A Comprehensive Evaluation of Five Evapotranspiration Datasets Based on Ground and GRACE Satellite Observations: Implications for Improvement of Evapotranspiration Retrieval Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. Methodology
3. Results
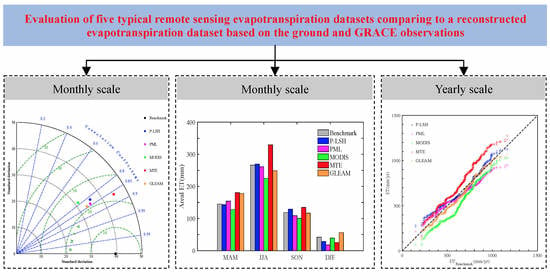
3.1. Evaluation of Yearly Scale ET Data
3.2. Evaluation of Seasonal-Scale ET Data
3.3. Evaluation of Monthly-Scale ET Data
3.4. Overall Evaluation of Five ET Products
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiong, Y.J.; Zhao, S.H.; Tian, F.; Qiu, G.Y. An evapotranspiration product for arid regions based on the three-temperature model and thermal remote sensing. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, S. Estimation of regional irrigation water requirement and water supply risk in the arid region of Northwestern China 1989–2010. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 128, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D. Aerosol-Cloud Interactions Control of Earth Radiation and Latent Heat Release Budgets. Space Sci. Rev. 2007, 125, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lee, X.; Xiao, W.; Liu, S.; Schultz, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, L. Global lake evaporation accelerated by changes in surface energy allocation in a warmer climate. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H.; Jasechko, S. Transpiration in the global water cycle. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 189–190, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntington, T.G. Evidence for intensification of the global water cycle: Review and synthesis. J. Hydrol. 2006, 319, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Kimball, J.S.; Nemani, R.R.; Running, S.W. A continuous satellite-derived global record of land surface evapotranspiration from 1983 to 2006. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, R.G.; Clemmens, A.J.; Burt, C.M.; Solomon, K.; O’Halloran, T. Prediction Accuracy for Projectwide Evapotranspiration Using Crop Coefficients and Reference Evapotranspiration. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2005, 131, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Fasullo, J.T.; Kiehl, J. Earth’s global energy budget. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 90, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuling, A.J.; Hirschi, M.; Ohmura, A.; Wild, M.; Reichstein, M.; Ciais, P.; Buchmann, N.; Ammann, C.; Montagnani, L.; Richardson, A.D.; et al. A regional perspective on trends in continental evaporation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orth, R.; Destouni, G. Drought reduces blue-water fluxes more strongly than green-water fluxes in Europe. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberg, J.W.; Melesss, A.M. Evapotranspiration Dynamics at an Ecohydrological Restoration Site: An Energy Balance and Remote Sensing Approach. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2006, 42, 565–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, G.; Katerji, N.; Perniola, M. Evapotranspiration of sweet sorghum: A general model and multilocal validity in semiarid environmental conditions. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 3237–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Caylor, K.K.; Villegas, J.C.; Barron-Gafford, G.A.; Breshears, D.D.; Huxman, T.E. Partitioning evapotranspiration across gradients of woody plant cover: Assessment of a stable isotope technique. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Kimball, J.S.; Running, S.W. A review of remote sensing based actual evapotranspiration estimation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2016, 3, 834–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhoff, A.L.; Paz, A.R.; Aragao, L.E.O.C.; Mu, Q.; Malhi, Y.; Collischonn, W.; Rocha, H.R.; Running, S.W. Assessment of the MODIS global evapotranspiration algorithm using eddy covariance measurements and hydrological modelling in the Rio Grande basin. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 1658–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Kobayashi, H.; Van Ingen, C.; Li, J.; Black, T.A.; Beringer, J.; Van Gorsel, E.; Knohl, A.; Law, B.E.; et al. Integration of MODIS land and atmosphere products with a coupled-process model to estimate gross primary productivity and evapotranspiration from 1 km to global scales. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2011, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thakur, J.K.; Singh, S.K.; Ekanthalu, V.S. Integrating remote sensing, geographic information systems and global positioning system techniques with hydrological modeling. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1595–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chirouze, J.; Boulet, G.; Jarlan, L.; Fieuzal, R.; Rodriguez, J.C.; Ezzahar, J.; Er-Raki, S.; Bigeard, G.; Merlin, O.; Garatuzapayan, J.; et al. Intercomparison of four remote-sensing-based energy balance methods to retrieve surface evapotranspiration and water stress of irrigated fields in semi-arid climate. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Cribb, M.; Sparrow, M. A simple method to estimate actual evapotranspiration from a combination of net radiation, vegetation index, and temperature. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2007, 112, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senay, G.B.; Budde, M.; Verdin, J.P.; Melesse, A.M. A Coupled Remote Sensing and Simplified Surface Energy Balance Approach to Estimate Actual Evapotranspiration from Irrigated Fields. Sensors 2007, 7, 979–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gokmen, M.; Vekerdy, Z.; Verhoef, A.; Verhoef, W.; Batelaan, O.; Van Der Tol, C. Integration of soil moisture in SEBS for improving evapotranspiration estimation under water stress conditions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuttleworth, W.J.; Wallace, J. Evaporation from sparse crops-an energy combination theory. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1985, 111, 839–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, R.E. Land Surface Processes and Climate—Surface Albedos and Energy Balance. In Advances in Geophysics; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983; Volume 25, pp. 305–353. [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans, W.J.; Kustas, W.P.; Anderson, M.C.; French, A.N. An intercomparison of the Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land (SEBAL) and the Two-Source Energy Balance (TSEB) modeling schemes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Kwast, J.; Timmermans, W.; Gieske, A.; Su, Z.; Olioso, A.; Jia, L.; Elbers, J.; Karssenberg, D.; De Jong, S. Evaluation of the Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) applied to ASTER imagery with flux-measurements at the SPARC 2004 site (Barrax, Spain). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhattarai, N.; Shaw, S.B.; Quackenbush, L.J.; Im, J.; Niraula, R. Evaluating five remote sensing based single-source surface energy balance models for estimating daily evapotranspiration in a humid subtropical climate. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 49, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Heinsch, F.A.; Nemani, R.R.; Running, S.W. Improvements of the MODIS terrestrial gross and net primary production global data set. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, R.H. Data assimilation methods in the Earth sciences. Adv. Water Resour. 2008, 31, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodesheim, P.; Jung, M.; Gans, F.; Mahecha, M.D.; Reichstein, M. Upscaled diurnal cycles of land–atmosphere fluxes: A new global half-hourly data product. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 1327–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, X. Energy Balance, Evaporation, and Surface Temperature. In Springer Atmospheric Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 191–213. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Lu, F.; Xiao, W.; Zhu, K.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, Z. Performance of 12 reference evapotranspiration estimation methods compared with the Penman-Monteith method and the potential influences in northeast China. Meteorol. Appl. 2019, 26, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Penman, H.L. Natural evaporation from open water, bare soil and grass. In Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Containing Papers of a Mathematical and Physical Character; The Royal Society: London, UK, 1948; Volume 193, pp. 120–145. [Google Scholar]
- Monteith, J.L. Evaporation and Environment, Symposia of the Society for Experimental Biology; Cambridge University Press (CUP): Cambridge, UK, 1965; pp. 205–234. [Google Scholar]
- Mallick, K.; Jarvis, A.; Fisher, J.B.; Tu, K.P.; Boegh, E.; Niyogi, D. Latent heat flux and canopy conductance based on penman–monteith, priestley–taylor equation, and bouchet’s complementary hypothesis. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 419–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanella, D.; Ramírez-Cuesta, J.M.; Intrigliolo, D.S.; Consoli, S. Combining Electrical Resistivity Tomography and Satellite Images for Improving Evapotranspiration Estimates of Citrus Orchards. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cleugh, H.A.; Leuning, R.; Mu, Q.; Running, S.W. Regional evaporation estimates from flux tower and MODIS satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Heinsch, F.A.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Development of a global evapotranspiration algorithm based on MODIS and global meteorology data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 111, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Kimball, J.S.; Nemani, R.R.; Running, S.W.; Hong, Y.; Gourley, J.J.; Yu, Z. Vegetation Greening and Climate Change Promote Multidecadal Rises of Global Land Evapotranspiration. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuning, R.; Zhang, Y.; Rajaud, A.; Cleugh, H.; Tu, K. A simple surface conductance model to estimate regional evaporation using MODIS leaf area index and the Penman-Monteith equation. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kong, D.; Gan, R.; Chiew, F.H.; McVicar, T.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y. Coupled estimation of 500 m and 8-day resolution global evapotranspiration and gross primary production in 2002–2017. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 222, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, D.G.; Holmes, T.; De Jeu, R.A.M.; Gash, J.H.; Meesters, A.G.C.A.; Dolman, A. Global land-surface evaporation estimated from satellite-based observations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martens, B.; Gonzalez Miralles, D.; Lievens, H.; Van Der Schalie, R.; De Jeu, R.A.M.; Fernández-Prieto, D.; Beck, H.E.; Dorigo, W.A.; Verhoest, N. GLEAM v3: Satellite-based land evaporation and root-zone soil moisture. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 1903–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, M.; Reichstein, M.; Bondeau, A. Towards global empirical upscaling of FLUXNET eddy covariance observations: Validation of a model tree ensemble approach using a biosphere model. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 2001–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granata, F.; Gargano, R.; de Marinis, G. Artificial intelligence based approaches to evaluate actual evapotranspiration in wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhamarine, Y.; Malik, A.; Souag-Gamane, D.; Kisi, O. Artificial intelligence models versus empirical equations for modeling monthly reference evapotranspiration. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 30001–30019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Reichstein, M.; Ciais, P.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Sheffield, J.; Goulden, M.L.; Bonan, G.; Cescatti, A.; Chen, J.; De Jeu, R.; et al. Recent decline in the global land evapotranspiration trend due to limited moisture supply. Nature 2010, 467, 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granata, F. Evapotranspiration evaluation models based on machine learning algorithms—A comparative study. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 217, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Yuan, G.; Wang, L.; Sun, X.; Sun, R. Comparison of Remotely Sensed Evapotranspiration Models Over Two Typical Sites in an Arid Riparian Ecosystem of Northwestern China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalm, C.R.; Huntinzger, D.N.; Michalak, A.M.; Fisher, J.; Kimball, J.S.; Mueller, B.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y. Sensitivity of inferred climate model skill to evaluation decisions: A case study using CMIP5 evapotranspiration. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 024028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Zhang, K.; Xue, X.; Hong, Z.; Hong, Y.; Gourley, J.J. Water balance-based actual evapotranspiration reconstruction from ground and satellite observations over the conterminous United States. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 6485–6499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Zhang, L.; Chang, Q.; Fu, D.; Cen, Y.; Tong, Q. Evaluating an Enhanced Vegetation Condition Index (VCI) Based on VIUPD for Drought Monitoring in the Continental United States. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Peña-Arancibia, J.L.; McVicar, T.; Chiew, F.H.S.; Vaze, J.; Liu, C.; Lu, X.; Zheng, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; et al. Multi-decadal trends in global terrestrial evapotranspiration and its components. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, M.; Reichstein, M.; Margolis, H.A.; Cescatti, A.; Richardson, A.D.; Arain, M.A.; Arneth, A.; Bernhofer, C.; Bonal, D.; Chen, J.; et al. Global patterns of land-atmosphere fluxes of carbon dioxide, latent heat, and sensible heat derived from eddy covariance, satellite, and meteorological observations. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mueller, B.; Hirschi, M.; Jimenez, C.; Ciais, P.; Dirmeyer, P.A.; Dolman, A.J.; Fisher, J.B.; Jung, M.; Ludwig, F.; Maignan, F. Benchmark products for land evapotranspiration: Landflux-eval multi-data set synthesis. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 3707–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Heinsch, F.A.; Liu, M.; Tian, H.; Running, S.W. Evaluating water stress controls on primary production in biogeochemical and remote sensing based models. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2007, 112, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chia, M.Y.; Huang, Y.F.; Koo, C.H.; Fung, K.F. Recent Advances in Evapotranspiration Estimation Using Artificial Intelligence Approaches with a Focus on Hybridization Techniques—A Review. Agronony 2020, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Kimball, J.S.; Mu, Q.; Jones, L.A.; Goetz, S.; Running, S.W. Satellite based analysis of northern ET trends and associated changes in the regional water balance from 1983 to 2005. J. Hydrol. 2009, 379, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chiew, F.H.S.; Peña-Arancibia, J.; Sun, F.; Li, H.; Leuning, R. Global variation of transpiration and soil evaporation and the role of their major climate drivers. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 6868–6881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Or, D.; Lehmann, P.; Shahraeeni, E.; Shokri, N. Advances in Soil Evaporation Physics-A Review. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.B.; Tu, K.P.; Baldocchi, D.D. Global estimates of the land–atmosphere water flux based on monthly AVHRR and ISLSCP-II data, validated at 16 FLUXNET sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 901–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Name | Acronyms | Temporal Coverage | Resolution | Algorithm | Key Equations | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual evapotranspiration reconstruction | Recon | April 2002 to September 2013 | Monthly, 0.125° | Simple water balance | | The resolution of Grace satellite is coarse, and the accuracy of ET in small watershed is affected. | Wan et al. (2015) |
| Process-based land surface evapotranspiration/heat flux | P-LSH | January 1982 to December 2013 | Monthly, 0.5° | Modified Penman-Monteith | No considered canopy interception | K. Zhang et al. (2015) | |
| Penman–Monteith–Leuning | PML | July 2002 to August 2019 | 8 day, 500 m | Modified Penman-Monteith-Leuning | Soil evaporation simplifies the physical process. | Y Q. Zhang et al. (2019) | |
| Moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer | MODIS | January 2000 to Present | 8 day, 500 m | Penman-Monteith-Leuning | Biome Properties Look-Up Table is an empirical value. Unused flux tower data calibration parameters. | Mu et al. (2011) | |
| Model tree ensemble | MTE | January 1982 to December 2008 | Monthly, 0.5° | TRIAL + ERROR | No specific equation | No physical process | Jung et al. (2011) |
| Global land evaporation amsterdam model | GLEAM | 1980 to 2020 | Monthly, 0.25° | Modified Priestley-Taylor | Simplified impedance | Martens et al. (2017) |
| Five ET datasets vs. Recon | Bias (mm/year) | RMSE (mm/year) | R |
|---|---|---|---|
| P-LSH vs. Recon | −22.94 | 92.62 | 0.92 |
| PML vs. Recon | 17.73 | 83.44 | 0.93 |
| MODIS vs. Recon | -106.71 | 145.90 | 0.89 |
| MTE vs. Recon | 99.45 | 126.39 | 0.95 |
| GLEAM vs Recon | 23.18 | 87.78 | 0.92 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chao, L.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Feng, J.; Zhang, M. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Five Evapotranspiration Datasets Based on Ground and GRACE Satellite Observations: Implications for Improvement of Evapotranspiration Retrieval Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13122414
Chao L, Zhang K, Wang J, Feng J, Zhang M. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Five Evapotranspiration Datasets Based on Ground and GRACE Satellite Observations: Implications for Improvement of Evapotranspiration Retrieval Algorithm. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(12):2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13122414
Chicago/Turabian StyleChao, Lijun, Ke Zhang, Jingfeng Wang, Jin Feng, and Mengjie Zhang. 2021. "A Comprehensive Evaluation of Five Evapotranspiration Datasets Based on Ground and GRACE Satellite Observations: Implications for Improvement of Evapotranspiration Retrieval Algorithm" Remote Sensing 13, no. 12: 2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13122414
APA StyleChao, L., Zhang, K., Wang, J., Feng, J., & Zhang, M. (2021). A Comprehensive Evaluation of Five Evapotranspiration Datasets Based on Ground and GRACE Satellite Observations: Implications for Improvement of Evapotranspiration Retrieval Algorithm. Remote Sensing, 13(12), 2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13122414