Physics-Based Relationship for Pore Pressure and Vertical Stress Monitoring Using Seismic Velocity Variations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theory
2.1. Velocity Change Due to Induced Stress
2.2. Velocity Change Due to Surface Load and Pore Pressure
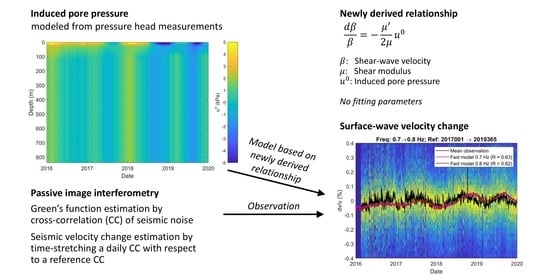
3. Model Validation
3.1. Static Model
3.2. Stress Model
3.3. Shear-Wave Velocity Change
3.4. Surface-Wave Dispersion Forward Modeling
3.5. Passive Image Interferometry
3.6. Model Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Stress-Induced Compressional-Wave Velocity Change
Appendix B. Rotation Approximation


References
- Rawlinson, N.; Fichtner, A.; Sambridge, M.; Young, M.K. Chapter One—Seismic Tomography and the Assessment of Uncertainty. Adv. Geophys. 2014, 55, 1–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sens-Schönfelder, C.; Wegler, U. Passive image interferometry and seasonal variations of seismic velocities at Merapi Volcano, Indonesia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenguier, F.; Shapiro, N.M.; Campillo, M.; Ferrazzini, V.; Duputel, Z.; Coutant, O.; Nercessian, A. Towards forecasting volcanic eruptions using seismic noise. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wegler, U.; Nakahara, H.; Sens-Schönfelder, C.; Korn, M.; Shiomi, K. Sudden drop of seismic velocity after the 2004 Mw 6.6 mid-Niigata earthquake, Japan, observed with Passive Image Interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvermoser, J.; Hadziioannou, C.; Stähler, S.C. Structural monitoring of a highway bridge using passive noise recordings from street traffic. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 138, 3864–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voisin, C.; Guzmán, M.A.R.; Réfloch, A.; Taruselli, M.; Garambois, S. Groundwater Monitoring with Passive Seismic Interferometry. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2017, 9, 1414–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clements, T.; Denolle, M.A. Tracking groundwater levels using the ambient seismic field. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 6459–6465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakata, N.; Snieder, R. Estimating near-surface shear wave velocities in Japan by applying seismic interferometry to KiK-net data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivet, D.; Brenguier, F.; Cappa, F. Improved detection of preeruptive seismic velocity drops at the Piton de La Fournaise volcano. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 6332–6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Brenguier, F.; Campillo, M.; Lecointre, A.; Takeda, T.; Aoki, Y. Seasonal crustal seismic velocity changes throughout Japan. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 7987–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Aslam, K.; Daub, E. Seismic Velocity Changes Caused by Water Table Fluctuation in the New Madrid Seismic Zone and Mississippi Embayment. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2020JB019524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andajani, R.D.; Tsuji, T.; Snieder, R.; Ikeda, T. Spatial and temporal influence of rainfall on crustal pore pressure based on seismic velocity monitoring. Earth Planets Space 2020, 72, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dost, B.; Ruigrok, E.; Spetzler, J. Development of seismicity and probabilistic hazard assessment for the Groningen gas field. Neth. J. Geosci. 2017, 96, s235–s245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Eijs, R.M.; van der Wal, O. Field-wide reservoir compressibility estimation through inversion of subsidence data above the Groningen gas field. Neth. J. Geosci. 2017, 96, s117–s129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Ginkel, J.; Ruigrok, E.; Herber, R. Using horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratios to construct shear-wave velocity profiles. Solid Earth 2020, 11, 2015–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokker, E.B.; Ruigrok, E.N. Quality parameters for passive image interferometry tested at the Groningen network. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 218, 1367–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Paulssen, H. Compaction of the Groningen gas reservoir investigated with train noise. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 223, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenguier, F.; Courbis, R.; Mordret, A.; Campman, X.; Boué, P.; Chmiel, M.; Takano, T.; Lecocq, T.; Van der Veen, W.; Postif, S.; et al. Noise-based ballistic wave passive seismic monitoring. Part 1: Body waves. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 221, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mordret, A.; Courbis, R.; Brenguier, F.; Chmiel, M.; Garambois, S.; Mao, S.; Boué, P.; Campman, X.; Lecocq, T.; Van der Veen, W.; et al. Noise-based ballistic wave passive seismic monitoring–Part 2: Surface waves. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 221, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromp, J.; Trampert, J. Effects of induced stress on seismic forward modelling and inversion. Geophys. J. Int. 2018, 213, 851–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjar, E.; Holt, R.M.; Raaen, A.; Horsrud, P. Petroleum Related Rock Mechanics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dinoloket. Groundwater Research; Borehole Identification B08C0952. 2020. Available online: https://www.dinoloket.nl/ondergrondgegevens (accessed on 5 June 2020).
- KNMI. Netherlands Seismic and Acoustic Network. Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI), Other/Seismic Network, 1993. Available online: http://rdsa.knmi.nl/network/NL/ (accessed on 16 May 2020). [CrossRef]
- Kruiver, P.P.; van Dedem, E.; Romijn, R.; de Lange, G.; Korff, M.; Stafleu, J.; Gunnink, J.L.; Rodriguez-Marek, A.; Bommer, J.J.; van Elk, J.; et al. An integrated shear-wave velocity model for the Groningen gas field, The Netherlands. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2017, 15, 3555–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romijn, R. Groningen Velocity Model 2017; Technical Report; Nederlandse Aardolie Maatschappij: Assen, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, R. A spectral element method for surface wave dispersion and adjoints. Geophys. J. Int. 2018, 215, 267–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.B.; Miller, R.D.; Xia, J. Imaging dispersion curves of surface waves on multi-channel record. In Proceedings of the 1998 SEG Annual Meeting; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wapenaar, K.; Slob, E.; Snieder, R.; Curtis, A. Tutorial on seismic interferometry: Part 2—Underlying theory and new advances. Geophysics 2010, 75, 75A211–75A227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobkis, O.I.; Weaver, R.L. Coda-wave interferometry in finite solids: Recovery of P-to-S conversion rates in an elastodynamic billiard. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 254302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z.; Tsai, V.C.; Clayton, R.W. Spurious velocity changes caused by temporal variations in ambient noise frequency content. Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 194, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, V.C. A model for seasonal changes in GPS positions and seismic wave speeds due to thermoelastic and hydrologic variations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hillers, G.; Campillo, M.; Ma, K.F. Seismic velocity variations at TCDP are controlled by MJO driven precipitation pattern and high fluid discharge properties. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 391, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Campillo, M.; van der Hilst, R.D.; Brenguier, F.; Stehly, L.; Hillers, G. High Temporal Resolution Monitoring of Small Variations in Crustal Strain by Dense Seismic Arrays. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]













Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fokker, E.; Ruigrok, E.; Hawkins, R.; Trampert, J. Physics-Based Relationship for Pore Pressure and Vertical Stress Monitoring Using Seismic Velocity Variations. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2684. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142684
Fokker E, Ruigrok E, Hawkins R, Trampert J. Physics-Based Relationship for Pore Pressure and Vertical Stress Monitoring Using Seismic Velocity Variations. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(14):2684. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142684
Chicago/Turabian StyleFokker, Eldert, Elmer Ruigrok, Rhys Hawkins, and Jeannot Trampert. 2021. "Physics-Based Relationship for Pore Pressure and Vertical Stress Monitoring Using Seismic Velocity Variations" Remote Sensing 13, no. 14: 2684. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142684
APA StyleFokker, E., Ruigrok, E., Hawkins, R., & Trampert, J. (2021). Physics-Based Relationship for Pore Pressure and Vertical Stress Monitoring Using Seismic Velocity Variations. Remote Sensing, 13(14), 2684. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142684