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020299