Classification of Electronic Devices Using a Frequency-Swept Harmonic Radar Approach
Abstract
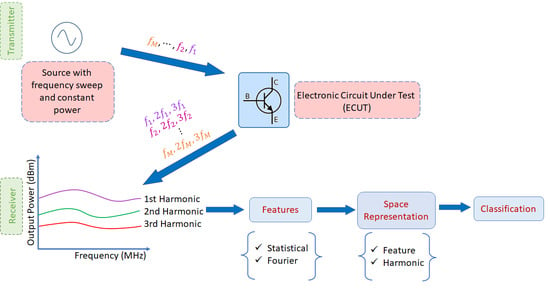
:1. Introduction
2. Frequency-Swept Harmonic Radar Approach
3. Features Used for Target Classification
3.1. Statistical Features
3.2. Fourier Features
4. Simulations
5. Simulation Results and Performance Analysis
5.1. Statistical Feature Results
5.2. Fourier Feature Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Powers, E.; Hong, J.; Kim, Y. Cross sections and radar equation for nonlinear scatterers. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1981, AES-17, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.; Hai-yong, W. The re-radiation characteristics of nonlinear target in harmonic radar detection. In Proceedings of the 2008 China-Japan Joint Microwave Conference, Shanghai, China, 10–12 September 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 661–664. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, S.A. Nonlinear Microwave and RF Circuits; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jablonski, D.G.; Ko, H.W.; Oursler, D.A.; Smith, D.G.; White, D.M. System and Method of Radar Detection of Non-Linear Interfaces. U.S. Patent 6,765,527, 20 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzaro, G.J.; Martone, A.F.; McNamara, D.M. Detection of RF electronics by multitone harmonic radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2014, 50, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aniktar, H.; Baran, D.; Karav, E.; Akkaya, E.; Birecik, Y.S.; Sezgin, M. Getting the bugs out: A portable harmonic radar system for electronic countersurveillance applications. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2015, 16, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arazm, F.; Benson, F.A. Nonlinearities in metal contacts at microwave frequencies. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 1980, EMC-22, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, C.; Hartnagel, H.L. Passive-intermodulation analysis between rough rectangular waveguide flanges. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2005, 53, 2515–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayvaci, H.T.; Ilbegi, H.; Yetik, I.S. Classification of Electronic Devices With Power-Swept Signals Using Harmonic Radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 56, 2292–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayvaci, H.T.; Shahi, M.; Ilbegi, H.; Yetik, I.S. A Linear Model for Classification of Electronic Devices Using Harmonic Radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2021, 57, 3614–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzaro, G.J.; Sherbondy, K.D. Combined Linear and Nonlinear Radar: Waveform Generation and Capture; Technical Report; Army Research Lab Adelphi MD Sensors and Electron Devices Directorate: Adelphi, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzaro, G.J.; Gallagher, K.A.; Sherbondy, K.D.; Martone, A.F. Nonlinear radar: A historical overview and a summary of recent advancements. In Proceedings of the Radar Sensor Technology XXIV, Online, 27 April–8 May 2020; Volume 11408, p. 114080E. [Google Scholar]
- Kosinski, J.A.; Palmer, W.D.; Steer, M.B. Unified understanding of RF remote probing. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 3055–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martone, A.F.; Ranney, K.I.; Sherbondy, K.D.; Gallagher, K.A.; Mazzaro, G.J.; Narayanan, R.M. An overview of spectrum sensing for harmonic radar. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Symposium on Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering (ISFEE), Bucharest, Romania, 30 June–2 July 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neal, M.E.; Landis, D.; Rothwell, E.; Kempel, L.; Reinhard, D. Tracking insects with harmonic radar: A case study. Am. Entomol. 2004, 50, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colpitts, B.G.; Boiteau, G. Harmonic radar transceiver design: Miniature tags for insect tracking. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2004, 52, 2825–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psychoudakis, D.; Moulder, W.; Chen, C.C.; Zhu, H.; Volakis, J.L. A portable low-power harmonic radar system and conformal tag for insect tracking. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2008, 7, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, N.; Brooker, G. Toward the development of millimeter wave harmonic sensors for tracking small insects. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 5669–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanesio, D.; Bottigliero, S.; Saccani, M.; Maggiora, R.; Viscardi, A.; Gallesi, M.M. An harmonic radar prototype for insect tracking in harsh environments. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Radar Conference (RADAR), Washington, DC, USA, 28–30 April 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 648–653. [Google Scholar]
- Storz, G.; Lavrenko, A. Compact low-cost FMCW harmonic radar for short range insect tracking. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Radar Conference (RADAR), Washington, DC, USA, 28–30 April 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 642–647. [Google Scholar]
- Lavrenko, A.; Litchfield, B.; Woodward, G.; Pawson, S. Design and evaluation of a compact harmonic transponder for insect tracking. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Components Lett. 2020, 30, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottigliero, S.; Milanesio, D.; Saccani, M.; Maggiora, R.; Viscardi, A.; Gallesi, M.M. An innovative harmonic radar prototype for miniaturized lightweight passive tags tracking. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Boston, MA, USA, 22–26 April 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Saebboe, J.; Viikari, V.; Varpula, T.; Seppä, H.; Cheng, S.; Al-Nuaimi, M.; Hallbjörner, P.; Rydberg, A. Harmonic automotive radar for VRU classification. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Radar Conference “Surveillance for a Safer World” (RADAR 2009), Bordeaux, France, 12–16 October 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelnour, A.; Lazaro, A.; Villarino, R.; Kaddour, D.; Tedjini, S.; Girbau, D. Passive harmonic RFID system for buried assets localization. Sensors 2018, 18, 3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mondal, S.; Kumar, D.; Chahal, P. Recent Advances and Applications of Passive Harmonic RFID Systems: A Review. Micromachines 2021, 12, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, W.J. Active Improvised Explosive Device (IED) Electronic Signature Detection. U.S. Patent 8,063,813, 22 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Holly, S.; Harrington, D.E. Multi-Band Receiver Using Harmonic Synchronous Detection. U.S. Patent 8,903,669, 8 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lehtola, G.E. RF Receiver Sensing by Harmonic Generation. U.S. Patent 7,864,107, 4 January 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ilbegi, H.; Hayvaci, H.T.; Yetik, I.S.; Yilmaz, A.E. Distinguishing electronic devices using harmonic radar. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Seattle, WA, USA, 8–12 May 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1527–1530. [Google Scholar]
- Ilbegi, H.; Hayvaci, H.; Yetik, I. Distinguishing electronic devices using Fourier features derived from harmonic radar. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electromagnetics in Advanced Applications (ICEAA), Verona, Italy, 11–15 September 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1502–1505. [Google Scholar]
- Shahi, M.; Ilbegi, H.; Yetik, I.S.; Hayvaci, H.T. Distinguishing Electronic Devices Using Harmonic Radar Based on a Linear Model. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Electromagnetics in Advanced Applications (ICEAA), Granada, Spain, 9–13 September 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1260–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzaro, G.J.; Sherbondy, K.D. Harmonic nonlinear radar: From benchtop experimentation to short-range wireless data collection. In Proceedings of the Radar Sensor Technology XXIII, Baltimore, MD, USA, 15–17 April 2019; Volume 11003, p. 110030F. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzaro, G.J.; Martone, A.F.; Ranney, K.I.; Narayanan, R.M. Nonlinear radar for finding RF electronics: System design and recent advancements. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2017, 65, 1716–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzaro, G.J.; Ranney, K.I.; Gallagher, K.A.; Martone, A.F. Multitone Radar with Range Determination and Method of Use. U.S. Patent 10,203,405, 12 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzaro, G.J.; Ranney, K.I.; Gallagher, K.A.; McGowan, S.F.; Martone, A.F. Simultaneous-Frequency Nonlinear Radar: Hardware Simulation; Technical Report; Army Research Lab Sensors and Electron Devices Directorate: Adelphi, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, T.; Hamran, S.E. Harmonic synthetic aperture radar processing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 2066–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzaro, G.J.; Gallagher, K.A.; Martone, A.F.; Narayanan, R.M. Stepped-frequency nonlinear radar simulation. In Proceedings of the Radar Sensor Technology XVIII, Baltimore, MD, USA, 29 May 2014; Volume 9077, p. 90770U. [Google Scholar]
- Ranney, K.; Gallagher, K.; Martone, A.; Mazzaro, G.; Sherbondy, K.; Narayanan, R. Instantaneous, stepped-frequency, nonlinear radar. In Proceedings of the Radar Sensor Technology XIX and Active and Passive Signatures VI, Baltimore, MD, USA, 20–23 April 2015; Volume 9461, p. 946122. [Google Scholar]
- McGowan, S.F.; Mazzaro, G.J.; Sherbondy, K.D.; Narayanan, R.M. Harmonic Phase Response of Nonlinear Radar Targets; Technical Report; Army Research Lab Sensors and Electron Devices Directorate: Adelphi, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzaro, G.J. Detection of Radio-Frequency Electronics by Stimulated Emission of Carrier Modulation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2021, 58, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, K. Harmonic Radar: Theory and Applications to Nonlinear Target Detection, Tracking, Imaging and Classification. Ph.D. Thesis, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Boylestad, R.L.; Nashelsky, L. Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory; Pearson Educación: Essex, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tooley, M. Electronic Circuits-Fundamentals & Applications; Routledge: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, B.W. Analogue Electronics for Higher Studies; Macmillan International Higher Education: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Floyd, T.L. Electronics Fundamentals: Circuits, Devices and Applications (Floyd Electronics Fundamentals Series); Prentice-Hall Inc.: Essex, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Joanes, D.; Gill, C. Comparing measures of sample skewness and kurtosis. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. D (Stat.) 1998, 47, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, R.O.; Hart, P.E.; Stork, D.G. Pattern Classification; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]


















| SNR = 8 dB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variance | Device 1 | Device 2 | Device 3 | |
| Device 1 | 100% | 0% | 0% | |
| Device 2 | 0% | 100% | 0% | |
| Device 3 | 0% | 0% | 100% | |
| Skewness | Device 1 | Device 2 | Device 3 | |
| Device 1 | 74% | 25.8% | 0.2% | |
| Device 2 | 19.1% | 80.7% | 0.2% | |
| Device 3 | 0% | 0% | 100% | |
| Kurtosis | Device 1 | Device 2 | Device 3 | |
| Device 1 | 88.7% | 9.8% | 1.5% | |
| Device 2 | 13.8% | 84.3% | 1.9% | |
| Device 3 | 0.1% | 0% | 99.9% | |
| SNR = 8 dB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2nd Harmonic | Device 1 | Device 2 | Device 3 | |
| Device 1 | 54.8% | 40.2% | 5% | |
| Device 2 | 31.3% | 67.8% | 0.9% | |
| Device 3 | 0.5% | 0.3% | 99.2% | |
| 3rd Harmonic | Device 1 | Device 2 | Device 3 | |
| Device 1 | 83.3% | 15.5% | 1.2% | |
| Device 2 | 14.6% | 77.2% | 8.2% | |
| Device 3 | 0.7% | 2.9% | 96.4% | |
| Device | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 100% | 99.4% | 88.7% | 99% | 89.6% |
| Std. Dev. | 0% | 1.1% | 4.6% | 1.4% | 4.8% |
| Min | 100% | 95.2% | 73.8% | 92.9% | 71.4% |
| Max | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| SNR = 8 dB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Frequency | Device 1 | Device 2 | Device 3 | |
| Device 1 | 63.6% | 36.2% | 0.2% | |
| Device 2 | 40.5% | 59.3% | 0.2% | |
| Device 3 | 1% | 0.2% | 98.8% | |
| Mid Frequency | Device 1 | Device 2 | Device 3 | |
| Device 1 | 63.4% | 36.3% | 0.3% | |
| Device 2 | 39% | 60.3% | 0.7% | |
| Device 3 | 1.1% | 0.4% | 98.5% | |
| High Frequency | Device 1 | Device 2 | Device 3 | |
| Device 1 | 60.1% | 36.9% | 3% | |
| Device 2 | 44.5% | 52.4% | 3.1% | |
| Device 3 | 9.3% | 5.8% | 84.9% | |
| SNR = 8 dB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2nd Harmonic | Device 1 | Device 2 | Device 3 | |
| Device 1 | 50.8% | 47.3% | 1.9% | |
| Device 2 | 47.5% | 47.8% | 4.7% | |
| Device 3 | 4.7% | 7.1% | 88.2% | |
| 3rd Harmonic | Device 1 | Device 2 | Device 3 | |
| Device 1 | 48.5% | 39.9% | 11.6% | |
| Device 2 | 36.3% | 61.4% | 2.3% | |
| Device 3 | 9.4% | 2.7% | 87.9% | |
| SNR = 8 dB | ||
|---|---|---|
| Harmonic Space | ||
| Variance | 100% | |
| Skewness | 84.90% | |
| Kurtosis | 90.97% | |
| Low Frequency | 73.90% | |
| Mid Frequency | 74.07% | |
| High Frequency | 65.80% | |
| Statistical Feature Space | Fourier Feature Space | |
| 2nd Harmonic | 73.93% | 62.27% |
| 3rd Harmonic | 85.63% | 65.93% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ilbegi, H.; Turan, H.I.; Yetik, I.S.; Hayvaci, H.T. Classification of Electronic Devices Using a Frequency-Swept Harmonic Radar Approach. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122953
Ilbegi H, Turan HI, Yetik IS, Hayvaci HT. Classification of Electronic Devices Using a Frequency-Swept Harmonic Radar Approach. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(12):2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122953
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlbegi, Handan, Halil Ibrahim Turan, Imam Samil Yetik, and Harun Taha Hayvaci. 2022. "Classification of Electronic Devices Using a Frequency-Swept Harmonic Radar Approach" Remote Sensing 14, no. 12: 2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122953
APA StyleIlbegi, H., Turan, H. I., Yetik, I. S., & Hayvaci, H. T. (2022). Classification of Electronic Devices Using a Frequency-Swept Harmonic Radar Approach. Remote Sensing, 14(12), 2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122953