Atmospheric Correction of Airborne Hyperspectral CASI Data Using Polymer, 6S and FLAASH
Abstract
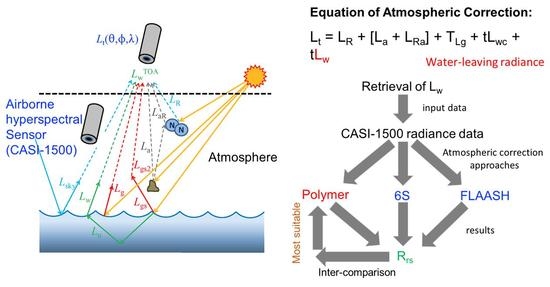
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Airborne Hyperspectral Data
2.2. Satellite and Reanalysis Data
2.3. Polymer Atmospheric Correction Approach
2.4. 6S Atmospheric Correction Approach
2.5. FLAASH Atmospheric Correction Approach
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CASI-1500 Radiance and Apparent Reflectance
3.2. Polymer, 6S, and FLAASH Results for CASI-1500
3.3. Comparison of the Polymer Results for CASI-1500 and MODIS
3.4. Variation of Polymer Results with Aerosol and Water Vapor for CASI-1500
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison among Polymer, 6S, and FLAASH
4.2. Discrepancy of the CASI-1500 and MODIS Rrs with Polymer
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Perk, R.L.; Gurlin, D.; Rundquist, D.C.; Leavitt, B.C.; Barrow, T.M.; Brakhage, P. Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid productive waters using airborne hyperspectral data. Water Res. 2012, 46, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gould, R.W., Jr.; Arnone, R.A. Remote sensing estimates of inherent optical properties in a coastal environment. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallio, K.; Kutser, T.; Hannonen, T.; Koponen, S.; Pulliainen, J.; Vepsaälaäinen, J.; Pyhaälahti, T. Retrieval of water quality from airborne imaging spectrometry of various lake types in different seasons. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 268, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Franz, B.; Ahmad, Z.; Healy, R.; Knobelspiesse, K.; Gao, B.; Proctor, C.; Zhai, P.-W. Atmospheric correction for hyperspectral ocean color retrieval with application to the Hyperspectral Imager for the Coastal Ocean (HICO). Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, B.C.; Montes, M.J.; Davis, C.O.; Goetz, A.F.H. Atmospheric correction algorithms for hyperspectral remote sensing data of land and ocean. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, S17–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.C.; Davis Curtiss, O.; Goetz, A.F.H. A review of atmospheric correction techniques for hyperspectral remote sensing of land surfaces and ocean colour. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Denver, CO, USA, 31 July–4 August 2006; pp. 1979–1981. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.-C.; Montes, M.J.; Ahmad, Z.; Davis, C.O. Atmospheric correction algorithm for hyperspectral remote sensing of ocean color from space. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qu, Z.; Goetz, A.F.H.; Heidebrecht, K.B. High accuracy atmospheric correction for hyperspectral data (HATCH). In Proceedings of the Ninth JPL Airborne Earth Science Workshop, 23–25 February 2000; Green, R.O., Ed.; Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.-C.; Heidebrecht, K.H.; Goetz, A.F.H. Derivation of scaled surface reflectances from AVIRIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 44, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, F.A. Use of airborne imaging spectrometer data to map minerals associated with hydrothermally altered rocks in the northern Grapevine Mountains, Nevada and California. Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 24, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.N.; King, T.V.V. Causes of spurious features in spectral reflectance data. In Proceedings of the 3rd Airborne Imaging Spectrometer Data Analysis Workshop; Vane, G., Ed.; Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 1987; pp. 49–61. [Google Scholar]
- Conel, J.E.; Green, R.O.; Vane, G.; Bruegge, C.J.; Alley, R.E. AIS-2 radiometry and a comparison of methods for the recovery of ground reflectance. In Proceedings of the 3rd Airborne Imaging Spectrometer Data Analysis Workshop; Vane, G., Ed.; Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 1987; pp. 18–47. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, D.A.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Lyon, R. Comparison of various techniques for calibration of AIS data. In Proceedings of the 2nd Airborne Imaging Spectrometer Data Analysis Workshop; Vane, G., Goetz, A.F.H., Eds.; Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 1986; pp. 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz, F.; Deschamps, P.-Y.; Ramon, D. Atmospheric correction in presence of sun glint: Application to MERIS. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 9783–9800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pu, R.; Landry, S.; Zhang, J. Evaluation of Atmospheric Correction Methods in Identifying Urban Tree Species with WorldView-2 Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1886–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanonckelen, S.; Lhermitte, S.; Van Rompaey, A. The effect of atmospheric and topographic correction methods on land cover classification accuracy. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 24, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Hajj, M.; Bégué, A.; Lafrance, B.; Hagolle, O.; Dedieu, G.; Rumeau, M. Relative Radiometric Normalization and Atmospheric Correction of a SPOT 5 Time Series. Sensors 2008, 8, 2774–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eugenio, F.; Marcello, J.; Martin, J.; Esparragón, D.R. Benthic habitat mapping using multispectral high-resolution imagery: Evaluation of shallow water atmospheric correction techniques. Sensors 2017, 17, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marcello, J.; Eugenio, F.; Perdomo, U.; Medina, A. Assessment of Atmospheric Algorithms to Retrieve Vegetation in Natural Protected Areas Using Multispectral High-resolution Imagery. Sensors 2016, 16, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.C.; Jung, J.; Lee, J.; Choi, S.U.; Hong, S.Y.; Heo, J. Optimal Atmospheric Correction for Above-Ground Forest Biomass Estimation with the ETM+ Remote Sensor. Sensors 2015, 15, 18865–18886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinmetz, F.; Ramon, D. Sentinel-2 MSI and Sentinel-3 OLCI consistent ocean colour products using POLYMER. In Remote Sensing of the Open and Coastal Ocean and Inland Waters; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; p. 107780E. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Hu, C.; Cannizzaro, J.; English, D.; Barnes, B.B.; Carlson, P.; Yarbro, L. Comparison of two atmospheric correction approaches applied to MODIS measurements over north American waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 442–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Lee, Z.P.; Wei, J.W.; Du, K.P. A Scheme of Atmospheric Correction with A Revised POLYMER model Using Same-day Observations. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 26953–26976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.; Tanré, D.; Deuzé, J.; Herman, M.; Morcrette, J.; Kotchenova, S. Second simulation of a satellite signal in the solar spectrum-vector (6SV) 6S User Guide Version 3. In Remote Sensing: Models and Methods for Image Processing; Schowengerdt, R.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kotchenova, S.Y.; Vermote, E.F. Validation of a vector version of the 6S radiative transfer code for atmospheric correction of satellite data, Part II: Homogeneous Lambertian and anisotropic surfaces. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 4455–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotchenova, S.Y.; Vermote, E.F.; Matarrese, R.; Klemm, F.J., Jr. Validation of a vector version of the 6S radiative transfer code for atmospheric correction of satellite data, Part I: Path radiance. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 6762–6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, L.Y.; Liu, L.L.; Peng, D.L.; Jiao, Q.J.; Zhang, H. A Landsat-5 atmospheric correction based on MODIS atmosphere products and 6S model. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1609–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, F.A. Comparison of ATREM, ACORN, and FLAASH atmospheric corrections using low-altitude AVIRIS data of Boulder, Colorado. In Proceedings of the 13th JPL Airborne Geosci. Workshop; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Carder, K. Atmospheric correction for airborne sensors: Comment on a scheme used for CASI. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 79, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler-Golden, S.; Berk, A.; Bernstein, L.S.; Richtsmeier, S.; Acharya, P.K.; Matthew, M.W.; Anderson, G.P.; Allred, C.L.; Jeong, L.S.; Chetwynd, J.H. FLAASH, a modtran4 atmospheric correction package for hyperspectral data retrievals and simulations. In Proceedings of the 7th JPL Airborne Earth Sci Workshop, Pasadena, CA, USA, 12–16 January 1998; Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.; Kim, S.H.; Baek, S.; Kim, H.; Oh, J. A Preliminary Study on Benthic Mapping of Uljin Coast Based on Airborne Hyperspectral Imagery Towards the Whitening Detection. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 114, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C.; Munk, W. Measurement of the roughness of the sea surface from photographs of the sun’s glitter. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1954, 44, 838–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Bailey, S.W. Correction of sun glint contamination on the SeaWiFS ocean and atmosphere products. Appl. Opt. 2001, 40, 4790–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, T.; Anderson, G.P.; Felde, G.W.; Hoke, M.L.; Ratkowski, A.J.; Chetwynd, J.H.; Gardner, J.A.; Adler-Golden, S.M.; Matthew, M.W.; Berk, A. FLAASH, a MODTRAN4-based atmospheric correction algorithm, its application and validation. IEEE Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. Symp. 2002, 3, 1414–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Schowengerdt, R.A. Remote Sensing: Models and Methods for Image Processing; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Lee, Z.-P.; Shang, S. A system to measure the data quality of spectral remote sensing reflectance of aquatic environments. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 8189–8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Wang, M. Retrieval of water-leaving radiance and aerosol optical thickness over the oceans with SeaWiFS: A preliminary algorithm. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C. Land adjacency effects on MODIS Aqua top-of-atmosphere radiance in the shortwave infrared: Statistical assessment and correction. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 4802–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Band Number | Center Wavelength (nm) | Band Number | Center Wavelength (nm) | Band Number | Center Wavelength (nm) | Band Number | Center Wavelength (nm) | Full Width at Half Maximum (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 370.2 | 13 | 542.8 | 25 | 715.1 | 37 | 887.1 | 7.2 |
| 2 | 384.6 | 14 | 557.2 | 26 | 729.4 | 38 | 901.5 | |
| 3 | 399 | 15 | 571.5 | 27 | 743.7 | 39 | 915.8 | |
| 4 | 413.4 | 16 | 585.9 | 28 | 758.1 | 40 | 930.2 | |
| 5 | 427.8 | 17 | 600.3 | 29 | 772.4 | 41 | 944.5 | |
| 6 | 442.2 | 18 | 614.6 | 30 | 786.8 | 42 | 958.8 | |
| 7 | 456.6 | 19 | 629.0 | 31 | 801.1 | 43 | 973.2 | |
| 8 | 471 | 20 | 643.3 | 32 | 815.4 | 44 | 987.5 | |
| 9 | 485.3 | 21 | 657.7 | 33 | 829.8 | 45 | 1001.9 | |
| 10 | 499.7 | 22 | 672.0 | 34 | 844.1 | 46 | 1016.2 | |
| 11 | 514.1 | 23 | 686.4 | 35 | 858.5 | 47 | 1030.6 | |
| 12 | 528.5 | 24 | 700.7 | 36 | 872.8 | 48 | 1044.9 |
| Parameters | Data Source | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solar zenith angle | – | – | – | 33.663° |
| Solar azimuth angle | – | – | – | 239.218° |
| Sensor zenith angle | – | – | – | By pixel |
| Sensor azimuth angle | – | – | – | 270° |
| Total water vapour | MYD05 | 1 km × 1 km | Daily | 1.77 cm |
| Total ozone | MYD07 | 1 km × 1 km | Daily | 0.34 cm-atm |
| Aerosol model | – | – | – | Maritime |
| aot_550 | MERRA-2 | 0.5° × 0.625° | Hourly | 0.32 |
| Wind speed | MERRA-2 | 0.5° × 0.625° | Hourly | 1.91 m s−1 |
| Wind azimuth angle | – | – | – | 313.004° |
| Chl-a concentration | MODIS-Aqua Level-2 | 1 km × 1 km | Daily | 3.76 mg m−3 |
| Sea water salinity | – | 34.3 ppt |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Image center location | 37.05057344°N, 129.41963701°E. |
| Sensor altitude | 2 km |
| Ground elevation | 0.01 km |
| Pixel size | 1 m |
| Flight date | 4-May-19 |
| Flight time GMT | 5:17:47 |
| Atmospheric model | Mid-Latitude Summer |
| Aerosol model | Maritime |
| Aerosol retrieval | None |
| Initial visibility | 14.85 km |
| Water retrieval | Yes |
| Water absorption feature | 940 nm |
| Modtran resolution | 5 cm−1 |
| Modtran multiscatter model | Scaled DISORT |
| DISCORT streams number | 8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, M.; Hu, Y.; Tian, H.; Khan, F.A.; Liu, Q.; Goes, J.I.; Gomes, H.d.R.; Kim, W. Atmospheric Correction of Airborne Hyperspectral CASI Data Using Polymer, 6S and FLAASH. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5062. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13245062
Yang M, Hu Y, Tian H, Khan FA, Liu Q, Goes JI, Gomes HdR, Kim W. Atmospheric Correction of Airborne Hyperspectral CASI Data Using Polymer, 6S and FLAASH. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(24):5062. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13245062
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Mengmeng, Yong Hu, Hongzhen Tian, Faisal Ahmed Khan, Qinping Liu, Joaquim I. Goes, Helga do R. Gomes, and Wonkook Kim. 2021. "Atmospheric Correction of Airborne Hyperspectral CASI Data Using Polymer, 6S and FLAASH" Remote Sensing 13, no. 24: 5062. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13245062
APA StyleYang, M., Hu, Y., Tian, H., Khan, F. A., Liu, Q., Goes, J. I., Gomes, H. d. R., & Kim, W. (2021). Atmospheric Correction of Airborne Hyperspectral CASI Data Using Polymer, 6S and FLAASH. Remote Sensing, 13(24), 5062. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13245062