Retrieving High-Resolution Aerosol Optical Depth from GF-4 PMS Imagery in Eastern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
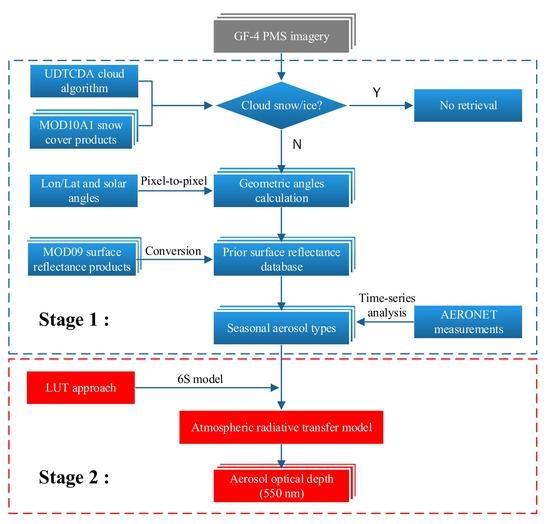
- Since band 10 in MOD09 has the highest coincidence degree with band 2 in GF-4, MOD09 band 10 was used supporting AOD retrieval. However, there are still differences between MODIS band 10 and GF-4 band 2. Conversion was performed to resolve the difference in the central wavelength, bandwidth, and absorption peaks between the MODIS and PMS blue band. The aerosol types were determined by analyzing the aerosol optical properties in a long time series [24].
- (2)
- Because pixel-by-pixel geometric information of the GF-4 PMS image was not available, we calculated the observed zenith angle, relative azimuth angle, and solar zenith angle of each pixel in the PMS image.
- (3)
- In terms of removing useless pixels, we use the universal dynamic threshold cloud detection algorithm(UDTCDA) [25] to reconstruct the dynamic threshold pixel by pixel and remove the cloud pixels. MOD10A1 data were used to mask snow pixels.
- (4)
- The 6S [19] radiation transfer model was used to establish quantitative relationship between the relative position of the sun and the satellite, LSR, AOD, and the apparent reflectance in the blue wave bands. The AOD can be calculated by comparing the satellite apparent reflectance with that simulated from the 6S model for pixels meeting the retrieval conditions (no cloud and snow, LSR(0.483–0.493μm) < 0.15) [26].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Introduction
2.1.1. GF-4 PMS Data
2.1.2. AERONET AOD Measurements
2.2. AOD Retrieval for GF-4 PMS Imagery
2.2.1. Surface Reflectance Estimation
2.2.2. Calculation of Pixel-By-Pixel Imaging via the Geometric Angle
2.2.3. Aerosol Type Assumption
2.2.4. Cloud and Snow Screening
2.3. Validation Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Validation against AERONET Ground Measurements
3.2. Comparison with Operational MOD04 AOD Products
3.3. Retrieval Uncertainty Related to LSR Variations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Lyapustin, A.; Sun, L.; Peng, Y.; Xue, W.; Su, T.; Cribb, M. Reconstructing 1-km-resolution high-quality PM2.5 data records from 2000 to 2018 in China: Spatiotemporal variations and policy implications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112–136. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Peng, Y.; Sun, L.; Yan, X. A regionally robust high-spatial-resolution aerosol retrieval algorithm for MODIS images over Eastern China. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2019, 57, 4748–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Xue, W.; Sun, L.; Fan, T.; Liu, L.; Su, T.; Cribb, M. The ChinaHighPM10 dataset: Generation, validation, and spatiotemporal variations from 2015 to 2019 across China. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Pinker, R.T.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Xue, W.; Li, R.; Cribb, M. Himawari-8-derived diurnal variations in ground-level PM 2.5 pollution across China using the fast space-time Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LightGBM). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 7863–7880. [Google Scholar]
- Colvile, R.; Hutchinson, E.J.; Mindell, J.; Warren, R. The transport sector as a source of air pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 1537–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clarke, A.; Collins, W.; Rasch, P.; Kapustin, V.; Moore, K.; Howell, S.; Fuelberg, H. Dust and pollution transport on global scales: Aerosol measurements and model predictions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 32555–32569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Sendra, C. Algorithm for automatic atmospheric corrections to visible and near-IR satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1988, 9, 1357–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.; Remer, L.; Kleidman, R.; Mattoo, S.; Ichoku, C.; Kahn, R.; Eck, T. Global evaluation of the Collection 5 MODIS dark-target aerosol products over land. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10399–10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Sun, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhong, B. Aerosol optical depth retrieval by HJ-1/CCD supported by MODIS surface reflectance data. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.-p.; Sun, L. Retrieval of aerosol optical depth over arid areas from MODIS data. Atmos 2016, 7, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Tanreé, D.; Mattoo, S.; Kaufman, Y.J. Algorithm for Remote Sensing of Tropospheric Aerosol over Dark Targets from MODIS: Collections 005 and 051: Revision 2; February 2009. MODIS Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document, 2009. Available online: https://atmosphere-imager.gsfc.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/ModAtmo/ATBD_MOD04_C005_rev2_0.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Vermote, E.F.; Kaufman, Y.J. Second-generation operational algorithm: Retrieval of aerosol properties over land from retrieval of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer spectral reflectance. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, N.C.; Tsay, S.-C.; King, M.D.; Herman, J.R. Deep blue retrievals of Asian aerosol properties during ACE-Asia. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2006, 44, 3180–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.; Jeong, M.J.; Bettenhausen, C.; Sayer, A.; Hansell, R.; Seftor, C.; Huang, J.; Tsay, S.C. Enhanced Deep Blue aerosol retrieval algorithm: The second generation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9296–9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munchak, L.; Levy, R.; Mattoo, S.; Remer, L.; Holben, B.; Schafer, J.; Hostetler, C.; Ferrare, R. MODIS 3 km aerosol product: Applications over land in an urban/suburban region. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1747–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Peng, Y.; Sun, L. MODIS Collection 6.1 aerosol optical depth products over land and ocean: Validation and comparison. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 201, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S. The physical science basis: Contribution of Working Group I to the fourth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Intergov. Panel Clim. Chang. Clim. Chang. 2007, 2007, 996. [Google Scholar]
- Remer, L.; Mattoo, S.; Levy, R.; Munchak, L. MODIS 3 km aerosol product: Algorithm and global perspective. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1829–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Korkin, S.; Huang, D. MODIS collection 6 MAIAC algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5741–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Laszlo, I.; Kahn, R.; Korkin, S.; Remer, L.; Levy, R.; Reid, J.S. Multiangle implementation of atmospheric correction (MAIAC): 2. Aerosol algorithm. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.; Nichol, J.; Lee, K. Retrieval of Aerosol Optical Thickness Using MODIS 500 × 500 m, a study in Hong Kong and Pearl River Delta Region. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3318–3327. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Sun, L. Comparison and evaluation of different MODIS aerosol optical depth products over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Sun, L.; Peng, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Bilal, M.; Ma, Y. An improved high-spatial-resolution aerosol retrieval algorithm for MODIS images over land. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 12291–12307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotchenova, S.Y.; Vermote, E.F. Validation of a vector version of the 6S radiative transfer code for atmospheric correction of satellite data. Part II. Homogeneous Lambertian and anisotropic surfaces. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 4455–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Wei, J.; Wang, J.; Mi, X.; Guo, Y.; Lv, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gan, P.; Zhou, X.; Jia, C. A universal dynamic threshold cloud detection algorithm (UDTCDA) supported by a prior surface reflectance database. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 7172–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wei, J.; Bilal, M.; Tian, X.; Jia, C.; Guo, Y.; Mi, X. Aerosol optical depth retrieval over bright areas using Landsat 8 OLI images. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilal, M.; Nichol, J.E. Evaluation of MODIS aerosol retrieval algorithms over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region during low to very high pollution events. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 7941–7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giles, D.M.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Sinyuk, A.; Schafer, J.; Sorokin, M.G.; Slutsker, I. Aerosol robotic network (AERONET) version 3 aerosol optical depth and retrieval products. In Proceedings of the American Geophysical Union (AGU) Fall Meeting, New Orleans, LA, USA, 11–15 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Giles, D.M.; Sinyuk, A.; Sorokin, M.G.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Lewis, J.R.; Campbell, J.R. Advancements in the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Version 3 database–automated near-real-time quality control algorithm with improved cloud screening for Sun photometer aerosol optical depth (AOD) measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, S.; Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Chen, C.; Yang, L.; Hu, X.; Liu, B.; Chen, N.; Du, B.; et al. Adapting the Dark Target Algorithm to Advanced MERSI Sensor on the FengYun-3-D Satellite: Retrieval and Validation of Aerosol Optical Depth Over Land. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 3021021, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, B.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Yang, L.; Chen, X.; Hou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Li, L.; Qie, L. A Dark Target Method for Himawari-8/AHI Aerosol Retrieval: Application and Validation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Cai, Z. Enhanced Aerosol Estimations From Suomi-NPP VIIRS Images over Heterogeneous Surfaces. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 9534–9543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Laszlo, I.; Li, Z.; Wei, J.; Kalluri, S. Refining aerosol optical depth retrievals over land by constructing the relationship of spectral surface reflectances through deep learning: Application to Himawari-8. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 251, 112093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Xue, Y.; Guang, J.; Mei, L.; She, L.; Li, Y.; Che, Y.; Fan, C. Deriving a Global and Hourly Data Set of Aerosol Optical Depth Over Land Using Data From Four Geostationary Satellites: GOES-16, MSG-1, MSG-4, and Himawari-8. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 1538–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Liu, Q.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Wei, J. Improving MODIS Aerosol Estimates Over Land with the Surface BRDF Reflectances Using the 3-D Discrete Cosine Transform and RossThick-LiSparse Models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanré, D.; Herman, M.; Deschamps, P.; De Leffe, A. Atmospheric modeling for space measurements of ground reflectances, including bidirectional properties. Appl. Opt. 1979, 18, 3587–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.F.; Tanré, D.; Deuze, J.L.; Herman, M.; Morcette, J.-J. Second simulation of the satellite signal in the solar spectrum, 6S: An overview. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 1997, 35, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vermote, E. MODIS Surface Reflectance User’s Guide (Collection 6). 2020. Available online: https://modis-land.gsfc.nasa.gov/pdf/MOD09_C61_UserGuide_v1.5.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Wald, A.E.; Remer, L.A.; Bo-Cai, G.; Rong-Rong, L.; Flynn, L. The MODIS 2.1-/spl mu/m channel-correlation with visible reflectance for use in remote sensing of aerosol. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 1997, 35, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, L.; Tao, J.; Han, D.; Wang, Z.; Su, L.; Fan, M.; Yu, C. Retrieval of aerosol optical depth over bright targets in the urban areas of North China during winter. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, T.; Eisemann, D.W. Determination of look angles to geostationary communication satellites. J. Surv. Eng. 1994, 120, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumka, U.; Kaskaoutis, D.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Sheoran, R. Identification of key aerosol types and mixing states in the central Indian Himalayas during the GVAX campaign: The role of particle size in aerosol classification. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamill, P.; Giordano, M.; Ward, C.; Giles, D.; Holben, B. An AERONET-based aerosol classification using the Mahalanobis distance. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 213–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korras-Carraca, M.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Matsoukas, C.; Gkikas, A.; Papadimas, C. The regime of aerosol asymmetry parameter over Europe, the Mediterranean and the Middle East based on MODIS satellite data: Evaluation against surface AERONET measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 13113–13132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quan, W.; Lin, S.; Jing, W. Improvement of universal dynamic threshold cloud detection algorithm and its application in high resolution satellite. AcOpS 2018, 38, 376–385. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; He, X.; de Leeuw, G.; Mei, L.; Che, Y.; Rippin, W.; Guang, J.; Hu, Y. Long-time series aerosol optical depth retrieval from AVHRR data over land in North China and Central Europe. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 471–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ding, J.; Wang, J.; Ge, X.; Raxidin, M.; Liang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, X.; Ding, Y. Retrieval of fine-resolution aerosol optical depth (AOD) in semiarid urban areas using Landsat data: A case study in Urumqi, NW China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, Y.; Hao, Z.; Chen, J.; He, D.; Tian, Q.; Mao, Z.; Pan, D. Retrieval of Urban Aerosol Optical Depth from Landsat 8 OLI in Nanjing, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omari, K.; Abuelgasim, A.; Alhebsi, K. Aerosol optical depth retrieval over the city of Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates (UAE) using Landsat-8 OLI images. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhao, W.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Q. Landsat 8-based retrieval methods for aerosol optical depths in the Beijing area. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Wang, F.; Jia, L.L.; Ding, Y. Retrieval and validation of aerosol optical depth using GF-1 WFV cameras data—ScienceDirect. AdSpR 2020, 65, 997–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Fan, M.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.; Tao, M.; Wei, J.; Wang, Q. A simplified aerosol retrieval algorithm for Himawari-8 Advanced Himawari Imager over Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 199, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Sun, L.; Huang, B.; Bilal, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L. Verification, improvement and application of aerosol optical depths in China Part 1: Inter-comparison of NPP-VIIRS and Aqua-MODIS. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 175, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Band | Wavelength (μm) | Description | Spatial Resolution (m) | Width (km) | |
| GF-4 | 12345 | 0.45–0.90 0.45–0.52 0.52–0.60 0.63–0.69 0.76–0.90 | Visible to NIR Blue Green Red NIR | 50 | 400 |
| 6 | 3.5–4.1 | Mid-IR | 400 | ||
| MODIS | 10 | 0.483–0.493 | Blue |
| Model | g | RP-CRI | IP-CRI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (470/550/660 nm) | (470/550/660 nm) | (470/550/660 nm) | (470/550/660 nm) | ||
| Beijing | Spring | 0.920/0.925/0.932 | 0.710/0.684/0.662 | 1.521/1.529/1.536 | 0.008/0.007/0.006 |
| Summer | 0.947/0.948/0.949 | 0.720/0.693/0.669 | 1.478/1.479/1.480 | 0.007/0.006/0.006 | |
| Autumn | 0.910/0.912/0.913 | 0.709/0.683/0.660 | 1.520/1.522/1.524 | 0.013/0.011/0.011 | |
| Winter | 0.889/0.893/0.896 | 0.704/0.677/0.654 | 1.533/1.539/1.545 | 0.016/0.014/0.013 | |
| Xuzhou | Spring | 0.930/0.940/0.949 | 0.728/0.698/0.672 | 1.463/1.478/1.493 | 0.006/0.005/0.004 |
| Summer | 0.959/0.958/0.956 | 0.738/0.698/0.662 | 1.398/1.409/1.419 | 0.007/0.006/0.005 | |
| Autumn | 0.937/0.941/0.945 | 0.728/0.700/0.676 | 1.467/1.473/1.478 | 0.007/0.006/0.005 | |
| Winter | 0.907/0.912/0.916 | 0.705/0.670/0.639 | 1.483/1.499/1.513 | 0.010/0.009/0.008 |
| Sites | N | r | RMSE | MAE | RMB | within EE (%) | Above EE (%) | Below EE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 104 | 0.897 | 0.126 | 0.09 | 1.082 | 70.31 | 18.54 | 11.15 |
| Beijing_PKU | 70 | 0.919 | 0.139 | 0.105 | 0.964 | 68.2 | 16.87 | 14.93 |
| Beijing-CAMS | 56 | 0.874 | 0.148 | 0.093 | 0.971 | 69.24 | 16.32 | 14.44 |
| Beijing_RADI | 41 | 0.893 | 0.155 | 0.091 | 1.02 | 67.87 | 17.58 | 14.55 |
| XiangHe | 84 | 0.945 | 0.113 | 0.081 | 0.975 | 74.69 | 16.97 | 8.34 |
| XuZhou | 74 | 0.942 | 0.08 | 0.095 | 1.044 | 72.87 | 16.44 | 10.69 |
| urban areas | 271 | 0.895 | 0.143 | 0.096 | 1.011 | 69.01 | 17.5 | 13.49 |
| rural areas | 158 | 0.943 | 0.097 | 0.088 | 1.009 | 73.84 | 16.72 | 9.44 |
| All sites | 429 | 0.922 | 0.122 | 0.089 | 1.05 | 71.33 | 17.88 | 10.79 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Wei, J.; Zhang, N.; He, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Yu, H.; Sun, L. Retrieving High-Resolution Aerosol Optical Depth from GF-4 PMS Imagery in Eastern China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3752. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183752
Sun Z, Wei J, Zhang N, He Y, Sun Y, Liu X, Yu H, Sun L. Retrieving High-Resolution Aerosol Optical Depth from GF-4 PMS Imagery in Eastern China. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(18):3752. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183752
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zhendong, Jing Wei, Ning Zhang, Yulong He, Yu Sun, Xirong Liu, Huiyong Yu, and Lin Sun. 2021. "Retrieving High-Resolution Aerosol Optical Depth from GF-4 PMS Imagery in Eastern China" Remote Sensing 13, no. 18: 3752. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183752
APA StyleSun, Z., Wei, J., Zhang, N., He, Y., Sun, Y., Liu, X., Yu, H., & Sun, L. (2021). Retrieving High-Resolution Aerosol Optical Depth from GF-4 PMS Imagery in Eastern China. Remote Sensing, 13(18), 3752. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183752