High-Precision GNSS PWV and Its Variation Characteristics in China Based on Individual Station Meteorological Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Observation Data
2.2. Establishment of Site-Specific Piecewise-Linear Tm-Ts Relationship
2.3. PWV from Site-Specific Piecewise-Linear Tm-Ts Relationship
2.4. PWV from Radiosonde
2.5. Fitting Function of the PWV Time Series
3. Evaluation and Comparison
3.1. Spatial Distribution and Time-Varying Characteristics of the Tm-Ts Coefficient
3.2. Comparison with Bevis Tm-Ts Relationship
3.3. Comparison with GPS-Derived PWV and Radiosonde PWV
4. Variations Characteristics of GNSS PWV
4.1. Spatial Distribution of PWV in China
4.2. Seasonal Variations of PWV in China
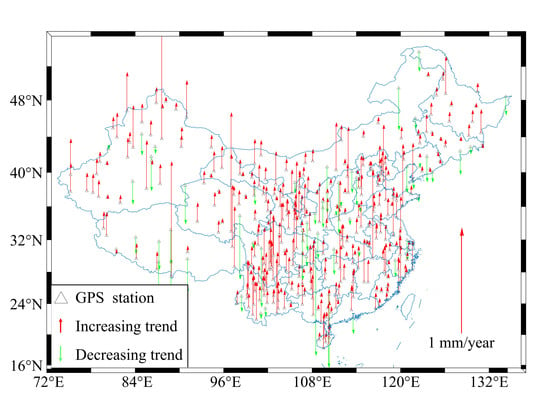
4.3. Long-Term Variation Trend of PWV in China
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Philipona, R.; Dürr, B.; Ohmura, A.; Ruckstuhl, C. Anthropogenic greenhouse forcing and strong water vapor feedback increase temperature in Europe. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendt, G.; Dick, G.; Reigber, C.; Tomassini, M.; Liu, Y.; Ramatschi, M. Near real time GPS water vapor monitoring for numerical weather prediction in Germany. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2004, 82, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boutiouta, S.; Lahcene, A. Preliminary study of GNSS meteorology techniques in Algeria. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 5105–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapucci, L.F. Evaluation of modeling water-vapor-weighted mean tropospheric temperature for GNSS-integrated water vapor estimates in Brazil. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2014, 53, 715–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, T.; Wickert, J.; Deng, Z.; Heise, S.; Dick, G.; Vey, S.; Schöne, T. Homogenized time series of the atmospheric water vapor content obtained from the GNSS reprocessed data. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 2443–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Su, K. PPP models and performances from single-to quad-frequency BDS observations. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Gao, C.; Li, J. Atmospheric sounding from Fengyun-3C GPS radio occultation observations: First results and validation. Adv. Meteorol. 2019, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, S.; Li, Z.; Cho, J. Integrated water vapor field and multiscale variations over China from GPS measurements. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 3008–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.; Guerova, G.; Douša, J.; Dick, G.; de Haan, S.; Pottiaux, E.; van Malderen, R. Advanced GNSS Tropospheric Products for Monitoring Severe Weather Events and Climate; COST Action ES1206 Final Action Dissemination Report; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; p. 563. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, A.; Kirchengast, G.; Foelsche, U.; Kornblueh, L.; Manzini, E.; Bengtsson, L. GNSS occultation sounding for climate monitoring. Phys. Chem. Earth Part A Solid Earth Geod. 2001, 26, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.L.; Benjamin, S.G.; Gutman, S.I.; Sahm, S. Short-range forecast impact from assimilation of GPS-IPW observations into the Rapid Update Cycle. Mon. Weather Rev. 2007, 135, 2914–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtidis, K.; Stathopoulos, S.; Georgoulias, A.; Alexandri, G.; Rapsomanikis, S. A study of the impact of synoptic weather conditions and water vapor on aerosol–cloud relationships over major urban clusters of China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 10955–10964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bevis, M.; Businger, S.; Herring, T.A.; Rocken, C.; Anthes, R.A.; Ware, R.H. GPS meteorology: Remote sensing of atmospheric water vapor using the Global Positioning System. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 15787–15801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.J.; Rosenfeld, S. Estimating mean weighted temperature of the atmosphere for Global Positioning System applications. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 21719–21730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bokoye, A.I. Multisensor analysis of integrated atmospheric water vapor over Canada and Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emardson, T.R.; Derks, H.J. On the relation between the wet delay and the integrated precipitable water vapour in the European atmosphere. Meteorol. Appl. A J. Forecast. Pract. Appl. Train. Tech. Model. 2000, 7, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Dai, A.; Hove, T.V.; Baelen, J.V. A near-global, 2-hourly data set of atmospheric precipitable water from ground-based GPS measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.P.; Liu, J.N.; Zhu, W.Y.; Huang, C. Remote sensing of PWV using ground-based GPS data in Wuhan region. Prog. Astron. 2005, 23, 169–179. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B.; He, C. Nonlinear relationships between the surface temperature and the weighted mean temperature. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2015, 40, 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Jade, S.; Vijayan, M. GPS-based atmospheric precipitable water vapor estimation using meteorological parameters interpolated from NCEP global reanalysis data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Means, J.D.; Cayan, D. Precipitable water from GPS Zenith delays using North American regional reanalysis meteorology. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yao, Y.; Yao, W.; Zhang, S. GNSS-derived PWV and comparison with radiosonde and ECMWF ERA-Interim data over mainland China. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2019, 182, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Li, X.; Cheng, J.; Dick, G.; Ge, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Real-time tropospheric delay retrieval from multi-GNSS PPP ambiguity resolution: Validation with final troposphere products and a numerical weather model. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abimbola, O.J.; Falaiye, O.A.; Omojola, J. Estimation of Precipitable Water Vapour in Nigeria Using NIGNET GNSS/GPS, NCEP-DOE Reanalysis II and Surface Meteorological Data. J. Phys. Sci. 2017, 28, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, B.; Sensing, R. A real-time precipitable water vapor monitoring system using the national GNSS network of China: Method and preliminary results. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. 2019, 12, 1587–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yue, S. A globally applicable, season-specific model for estimating the weighted mean temperature of the atmosphere. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yu, C.; Zhang, B.; Guo, J. An improved global zenith tropospheric delay model GZTD2 considering diurnal variations. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2016, 23, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, J.; Sun, Z. Construction and Service of the National Geodetic Datum. Geomat. World 2018, 25, 39–41, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, R.; Shi, H. Construction and Application of Tectonic and Environmental Observation Network of Mainland China. J. Eng. Stud. 2012, 4, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.; Park, P.-H.; Zhu, W. Micro-plate tectonics and kinematics in Northeast Asia inferred from a dense set of GPS observations. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 257, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dach, R.; Lutz, S.; Walser, P.; Fridez, P. Bernese GNSS Software, version 5.2; Astronomical Institute, University of Bern: Bern, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Joint Inversion of GPS, Leveling, and InSAR Data for The 2013 Lushan (China) Earthquake and Its Seismic Hazard Implications. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saastamoinen, J. Contributions to the theory of atmospheric refraction. Bull. Géodésique 1973, 107, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Luo, O. Variability and climatology of PWV from global 13-year GPS observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 1918–1924. [Google Scholar]
- Liou, Y.-A.; Teng, Y.-T.; Van Hove, T.; Liljegren, J.C. Comparison of Precipitable Water Observations in the Near Tropics by GPS, Microwave Radiometer, and Radiosondes. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Dai, A. Global estimates of water-vapor-weighted mean temperature of the atmosphere for GPS applications. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Spatial distribution, temporal variation, and transport characteristics of atmospheric water vapor over Central Asia and the arid region of China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2019, 172, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ding, Y. Analysis of the basic features of the onset of Asian summer monsoon. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2007, 21, 511–526. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Yang, P.; Yao, W.; Yao, Y. Hourly PWV Dataset Derived from GNSS Observations in China. Sensors 2020, 20, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gui, K.; Che, H.; Chen, Q.; Zeng, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Long, Q.; Sun, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liao, T.; et al. Water vapor variation and the effect of aerosols in China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 165, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durre, I.; Williams, C.N.; And, X.Y.; Vose, R.S. Radiosonde-based trends in precipitable water over the Northern Hemisphere: An update. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R. Characteristics of Water Vapor, Precipitation, Temperature and Humidity in Mainland China Based on IGRA and TRMM PR. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, M.S.; Jin, X.; Liu, Z.; Nichol, J.; Chan, P. Multi-sensors study of precipitable water vapour over mainland China. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 3146–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Name | Number | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) | Height (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YICHUN | 50,774 | 47.72 | 128.83 | 264.8 |
| HARBIN | 50,953 | 45.93 | 126.57 | 118.3 |
| SIMAO | 56,964 | 22.77 | 100.98 | 1303.0 |
| ANQING | 58,424 | 30.62 | 116.97 | 62.0 |
| Statistics | Bevis | TVGG | NN-I | Piecewise Linear |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bias (K) | −0.74 | −1.25 | 0.03 | 0.00 |
| RMS (K) | 4.58 | 3.84 | 3.62 | 3.38 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, M.; Jin, S.; Li, Z.; Cao, Y.; Ping, F.; Tang, X. High-Precision GNSS PWV and Its Variation Characteristics in China Based on Individual Station Meteorological Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13071296
Wu M, Jin S, Li Z, Cao Y, Ping F, Tang X. High-Precision GNSS PWV and Its Variation Characteristics in China Based on Individual Station Meteorological Data. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(7):1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13071296
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Mingliang, Shuanggen Jin, Zhicai Li, Yunchang Cao, Fan Ping, and Xu Tang. 2021. "High-Precision GNSS PWV and Its Variation Characteristics in China Based on Individual Station Meteorological Data" Remote Sensing 13, no. 7: 1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13071296
APA StyleWu, M., Jin, S., Li, Z., Cao, Y., Ping, F., & Tang, X. (2021). High-Precision GNSS PWV and Its Variation Characteristics in China Based on Individual Station Meteorological Data. Remote Sensing, 13(7), 1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13071296