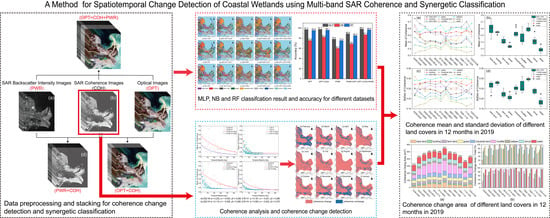
Spatiotemporal Change Detection of Coastal Wetlands Using Multi-Band SAR Coherence and Synergetic Classification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Datasets and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Interferometric Coherence Processing
2.3.2. Coherence Change Detection
2.3.3. Supervised Classification
2.3.4. Accuracy Assessment
- (i)
- Recall
- (ii)
- Precision
- (iii)
- Accuracy
- (iv) F1 Score
3. Results
3.1. Coherence Comparison
3.2. Synergetic Classification
3.3. Coherence Change Area
4. Discussion
4.1. Interferometric Coherence Analysis
4.2. Synergetic Classification Accuracy
4.3. Driving Factors of Coherence Change
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tiner, R.W.; Lang, M.W.; Klemas, V. (Eds.) Remote Sensing of Wetlands: Applications and Advances, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 119–136. [Google Scholar]
- Vymazal, J. Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment. Water 2010, 2, 530–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gedan, K.B.; Kirwan, M.L.; Wolanski, E.; Barbier, E.B.; Silliman, B.R. The present and future role of coastal wetland vegetation in protecting shorelines: Answering recent challenges to the paradigm. Clim. Change 2011, 106, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, N.J.; Phinn, S.R.; DeWitt, M.; Ferrari, R.; Johnston, R.; Lyons, M.B.; Clinton, N.; Thau, D.; Fuller, R.A. The global distribution and trajectory of tidal flats. Nature 2019, 565, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prigent, C.; Papa, F.; Aires, F.; Jimenez, C.; Rossow, W.B.; Matthews, E. Changes in land surface water dynamics since the 1990s and relation to population pressure. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L08403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Junk, W.J.; Piedade, M.T.F.; Lourival, R.; Wittmann, F.; Kandus, P.; Lacerda, L.D.; Bozelli, R.L.; Esteves, F.d.A.; Nunes da Cunha, C.; Maltchik, L. Brazilian wetlands: Their definition, delineation, and classification for research, sustainable management, and protection. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2014, 24, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wdowinski, S.; Kim, S.-W.; Amelung, F.; Dixon, T.H.; Miralles-Wilhelm, F.; Sonenshein, R. Space-Based detection of wetlands’ surface water level changes from L-band SAR interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T.-H.; Simard, M.; Denbina, M.; Lamb, M.P. Monitoring Water Level Change and Seasonal Vegetation Change in the Coastal Wetlands of Louisiana Using L-Band Time-Series. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisco, B.; Ahern, F.; Murnaghan, K.; White, L.; Canisus, F.; Lancaster, P. Seasonal Change in Wetland Coherence as an Aid to Wetland Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahdianpari, M.; Salehi, B.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Brisco, B.; Mahdavi, S.; Amani, M.; Granger, J.E. Fisher Linear Discriminant Analysis of coherency matrix for wetland classification using PolSAR imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 300–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, E.W. Monitoring flooding in coastal wetlands by using radar imagery and ground-based measurements. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 2495–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, L.; Brisco, B.; Pregitzer, M.; Tedford, B.; Boychuk, L. RADARSAT-2 Beam Mode Selection for Surface Water and Flooded Vegetation Mapping. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 40, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Töyrä, J.; Pietroniro, A. Towards operational monitoring of a northern wetland using geomatics-based techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 174–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsdorf, D.E.; Melack, J.M.; Dunne, T.; Mertes, L.A.K.; Hess, L.L.; Smith, L.C. Interferometric radar measurements of water level changes on the Amazon flood plain. Nature 2000, 404, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Shao, Y.; Xu, J.; Wan, Z.; Fang, L. Analysis of ALOS PALSAR InSAR data for mapping water level changes in Yellow River Delta wetlands. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 34, 2047–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, F.; Brown, I.; Castellazzi, P.; Espinosa, L.; Guittard, A.; Hong, S.-H.; Rivera-Monroy, V.H.; Wdowinski, S. Assessment of hydrologic connectivity in an ungauged wetland with InSAR observations. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 024003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver-Cabrera, T.; Wdowinski, S. InSAR-Based Mapping of Tidal Inundation Extent and Amplitude in Louisiana Coastal Wetlands. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canisius, F.; Brisco, B.; Murnaghan, K.; Van Der Kooij, M.; Keizer, E. SAR Backscatter and InSAR Coherence for Monitoring Wetland Extent, Flood Pulse and Vegetation: A Study of the Amazon Lowland. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferretti, A.; Monti-Guarnieri, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. InSAR Principles: Guidelines for SAR Interferometry Processing and Interpretation; ESA Publications: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey, I.I.I.E.; Lu, Z.; Rangoonwala, A.; Rykhus, R. Multiple Baseline Radar Interferometry Applied to Coastal Land Cover Classification and Change Analyses. GIScience Remote Sens. 2006, 43, 283–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Wdowinski, S.; Amelung, F.; Dixon, T.H.; Won, J. Interferometric Coherence Analysis of the Everglades Wetlands, South Florida. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 5210–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Tian, B.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, J. A method for monitoring hydrological conditions beneath herbaceous wetlands using multi-temporal ALOS PALSAR coherence data. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 6, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisco, B.; Murnaghan, K.; Wdowinski, S.; Hong, S.-H. Evaluation of RADARSAT-2 Acquisition Modes for Wetland Monitoring Applications. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 41, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, A.W.; Vicente-Guijalba, F.; Lopez-Martinez, C.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Litzinger, M.; Kristen, H.; Mestre-Quereda, A.; Ziółkowski, D.; Lavalle, M.; Notarnicola, C.; et al. Sentinel-1 InSAR Coherence for Land Cover Mapping: A Comparison of Multiple Feature-Based Classifiers. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amani, M.; Poncos, V.; Brisco, B.; Foroughnia, F.; DeLancey, E.R.; Ranjbar, S. InSAR Coherence Analysis for Wetlands in Alberta, Canada Using Time-Series Sentinel-1 Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Pu, S.; Wu, X.; Bi, N.; Wang, H. Spatiotemporal Changes of Coastline over the Yellow River Delta in the Previous 40 Years with Optical and SAR Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Yin, S.; Li, D.; Zhu, Q.; Chang, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, G. Synergetic Classification of Coastal Wetlands over the Yellow River Delta with GF-3 Full-Polarization SAR and Zhuhai-1 OHS Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Ding, D.; Qiao, L.; Xu, J.; Li, G.; Wang, H. Coastal Dam Inundation Assessment for the Yellow River Delta: Measurements, Analysis and Scenario. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Peng, S.; Ciais, P.; Chen, Y. Future impacts of climate change on inland Ramsar wetlands. Nature Climate Change 2021, 11, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Bi, N.; Xu, J.; Nittrouer, J.A.; Yang, Z.; Saito, Y.; Wang, H. Stepwise morphological evolution of the active Yellow River (Huanghe) delta lobe (1976–2013): Dominant roles of riverine discharge and sediment grain size. Geomorphology 2017, 292, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.-L.; Li, X.-Y. Coastline change of the Yellow River estuary and its response to the sediment and runoff (1976–2005). Geomorphology 2011, 127, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvitski, J.; Ángel, J.R.; Saito, Y.; Overeem, I.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Wang, H.; Olago, D. Earth’s sediment cycle during the Anthropocene. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez Martinez, C.; Fabregas, X.; Pottier, E. A New Alternative for SAR Imagery Coherence Estimation. In Proceedings of the 5th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar(EUSAR’04), Ulm, Germany, 25–27 May 2004; pp. 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.; Kim, D.; Lavalle, M.; Yun, S. Coherent Change Detection Using InSAR Temporal Decorrelation Model: A Case Study for Volcanic Ash Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 5765–5775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washaya, P.; Balz, T.; Mohamadi, B. Coherence Change-Detection with Sentinel-1 for Natural and Anthropogenic Disaster Monitoring in Urban Areas. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patricia, F.; Joao Manuel, R. Computational Vision and Medical Image Processing, 1st ed.; Tavares, J.M.R.S., Jorge, R.M.N., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2012; pp. 111–114. [Google Scholar]
- Goh, T.Y.; Basah, S.N.; Yazid, H.; Aziz Safar, M.J.; Ahmad Saad, F.S. Performance analysis of image thresholding: Otsu technique. Measurement 2018, 114, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralick, R.M.; Sternberg, S.R.; Zhuang, X. Image Analysis Using Mathematical Morphology. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1987, PAMI-9, 532–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, A.; Nigam, K. A Comparison of Event Models for Naive Bayes Text Classification. In Proceedings of the AAAI-98 Workshop on Learning for Text Categorization, Madison, WI, USA, 26–27 July 1998; pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pal, M. Random forest classifier for remote sensing classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, E.R.; James, L.M. Learning Internal Representations by Error Propagation. In Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition: Foundations; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1987; pp. 318–362. [Google Scholar]
- Sarle, W.S. Neural Networks and Statistical Models; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadimanesh, F.; Salehi, B.; Mahdianpari, M.; Brisco, B.; Motagh, M. Multi-Temporal, multi-frequency, and multi-polarization coherence and SAR backscatter analysis of wetlands. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 142, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-W.; Lu, Z.; Jones, J.W.; Shum, C.K.; Lee, H.; Jia, Y. Monitoring Everglades freshwater marsh water level using L-band synthetic aperture radar backscatter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 150, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, H. Mapping Tidal Flats of the Bohai and Yellow Seas Using Time Series Sentinel-2 Images and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Sensors | Acquisition Date (yyyy.mm.dd) | Imaging Mode | Resolution (m) (Range × Azimuth) | Polarization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-1B (C-band SAR) | 2019.02.28 | IW (Interferometric wide swath) | 2.3 × 14 | VH + VV |
| 2019.03.24 | ||||
| 2019.04.29 | ||||
| 2019.05.23 | ||||
| 2019.06.16 | ||||
| 2019.07.10 | ||||
| 2019.08.03 | ||||
| 2019.08.27 | ||||
| 2019.09.20 | ||||
| 2019.10.26 | ||||
| 2019.11.19 | ||||
| 2019.12.25 | ||||
| 2020.01.06 | ||||
| ALOS-2 PALSAR (L-band SAR) | 2014.12.06 | Stripmap | 4.3 × 3.4 | HV + HH |
| 2015.07.18 | ||||
| 2015.09.26 | ||||
| 2015.10.24 | ||||
| 2016.07.16 | ||||
| 2016.12.03 | ||||
| 2017.03.25 | ||||
| 2018.11.03 | ||||
| 2019.05.18 | ||||
| Sentinel-2A (Optical) | 2019.09.29 | MSI (Multispectral instrument) | 10 × 10 | —— |
| Class | Training Samples (Pixel) | Validation Samples (Pixel) |
|---|---|---|
| Bare land | 3429 | 1169 |
| Building | 3541 | 1201 |
| Farm land | 4587 | 1513 |
| Grass | 1950 | 631 |
| Industrial land | 2518 | 855 |
| Mudflat | 6570 | 2198 |
| Saltpan | 2445 | 804 |
| Shrub | 1317 | 523 |
| Water | 9902 | 3293 |
| Total | 36,259 | 12,187 |
| Predicted Label | Positive | Negative | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Real Label | |||
| Positive | TP | FN | |
| Negative | FP | TN | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Li, P.; Tu, C.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Feng, Z.; Shen, F.; Li, Z. Spatiotemporal Change Detection of Coastal Wetlands Using Multi-Band SAR Coherence and Synergetic Classification. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2610. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112610
Liu J, Li P, Tu C, Wang H, Zhou Z, Feng Z, Shen F, Li Z. Spatiotemporal Change Detection of Coastal Wetlands Using Multi-Band SAR Coherence and Synergetic Classification. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(11):2610. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112610
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jie, Peng Li, Canran Tu, Houjie Wang, Zhiwei Zhou, Zhixuan Feng, Fang Shen, and Zhenhong Li. 2022. "Spatiotemporal Change Detection of Coastal Wetlands Using Multi-Band SAR Coherence and Synergetic Classification" Remote Sensing 14, no. 11: 2610. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112610
APA StyleLiu, J., Li, P., Tu, C., Wang, H., Zhou, Z., Feng, Z., Shen, F., & Li, Z. (2022). Spatiotemporal Change Detection of Coastal Wetlands Using Multi-Band SAR Coherence and Synergetic Classification. Remote Sensing, 14(11), 2610. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112610