SII-Net: Spatial Information Integration Network for Small Target Detection in SAR Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
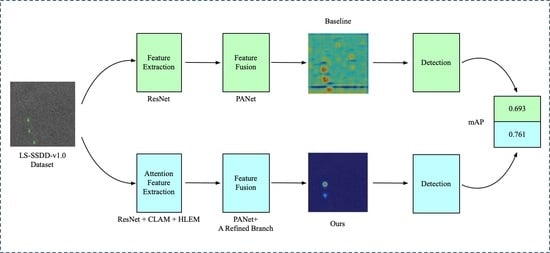
- We propose a channel-location attention mechanism (CLAM) that embeds positional information into channel information along with two spatial directions. By modeling inter-channel similarity and spatial correlation, the CLAM yields impressive performance in enhancing the feature extraction ability of the backbone.
- (2)
- To address the location information loss of small targets at the high level, a well-designed module called the high-level features enhancement module (HLEM) is customized to upgrade the performance of the high feature layer of the backbone network by multiscale pooling operation.
- (3)
- Considering the fact that inshore ship targets are susceptible to interference from surrounding objects, a new refined branch of feature is proposed to optimize the features after fusing each feature layer. The refined branch can make the network enhance the difference between target and background to effectively distinguish the target from the background.
2. Methods
2.1. The Motivation of the Proposed Method
2.2. Overview of the Processing Scheme
2.3. Pre-Processing Method
2.3.1. Scale Match
2.3.2. Add False Samples
2.4. Channel-Location Attention Mechanism (CLAM)
2.5. High-Level Features Enhancement Module (HLEM)
2.6. A Refined Branch
3. Experiments
3.1. Introduction of the Datasets
- (1)
- LS-SSDD-v1.0: LS-SSDD-v1.0 is a large-scale background SAR ship detection dataset. There are 15 large-scale images with 24,000 × 16,000 pixels in LS-SSDD-v1.0 from Sentinel-1 (the first 10 images are selected as a training set, and the remaining are selected as a test set). The 15 large-scale images are cut into 9000 sub-images with 800 × 800 pixels by the publisher of the dataset. At the same time, it contains a wealth of pure background images. SAR ships in LS-SSDD-v1.0 are provided with various resolutions around 5 m, and VV and VH polarizations. According to the setting of the original reports in [31], the training set has 6000 images, and the test set has 3000 images. We set the ratio of the training set and test set to 6:3. This is mainly used for small ship detection.
- (2)
- SSDD: SSDD is the first public SAR ship detection dataset proposed by Li et al. in 2017. It consists of 1160 images of approximately 500 × 500 pixels, acquired by RadarSat-2, TerraSAR-X, and Sentinel-1. The dataset contains 2540 ships, with resolutions ranging from 1 m to 15 m, and HH, HV, VV, and VH polarizations. We set the ratio of the training set and test set to 8:2, the last number of the picture name is 1 or 9 is set as the test set, and the rest is set as the training set.
- (3)
- SAR-Ship-Dataset: The SAR-Ship-Dataset is a SAR ship detection dataset published by Wang et al. in 2019. There are 43,819 images with 256 × 256 pixels from Sentinel-1 and Gaofen-3. It contains 59,535 ships with a resolution of 3 m, 5 m, and 8 m, etc., and HH, HV, VV, and VH polarizations. In the same way as the original reports in [33], we randomly set the ratio of the training set, validation set, and the test set to 7:2:1.
3.2. Evaluation Criterions
3.3. Implement Details
3.4. Results on Small Target Dataset LS-SSDD-v1.0
3.5. Results on Other Datasets
4. Ablation Experiment
4.1. Effectiveness of CLAM
4.2. Effectiveness of HLEM
4.3. Effectiveness of R-Branch
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leng, X.; Ji, K.; Yang, K.; Zou, H. A Bilateral CFAR Algorithm for Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xu, P.; Guo, Z. SAR Ship Detection Using Sea-Land Segmentation-Based Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Workshop on Remote Sensing with Intelligent Processing (RSIP), Shanghai, China, 19–21 May 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.; Ji, K.; Leng, X.; Lin, Z. Contextual Region-Based Convolutional Neural Network with Multilayer Fusion for SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Wu, H.; Zhong, Z.-C.; Zheng, L.; Deng, Q.; Hu, H. TWC-Net: A SAR Ship Detection Using Two-Way Convolution and Multiscale Feature Mapping. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X. High-Speed Ship Detection in SAR Images Based on a Grid Convolutional Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhan, R. R2FA-Det: Delving into High-Quality Rotatable Boxes for Ship Detection in SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Su, H.; Ming, J.; Wang, C.; Yan, M.; Kumar, D.P.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X. Precise and Robust Ship Detection for High-Resolution SAR Imagery Based on HR-SDNet. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Y.; Wei, S. Automatic Ship Detection Based on RetinaNet Using Multi-Resolution Gaofen-3 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Z.; Leng, X.; Lei, Y.; Xiong, B.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. BiFA-YOLO: A Novel YOLO-Based Method for Arbitrary-Oriented Ship Detection in High-Resolution SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, N.; Gao, X. A Robust One-Stage Detector for Multiscale Ship Detection with Complex Background in Massive SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhuang, L. SSS-YOLO: Towards More Accurate Detection for Small Ships in SAR Image. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 12, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, Y.; Mehta, M.; Goel, N.; Bhardwaj, P.; Gupta, D.; Khanna, A. YOLOv3 Remote Sensing SAR Ship Image Detection. In Data Analytics and Management; Khanna, A., Gupta, D., Pólkowski, Z., Bhattacharyya, S., Castillo, O., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 519–531. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.; Zhuge, Y.; Claramunt, C.; Men, S. N-YOLO: A SAR Ship Detection Using Noise-Classifying and Complete-Target Extraction. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Shi, J.; Wei, S. SAR Ship Detection Based on an Improved Faster R-CNN Using Deformable Convolution. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 3565–3568. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, J.; Tian, R.; Luo, Q.; Jin, J.; Tang, B. Multi-Scale Rotation-Invariant Haar-Like Feature Integrated CNN-Based Ship Detection Algorithm of Multiple-Target Environment in SAR Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 10070–10087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, T.; Lei, P.; Bai, X. A Hierarchical Convolution Neural Network (CNN)-Based Ship Target Detection Method in Spaceborne SAR Imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Ji, K.; Leng, X.; Kuang, G. Squeeze and Excitation Rank Faster R-CNN for Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xiong, B.; Kuang, G. Attention Receptive Pyramid Network for Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 2738–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06521. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Fu, K. An Anchor-Free Method Based on Feature Balancing and Refinement Network for Multiscale Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 1331–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; He, C.; Hu, C.; Pei, H.; Jiao, L. A Deep Neural Network Based on an Attention Mechanism for SAR Ship Detection in Multiscale and Complex Scenarios. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 104848–104863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Lang, P.; Fu, X.; Qin, R.; Dong, J.; Liu, C. A Regional Attention-Based Detector for SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 13, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; He, Y.; Wang, J.; Hussain, A.; Zhou, H. Anchor-Free Convolutional Network with Dense Attention Feature Aggregation for Ship Detection in SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W. A Lightweight Faster R-CNN for Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.-W.; Zhang, X. ShipDeNet-20: An Only 20 Convolution Layers and <1-MB Lightweight SAR Ship Detector. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 1234–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liang, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q.; Liao, G. A Novel Multidimensional Domain Deep Learning Network for SAR Ship Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, J. Learning Deep Ship Detector in SAR Images From Scratch. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 4021–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.; Sohn, K. Enriching SAR Ship Detection via Multistage Domain Alignment. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Huang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Xiang, X. Boosting Ship Detection in SAR Images With Complementary Pretraining Techniques. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 8941–8954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Ke, X.; Zhan, X.; Shi, J.; Wei, S.; Pan, D.; Li, J.; Su, H.; Zhou, Y.; et al. LS-SSDD-v1.0: A Deep Learning Dataset Dedicated to Small Ship Detection from Large-Scale Sentinel-1 SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qu, C.; Shao, J. Ship Detection in SAR Images Based on an Improved Faster R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 SAR in Big Data Era: Models, Methods and Applications (BIGSARDATA), Beijing, China, 13–14 November 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Y.; Wei, S. A SAR Dataset of Ship Detection for Deep Learning under Complex Backgrounds. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient Channel Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 11531–11539. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wu, F.; Li, X. FcaNet: Frequency Channel Attention Networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:abs/2012.11879. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual Attention Network for Scene Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3141–3149. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.; Chen, Q.; Yan, S. Network In Network. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1312.4400. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Li, Q.; Cao, Z.; Liu, N. Dense Attention Pyramid Networks for Multi-Scale Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 8983–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Ke, X. Quad-FPN: A Novel Quad Feature Pyramid Network for SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Fan, B.; Zhang, Q.; Xiang, S.; Pan, C. AugFPN: Improving Multi-Scale Feature Learning for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 12592–12601. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.B.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S.J. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 936–944. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Gong, Y.; Jiang, N.; Ye, Q.; Han, Z. Scale Match for Tiny Person Detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Snowmass Village, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020; pp. 1246–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path Aggregation Network for Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar]
- Hosang, J.; Benenson, R.; Schiele, B. Learning non-maximum suppression. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.02950. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Girshick, R.B.; Dollár, P. Rethinking ImageNet Pre-Training. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 4917–4926. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1405.0312. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.B.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-Local Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7794–7803. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Pang, J.; Cao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Feng, W.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. MMDetection: Open MMLab Detection Toolbox and Benchmark. arXiv 2019, arXiv:abs/1906.07155. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.B.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, Z.; Vasconcelos, N. Cascade R-CNN: Delving Into High Quality Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6154–6162. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Fu, Y.R. Rethinking Classification and Localization for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 10183–10192. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Li, B.; Yue, Y.; Li, Q.; Yan, J. Grid R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7355–7364. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, K.; Yang, S.; Loy, C.C.; Lin, D. Region Proposal by Guided Anchoring. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2960–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wan, F.; Liu, C.; Ji, R.; Ye, Q. FreeAnchor: Learning to Match Anchors for Visual Object Detection. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.02466. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, H.; He, T. FCOS: Fully Convolutional One-Stage Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9626–9635. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Chi, C.; Yao, Y.; Lei, Z.; Li, S.Z. Bridging the Gap Between Anchor-Based and Anchor-Free Detection via Adaptive Training Sample Selection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 9756–9765. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, T.; Sun, F.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, J. FoveaBox: Beyond Anchor-Based Object Detector. arXiv 2019, arXiv:abs/1904.03797. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Huo, C.; Xu, N.; Jiang, H.; Cao, Y.; Ni, L.; Pan, C. Multitask Learning for Ship Detection From Synthetic Aperture Radar Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 8048–8062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| No. | Method | r | p | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Faster R-CNN [50] | 0.720 | 0.766 | 0.694 |
| 2 | PANET [43] | 0.719 | 0.746 | 0.693 |
| 3 | Cascade R-CNN [51] | 0.711 | 0.794 | 0.689 |
| 4 | Double-Head R-CNN [52] | 0.719 | 0.743 | 0.695 |
| 5 | Grid R-CNN [53] | 0.711 | 0.664 | 0.683 |
| 6 | DCN [54] | 0.717 | 0.762 | 0.691 |
| 7 | Guided Anchoring [55] | 0.638 | 0.801 | 0.598 |
| 8 | Free-Anchor [56] | 0.721 | 0.232 | 0.628 |
| 9 | FCOS [57] | 0.667 | 0.505 | 0.632 |
| 10 | ATSS [58] | 0.715 | 0.742 | 0.681 |
| 11 | FoveaBox [59] | 0.599 | 0.775 | 0.522 |
| 12 | SA Faster R-CNN+PBHT [49] | 0.778 | 0.748 | 0.751 |
| 13 | SE Faster R-CNN+PBHT [49] | 0.772 | 0.747 | 0.743 |
| 14 | MTL-Det [60] | - | - | 0.717 |
| 15 | SII-Net | 0.793 | 0.682 | 0.761 |
| Size | r | p | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|
| (0,100) | 0.005 | 1 | 0.005 |
| (100,400) | 0.630 | 0.576 | 0.568 |
| (400,900) | 0.911 | 0.886 | 0.894 |
| (900,1600) | 0.980 | 0.944 | 0.976 |
| Size | r | p | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|
| (0,100) | 0.120 | 0.764 | 0.101 |
| (100,400) | 0.766 | 0.513 | 0.687 |
| (400,900) | 0.933 | 0.875 | 0.918 |
| (900,1600) | 0.987 | 0.931 | 0.976 |
| No. | Method | r | p | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Faster R-CNN [50] | 0.401 | 0.601 | 0.353 |
| 2 | PANET [43] | 0.393 | 0.566 | 0.342 |
| 3 | Cascade R-CNN [51] | 0.376 | 0.645 | 0.337 |
| 4 | Double-Head R-CNN [52] | 0.385 | 0.556 | 0.337 |
| 5 | Grid R-CNN [53] | 0.414 | 0.425 | 0.367 |
| 6 | DCN [54] | 0.393 | 0.601 | 0.346 |
| 7 | Guided Anchoring [55] | 0.353 | 0.649 | 0.308 |
| 8 | Free-Anchor [56] | 0.456 | 0.700 | 0.273 |
| 9 | FCOS [57] | 0.291 | 0.534 | 0.245 |
| 10 | ATSS [58] | 0.376 | 0.543 | 0.327 |
| 11 | FoveaBox [59] | 0.272 | 0.527 | 0.230 |
| 12 | SA Faster R-CNN+PBHT [49] | 0.526 | 0.579 | 0.466 |
| 13 | SE Faster R-CNN+PBHT [49] | 0.517 | 0.579 | 0.455 |
| 14 | MTL-Det [60] | - | - | 0.387 |
| 15 | SII-Net | 0.554 | 0.461 | 0.469 |
| No. | Method | r | p | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Faster R-CNN [50] | 0.908 | 0.824 | 0.887 |
| 2 | PANET [43] | 0.911 | 0.812 | 0.890 |
| 3 | Cascade R-CNN [51] | 0.909 | 0.840 | 0.890 |
| 4 | Double-Head R-CNN [52] | 0.916 | 0.811 | 0.897 |
| 5 | Grid R-CNN [53] | 0.886 | 0.785 | 0.800 |
| 6 | DCN [54] | 0.909 | 0.818 | 0.886 |
| 7 | Guided Anchoring [55] | 0.807 | 0.852 | 0.768 |
| 8 | Free-Anchor [56] | 0.877 | 0.665 | 0.778 |
| 9 | FCOS [57] | 0.895 | 0.792 | 0.823 |
| 10 | ATSS [58] | 0.887 | 0.803 | 0.865 |
| 11 | FoveaBox [59] | 0.793 | 0.858 | 0.704 |
| 12 | SA Faster R-CNN+PBHT [49] | 0.927 | 0.829 | 0.908 |
| 13 | SE Faster R-CNN+PBHT [49] | 0.922 | 0.827 | 0.902 |
| 14 | MTL-Det [60] | - | - | 0.887 |
| 15 | SII-Net | 0.934 | 0.819 | 0.916 |
| No. | Method | r | p | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Faster R-CNN [50] | 0.904 | 0.870 | 0.897 |
| 2 | PANET [43] | 0.919 | 0.868 | 0.911 |
| 3 | Cascade R-CNN [51] | 0.908 | 0.941 | 0.905 |
| 4 | Double-Head R-CNN [52] | 0.919 | 0.869 | 0.911 |
| 5 | Grid R-CNN [53] | 0.897 | 0.877 | 0.889 |
| 6 | DCN [54] | 0.930 | 0.862 | 0.922 |
| 7 | Guided Anchoring [55] | 0.904 | 0.946 | 0.900 |
| 8 | Free-Anchor [56] | 0.926 | 0.723 | 0.910 |
| 9 | HR-SDNet [7] | 0.909 | 0.964 | 0.908 |
| 10 | DAPN [38] | 0.913 | 0.855 | 0.905 |
| 11 | SER Faster R-CNN [18] | 0.922 | 0.861 | 0.915 |
| 12 | ARPN [19] | 0.906 | 0.854 | 0.898 |
| 13 | Quad-FPN [39] | 0.957 | 0.895 | 0.952 |
| 14 | SII-Net | 0.968 | 0.861 | 0.955 |
| No. | Method | r | p | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Faster R-CNN [50] | 0.932 | 0.868 | 0.917 |
| 2 | PANET [43] | 0.934 | 0.868 | 0.920 |
| 3 | Cascade R-CNN [51] | 0.934 | 0.905 | 0.922 |
| 4 | Double-Head R-CNN [52] | 0.941 | 0.884 | 0.929 |
| 5 | Grid R-CNN [53] | 0.930 | 0.851 | 0.914 |
| 6 | DCN [54] | 0.932 | 0.862 | 0.918 |
| 7 | Guided Anchoring [55] | 0.938 | 0.925 | 0.927 |
| 8 | Free-Anchor [56] | 0.949 | 0.839 | 0.937 |
| 9 | HR-SDNet [7] | 0.932 | 0.921 | 0.922 |
| 10 | DAPN [38] | 0.933 | 0.872 | 0.919 |
| 11 | SER Faster R-CNN [18] | 0.935 | 0.867 | 0.921 |
| 12 | ARPN [19] | 0.920 | 0.881 | 0.913 |
| 13 | Quad-FPN [39] | 0.961 | 0.775 | 0.943 |
| 14 | SII-Net | 0.955 | 0.765 | 0.932 |
| CLAM | HLEM | R-Branch | r | p | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | O | O | 0.760 | 0.651 | 0.719 |
| P | O | O | 0.767 | 0.724 | 0.740 |
| P | P | O | 0.772 | 0.744 | 0.748 |
| P | P | P | 0.793 | 0.682 | 0.761 |
| CLAM | HLEM | R-Branch | r | p | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | P | P | 0.764 | 0.756 | 0.737 |
| P | P | P | 0.793 | 0.682 | 0.761 |
| CLAM | HLEM | R-Branch | r | p | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | O | O | 0.760 | 0.651 | 0.719 |
| P | O | O | 0.767 | 0.724 | 0.740 |
| CLAM | HLEM | R-Branch | r | p | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | O | P | 0.763 | 0.664 | 0.728 |
| P | P | P | 0.793 | 0.682 | 0.761 |
| CLAM | HLEM | R-Branch | r | p | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | O | O | 0.760 | 0.651 | 0.719 |
| O | P | O | 0.776 | 0.741 | 0.751 |
| CLAM | HLEM | R-Branch | r | p | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | P | O | 0.772 | 0.744 | 0.748 |
| P | P | P | 0.793 | 0.682 | 0.761 |
| CLAM | HLEM | R-Branch | r | p | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | O | O | 0.760 | 0.651 | 0.719 |
| O | O | P | 0.765 | 0.716 | 0.734 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, N.; He, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, C.; Xing, X. SII-Net: Spatial Information Integration Network for Small Target Detection in SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030442
Su N, He J, Yan Y, Zhao C, Xing X. SII-Net: Spatial Information Integration Network for Small Target Detection in SAR Images. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(3):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030442
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Nan, Jiayue He, Yiming Yan, Chunhui Zhao, and Xiangwei Xing. 2022. "SII-Net: Spatial Information Integration Network for Small Target Detection in SAR Images" Remote Sensing 14, no. 3: 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030442
APA StyleSu, N., He, J., Yan, Y., Zhao, C., & Xing, X. (2022). SII-Net: Spatial Information Integration Network for Small Target Detection in SAR Images. Remote Sensing, 14(3), 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030442