A Multi-Frequency Galileo PPP-RTK Convergence Analysis with an Emphasis on the Role of Frequency Spacing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Processing Strategy
2.1. Observation Model
2.2. Experimental Setup
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
3.1. Formal Analysis
3.1.1. Frequency Spacing
3.1.2. More Frequencies, Shorter Convergence Time?
3.1.3. Impact of Satellite Code Bias Corrections
3.2. Empirical Analysis
3.2.1. Network Corrections
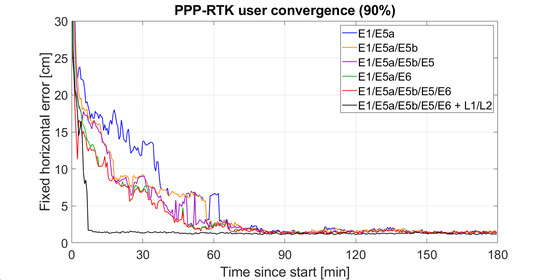
3.2.2. Galileo-Only PPP-RTK Positioning
3.2.3. Galileo+GPS PPP-RTK Positioning
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leandro, R.; Landau, H.; Nitschke, M.; Glocker, M.; Seeger, S.; Chen, X.; Deking, A.; BenTahar, M.; Zhang, F.; Ferguson, K.; et al. RTX positioning: The next generation of cm-accurate real-time GNSS positioning. In Proceedings of the 24th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2011), Portland, OR, USA, 20–23 September 2011; pp. 1460–1475. [Google Scholar]
- Banville, S.; Collins, P.; Zhang, W.; Langley, R. Global and regional ionospheric corrections for faster PPP convergence. Navigation 2014, 61, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odijk, D.; Zhang, B.; Khodabandeh, A.; Odolinski, R.; Teunissen, P.J.G. On the estimability of parameters in undifferenced, uncombined GNSS network and PPP-RTK user models by means of S-system theory. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 15–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Odijk, D.; Zhang, B. PPP-RTK: Results of CORS network-based PPP with integer ambiguity resolution. J. Aeronaut. Astronaut. Aviat. 2010, 42, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Guo, G. Predicting atmospheric delays for rapid ambiguity resolution in precise point positioning. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 54, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psychas, D.; Verhagen, S. Real-Time PPP-RTK Performance Analysis Using Ionospheric Corrections from Multi-Scale Network Configurations. Sensors 2020, 20, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, Q.; Li, G. Inter-system PPP ambiguity resolution between GPS and BeiDou for rapid initialization. J. Geod. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsigianni, G.; Loyer, S.; Perosanz, F. PPP and PPP-AR Kinematic Post-Processed Performance of GPS-Only, Galileo-Only and Multi-GNSS. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Jiang, W.; Laurichesse, D.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, J. Assessing GPS/Galileo real-time precise point positioning with ambiguity resolution based on phase biases from CNES. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 810–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadarajah, N.; Khodabandeh, A.; Wang, K.; Choudhury, M.; Teunissen, P.J.G. Multi-GNSS PPP-RTK: From Large- to Small-Scale Networks. Sensors 2018, 18, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ge, M.; Schuh, H. GPS+Galileo+BeiDou precise point positioning with triple-frequency ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X.; Wickert, J. Multi-GNSS phase delay estimation and PPP ambiguity resolution: GPS, BDS, GLONASS, Galileo. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 579–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhao, Q.; Verhagen, S.; Psychas, D.; Liu, X. Assessing the Performance of Multi-GNSS PPP-RTK in the Local Area. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brack, A.; Männel, B.; Schuh, H. GLONASS FDMA data for RTK positioning: A five-system analysis. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Bock, Y. Triple-frequency GPS precise point positioning with rapid ambiguity resolution. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Li, P.; Gao, Y.; Heck, B. A Unified Model for Multi-Frequency PPP Ambiguity Resolution and Test Results with Galileo and BeiDou Triple-Frequency Observations. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, P. Improving the Performance of Galileo Uncombined Precise Point Positioning Ambiguity Resolution Using Triple-Frequency Observations. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Feng, G.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Ren, X. Triple-frequency PPP ambiguity resolution with multi-constellation GNSS: BDS and Galileo. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1105–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Guo, J.; Meng, X.; Kao, G. Speeding up PPP ambiguity resolution using triple-frequency GPS/BeiDou/Galileo/QZSS data. GPS Solut. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. GNSS Precise Point Positioning. In Position, Navigation, and Timing Technologies in the 21st Century: Integrated Satellite Navigation, Sensor Systems, and Civil Applications, 1st ed.; Morton, Y.J., van Diggelen, F., Spilker, J.J., Parkinson, B.W., Lo, S., Gao, G., Eds.; Wiley-IEEE Press: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Chapter 20. [Google Scholar]
- GNSS Science Support Centre. Galileo Signal Plan. 2020. Available online: https://gssc.esa.int/navipedia/index.php/Galileo_Signal_Plan (accessed on 3 December 2020).
- GNSS Science Support Centre. Galileo High Accuracy Service (HAS). 2021. Available online: https://gssc.esa.int/navipedia/index.php/Galileo_High_Accuracy_Service_(HAS) (accessed on 2 January 2021).
- European GNSS Agency. GNSS User Technology Report. Issue 3; European GNSS Agency, 2020; Available online: https://www.euspa.europa.eu/simplecount_pdf/tracker?file=uploads/technology_report_2020.pdf (accessed on 3 December 2020). [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Geng, G.; Guo, G.; Meng, X. On the Choice of the Third-Frequency Galileo Signals in Accelerating PPP Ambiguity Resolution in Case of Receiver Antenna Phase Center Errors. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Liu, G.; Li, X.; Zhou, F.; Feng, G.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, K. Galileo PPP rapid ambiguity resolution with five-frequency observations. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Guo, G. Beyond three frequencies: An extendable model for single-epoch decimeter-level point positioning by exploiting Galileo and BeiDou-3 signals. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. Theory of integer equivariant estimation with application to GNSS. J. Geod. 2003, 77, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laurichesse, D.; Banville, S. Instantaneous Centimeter-Level Multi-Frequency Precise Point Positioning. GPS World, Innovation Column. July 2018. Available online: https://www.gpsworld.com/innovation-instantaneous-centimeter-level-multi-frequency-precise-point-positioning/ (accessed on 3 December 2020).
- Guo, J.; Geng, J.; Wang, C. Impact of the third frequency GNSS pseudorange and carrier phase observations on rapid PPP convergences. GPS Solut. 2021, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Xin, S. Toward single-epoch 10-centimeter precise point positioning using Galileo E1/E5a and E6 signals. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Technical Meeting of the ION Satellite Division (ION GNSS+ 2019), Miami, FL, USA, 16–20 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann-Wellenhof, B.; Lichtenegger, H.; Wasle, E. GNSS—Global Navigation Satellite Systems: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and More; Springer: Wien, Austria, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baarda, W. S-transformations and criterion matrices. In Publications on Geodesy, 18; Netherlands Geodetic Commission: Delft, The Netherlands, 1973; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. Zero Order Design: Generalized Inverses, Adjustment, the Datum Problem and S-Transformations. In Optimization and Design of Geodetic Networks; Grafarend, E., Sanso, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1985; pp. 11–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jonge, P. A Processing Strategy for the Application of the GPS in Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Prange, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Perosanz, F.; Romero, I.; Noll, C.; Sturze, A.; Weber, G.; et al. The Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) of the International GNSS Service (IGS)—Achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 1671–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoscience Australia. Weekly Station Coordinates from ARGN, SPRGN, AuScope and APREF. 2020. Available online: ftp://ftp.ga.gov.au/geodesy-outgoing/gnss/solutions/final/weekly/ (accessed on 3 December 2020).
- Johnston, G.; Riddell, A.; Hausler, G. The International GNSS Service. In Springer Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems, 1st ed.; Teunissen, P.J.G., Montenbruck, O., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Chapter 33; pp. 967–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saastamoinen, J. Contributions to the theory of atmospheric refraction. Bull. Geod. 1972, 105, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifadis, I. The Atmospheric Delay of Radio Waves: Modelling the Elevation Dependence on a Global Scale; Technical Report No 38L; Chalmers University of Technology: Gothenburg, Sweden, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Euler, H.; Goad, C. On optimal filtering for GPS dual-frequency observations without using orbit information. Bull. Géod. 1991, 65, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shen, Y.; Xu, P. Assessment of stochastic models for GPS measurements with different types of receivers. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 3219–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. An integrity and quality control procedure for use in multi sensor integration. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GPS 1990), Colorado Spring, CO, USA, 19–21 September 1990; pp. 513–522. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. The least-squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment: A method for fast GPS integer ambiguity estimation. J. Geod. 1995, 70, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. An Optimality Property of the Integer Least-Squares Estimator. J. Geod. 1999, 73, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Joosten, P.; Tiberius, C.C.J.M. Geometry-free ambiguity success rates in case of partial fixing. In Proceedings of the ION NTM 1999, San Diego, CA, USA, 25–27 January 1999; pp. 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- Wübbena, G.; Schmitz, M.; Bagge, A. PPP-RTK: Precise Point Positioning Using State-Space Representation in RTK Networks. In Proceedings of the 18th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2005), Long Beach, CA, USA, 13–16 September 2005; pp. 2584–2594. [Google Scholar]
- Odijk, D.; Teunissen, P.J.G. Characterization of between-receiver GPS-Galileo inter-system biases and their effect on mixed ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Assessment of precise orbit and clock products for Galileo, BeiDou, and QZSS from IGS Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX). GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Joosten, P.; Jonkman, N.F. Evaluation of long range GNSS ambiguity resolution. In Proceedings of the 8th European CGSIC IISC Meeting, Prague, Czech Republic, 2–3 December 1999; pp. 171–177. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Xie, W.; Guo, F.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Feng, G. The phase and code biases of Galileo and BDS-3 BOC signals: Effect on ambiguity resolution and precise positioning. J. Geod. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, M.; Aquino, M.; Vadakke Veettil, S. Estimation and analysis of multi-GNSS differential code biases using a hardware signal simulator. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Psychas, D.; Verhagen, S.; Teunissen, P.J.G. Precision analysis of partial ambiguity resolution-enabled PPP using multi-GNSS and multi-frequency signals. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 2075–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Teunissen, P.J.G.; Odijk, D. A Novel Un-differenced PPP-RTK concept. J. Navig. 2011, 64, S180–S191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Parameter | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Receiver clocks | ; |
| Satellite clocks | |
| Ionospheric delays | |
| Receiver phase biases | ; |
| Satellite phase biases | |
| Phase ambiguities | ; |
| Receiver code biases | ; |
| Satellite code biases | ; |
| -basis parameters |
| Provision of Satellite Code Biases | Estimating Satellite Code Biases | |
|---|---|---|
| E1+E5a+E5b | 17.5 | 18.0 |
| E1+E5a+E5b+E5 | 16.0 | 18.0 |
| E1+E5a+E6 | 13.0 | 13.0 |
| E1+E5a+E5b+E5+E6 | 12.0 | 12.5 |
| Horizontal | Vertical | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 50% | 90% | Mean | 50% | 90% | |
| Float | ||||||
| E1+E5a | 13.0 [67.0] | 9.5 [34.5] | 84.5 [ - ] | 45.5 [132.0] | 26.0 [74.5] | 130.0 [ - ] |
| E1+E5a+E5b | 13.0 [67.0] | 9.5 [34.5] | 84.5 [ - ] | 45.5 [132.0] | 26.0 [74.5] | 127.5 [ - ] |
| E1+E5a+E5b+E5 | 12.5 [67.0] | 8.5 [34.5] | 84.5 [ - ] | 45.0 [132.0] | 25.5 [74.0] | 127.5 [ - ] |
| E1+E5a+E6 | 12.5 [67.0] | 8.5 [30.0] | 75.0 [ - ] | 45.0 [132.0] | 25.5 [69.0] | 127.5 [ - ] |
| E1+E5a+E5b+E5+E6 | 12.5 [67.0] | 8.5 [30.0] | 75.0 [ - ] | 43.5 [105.0] | 24.5 [69.0] | 127.5 [ - ] |
| Fixed | ||||||
| E1+E5a | 12.5 [33.0] | 8.0 [24.5] | 37.0 [62.5] | 35.0 [ 62.5] | 22.0 [28.0] | 64.0 [144.0] |
| E1+E5a+E5b | 5.5 [18.0] | 3.5 [15.5] | 18.0 [57.0] | 27.0 [ 52.5] | 14.0 [22.5] | 53.0 [144.0] |
| E1+E5a+E5b+E5 | 5.0 [17.5] | 3.5 [14.0] | 17.0 [52.5] | 24.5 [ 48.5] | 14.0 [21.5] | 49.0 [120.5] |
| E1+E5a+E6 | 4.5 [15.5] | 3.5 [10.0] | 15.0 [39.0] | 23.5 [ 38.5] | 13.5 [19.5] | 38.0 [ 83.0] |
| E1+E5a+E5b+E5+E6 | 3.5 [15.0] | 2.0 [ 9.5] | 15.0 [39.0] | 20.5 [ 38.5] | 13.0 [18.0] | 38.0 [ 83.0] |
| Provision of Satellite Code Biases | Estimating Satellite Code Biases | |
|---|---|---|
| E1+E5a+E5b | 18.0 | 22.0 |
| E1+E5a+E5b+E5 | 17.0 | 21.0 |
| E1+E5a+E6 | 15.0 | 16.0 |
| E1+E5a+E5b+E5+E6 | 15.0 | 15.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Psychas, D.; Teunissen, P.J.G.; Verhagen, S. A Multi-Frequency Galileo PPP-RTK Convergence Analysis with an Emphasis on the Role of Frequency Spacing. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3077. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163077
Psychas D, Teunissen PJG, Verhagen S. A Multi-Frequency Galileo PPP-RTK Convergence Analysis with an Emphasis on the Role of Frequency Spacing. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(16):3077. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163077
Chicago/Turabian StylePsychas, Dimitrios, Peter J. G. Teunissen, and Sandra Verhagen. 2021. "A Multi-Frequency Galileo PPP-RTK Convergence Analysis with an Emphasis on the Role of Frequency Spacing" Remote Sensing 13, no. 16: 3077. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163077
APA StylePsychas, D., Teunissen, P. J. G., & Verhagen, S. (2021). A Multi-Frequency Galileo PPP-RTK Convergence Analysis with an Emphasis on the Role of Frequency Spacing. Remote Sensing, 13(16), 3077. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163077