Seasonality and Characterization Mapping of Restored Tidal Marsh by NDVI Imageries Coupling UAVs and Multispectral Camera
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Field Survey
2.3. UAV Surveys and Data Analysis
2.4. Multispectral Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Orthophoto
3.2. Vegetation Characterization by NDVI
3.3. Field Measurements of Marsh Characteristics
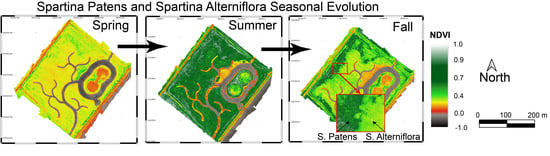
3.4. Marsh Seasonality
3.5. Example of Marsh Encroachment Monitoring
4. Discussion
4.1. Coastal Wetlands Monitoring by UAVs
4.2. Vegetation Species Characterization
4.3. Methodological Limitations and Future Advances
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moffett, K.B.; Nardin, W.; Silvestri, S.; Wang, C.; Temmerman, S. Multiple Stable States and Catastrophic Shifts in Coastal Wetlands: Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities in Validating Theory Using Remote Sensing and Other Methods. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10184–10226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nardin, W.; Larsen, L.; Fagherazzi, S.; Wiberg, P. Tradeoffs among hydrodynamics, sediment fluxes and vegetation community in the Virginia Coast Reserve, USA. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 210, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleri, J.R.; Lera, S.; Gerevini, A.; Staver, L.; Nardin, W. Empirical observations and numerical modelling of tides, channel morphology, and vegetative effects on accretion in a restored tidal marsh. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2019, 44, 2223–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagherazzi, S.; Mariotti, G.; Leonardi, N.; Canestrelli, A.; Nardin, W.; Kearney, W.S. Salt Marsh Dynamics in a Period of Accelerated Sea Level Rise. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2020, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.; Silliman, B. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourqurean, J.; Duarte, C.M.; Kennedy, H.; Marbà, N.; Holmer, M.; Mateo, M.; Apostolaki, E.; Kendrick, G.; Krause-Jensen, D.; McGlathery, K.J.; et al. Seagrass ecosystems as a globally significant carbon stock. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallenger, A.H.; Doran, K.; Howd, P.A. Hotspot of accelerated sea-level rise on the Atlantic coast of North America. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, W.B. The Disappearing Islands of the Chesapeake; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Craft, C.; Clough, J.; Ehman, J.; Joye, S.; Park, R.; Pennings, S.; Guo, H.; Machmuller, M. Forecasting the effects of accelerated sea-level rise on tidal marsh ecosystem services. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russ, E.R.; Palinkas, C. Seasonal-Scale and Decadal-Scale Sediment-Vegetation Interactions on the Subaqueous Susquehanna River Delta, Upper Chesapeake Bay. Chesap. Sci. 2018, 41, 2092–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudd, S.M.; Fagherazzi, S.; Morris, J.T.; Furbish, D.J. Flow, sedimentation, and biomass production on a vegetated salt marsh in South Carolina: Toward a predictive model of marsh morphologic and ecologic evolution. Ecogeomorphol. Tidal Marshes Coast. Estuar. Stud. 2004, 59, 165–187. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, J.T.; Sundareshwar, P.V.; Nietch, C.T.; Kjerfve, B.; Cahoon, D.R. Responses of coastal wetlands to rising sea level. Ecology 2002, 83, 2869–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmerman, S.; Bouma, T.J.; Govers, G.; Wang, Z.B.; De Vries, M.; Herman, P. Impact of vegetation on flow routing and sedimentation patterns: Three-dimensional modeling for a tidal marsh. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, M.L.; Murray, A.B. A coupled geomorphic and ecological model of tidal marsh evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6118–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fagherazzi, S.; Kirwan, M.L.; Mudd, S.M.; Guntenspergen, G.R.; Temmerman, S.; D’Alpaos, A.; Van De Koppel, J.; Rybczyk, J.M.; Reyes, E.; Craft, C.B.; et al. Numerical models of salt marsh evolution: Ecological, geomorphic, and climatic factors. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, L.A.; Croft, A.L. The effect of standing biomass on flow velocity and turbulence in Spartina alterniflora canopies. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 69, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.; Smith, J. Wave attenuation by flexible, idealized salt marsh vegetation. Coast. Eng. 2013, 83, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.G.; Kemp, W.M.; Boynton, W. The influence of waves and seagrass communities on suspended particulates in an estuarine embayment. Mar. Geol. 1984, 59, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Sinha, P. Mapping salt-marsh land-cover vegetation using high-spatial and hyperspectral satellite data to assist wetland inventory. GISci. Remote Sens. 2014, 51, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Fagherazzi, S.; Liu, Y. Classification mapping of salt marsh vegetation by flexible monthly NDVI time-series using Landsat imagery. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 213, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardin, W.; Vona, I.; Fagherazzi, S. Sediment deposition affects mangrove forests in the Mekong delta, Vietnam. Cont. Shelf Res. 2020, 213, 104319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddia, Y.; Nardin, W.; Corbau, C.; Franchi, G.; Stevenson, C.J.; Staver, L.W. Channels’ shape evolution detected by UAVs in a restored salt marsh. In Coastal Sediments; World Scientific: Singapore, 2019; pp. 1519–1527. [Google Scholar]
- Adão, T.; Hruška, J.; Pádua, L.; Bessa, J.; Peres, E.; Morais, R.; Sousa, J.J. Hyperspectral Imaging: A Review on UAV-Based Sensors, Data Processing and Applications for Agriculture and Forestry. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staver, L.W.; Stevenson, J.C.; Cornwell, J.C.; Nidzieko, N.J.; Owens, M.S.; Logan, L.; Kim, C.; Malkin, S.Y. Tidal Marsh Restoration at Poplar Island: II. Elevation Trends, Vegetation Development, and Carbon Dynamics. Wetlands 2020, 40, 1687–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardin, W.; Edmonds, D.; Fagherazzi, S. Influence of vegetation on spatial patterns of sediment deposition in deltaic islands during flood. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 93, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bullock, E.L.; Fagherazzi, S.; Nardin, W.; Vo-Luong, P.; Nguyen, P.; Woodcock, C.E. Temporal patterns in species zonation in a mangrove forest in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam, using a time series of Landsat imagery. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 147, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Delgado, R.; Cazacu, C.; Adamescu, M. Rapid Assessment of Ecological Integrity for LTER Wetland Sites by Using UAV Multispectral Mapping. Drones 2018, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, F.-M.; Müllerová, J.; Borgniet, L.; Dommanget, F.; Breton, V.; Evette, A. Using Single- and Multi-Date UAV and Satellite Imagery to Accurately Monitor Invasive Knotweed Species. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villoslada, M.; Bergamo, T.; Ward, R.; Burnside, N.; Joyce, C.; Bunce, R.; Sepp, K. Fine scale plant community assessment in coastal meadows using UAV based multispectral data. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 105979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doughty, C.L.; Cavanaugh, K.C. Mapping Coastal Wetland Biomass from High Resolution Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, I.; Cawkwell, F.; Dwyer, E.; Barrett, B.; Green, S. Satellite remote sensing of grasslands: From observation to management. J. Plant Ecol. 2016, 9, 649–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baena, S.; Moat, J.; Whaley, O.; Boyd, D. Identifying species from the air: UAVs and the very high resolution challenge for plant conservation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cornwell, J.C.; Owens, M.S.; Staver, L.W.; Stevenson, J.C. Tidal Marsh Restoration at Poplar Island I: Transformation of Estuarine Sediments into Marsh Soils. Wetlands 2020, 40, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, W.; Paul, S. Sarbanes Ecosystem Restoration Project at Poplar Island. In Engineering for Sustainable Communities: Principles and Practices; US Army Corps of Engineering: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2017; pp. 411–417. [Google Scholar]
- Kent, J. Water Level Variations at Poplar Island, MD; NOAA Technical Report NOS-OPS 076; NOAA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2015.
- Drummond, C.D.; Harley, M.D.; Turner, I.L.; A Matheen, A.N.; Glamore, W.C. UAV applications to coastal engineering. In Proceedings of the Australasian Coasts & Ports Conference 2015: 22nd Australasian Coastal and Ocean Engineering Conference and the 15th Australasian Port and Harbour Conference, Auckland, New Zealand, 15–18 September 2015; p. 267. [Google Scholar]
- Clapuyt, F.; Vanacker, V.; Van Oost, K. Reproducibility of UAV-based earth topography reconstructions based on Structure-from-Motion algorithms. Geomorphology 2016, 260, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, I.L.; Harley, M.; Drummond, C.D. UAVs for coastal surveying. Coast. Eng. 2016, 114, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Kawahara, Y. UAV Photogrammetry for Monitoring Changes in River Topography and Vegetation. Procedia Eng. 2016, 154, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mancini, F.; Dubbini, M.; Gattelli, M.; Stecchi, F.; Fabbri, S.; Gabbianelli, G. Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) for High-Resolution Reconstruction of Topography: The Structure from Motion Approach on Coastal Environments. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6880–6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hugenholtz, C.H.; Whitehead, K.; Brown, O.W.; Barchyn, T.E.; Moorman, B.; LeClair, A.; Riddell, K.; Hamilton, T. Geomorphological mapping with a small unmanned aircraft system (sUAS): Feature detection and accuracy assessment of a photogrammetrically-derived digital terrain model. Geomorphology 2013, 194, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casella, E.; Rovere, A.; Pedroncini, A.; Stark, C.P.; Casella, M.; Ferrari, M.; Firpo, M. Drones as tools for monitoring beach topography changes in the Ligurian Sea (NW Mediterranean). Geo-Mar. Lett. 2016, 36, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, M.; Robson, S.; D’Oleire-Oltmanns, S.; Niethammer, U. Optimising UAV topographic surveys processed with structure-from-motion: Ground control quality, quantity and bundle adjustment. Geomorphology 2017, 280, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westoby, M.J.; Brasington, J.; Glasser, N.F.; Hambrey, M.J.; Reynolds, J.M. ‘Structure-from-Motion’photogrammetry: A low-cost, effective tool for geoscience applications. Geomorphology 2012, 179, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cook, K. An evaluation of the effectiveness of low-cost UAVs and structure from motion for geomorphic change detection. Geomorphology 2017, 278, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agisoft, L.L.C. PhotoScan User Manual, Professional Edition, Version 1.4. 2018. Available online: http://www.agisoft.com/pdf/photoscan-pro_1_4_en.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2018).
- Taddia, Y.; Russo, P.; Lovo, S.; Pellegrinelli, A. Multispectral UAV monitoring of submerged seaweed in shallow water. Appl. Geomat. 2019, 12, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pomeroy, L.R.; Darley, W.M.; Dunn, E.L.; Gallagher, J.L.; Haines, E.B.; Whitney, D.M. Primary Production. In The Ecology of a Salt Marsh; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981; pp. 39–67. [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher, J.L.; Somers, G.F.; Grant, D.M.; Seliskar, D.M. Persistent Differences in Two Forms of Spartina Alterniflora: A Common Garden Experiment. Ecology 1988, 69, 1005–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonard, R.I.; Judd, F.W.; Stalter, R. The Biological Flora of Coastal Dunes and Wetlands: Spartina patens (W. Aiton) G.H. Muhlenberg. J. Coast. Res. 2010, 265, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ali, Z.M.; Abdullah, M.; Asadalla, N.B.; Gholoum, M. A comparative study of remote sensing classification methods for monitoring and assessing desert vegetation using a UAV-based multispectral sensor. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, I.; Hall, O.; Jirström, M. Remote Sensing of Yields: Application of UAV Imagery-Derived NDVI for Estimating Maize Vigor and Yields in Complex Farming Systems in Sub-Saharan Africa. Drones 2018, 2, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, T.D.; Roberts, B.J. Effects of seasonality and environmental gradients on Spartina alterniflora allometry and primary production. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 9676–9688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raposa, K.B.; Wasson, K.; Smith, E.; Crooks, J.A.; Delgado, P.; Fernald, S.H.; Ferner, M.C.; Helms, A.; Hice, L.A.; Mora, J.W.; et al. Assessing tidal marsh resilience to sea-level rise at broad geographic scales with multi-metric indices. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 204, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schieder, N.W.; Walters, D.C.; Kirwan, M.L. Massive Upland to Wetland Conversion Compensated for Historical Marsh Loss in Chesapeake Bay, USA. Chesap. Sci. 2017, 41, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizad, K.; Hagen, S.C.; Medeiros, S.C.; Bilskie, M.V.; Morris, J.T.; Balthis, L.; Buckel, C.A. Dynamic responses and implications to coastal wetlands and the surrounding regions under sea level rise. PLoS ONE 2016, 13, e0205176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boesch, D.F.; Atkinson, L.P.; Boicourt, W.C.; Boon, J.D.; Cahoon, D.R.; Dalrymple, R.; Ezer, T.A.; Horton, B.P.; Johnson, Z.P.; Kopp, R.E.; et al. Updating Maryland’s Sea-Level Rise Projections; Special Report of the Scientific and Technical Working Group to the Maryland Climate Change Commission; University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science: Cambridge, MD, USA, 2013; 22p. [Google Scholar]
- Boesch, D.F.; Boicourt, W.C.; Cullather, R.I.; Ezer, T.; Galloway, G.E., Jr.; Johnson, Z.P.; Kilbourne, K.H.; Kirwan, M.L.; Kopp, R.E.; Land, S.; et al. Sea-Level Rise: Projections for Maryland; University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science: Cambridge, MD, USA, 2018; 27p. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton-Grier, A.E.; Wowk, K.; Bamford, H. Future of our coasts: The potential for natural and hybrid infrastructure to enhance the resilience of our coastal communities, economies and ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 51, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutton-Grier, A.; Gittman, R.; Arkema, K.; Bennett, R.; Benoit, J.; Blitch, S.; Burks-Copes, K.; Colden, A.; Dausman, A.; DeAngelis, B.; et al. Investing in Natural and Nature-Based Infrastructure: Building Better Along Our Coasts. Sustainability 2018, 10, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farris, A.S.; Defne, Z.; Ganju, N.K. Identifying Salt Marsh Shorelines from Remotely Sensed Elevation Data and Imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klemas, V.V. Coastal and Environmental Remote Sensing from Unmanned Aerial Vehicles: An Overview. J. Coast. Res. 2015, 315, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinton, D.; Canestrelli, A.; Fantuzzi, L. A UAV-Based Dye-Tracking Technique to Measure Surface Velocities over Tidal Channels and Salt Marshes. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, C.; Jóźków, G. Remote sensing platforms and sensors: A survey. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, A.; Long, B.; Archambault, P. Salt-marsh characterization, zonation assessment and mapping through a dual-wavelength LiDAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, D.J.; Schweik, C.M.; Wicks, R.; Bowlick, F.; Carullo, M. Developing a land cover classification of salt marshes using uas time-series imagery and an open source workflow. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 42, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]










| Aircraft Specifications | ||
| Type | DJI Phantom 3 Professional | |
| Take off weight | 1280 g | |
| Max flight speed | 16 m/s | |
| Max flight time * | 18–20 min | |
| Hovering accuracy | Horizontal | ±0.3–1.5 m |
| Vertical | ±0.1–0.5 m | |
| Camera Specification | ||
| Name | DJI FC300X | MicaSense RedEdge-M |
| Type | RGB | Multispectral with Global Shutter |
| Focal length | 3.6 mm | 5.5 mm |
| 35 mm equiv. focal length | 20 mm | 39.7 mm |
| Image resolution | 4000 × 3000 | 1280 × 960 |
| Field of view | 84° | 48.8° |
| GSD at 40 m altitude | ≈1.8 cm | ≈2.8 cm |
| April | May | August | October | November |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. pumilus | ||||
| Area A | ||||
| 0.28 | 0.45 | 0.73 | 0.71 | 0.70 |
| Area B | ||||
| 0.26 | 0.37 | 0.76 | 0.77 | 0.74 |
| Area C | ||||
| 0.29 | 0.39 | 0.68 | 0.66 | 0.63 |
| Area D | ||||
| 0.27 | 0.39 | 0.76 | 0.66 | 0.62 |
| S. alterniflora | ||||
| Area E | ||||
| 0.23 | 0.36 | 0.67 | 0.43 | 0.33 |
| Area F | ||||
| 0.23 | 0.41 | 0.64 | 0.43 | 0.35 |
| Area G | ||||
| 0.26 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.30 | 0.32 |
| Area H | ||||
| 0.26 | 0.49 | 0.60 | 0.33 | 0.31 |
| Month Identification | Date (Day/Month/Year) |
|---|---|
| April 2019 | 3 April 2019 |
| May 2019 | 2 May 2019 |
| August 2019 | 29 August 2019 |
| October 2019 | 3 October 2019 |
| November 2019 | 14 November 2019 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nardin, W.; Taddia, Y.; Quitadamo, M.; Vona, I.; Corbau, C.; Franchi, G.; Staver, L.W.; Pellegrinelli, A. Seasonality and Characterization Mapping of Restored Tidal Marsh by NDVI Imageries Coupling UAVs and Multispectral Camera. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4207. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214207
Nardin W, Taddia Y, Quitadamo M, Vona I, Corbau C, Franchi G, Staver LW, Pellegrinelli A. Seasonality and Characterization Mapping of Restored Tidal Marsh by NDVI Imageries Coupling UAVs and Multispectral Camera. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(21):4207. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214207
Chicago/Turabian StyleNardin, William, Yuri Taddia, Michela Quitadamo, Iacopo Vona, Corinne Corbau, Giulia Franchi, Lorie W. Staver, and Alberto Pellegrinelli. 2021. "Seasonality and Characterization Mapping of Restored Tidal Marsh by NDVI Imageries Coupling UAVs and Multispectral Camera" Remote Sensing 13, no. 21: 4207. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214207
APA StyleNardin, W., Taddia, Y., Quitadamo, M., Vona, I., Corbau, C., Franchi, G., Staver, L. W., & Pellegrinelli, A. (2021). Seasonality and Characterization Mapping of Restored Tidal Marsh by NDVI Imageries Coupling UAVs and Multispectral Camera. Remote Sensing, 13(21), 4207. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214207