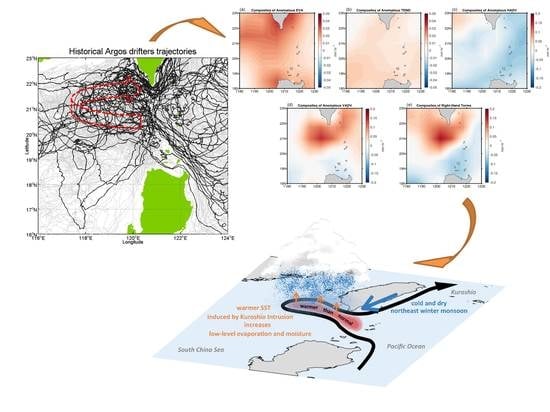
Impacts of the Kuroshio Intrusion through the Luzon Strait on the Local Precipitation Anomaly
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
3. Kuroshio Intrusion Characteristics
4. Atmospheric Responses to Kuroshio Intrusion
4.1. Composite Analysis
4.2. Backward Running Composite Analysis
4.3. Mechanism of Kuroshio Intrusion Triggering the Local Precipitation Anomaly
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nitani, H. Beginning of the Kuroshio. In Kuroshio, Its Physical Aspects; Stommel, H., Yoshida, K., Eds.; University of Tokyo Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1972; pp. 129–163. [Google Scholar]
- Nan, F.; Xue, H.; Chai, F.; Shi, L.; Shi, M.; Guo, P. Identification of different types of Kuroshio intrusion into the South China Sea. Ocean Dyn. 2011, 61, 1291–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.P.; Su, J.L. Hydrological analysis of Kuroshio water intrusion into the South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2000, 19, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.R.; Chiang, T.L. Mesoscale eddies in the northern South China Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part II 2007, 54, 1575–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, P.; Chai, F.; Shi, L.; Xue, H.J.; Chao, Y. A census of eddy activities in the South China Sea during 1993–2007. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, C03012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frenger, I.; Gruber, N.; Knutti, R.; Münnich, M. Imprint of Southern Ocean eddies on winds, clouds and rainfall. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashizume, H.; Xie, S.P.; Liu, W.T.; Takeuchi, K. Local and remote atmospheric response to tropical instability waves: A global view from space. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 10173–10185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, M.; Xie, S.P. Covariations of sea surface temperature and wind over the Kuroshio and its extension: Evidence for ocean-to-atmospheric feedback. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 1404–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthes, R.A. The height of the planetary boundary layer and production of the circulation in a sea-breeze model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1987, 35, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kousky, V.E. Diurnal rainfall variability in Northeast Brazil. Mon. Weather Rev. 1980, 108, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, R.; Turco, R.P. Air pollutant transport in a coastal environment. Part 1: Two-dimensional simulations of sea-breeze and mountain effects. J. Atmos. Sci. 1994, 51, 2285–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franchito, S.H.; Rao, V.B.; Stech, J.L.; Lorenzzetti, J.A. The effect of coastal upwelling on the sea-breeze circulation at Cabo Frio, Brazil: A numerical experiment. Ann. Geophys. 1998, 16, 866–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindzen, R.S.; Nigam, S. On the Role of Sea Surface Temperature Gradients in Forcing Low-Level Winds and Convergence in the Tropics. J. Atmos. Sci. 1987, 44, 2418–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallace, J.M.; Mitchell, T.P.; Deser, C. The Influence of Sea-Surface Temperature on Surface Wind in the Eastern Equatorial Pacific—Seasonal and Interannual Variability. J. Climate 1989, 2, 1492–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, S.P.; McPhaden, M.J.; Wallace, J.M. The influence of sea surface temperature on surface wind in the eastern equatorial Pacific. J. Clim. 1989, 2, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashizume, H.; Xie, S.-P.; Fujiwara, M.; Shiotani, M.; Watanabe, T.; Tanimoto, Y.; Liu, W.T.; Takeuchi, K. Direct observations of atmospheric boundary layer response to slow SST variations over the eastern equatorial Pacific. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 3379–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inatsu, M.; Mukougawa, H.; Xie, S.-P. Tropical and extratropical SST effects on the midlatitude storm track. J. Meteor. Soc. Jpn. 2002, 80, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Small, R.J.; Xie, S.-P.; Wang, Y. Numerical simulation of atmospheric response to Pacific Tropical Instability Waves. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 3722–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.T.; Xie, X. Double intertropical convergence zones—A new look using scatterometer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Z.W.; Zheng, Q.; Kuo, Y.C.; Gopalakrishnan, G.; Lee, C.Y.; Ho, C.R.; Kuo, N.J.; Huang, S.J. Impacts of coastal upwelling off east Vietnam on the regional winds system: An air-sea-land interaction. Dyn. Atmos. Oceans 2016, 76, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chern, C.S. The warm-core eddy in the northern South China Sea, I: Preliminary observations on the warm-core eddy. Acta Oceanogr. Taiwan 1987, 18, 92–103. [Google Scholar]
- Farris, A.; Wimbush, M. Wind-induced Kuroshio intrusion into the South China Sea. J. Oceanogr. 1996, 52, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, E.J.; Hurlburt, H.E. The nondeterministic nature of Kuroshio penetration and eddy shedding in the South China Sea. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2001, 31, 1712–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehl, J.J.; Sheremet, V.A. Identification of a cusp catastrophe in a gap-leaping western boundary current. J. Mar. Res. 2009, 67, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.R.; Hsin, Y.C. The forcing mechanism leading to the Kuroshio intrusion into the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, C07015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gill, A.E. Atmosphere-Ocean Dynamics; Appendix 3; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 599–600. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, R.R.; Yau, M.K. A Short Course in Cloud Physics, 3rd ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1989; Volume 16. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.D.; Tang, T.Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Ko, M.T.; Chung, W.S. Upper-ocean current around Taiwan. Deep Sea Res. Part II 2003, 50, 1085–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Han, W.; Hu, D. Surface Kuroshio path in the Luzon Strait area derived from satellite remote sensing data. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, C11007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Qiu, B.; Tian, J. Anticyclonic Eddy Sheddings from Kuroshio Loop and the Accompanying Cyclonic Eddy in the Northeastern South China Sea. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2017, 47, 1243–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaw, P.T. The seasonal variation of the intrusion of the Philippine sea water into the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, F.; Xue, H.; Yu, F. Kuroshio intrusion into the South China Sea: A review. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 137, 314–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, S.P.; Chang, C.H.; Xie, Q.; Wang, D. Intraseasonal variability in the summer South China Sea: Wind jet, cold filament, and recirculations. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, C10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdain, N.; Lengaigne, M.; Vialard, J.; Madec, G.; Menkes, C.; Vincent, E.; Jullien, S.; Barnier, B. Observation based estimates of surface cooling inhibition by heavy rainfall under tropical cyclones. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2012, 43, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chow, C.H.; Liu, Q.; Xie, S.P. Effects of Kuroshio Intrusions on the atmosphere northeast of Taiwan Island. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toy, M.; Johnson, R. The Influence of an SST Front on a Heavy Rainfall Event over Coastal Taiwan during TiMREX. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 3223–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]










| Product | Source | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Solution | Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute dynamic topography (ADT) | http://apdrc.soest.hawaii.edu/ (accessed on 12 July 2020) | 0.25° | weekly | January 1993–May 2019 |
| Absolute geostrophic currents (AGC) | http://apdrc.soest.hawaii.edu/ (accessed on 18 June 2020) | 0.25° | weekly | January 1993–May 2019 |
| ASCAT sea surface winds (SSWs) | http://www.remss.com/mission/qscat. | 0.25° | daily | March 2007–December 2019 |
| MURSST level 4 analysis (SST) | https://podaac.jpl.nasa.gov/dataset/MUR-JPL-L4-GLOB-v4.1 | 0.01° | daily | June 2002–May 2019 |
| TRMM daily 3B42-v7 (Precipitation) | https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/datasets/TRMM_3B42_Daily_7/ | 0.25° | daily | January 1998–December 2019 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, W.-P.; Wu, D.-R.; Zheng, Z.-W.; Gopalakrishnan, G.; Ho, C.-R.; Zheng, Q.; Huang, C.-F.; Ho, H.; Weng, M.-C. Impacts of the Kuroshio Intrusion through the Luzon Strait on the Local Precipitation Anomaly. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061113
Fang W-P, Wu D-R, Zheng Z-W, Gopalakrishnan G, Ho C-R, Zheng Q, Huang C-F, Ho H, Weng M-C. Impacts of the Kuroshio Intrusion through the Luzon Strait on the Local Precipitation Anomaly. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(6):1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061113
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Wen-Pin, Ding-Rong Wu, Zhe-Wen Zheng, Ganesh Gopalakrishnan, Chung-Ru Ho, Quanan Zheng, Chen-Fen Huang, Hua Ho, and Min-Chuan Weng. 2021. "Impacts of the Kuroshio Intrusion through the Luzon Strait on the Local Precipitation Anomaly" Remote Sensing 13, no. 6: 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061113
APA StyleFang, W. -P., Wu, D. -R., Zheng, Z. -W., Gopalakrishnan, G., Ho, C. -R., Zheng, Q., Huang, C. -F., Ho, H., & Weng, M. -C. (2021). Impacts of the Kuroshio Intrusion through the Luzon Strait on the Local Precipitation Anomaly. Remote Sensing, 13(6), 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061113