Seasonal and Interannual Variations in China’s Groundwater Based on GRACE Data and Multisource Hydrological Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.1.1. GRACE
2.1.2. GLDAS
2.1.3. E2O
2.1.4. WGHM
2.1.5. In Situ Measurements
2.1.6. TRMM
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Deriving GWS
2.2.2. Median Trend Analysis and Mann-Kendall Test
2.2.3. The Empirical Orthogonal Function (EOF) Decomposition
2.2.4. Three-Cornered Hat Method
3. Results
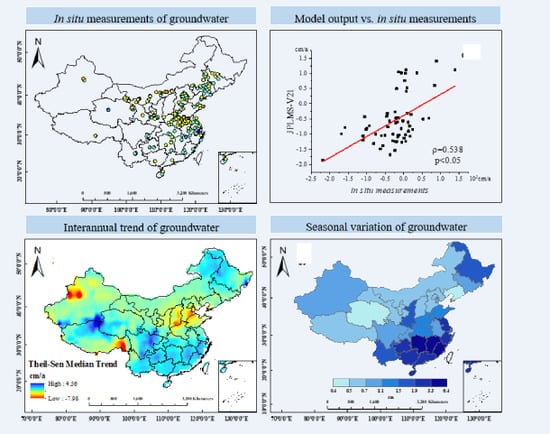
3.1. Comparison of Different GWS Data Sets
3.2. EOF Analysis of GWS Changes in China
3.3. Interannual Variation in GWS
3.4. Seasonal Variation in GWS
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aeschbach-Hertig, W.; Gleeson, T. Regional strategies for the accelerating global problem of groundwater depletion. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G. Influence and Control Strategy for Local Settlement for High-Speed Railway Infrastructure. Engineering 2016, 2, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Yao, H.-l.; Hu, M.-l.; Lu, Z.; Yu, D.-m.; Chen, F.-g. Study of moisture dynamic response and underground drainage test of subgrade model under water level fluctuation. Rock Soil Mech. 2012, 33, 2917–2922. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B. Three-dimensional seepage-stress coupling analysis of bridge foundation behaviors induced by precipitation. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2009, 28, 3277–3281. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.-n.; Miao, Y.-d.; LIAO, C.-b. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of influences of ground subsidence on composite foundation. Rock Soil Mech. 2012, 33, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.; Shum, C.; Zhong, M.; Pan, Y. Groundwater storage changes in China from satellite gravity: An overview. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.; Jambor, U.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C.-J.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M. The global land data assimilation system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Mitchell, K.; Schaake, J.; Xue, Y.; Pan, H.L.; Koren, V.; Duan, Q.Y.; Ek, M.; Betts, A. Modeling of land surface evaporation by four schemes and comparison with FIFE observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 7251–7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koster, R.D.; Suarez, M.J. Modeling the land surface boundary in climate models as a composite of independent vegetation stands. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 2697–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Wood, E.F.; Burges, S.J. A simple hydrologically based model of land surface water and energy fluxes for general circulation models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1994, 99, 14415–14428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, D.M.; Oleson, K.W.; Flanner, M.G.; Thornton, P.E.; Swenson, S.C.; Lawrence, P.J.; Zeng, X.; Yang, Z.-L.; Levis, S.; Sakaguchi, K.; et al. Parameterization improvements and functional and structural advances in Version 4 of the Community Land Model. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2011, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.B.; Mercado, L.M.; Sitch, S.; Jones, C.D.; Gedney, N.; Best, M.J.; Pryor, M.; Rooney, G.G.; Essery, R.L.H.; Blyth, E.; et al. The Joint UK Land Environment Simulator (JULES), model description—Part 2: Carbon fluxes and vegetation dynamics. Geosci. Model Dev. 2011, 4, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alcamo, J.; Döll, P.; Kaspar, F.; Siebert, S. Global Change and Global Scenarios of Water Use and Availability: An Application of WaterGAP 1.0; Center for Environmental Systems Research: Kassel, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; Federer, C.A.; Schloss, A.L. Potential evaporation functions compared on US watersheds: Possible implications for global-scale water balance and terrestrial ecosystem modeling. J. Hydrol. 1998, 207, 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beek, L.P.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P. The Global Hydrological Model PCR-GLOBWB: Conceptualization, Parameterization and Verification; Report Department of Physical Geography, Utrecht University : Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; Available online: http://vanbeek.geo.uu.nl/suppinfo/vanbeekbierkens2009.pdf.
- Bierkens, M.F.P. Global hydrology 2015: State, trends, and directions. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 4923–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döll, P.; Müller Schmied, H.; Schuh, C.; Portmann, F.T.; Eicker, A. Global-scale assessment of groundwater depletion and related groundwater abstractions: Combining hydrological modeling with information from well observations and GRACE satellites. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 5698–5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Velicogna, I.; Famiglietti, J.S. Satellite-based estimates of groundwater depletion in India. Nature 2009, 460, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Güntner, A. Improvement of global hydrological models using GRACE data. Surv. Geophys. 2008, 29, 375–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landerer, F.W.; Swenson, S. Accuracy of scaled GRACE terrestrial water storage estimates. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, S.; Wahr, J. Post-processing removal of correlated errors in GRACE data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, M.M.; Wiese, D.N.; Yuan, D.-N.; Boening, C.; Landerer, F.W. Improved methods for observing Earth’s time variable mass distribution with GRACE using spherical cap mascons. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 2648–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, D.N.; Landerer, F.W.; Watkins, M.M. Quantifying and reducing leakage errors in the JPL RL05M GRACE mascon solution. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 7490–7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Save, H.; Bettadpur, S.; Tapley, B.D. High-resolution CSR GRACE RL05 mascons. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2016, 121, 7547–7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Pan, Y.; Gong, H.; Yeh, P.J.F.; Li, X.; Zhou, D.; Zhao, W. Subregional-scale groundwater depletion detected by GRACE for both shallow and deep aquifers in North China Plain. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Zhong, M.; Lemoine, J.M.; Biancale, R.; Hsu, H.T.; Xia, J. Evaluation of groundwater depletion in North China using the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) data and ground-based measurements. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; de Linage, C.; Famiglietti, J.; Zender, C.S. Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) detection of water storage changes in the Three Gorges Reservoir of China and comparison with in situ measurements. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhong, M.; Feng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Wu, D. Groundwater depletion in the West Liaohe River Basin, China and its Implications revealed by GRACE and in situ measurements. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, H.; Leblanc, M.; Tweed, S.; Liu, W. Groundwater depletion in the Hai River Basin, China, from in situ and GRACE observations. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 671–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shamsudduha, M.; Taylor, R.; Longuevergne, L. Monitoring groundwater storage changes in the highly seasonal humid tropics: Validation of GRACE measurements in the Bengal Basin. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Earth2Observe. Global Earth Observation for Integrated Water Resource Assessment. Available online: http://www.earth2observe.eu/ (accessed on 1 January 2018).
- Döll, P.; Kaspar, F.; Lehner, B. A global hydrological model for deriving water availability indicators: model tuning and validation. J. Hydrol. 2003, 270, 105–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Institute of Geological Environment Monitoring (CIGEM). China Geological Environment Monitoring: Groundwater Yearbook; China Land Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 35 Voss, K.A.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Lo, M.; de Linage, C.; Rodell, M.; Swenson, S.C. Groundwater depletion in the Middle East from GRACE with implications for transboundary water management in the Tigris-Euphrates-Western Iran region. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- 36 Long, D.; Chen, X.; Scanlon, B.R.; Wada, Y.; Hong, Y.; Singh, V.P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Han, Z.; Yang, W. Have GRACE satellites overestimated groundwater depletion in the Northwest India Aquifer? Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theil, H. A rank-invariant method of linear and polynomial regression analysis. In Henri Theil’s Contributions to Economics and Econometrics; Raj, B., Koerts, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1992; pp. 345–381. [Google Scholar]
- Hoaglin, D.C.; Mosteller, F.; Tukey, J.W. Understanding Robust and Exploratory Data Analysis; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econ. J. Econom. Soc. 1945, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Dorrelation Methods; Griffin: Oxford, England, 1948; Available online: https://psycnet.apa.org/record/1948-15040-000.
- Gilbert, R.O. Statistical Methods for Environmental Pollution Monitoring; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Asoka, A.; Gleeson, T.; Wada, Y.; Mishra, V. Relative contribution of monsoon precipitation and pumping to changes in groundwater storage in India. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorenz, E.N. Empirical orthogonal functions and statistical weather prediction. Open J. Stat. 1956, 3, 1–52. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, R.; Petrovic, S.; Güntner, A.; Barthelmes, F.; Wünsch, J.; Kusche, J. Periodic components of water storage changes from GRACE and global hydrology models. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, T.M.; Reynolds, R.W.; Livezey, R.E.; Stokes, D.C. Reconstruction of historical sea surface temperatures using empirical orthogonal functions. J. Clim. 1996, 9, 1403–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arneborg, L.; Wåhlin, A.; Björk, G.; Liljebladh, B.; Orsi, A. Persistent inflow of warm water onto the central Amundsen shelf. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Hou, X.; Hong, Y.; Scanlon, B.R.; Longuevergne, L. Global analysis of spatiotemporal variability in merged total water storage changes using multiple GRACE products and global hydrological models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 198–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preisendorfer, R.W.; Mobley, C.D.; Barnett, T.P. The principal discriminant method of prediction: Theory and evaluation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1988, 93, 10815–10830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.G.; Montecino, H.D.; Yakubu, C.I.; Heck, B. Uncertainties of the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment time-variable gravity-field solutions based on three-cornered hat method. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 015015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awange, J.; Ferreira, V.; Forootan, E.; Andam-Akorful, S.; Agutu, N.; He, X. Uncertainties in remotely sensed precipitation data over Africa. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 303–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torcaso, F.; Ekstrom, C.; Burt, E.; Matsakis, D. Estimating Frequency Stability and Cross-Correlations; Naval Observatory: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Galindo, F.J.; Palacio, J. Estimating the Instabilities of N Correlated Clocks; Real Observatorio de la Armada (SPAIN): Cádiz, Spain, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, T.; Gross, R.; Dickey, J. Multi-reference evaluation of uncertainty in Earth orientation parameter measurements. J. Geod. 2005, 79, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koot, L.; De Viron, O.; Dehant, V. Atmospheric angular momentum time-series: characterization of their internal noise and creation of a combined series. J. Geod. 2006, 79, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, F.J.; Palacio, J. Post-processing ROA data clocks for optimal stability in the ensemble timescale. Metrologia 2003, 40, S237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Wang, H.; Steffen, H.; Wu, P.; Jia, L.; Jiang, L.; Shen, Q. Groundwater storage changes in the Tibetan Plateau and adjacent areas revealed from GRACE satellite gravity data. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 449, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farinotti, D.; Longuevergne, L.; Moholdt, G.; Duethmann, D.; Mölg, T.; Bolch, T.; Vorogushyn, S.; Güntner, A. Substantial glacier mass loss in the Tien Shan over the past 50 years. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Wang, Q.; Chang, L.; Sun, W. Changes in mountain glaciers, lake levels, and snow coverage in the Tianshan monitored by GRACE, ICESat, altimetry, and MODIS. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacob, T.; Wahr, J.; Pfeffer, W.T.; Swenson, S. Recent contributions of glaciers and ice caps to sea level rise. Nature 2012, 482, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, A.S.; Moholdt, G.; Cogley, J.G.; Wouters, B.; Arendt, A.A.; Wahr, J.; Berthier, E.; Hock, R.; Pfeffer, W.T.; Kaser, G. A reconciled estimate of glacier contributions to sea level rise: 2003 to 2009. Science 2013, 340, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodell, M.; Famiglietti, J.; Wiese, D.; Reager, J.; Beaudoing, H.; Landerer, F.W.; Lo, M.-H. Emerging trends in global freshwater availability. Nature 2018, 557, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Changming, L.; Jingjie, Y.; Kendy, E. Groundwater exploitation and its impact on the environment in the North China Plain. Water Int. 2001, 26, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, Y.; Pacenka, S.; Gao, W.; Zhang, M.; Sui, P.; Steenhuis, T.S. Recharge and groundwater use in the North China Plain for six irrigated crops for an eleven year period. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geographic Data Sharing Infrastructure. College of Urban and Environmental Science, Peking University. Available online: http://geodata.pku.edu.cn (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- Li, B.; Rodell, M.; Kumar, S.; Beaudoing, H.K.; Getirana, A.; Zaitchik, B.F.; de Goncalves, L.G.; Cossetin, C.; Bhanja, S.; Mukherjee, A. Global GRACE data assimilation for groundwater and drought monitoring: advances and challenges. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 7564–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tangdamrongsub, N.; Steele-Dunne, S.; Gunter, B.; Ditmar, P.; Weerts, A. Data assimilation of GRACE terrestrial water storage estimates into a regional hydrological model of the Rhine River basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tangdamrongsub, N.; Han, S.-C.; Tian, S.; Müller Schmied, H.; Sutanudjaja, E.H.; Ran, J.; Feng, W. Evaluation of groundwater storage variations estimated from GRACE data assimilation and state-of-the-art land surface models in Australia and the North China Plain. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eicker, A.; Schumacher, M.; Kusche, J.; Döll, P.; Schmied, H.M. Calibration/data assimilation approach for integrating GRACE data into the WaterGAP Global Hydrology Model (WGHM) using an ensemble Kalman filter: First results. Surv. Geophys. 2014, 35, 1285–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girotto, M.; De Lannoy, G.J.; Reichle, R.H.; Rodell, M.; Draper, C.; Bhanja, S.N.; Mukherjee, A. Benefits and pitfalls of GRACE data assimilation: A case study of terrestrial water storage depletion in India. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 4107–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]















© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Liu, K.; Wang, M. Seasonal and Interannual Variations in China’s Groundwater Based on GRACE Data and Multisource Hydrological Models. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050845
Zhang J, Liu K, Wang M. Seasonal and Interannual Variations in China’s Groundwater Based on GRACE Data and Multisource Hydrological Models. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(5):845. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050845
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jianxin, Kai Liu, and Ming Wang. 2020. "Seasonal and Interannual Variations in China’s Groundwater Based on GRACE Data and Multisource Hydrological Models" Remote Sensing 12, no. 5: 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050845
APA StyleZhang, J., Liu, K., & Wang, M. (2020). Seasonal and Interannual Variations in China’s Groundwater Based on GRACE Data and Multisource Hydrological Models. Remote Sensing, 12(5), 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12050845