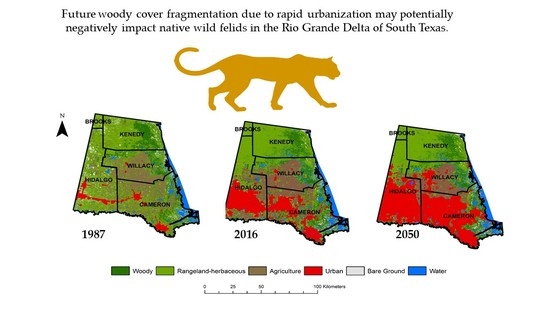
Land Cover Trends in South Texas (1987–2050): Potential Implications for Wild Felids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- 1)
- Perform a land use land cover analysis to assess the extent and change of woody cover in the Rio Grande Delta and surrounding rangelands of Texas from 1987 to 2016.
- 2)
- Quantify the spatial and temporal distribution of woody cover to determine the extent of potential fragmentation that has occurred since 1987.
- 3)
- Predict future trends in land cover change from 2020 to 2050 based on housing density projection models and discuss its potential effects on native felid populations.
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanderson, E.W.; Jaiteh, M.; Levy, M.A.; Redford, K.H.; Wannebo, A.V.; Woolmer, G. The human footprint and the last of the wild: The human footprint is a global map of human influence on the land surface, which suggests that human beings are stewards of nature, whether we like it or not. BioScience 2002, 52, 891–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, M.L. Effects of urbanization on species richness: A review of plants and animals. Urban Ecosyst. 2008, 11, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seto, K.C.; Fragkias, M.; Güneralp, B.; Reilly, M.K. A meta-analysis of global urban land expansion. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehrt, S.D. The urban ecosystem. In Urban Carnivores; Gehrt, S.D., Riley, S.P.D., Cypher, B.L., Eds.; The John Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2010; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2014 Revision Highlights. United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs; Population Division: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zemanova, M.A.; Perotto-Baldivieso, H.L.; Dickins, E.L.; Gill, A.B.; Leonard, J.P.; Wester, D.B. Impact of deforestation on habitat connectivity thresholds for large carnivores in tropical forests. Ecol. Process 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lombardi, J.V.; Comer, C.E.; Scognamillo, D.G.; Conway, W.C. Coyote, fox, and bobcat response to anthropogenic and natural landscape features in a small urban area. Urban Ecosyst. 2017, 20, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janečka, J.E.; Tewes, M.E.; Laack, L.L.; Caso, A.; Grassman, L.I., Jr.; Haines, A.M.; Shindle, D.M.; Davis, B.W.; Murphy, W.J.; Honeycutt, R.L. Reduced genetic diversity and isolation of remnant ocelot populations occupying a severely fragmented landscape in southern Texas. Anim. Conserv. 2011, 14, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janečka, J.E.; Tewes, M.E.; Davis, I.A.; Haines, A.M.; Caso, A.; Blankenship, T.L.; Honeycutt, R.L. Genetic differences in the response to landscape fragmentation by a habitat generalist, the bobcat, and a habitat specialist, the ocelot. Conserv. Genet. 2016, 17, 1093–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, J.R.; DeCesare, N.J.; Olson, L.E.; Kolbe, J.A.; Hebblewhite, M.; Parks, S.A. Combining resource selection and movement behavior to predict corridors for Canada lynx at their southern range periphery. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 157, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, K.R. Relative sensitivities of mammalian carnivores to habitat fragmentation. Conserv. Biol. 2002, 16, 488–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, P.; Riley, S.P.D.; Sauvajot, R.M. Mountain lions (Puma concolor). In Urban Carnivores; Gehrt, S.D., Riley, S.P.D., Cypher, B.L., Eds.; The John Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2010; pp. 141–156. [Google Scholar]
- Olsoy, P.J.; Zeller, K.A.; Hicke, J.A.; Quigley, H.B.; Rabinowitz, A.R.; Thornton, D.H. Quantifying the effects of deforestation and fragmentation on a range-wide conservation plan for jaguars. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 203, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, S.P.D.; Serieys, L.E.; Pollinger, J.P.; Sikich, J.A.; Dalbeck, L.; Wayne, R.K.; Ernest, H.B. Individual behaviors dominate the dynamics of an urban mountain lion population isolated by roads. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 1989–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ernest, H.B.; Vickers, T.W.; Morrison, S.A.; Buchalski, M.R.; Boyce, W.M. Fractured genetic connectivity threatens a southern California puma (Puma concolor) population. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mora, F. Nation-wide indicators of ecological integrity in Mexico: The status of mammalian apex-predators and their habitat. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 82, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidly, D.J.; Bradley, R.D. The Mammals of Texas, 7th ed.; University of Texas Press: Austin, TX, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Horne, J.S.; Haines, A.M.; Tewes, M.E.; Laack, L.L. Habitat partitioning by sympatric ocelots and bobcats: Implications for recovery of ocelots in southern Texas. Southwest Nat. 2009, 54, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Santin, L.; Harveson, P.M.; Harveson, L.A. Suitable habitats for cougars (Puma concolor) in Texas and Northern Mexico. Southwest Nat. 2012, 57, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, D.M., Jr. An International Borderland of Concern: Conservation of Biodiversity in the Lower Rio Grande Valley (No. 2016-5078); US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2016.
- Jackson, V.L.; Laack, L.L.; Zimmerman, E.G. Landscape metrics associated with habitat use by ocelots in south Texas. J. Wildl. Manag. 2005, 69, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.K.; Golla, J.M.; Broman, D.; Blakenship, T.; Heilbrun, R. Estimating density of an elusive carnivore in urban areas: Use of spatially explicit capture-recapture models for city-dwelling bobcats. Urban Ecosyst. 2019, 22, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, L. Carnivores of the World, 2nd ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Fipps, G.; Lacey, R.E.; Thomson, S.J. Landsat satellite multi-spectral image classification of land cover and land use changes for GIS-based urbanization analysis in irrigation districts of Lower Rio Grande Valley of Texas. Appl. Remote Sens. J. 2011, 2, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, D.J.; Schultz, A.D.; Dixon, J.R.; Dickerson, B.E.; Forstner, M.R. Decline of red-eared sliders (Trachemys scripta elegans) and Texas spiny softshells (Apalone spinifera emoryi) in the Lower Rio Grande Valley of Texas. Chelonian Conserv. Biol. 2012, 11, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, A.M.; Leu, M.; Svancara, L.K.; Scott, J.M.; Reese, K.P. A theoretical approach to using human footprint data to assess landscape level conservation efforts. Conserv. Lett. 2008, 1, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, K. Status and Management of Native South Texas Brushlands; U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Ecological Service Office: Corpus Christi, TX, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay, T.A.; White, W.A.; Raney, J.A. Native woodland loss during the mid-1900s in Cameron County, Texas. Southwest Nat. 2005, 50, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, A.M.; Tewes, M.E.; Laack, L.L.; Grant, W.E.; Young, J.H. Evaluating recovery strategies for an ocelot (Leopardus pardalis) population in the United States. Biol. Conserv. 2005, 126, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Goward, S.N.; Masek, J.G.; Irons, J.R.; Herold, M.; Cohen, W.B.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E. Landsat continuity: Issues and opportunities for land cover monitoring. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Updates to the Demographic and Spatial Allocation Models to Produce Integrated Climate and Land Use Scenarios (ICLUS) (Final Report, Version 2); U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- US Geological Survey Gap Analysis Program (GAP). National Land Cover Version 2.0. US Geological Survey. Available online: http://gapanalysis.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 15 October 2016).
- Bailey, R.G.; Cushwa, C.T. Ecoregions of North America; US Fish and Wildlife Service: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1981.
- Norwine, J.; Kuruvilla, J. The Changing Climate of South Texas, 1900–2100: Problems and Prospects, Impacts and Implications. In Center for Research Excellence in Science and Technology-Research on Environmental Sustainability in Semi-Arid Coastal Areas; Texas A&M University–Kingsville: Kingsville, TX, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, J.R. Introductory Digital Image Processing: Remote Sensing Perspective, 4th ed.; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cain, A.T.; Tuovila, V.R.; Hewitt, D.G.; Tewes, M.E. Effects of a highway and mitigation projects on bobcats in southern Texas. Biol. Conserv. 2003, 114, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, A.M.; Tewes, M.E.; Laack, L.L.; Horne, J.S.; Young, J.H. A habitat-based population viability analysis for ocelots (Leopardus pardalis) in the United States. Biol. Conserv. 2006, 132, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulighe, G.; Baiocchi, V.; Lupia, F. Horizontal accuracy assessment of very high-resolution Google Earth images in the city of Rome, Italy. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2016, 9, 342–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, J.M.; Perotto-Baldivieso, H.L.; Hernández, F.; Grahmann, E.D.; Rideout-Hanzak, S.; Edwards, J.T.; Page, M.T.; Shedd, T.M. Quantifying the spatial and temporal distribution of tanglehead (Heteropogon contortus) on South Texas rangelands. Ecol. Process. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hepcan, Ç.C.; Turan, I.A.; Özkan, M.B. Monitoring land use change in the Çeşme coastal zone, Turkey using aerial photographs and satellite imaging. Land Degrad. Dev. 2011, 22, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perotto-Baldivieso, H.L.; Wu, X.B.; Peterson, M.J.; Smeins, F.E.; Silvy, N.J.; Schwertner, T.W. Flooding-induced landscape changes along dendritic stream networks and implications for wildlife habitat. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 99, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierwagen, B.G.; Theobald, D.M.; Pyke, C.R.; Choate, A.; Groth, P.; Thomas, J.V.; Morefield, P. National housing and impervious surface scenarios for integrated climate impact assessments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 10, 20887–20892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tewes, M.E.; Everett, D.D. Status and distribution of the endangered ocelot and jaguarundi in Texas. In Cats of the World: Biology, Conservation, and Management; Miller, S.D., Ed.; National Wildlife Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Litvatis, J.A.; Reed, G.C.; Carroll, R.P.; Litvatis, M.K.; Tash, J.; Mahard, T.; Broman, D.J.; Callahan, C.; Ellingwood, M. Bobcats (Lynx rufus) as a model organism to investigate the effects of roads on wide-ranging carnivores. Environ. Manag. 2015, 55, 1366–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poessel, S.A.; Burdett, C.L.; Boydston, E.E.; Lyren, L.M.; Alonso, R.S.; Fisher, R.N.; Crooks, K.R. Roads influence movement and home ranges of a fragmentation-sensitive carnivore, the bobcat, in an urban landscape. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 180, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, S.P.D.; Sauvajot, R.M.; Fuller, T.K.; York, E.C.; Kamradt, D.A.; Bromley, C.; Wayne, R.K. Effects of urbanization and habitat fragmentation on bobcats and coyotes in southern California. Conserv. Biol. 2003, 17, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Archer, S.R.; Anderson, E.M.; Predick, K.I.; Schwinning Steidl, R.J.; Woods, S.R. Woody plant encroachment: Causes and consequences. In Rangeland Systems; Briske, D., Ed.; Springer Series on Environmental Management; Springer: Cham, Switerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Harveson, P.M.; Tewes, M.E.; Anderson, G.L.; Laack, L.L. Habitat use by ocelots in south Texas: Implications for restoration. Wildl. Soc. Bull. 2004, 32, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewes, M.E. Clinging to survival in the borderlands: Ocelots face dwindling habitat and growing isolation. The Wildlife Professional Sept/Oct. 2017, pp. 26–29. Available online: https://www.eastfoundation.net/media/46869/twp-ocelot-article.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- Young, J.K.; Golla, J.M.; Draper, J.P.; Broman, D.; Blakenship, T.; Heilbrun, R. Space use and movement of urban bobcats. Animals 2019, 9, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tigas, L.A.; Van Vuren, D.H.; Sauvajot, R.M. Behavioral responses of bobcats and coyotes to habitat fragmentation and corridors in an urban environment. Biol. Conserv. 2002, 108, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasey, W.C. Evaluating Translocation Strategies for Ocelot in the Tamaulipan Biotic Province. Ph.D. Dissertation, Texas A&M University-Kingsville, Kingsville, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Serieys, L.E.; Armenta, T.C.; Moriarty, J.G.; Boydston, E.E.; Lyren, L.M.; Poppenga, R.H.; Crooks, K.R.; Wayne, R.K.; Riley, S.P.D. Anticoagulant rodenticides in urban bobcats: Exposure, risk factors and potential effects based on a 16-year study. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 844–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, S.P.; Troyer, J.L.; Terwee, J.A.; Lyren, L.M.; Boyce, W.M.; Riley, S.P.D.; Roelke, M.E.; Crooks, K.R.; Vandewoude, S. Frequent transmission of immunodeficiency viruses among bobcats and pumas. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 10961–10969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bevins, S.N.; Carver, S.; Boydston, E.E.; Lyren, L.M.; Alldredge, M.; Logan, K.A.; Riley, S.P.D.; Fisher, R.N.; Vickers, T.W.; Boyce, W.; et al. Three pathogens in sympatric populations of pumas, bobcats, and domestic cats: Implications for infectious disease transmission. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía (INEGI). Anuario Estadístico y Geográfico de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos 2016; Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía: Ciudad de México, México, 2016. [Google Scholar]







| Year | N | Range | Mean | MSE | Kurtosis | KSE | Skewness | SSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1987 | PS | 18,348 | 0.09–32,927.40 | 5.18 | 1.83 | 16,941.25 | 0.04 | 128.06 | 0.02 |
| SI | 18,348 | 1.00–34.56 | 1.21 | 0.01 | 789.56 | 0.04 | 17.82 | 0.02 | |
| 1992 | PS | 55,121 | 0.09–22,036.05 | 2.15 | 0.49 | 27,139.99 | 0.02 | 155.50 | 0.01 |
| SI | 55,121 | 1.00–83.93 | 1.27 | 0.01 | 3,037.53 | 0.02 | 34.06 | 0.01 | |
| 2000 | PS | 42,878 | 0.09–21,107.97 | 2.22 | 0.56 | 26,976.00 | 0.02 | 154.98 | 0.01 |
| SI | 42,878 | 1.00–83.89 | 1.31 | 0.01 | 1,889.18 | 0.02 | 28.72 | 0.01 | |
| 2008 | PS | 53,104 | 0.09–19,960.78 | 2.29 | 0.44 | 29,340.98 | 0.02 | 157.60 | 0.01 |
| SI | 53,104 | 1.00–64.05 | 1.125 | 0.01 | 1,443.30 | 0.02 | 23.99 | 0.01 | |
| 2016 | PS | 36,104 | 0.09–1470.31 | 1.58 | 0.25 | 36,140.20 | 0.02 | 174.45 | 0.01 |
| SI | 36,104 | 1.00–126.97 | 1.32 | 0.01 | 4,312.14 | 0.02 | 40.58 | 0.01 |
| 1987–1992 | 1992–2000 | 2000–2008 | 2008–2016 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS | SI | PS | SI | PS | SI | PS | SI | |
| Kolmogorov–Smirnov Z | 77.20 | 5.10 | 1.70 | 3.96 | 30.64 | 6.50 | 31.32 | 5.50 |
| Asymp. Sig (2-tailed) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lombardi, J.V.; Perotto-Baldivieso, H.L.; Tewes, M.E. Land Cover Trends in South Texas (1987–2050): Potential Implications for Wild Felids. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040659
Lombardi JV, Perotto-Baldivieso HL, Tewes ME. Land Cover Trends in South Texas (1987–2050): Potential Implications for Wild Felids. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(4):659. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040659
Chicago/Turabian StyleLombardi, Jason V., Humberto L. Perotto-Baldivieso, and Michael E. Tewes. 2020. "Land Cover Trends in South Texas (1987–2050): Potential Implications for Wild Felids" Remote Sensing 12, no. 4: 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040659
APA StyleLombardi, J. V., Perotto-Baldivieso, H. L., & Tewes, M. E. (2020). Land Cover Trends in South Texas (1987–2050): Potential Implications for Wild Felids. Remote Sensing, 12(4), 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040659