A Novel Unsupervised Classification Method for Sandy Land Using Fully Polarimetric SAR Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
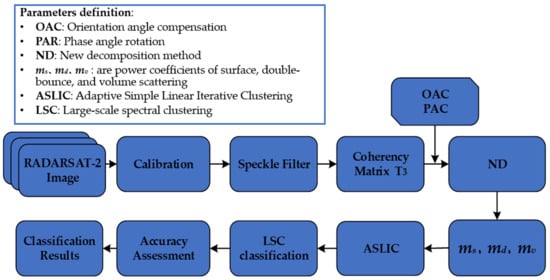
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Preprocessing
3.2. New Decomposition
3.2.1. Removal
3.2.2. Adaptive Model-Based Decomposition
3.3. LSC Classification
3.3.1. Superpixels Segmentation
3.3.2. LSC Classification
- Segment the PolSAR image into superpixels with ASLIC.
- Calculate the mean values of (ms, md, mv) in each superpixel region to form representative points.
- Calculate similarity matrix Z between representative points and Laplacian matrix Lrw.
- Calculate eigenvectors corresponding to the first K largest eigenvalues of matrix Lrw as a matrix Q = [q1, q2, … qk].
- Normalize matrix Q with Equation (24).
- Cluster the row vectors of normalization matrix V with k-means.
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Decomposition Results
4.2. Superpixels Generation Results
4.3. Classification Results
5. Discussion
- ND strategy can more effectively obtain polarization parameters than other decomposition strateges. There are two main reasons for this phenomenon. One is that the traditional decomposition strategy has a better performance for PolSAR imagery in other fields, but the characteristics of Hunshandake Sandy land are not very ideal. Another reason is that OAC and PAR are not performed and volume scattering models cannot adapt to the environment in natural and artificial areas during decomposition, which affects the decomposition result. After OAC and PAR strategy, which enhances the T11 and T22 elements of coherence matrix T3 power. Among them element T11 is relevant to surface scattering mechanism; element T22 is relevant to double-scattering mechanism. In other words, classes dominated by surface scattering and double-scattering mechanism can be classify accurately. Therefore, the polarization parameters extracted by ND strategy can be utilized to generate superpixels in Hunshandake Sandy land.
- There are the details that cannot be ignored of the classification result in Figure 10b, the obvious thing that can be observed is the road area around the lake. This phenomenon is not commission errors, classifying areas that are not roads as roads. This could be put down to the fact that both classes are predominantly surface scattering (water surface and roads surface) with relatively low surface roughness. The ground is very smooth after some small lakes degraded, which makes very similar to scattering mechanism of road. This would indicate that this specific environment has a polarimetric signature that could be associated with many classes.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, I.; Cawkwell, F.; Dwyer, E.; Barrett, B. Satellite remote sensing of grasslands: From observation to management. J. Plant Ecol. 2016, 6, 649–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Förster, M.; Schmidt, T.; Schuster, C. Multi-Temporal Detection of Grassland Vegetation with RapidEye Imagery and a Spectral-Temporal Library. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 4930–4933. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, A.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Younis, M.; Krieger, G.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K. A Tutorial on synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hajnsek, I.; Jagdhuber, T.; Schon, H. Potential of Estimating Soil Moisture under Vegetation Cover by Means of PolSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Jiao, L.; Hou, B.; Yang, S. POL-SAR image classification based on Wishart DBN and local spatial information. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 3292–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R. Polarisation: Applications in Remote Sensing; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 53–54. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, G.; Zhu, J.; Tang, Y.; Shen, P.; Zhu, Z. A Crop Classification Method Integrating GF-3 PolSAR and Sentinel-2A Optical Data in the Dongting Lake Basin. Sensors 2018, 18, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buckley, J.R.; Smith, A.M. Monitoring grasslands with RADARSAT 2 quad-pol imagery. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 3090–3093. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.M.; Buckley, J.R. Investigating RADARSAT-2 as a tool for monitoring grassland in western Canada. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 37, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Xu, B.; Yang, X. Using MODIS time series data to estimate aboveground biomass and its spatio-temporal variation in Inner Mongolia’s grassland between 2001 and 2011. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 7796–7810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Wang, H.J.F.; Liao, C.H. On the Use of Neumann Decomposition for Crop Classification Using Multi-Temporal RADARSAT-2 Polarimetric SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 8, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freeman, A.; Durden, S.L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, G.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Park, S.; Cui, Y.; Kobayashi, H. Hybrid Freeman/Eigenvalue Decomposition Method With Extended Volume Scattering Model. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Wang, X.S.; Li, Y.Z.; Sato, M. Adaptive model-based polarimetric decomposition using polinsarcoherence. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 1705–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Yang, J.; Kobayashi, H.; Park, S.E.; Singh, G. On Complete Model-Based Decomposition of Polarimetric SAR Coherency Matrix Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 1991–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Wang, X.S.; Li, Y.Z.; Sato, M. General Polarimetric Model-Based Decomposition for Coherency Matrix. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 1843–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, N.; Minh, N.P. A Four-Component Decomposition Model for PolSAR Data Using Asymmetric Scattering Component. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Singh, G.; Manickam, S.; Yamaguchi, Y. An adaptive general four-component scattering power decomposition with unitary transformation of coherency matrix (AG4U). IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 2110–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.X.; Burgin, M.S.; van Zyl, J.J. An optimal nonnegative eigenvalue decomposition for the Freeman and Durden three-component scattering model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2167–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, H.; Panigrahi, R.K. Polsar coherency matrix optimization through selective unitary rotations for model-based decomposition scheme. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 16, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himanshu, M.; Kumar, P.R. Non-negative scattering power decomposition for PolSAR data interpretation. IET Radar Sonar Navigation. 2018, 12, 593–602. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, W.Q.; Wang, S.; Hou, B. Semi-supervised Learning for Classification of Polarimetric SAR Images Based on SVM-Wishart. J. Radars 2015, 4, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiao, L.; Liu, F. Spectral Clustering Ensemble Applied to SAR Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 2126–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kersten, P.R.; Lee, J.-S.; Ainsworth, T.L. Unsupervised classification of polarimetric synthetic aperture radar images using fuzzy clustering and EM clustering. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Yang, W.; Bai, Y. Unsupervised classification of polarimetric SAR imagery using large-scale spectral clustering with spatial constraints. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 2816–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xia, J.; Tan, X.; Zhou, X. PolSAR Image Classification via Learned Superpixels and QCNN Integrating Color Feature. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Ni, J.; Yin, Q.; Li, W. Nearest-Regularized Subspace Classification for PolSAR Imagery Using Polarimetric Feature Vector and Spatial Information. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Malik, J. Normalized cuts and image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 888–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Yang, S.; Liu, X. Superpixel-Based Classification Using K Distribution and Spatial Context for Polarimetric SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lang, F.; Yang, J.; Yan, S. Superpixel Segmentation of Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Images Based on Generalized Mean Shift. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Y.; Milne, A.K.; Forster, B.C. Segmentation and Classification of Vegetated Areas Using Polarimetric SAR Image Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achanta, R.; Shaji, A.; Smith, K.; Lucchi, A.; Fua, P.; Süsstrunk, S. SLIC Superpixels Compared to State-of-the-Art Superpixel Methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Int. 2012, 34, 2274–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, F.; Guo, J.; Lang, F. Superpixel Segmentation for Polarimetric SAR Imagery Using Local Iterative Clustering. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Kou, H.; Jiao, L. Classification of polarimetric SAR images using multilayer autoencoders and superpixels. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 3072–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Shi, A.; Huang, H.; Mayer, H. BAS4Net: Boundary-Aware Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation Network for Very High Resolution Remote Sensing Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. In Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5398–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Hu, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, K.; Liu, X.; Yu, W. Superpixel-based classification of polarimetric synthetic aperture radar images. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE RadarCon (RADAR), Kansas City, MO, USA, 23–27 May 2011; pp. 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Qin, A.K.; Clausi, D.A.; Member, S. Unsupervised Polarimetric SAR Image Segmentation and Classification Using Region Growing With Edge Penalty. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1302–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Sun, X.; Diao, W.; Fu, K. FMSSD: Feature-Merged Single-Shot Detection for Multiscale Objects in Large-Scale Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 3377–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Wang, P.; Diao, W.; Fu, K. SRAF-Net: Shape Robust Anchor-Free Network for Garbage Dumps in Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Transactions Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Parameters | Statement |
|---|---|
| Wave mode | Fine quad polarization |
| Polarization types | HH VV HV VH |
| Sampling pixel spacing | ~4.73 m |
| Sampling line spacing | ~4.94 m |
| Pass direction | Descent |
| Ellipsoid name | WGS 84 |
| Land Cover | Number of Pixels | Number of Fields |
|---|---|---|
| Residents(RT) | 23,088 | 1 |
| Roads(RD) | 44,291 | 2 |
| Semi-vegetation Sand(SS) | 84,291 | 7 |
| Sandy Land(DL) | 127,600 | 5 |
| Saline Land(SL) | 43,600 | 3 |
| Vegetation(V) | 28,925 | 6 |
| Lakes(L) | 137,320 | 4 |
| Mean_ms (Zone 1) | Mean_md (Zone 2) | Mean_mv (Zone 3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HFED | 0.867 | 0.518 | 0.828 |
| HFEDV | 0.869 | 0.547 | 0.790 |
| ND | 0.988 | 0.604 | 0.710 |
| Class | HED-SC | ND-RF | ND-LSC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA (%) | UA (%) | PA (%) | UA (%) | PA (%) | UA (%) | |
| RT | 81.17 | 95.19 | 85.42 | 73.64 | 90.22 | 96.94 |
| RD | 89.05 | 64.51 | 91.35 | 68.69 | 98.75 | 95.45 |
| SS | 91.31 | 84.28 | 93.45 | 85.36 | 94.62 | 87.28 |
| DL | 87.82 | 89.64 | 86.19 | 90.39 | 93.21 | 87.13 |
| SL | 81.69 | 94.37 | 84.67 | 94.75 | 91.02 | 87.07 |
| V | 75.20 | 90.54 | 79.89 | 94.47 | 97.87 | 69.65 |
| L | 96.35 | 99.67 | 96.86 | 99.68 | 98.07 | 74.59 |
| OA (%) | 89.68 | 90.02 | 95.22 | |||
| Kappa | 0.8717 | 0.9205 | 0.9404 | |||
| Location | Longitude and Latitude | Land Cover |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 115°56′52″ E 42°42′23″ N | Vegetable I |
| 2 | 115°56′17″ E 42°42′12″ N | Vegetable II |
| 3 | 115°55′25″ E 42°42′1″ N | Semi-vegetation Sand |
| 4 | 115°54′21″ E 42°35′57″ N | Lake I |
| 5 | 115°55′46″ E 42°35′9″ N | Lake II |
| 6 | 115°54′21″ E 42°35′57″ N | Saline Land I |
| 7 | 115°54′39″ E 42°35′47″ N | Saline Land II |
| 8 | 115°59′9″ E 42°43′2″ N | Sandy Land I |
| 9 | 115°57′58″ E 42°41′39″ N | Sandy Land II |
| 10 | 115°56′2″ E 42°41′58″ N | Road I |
| 11 | 115°56′22″ E 42°39′41″ N | Road II |
| 12 | 115°56′2″ E 42°41′58″ N | Residents |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, W.; Sun, B.; Xiao, C.; Huang, P.; Xu, W.; Yang, W. A Novel Unsupervised Classification Method for Sandy Land Using Fully Polarimetric SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030355
Tan W, Sun B, Xiao C, Huang P, Xu W, Yang W. A Novel Unsupervised Classification Method for Sandy Land Using Fully Polarimetric SAR Data. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(3):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030355
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Weixian, Borong Sun, Chenyu Xiao, Pingping Huang, Wei Xu, and Wen Yang. 2021. "A Novel Unsupervised Classification Method for Sandy Land Using Fully Polarimetric SAR Data" Remote Sensing 13, no. 3: 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030355
APA StyleTan, W., Sun, B., Xiao, C., Huang, P., Xu, W., & Yang, W. (2021). A Novel Unsupervised Classification Method for Sandy Land Using Fully Polarimetric SAR Data. Remote Sensing, 13(3), 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030355