Limitations in Validating Derived Soil Water Content from Thermal/Optical Measurements Using the Simplified Triangle Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Geographical Description of the Study Site
2.2. Satellite Image Processing Operations
2.3. NDVI and Fr Derivation
2.4. Surface Radiant Temperature Derivation
2.5. Scaled Surface Radiant Temperature Derivation
2.6. T*- Fr Triangular Space
2.7. Soil Surface Moisture Availability Estimation (Mo)
2.8. Satellite Images
2.9. Ground Reference Measurements
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. T*/ Fr Spaces
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Variability of Moisture Availability
3.3. Soil Water Content Measurements
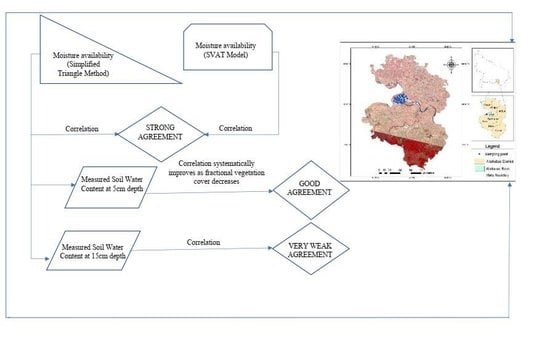
4. Validation
4.1. Comparison of Mo between the SVAT Model and the Simplified Triangle Method (Geomtric Model Algorithm)
4.2. Comparison of Mo with surface SWC measurements: the limits of validation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zribi, M.; Baghdadi, N.; Holah, N.; Fafin, O. New methodology for soil surface moisture estimation and its application to ENVISAT-ASAR multi-incidence data inversion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.K. Introductory Soil Science; Kalyani Publishers: New Delhi, India, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Capehart, W.J.; Carlson, T.N. Decoupling of surface and near-surface soil water content: A remote sensing perspective. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, G.K.; Aliyu, A.K. Determination of the influence of texture and organic matter on soil water holding capacity in and around Tomas Irrigation Scheme, Dambatta Local Government Kano State. Res. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 4, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.; Irmak, A.; Trezza, R.; Hendrickx, J.M.; Bastiaanssen, W.; Kjaersgaard, J. Satellite-based ET estimation in agriculture using SEBAL and METRIC. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 4011–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N. An overview of the “triangle method” for estimating surface evapotranspiration and soil moisture from satellite imagery. Sensor 2007, 7, 1612–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, Z. Microwave Remote Sensing of Soil Moisture; The International Institute for Geo-Information Science and Earth Observation: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mekonnen, D.F. Satellite Remote Sensing for Soil Moisture Estimation: Gumara Catchment, Ethiopia; The International Institute for Geo-Information Science and Earth Observation: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, J. Soil Moisture Modelling Using TWI and Satellite Imagery in the Stockholm Region; Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), School of Architecture and the Built Environment: Stockholm, Sweden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Filippucci, P.; Tarpanelli, A.; Massari, C.; Serafini, A.; Strati, V.; Alberi, M.; Raptis, K.G.C.; Mantovani, F.; Brocca, L. Soil moisture as a potential variable for tracking and quantifying irrigation: A case study with proximal gamma-ray spectroscopy data. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 136, 103502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zreda, M.; Desilets, D.; Ferré, T.P.A.; Scott, R.L. Measuring soil moisture content noninvasively at intermediate spatial scale using cosmic-ray neutrons. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mallick, K.; Bhattacharya, B.K.; Patel, N. Estimating volumetric surface moisture content for cropped soils using a soil wetness index based on surface temperature and NDVI. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 2009, 149, 1327–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.A.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.; Ahmad, M.-U.-D. Mapping root zine soil moisture using remotely sensed optical imagery. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2003, 129, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadeghi, M.; Babaeian, E.; Tuller Jones, S.B. The optical trapezoid model: A novel approach to remote sensing of soil moisture applied to Sentinal-2 and Landsat-8 observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babaerian, E.; Sadeghi, M.; Franz, T.E.; Jones, S.; Tulleer, M. Mapping soil moisture with the OPtical TRApezoid Model (OPTRAM) based on long-term ODIS observations Ebrahim. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 211, 425–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Petropoulos, G. A simplified triangle method for estimating evapotranspiration and surface soil moisture from optical and thermal measurements. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 7716–7729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, G.; Carlson, T.N.; Wooster, M.; Islam, S. A review of Ts/VI remote sensing-based methods for the retrieval of land surface energy fluxes and soil surface moisture. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2009, 33, 224–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allahabad Profile. Retrieved August Monday, 2015. Available online: http://allahabad.nic.in/geostructure.htm (accessed on 10 August 2015).
- National Disaster Risk Reduction Portal. Retrieved August Monady, 2015. Available online: http://nidm.gov.in/pdf/dp/Uttar.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2015).
- Agriculture Contingency Plan for District: Allahabad. Retrieved August Monday, 2015. Available online: http://agricoop.nic.in/Agriculture%20Contingency%20Plan/UP/UP62-Allahabad-28.07.14.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2015).
- Uttar Pradesh District Profile. Retrieved August Monday, 2015. Available online: http://zpdk.org.in/sites/default/files/districtprofile(2-2-10).pdf (accessed on 10 August 2015).
- LPSO. The Landsat 7 Science Data User’s Handbook; NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Greenbelt: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chander, G.; Markham, B.L.; Helder, D.L. Summary of current radiometric calibration coefficients for Landsat MSS, TM, ETM+,and EO-1 ALI sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunsell, N.A.; Gillies, R.R. Incorporating surface emissivity into a thermal atmospheric correction. Photogram. Eng. Remote Sens. 2002, 68, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar]
- Mallast, U.; Gloaguen, R.; Friesen, J.; Rödiger, T.; Geyer, S.; Merz, R.; Siebert, C. How to identify groundwater-caused thermal anomalies in lakes based on multi-temporal satellite data in semi-arid regions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 2773–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlson, T.N. Triangle models and misconceptions. Int. J. Remote Sens. Appl. 2013, 3, 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Gillies, R.R.; Carlson, T.N.; Kustas, W.P.; Humes, K.S. A verification of the ‘triangle’ method for obtaining surface soil water content and energy fluxes from remote measurements of the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and surface radiant temperature. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 3145–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wu, J.J.; Shi, P.J.; Yan, F. Modified triangle method to estimate soil moisture status with moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) products. Proc. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2008, 37, 555–560. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-F.; Son, N.-T.; Chang, L.-Y.; Chen, C.-C. Monitoring of soil moisture variability in relation to rice cropping systems in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta using MODIS data. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasim, A.A.; Usman, A.A. Triangle method for estimating soil surface wetness from satellite imagery in Allahabad District, Uttar Pradesh, India. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2016, 4, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasim, A.A. Derivation of surface soil water content using a simplified geometric method in Allahabad District, Uttar Pradesh India. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2015, 6, 1631–1637. [Google Scholar]
- Silva Fuzzo, D.F.; Carlson, T.N.; Kourgialas, N.N.; Petropoulos, G.P. Coupling remote sensing with a water balance model for soybean yield predictions over large areas. Earth Sci. Inform. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Threshold | No. of Points | R Squared | RMSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 cm | 15 cm | 5 cm | 15 cm | ||
| Threshold 0.3 | 10 | 0.434 | 0.349 | 0.191 | 0.189 |
| Threshold 0.4 | 15 | 0.494 | 0.102 | 0.256 | 0.449 |
| Threshold 0.5 | 26 | 0.338 | 0.325 | 0.231 | 0.229 |
| Threshold 0.6 | 58 | 0.206 | 0.229 | 0.284 | 0.289 |
| Threshold 0.7 | 38 | 0.123 | 0.150 | 0.283 | 0.285 |
| Without threshold | 58 | 0.192 | 0.142 | 0.285 | 0.294 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aliyu Kasim, A.; Nahum Carlson, T.; Shehu Usman, H. Limitations in Validating Derived Soil Water Content from Thermal/Optical Measurements Using the Simplified Triangle Method. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071155
Aliyu Kasim A, Nahum Carlson T, Shehu Usman H. Limitations in Validating Derived Soil Water Content from Thermal/Optical Measurements Using the Simplified Triangle Method. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(7):1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071155
Chicago/Turabian StyleAliyu Kasim, Abba, Toby Nahum Carlson, and Haruna Shehu Usman. 2020. "Limitations in Validating Derived Soil Water Content from Thermal/Optical Measurements Using the Simplified Triangle Method" Remote Sensing 12, no. 7: 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071155
APA StyleAliyu Kasim, A., Nahum Carlson, T., & Shehu Usman, H. (2020). Limitations in Validating Derived Soil Water Content from Thermal/Optical Measurements Using the Simplified Triangle Method. Remote Sensing, 12(7), 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071155