Challenges and Opportunities in Remote Sensing for Soil Salinization Mapping and Monitoring: A Review
Abstract
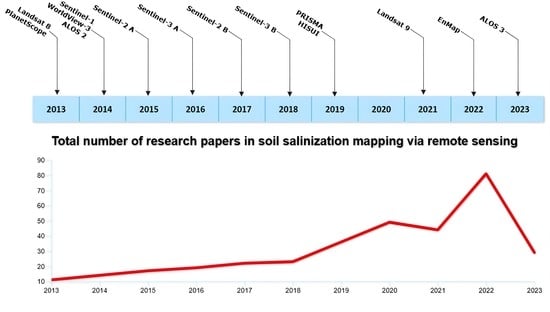
:1. Introduction
2. Remote Sensing for Mapping Soil Salinization
3. Uncovering Data Availability: Investigating the Scope and Scale of Accessible Data
3.1. Local Scale
3.2. Regional Scale
3.3. Global Scale
4. Mapping Approaches
5. Challenges in Salinization Mapping
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Soil Salinization as a Global Major Challenge|ITPS Soil Letter #3. Available online: https://www.fao.org/global-soil-partnership/resources/highlights/detail/en/c/1412475/ (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Shahid, S.A.; Zaman, M.; Heng, L. Introduction to Soil Salinity, Sodicity and Diagnostics Techniques. In Guideline for Salinity Assessment, Mitigation, and Adaptation Using Nuclear and Related Techniques; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daba, A.W.; Qureshi, A.S. Review of Soil Salinity and Sodicity Challenges to Crop Production in the Lowland Irrigated Areas of Ethiopia and Its Management Strategies. Land 2021, 10, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, F.; Schillaci, C.; Keshavarzi, A.; Başayiğit, L. Predictive Mapping of Electrical Conductivity and Assessment of Soil Salinity in a Western Türkiye Alluvial Plain. Land 2022, 11, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, P.; Kumar, R. Soil salinity: A serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okur, B.; Orcen, N. Soil Salinization and Climate Change. In Climate Change and Soil Interactions; Prasad, M.N.V., Pietrzykowski, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 331–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L. Climate Change Impacts on Soil Salinity in Agricultural Areas. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 72, 842–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Shaukat, M.; Ashraf, M.; Zhu, C.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, J. Salinity Stress in Arid and Semi-Arid Climates: Effects and Management in Field Crops. In Climate Change and Agriculture; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Global Predictions of Primary Soil Salinization under Changing Climate in the 21st Century. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W. A Brief Review on Soil Salinity Mapping by Optical and Radar Remote Sensing. In Research Developments in Saline Agriculture; Dagar, J.C., Yadav, R.S., Sharma, P.C., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L.; Scudiero, E. Review of Soil Salinity Assessment for Agriculture across Multiple Scales Using Proximal and/or Remote Sensors. Adv. Agron. 2019, 158, 1–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metternicht, G.I.; Zinck, J.A. Remote sensing of soil salinity: Potentials and constraints. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Xu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Q. Soil Salinization and Mitigation Measures in Land Reclamation Regions. In Soil Contamination—Current Consequences and Further Solutions; Larramendy, M.L., Soloneski, S., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Soil salinity: A global threat to sustainable development. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 39–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghadosi, M.M.; Hasanlou, M.; Eftekhari, K. Soil salinity mapping using dual-polarized SAR Sentinel-1 imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 40, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasim, N.; Maihemuti, B.; Sawut, R.; Abliz, A.; Dong, C.; Abdumutallip, M. Quantitative Estimation of Soil Salinization in an Arid Region of the Keriya Oasis Based on Multidimensional Modeling. Water 2020, 12, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azabdaftari, A.; Sunar, F. Soil Salinity Mapping Using Multitemporal Landsat Data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2016, XLI-B7, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelgasim, A.A.; Ammad, R. Mapping soil salinity in arid and semi-arid regions using Landsat 8 OLI satellite data. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2019, 13, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günal, E.; Wang, X.; Kılıc, O.M.; Budak, M.; Al Obaid, S.; Ansari, M.J.; Brestic, M. Potential of Landsat 8 OLI for mapping and monitoring of soil salinity in an arid region: A case study in Dushak, Turkmenistan. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avdan, U.; Kaplan, G.; Küçük Matcı, D.; Yigit Avdan, Z.; Erdem, F.; Tuğba Mizik, E.; lknur Demirtas, I. Soil salinity prediction models constructed by different remote sensors. Phys. Chem. Earth 2022, 128, 103230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahbeni, G. A PLSR model to predict soil salinity using Sentinel-2 MSI data. Open Geosci. 2021, 13, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceves, E.Á.; Guevara, H.J.P.; Enríquez, A.C.; Sánchez, M.F.; Mora, E.M. Determining Salinity and Ion Soil Using Satellite Image Processing. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 1549–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merembayev, T.; Amirgaliyev, Y.; Saurov, S.; Wójcik, W. Soil Salinity Classification Using Machine Learning Algorithms and Radar Data in the Case from the South of Kazakhstan. J. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 23, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smanov, Z.M.; Laiskhanov, S.U.; Poshanov, M.N.; Abikbayev, Y.R.; Duisekov, S.N.; Tulegenov, Y.A. Mapping of Cornfield Soil Salinity in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions. J. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 24, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.M.; Rastoskuev, V.V.; Sato, Y.; Shiozawa, S. Assessment of Hydro Saline Land Degradation by Using a Simple Approach of Remote Sensing Indicators. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 77, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, K. Recent Trend and Advance of Synthetic Aperture Radar with Selected Topics. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 716–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, B.; Dwyer, E.; Whelan, P. Soil Moisture Retrieval from Active Spaceborne Microwave Observations: An Evaluation of Current Techniques. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 210–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, J.; Snapir, B.; Waine, T.; Evans, J.; Corstanje, R. The Significance of Soil Properties to the Estimation of Soil Moisture from C-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2019, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhetaer, N.; Nurmemet, I.; Abulaiti, A.; Xiao, S.; Zhao, J. A Quantifying Approach to Soil Salinity Based on a Radar Feature Space Model Using ALOS PALSAR-2 Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Lambot, S. Analysis of Low-Frequency Drone-Borne GPR for Root-Zone Soil Electrical Conductivity Characterization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, P.; Giang, N.; Binh, N.; Hai, L.; Pham, T.-D.; Hasanlou, M.; Bui, D.T. Soil Salinity Mapping Using SAR Sentinel-1 Data and Advanced Machine Learning Algorithms: A Case Study at Ben Tre Province of the Mekong River Delta (Vietnam). Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehni, A.; Lounis, M. Remote Sensing Techniques for Salt-Affected Soil Mapping: Application to the Oran Region of Algeria. Procedia Eng. 2012, 33, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahbeni, G.; Székely, B. Salinity Levels Discrimination Using ERS-1/2 and Sentinel-1 SAR Time Series Data in Hortobágyi National Park, Hungary. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Mediterranean and Middle East Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (M2GARSS), Virtual, 7–9 March 2022; pp. 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrayini, E.; Noroozi, A.A. Modeling and Mapping of Soil Salinity and Alkalinity Using Remote Sensing Data and Topographic Factors: A Case Study in Iran. Environ. Model. Assess 2022, 27, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, I.H. Machine Learning: Algorithms, Real-World Applications and Research Directions. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V.; Golowich, S.; Smola, A. Support vector method for function approximation, regression estimation, and signal processing. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 9; Mozer, M.C., Jordan, M.I., Petsche, T., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997; pp. 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen, D.; Van Niekerk, A. Machine learning performance for predicting soil salinity using different combinations of geomorphometric covariates. Geoderma 2017, 299, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, S.; Yang, W.; Yang, X.; Ding, J. Comparison of machine learning algorithms for soil salinity predictions in three dryland oases located in Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region (XJUAR) of China. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 52, 256–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillel, D.; Braimoh, A.K.; Vlek, P.L.G. Soil Degradation Under Irrigation. In Land Use and Soil Resources; Braimoh, A.K., Vlek, P.L.G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, M.; Subash Chandra Bose, K.; Elavarasi, P.; Tawfik, E. Soil Salinity and Its Management. In Soil Moisture Importance; Meena, R.S., Datta, R., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; Volume 1, Chapter 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yu, L.; Du, Z.; Peng, D.; Hao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, P. An Overview of the Applications of Earth Observation Satellite Data: Impacts and Future Trends. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudiero, E.; Corwin, D.L.; Anderson, R.G.; Skaggs, T.H. Moving Forward on Remote Sensing of Soil Salinity at Regional Scale. Front. Environ. Sci. 2016, 4, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, V.; Ahmadi, H.; Jafari, M.; Moeini, A. Mapping Soil Salinity Using a Combined Spectral and Topographical Index with Artificial Neural Network. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0228494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Li, H.; Yin, C.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H. Soil Salinity Mapping Using Machine Learning Algorithms with the Sentinel-2 MSI in Arid Areas, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Muhaimeed, A.S.; Al-Shafie, W.M.; Al-Quraishi, A.M.F. Using Radar and Optical Data for Soil Salinity Modeling and Mapping in Central Iraq. In Environmental Remote Sensing and GIS in Iraq; Al-Quraishi, A., Negm, A., Eds.; Springer Water: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahbeni, G. Soil Salinity Mapping Using Landsat 8 OLI Data and Regression Modeling in the Great Hungarian Plain. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, K.; Kallel, A.; Rebah, Z.B.; Solaiman, B. Spatio-temporal monitoring of soil salinity and land cover changes using remote sensing techniques: Zaghouan case study (Tunisia). In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Signal and Image Processing (ATSIP), Sfax, Tunisia, 24–27 May 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biro Turk, K.; Aljughaiman, A. Land use/land cover assessment as related to soil and irrigation water salinity over an oasis in arid environment. Open Geosci. 2020, 12, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekka, C.; Petropoulos, G.P.; Triantakonstantis, D.; Detsikas, S.E.; Chalkias, C. Exploring the spatial patterns of soil salinity and organic carbon in agricultural areas of Lesvos Island, Greece, using Geoinformation Technologies. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakacsi, Z.; Tóth, T.; Makó, A.; Barna, G.; Laborczi, A.; Szabó, J.; Szatmári, G.; Pásztor, L. National level assessment of soil salinization and structural degradation risks under irrigation. Hung. Geogr. Bull. 2019, 68, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, A.A.; Koike, K.; Atwia, M.G.; El-Horiny, M.M.; Gemail, K.S. Mapping Soil Salinity Using Spectral Mixture Analysis of Landsat 8 OLI Images to Identify Factors Influencing Salinization in an Arid Region. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2019, 83, 101944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.P.; Qasim, S.; Bachri, S. Investigating Remote Sensing Properties for Soil Salinity Mapping: A Case Study in Korat Province of Thailand. Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-SayedGad, M.M.; Mohamed, M.H.A.; Mohamed, M.R. Soil salinity mapping using remote sensing and GIS. Geomatica 2022, 75, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howari, F.M.; Goodell, P.C.; Miyamoto, S. Spectral Properties of Salt Crusts Formed on Saline Soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, C.; Fu, X. Characteristics of Soil Salt Crust Formed by Mixing Calcium Chloride with Sodium Sulfate and the Possibility of Inhibiting Wind-Sand Flow. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metternicht, G.I.; Zinck, J.A. Spatial Discrimination of Salt- and Sodium-Affected Soil Surfaces. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 2571–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannari, A.; Guedon, A.M.; El-Harti, A.; Cherkaoui, F.Z.; El-Ghmari, A. Characterization of Slightly and Moderately Saline and Sodic Soils in Irrigated Agricultural Land using Simulated Data of Advanced Land Imaging (EO-1) Sensor. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2008, 39, 2795–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahbeni, G. Comparative Study of Machine-Learning-Based Classifiers for Soil Salinization Prediction using Sentinel-1 SAR and Sentinel-2 MSI Data. In Proceedings of the 2022 10th International Conference on Agro-Geoinformatics (Agro-Geoinformatics), Valencia, Spain, 7–9 July 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldshleger, N.; Chudnovsky, A.; Ben-Binyamin, R. Predicting Salinity in Tomato Using Soil Reflectance Spectral. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 6079–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, A.; Pan, K.; Li, Y.; Pan, X. Mapping the Salt Content in Soil Profiles Using Vis-NIR Hyperspectral Imaging. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2018, 82, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajakumari, S.; Mahesh, R.; Sarunjith, K.J.; Ramesh, R. Building spectral catalogue for salt marsh vegetation, hyperspectral and multispectral remote sensing. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2022, 53, 102435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.A.; Liou, Y.A.; Tran, H.P.; Hoang, P.P.; Nguyen, T.H. Soil Salinity Assessment by Using Near-Infrared Channel and Vegetation Soil Salinity Index Derived from Landsat 8 OLI Data: A Case Study in the Tra Vinh Province, Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2020, 7, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.B.; Castanheira, N.; Oliveira, A.R.; Paz, A.M.; Darouich, H.; Simionesei, L.; Farzamian, M.; Gonçalves, M.C. Soil salinity assessment using vegetation indices derived from Sentinel-2 multispectral data. Application to Lezíria Grande, Portugal. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 241, 106387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metternicht, G.I.; Zinck, J.A. Remote Sensing of Soil Salinization: Impact on Land Management; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Peng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhao, R.; Jiang, Q.; Fu, T.; Wang, F.; Shi, Z. Quantitative Estimation of Soil Salinity Using UAV-Borne Hyperspectral and Satellite Multispectral Images. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Ding, J.; Han, L.S.; Zhang, Z.; Ran, S. Digital mapping of soil salinization based on Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data combined with machine learning algorithms. Reg. Sustain. 2021, 2, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, F.; Yang, T.; Tian, Z.; Lai, J.; Zhu, W.; Long, B. Relating Hyperspectral Vegetation Indices with Soil Salinity at Different Depths for the Diagnosis of Winter Wheat Salt Stress. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Chang, C.; Song, J.; Zhuge, Y.; Wang, A. Precise Monitoring of Soil Salinity in China’s Yellow River Delta Using UAV-Borne Multispectral Imagery and a Soil Salinity Retrieval Index. Sensors 2022, 22, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Han, B.; Yang, F.; Fan, Y.; Jiang, L.; Chen, S.; Yang, W.; Gong, R.; Liang, T. Salinization Information Extraction Model Based on VI–SI Feature Space Combinations in the Yellow River Delta Based on Landsat 8 OLI Image. Geomat. Nat. Haz. Risk 2019, 10, 1863–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allbed, A.; Kumar, L. Soil Salinity Mapping and Monitoring in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions Using Remote Sensing Technology: A Review. Adv. Remote Sens. 2013, 2, 404–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Suomalainen, J.; Liu, J.; Hyyppä, J.; Kaartinen, H.; Haggren, H. A Review: Remote Sensing Sensors, Multi-Purposeful Application of Geospatial Data; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiri, D.; Simwanda, M.; Salekin, S.; Nyirenda, V.R.; Murayama, Y.; Ranagalage, M. Sentinel-2 Data for Land Cover/Use Mapping: A Review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, W.J.; Dash, J.; Watmough, G.; Milton, E.J. Evaluating the Capabilities of Sentinel-2 for Quantitative Estimation of Biophysical Variables in Vegetation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 82, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, C.; Lau, I.C.; Wheaton, B.; Cater, D.; Bourke, L.; Asada, N.; Kashimura, O.; Ong, C.C.; Cudahy, T. Estimating soil salinity using hyperspectral data in the Western Australian wheat belt. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium—IGARSS, Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 4325–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha Neto, O.; Teixeira, A.; Leão, R.; Moreira, L.; Galvão, L. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing for Detecting Soil Salinization Using ProSpecTIR-VS Aerial Imagery and Sensor Simulation. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hamid, H.T.; Hong, G. Hyperspectral remote sensing for extraction of soil salinization in the northern region of Ningxia. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 6, 2487–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Gong, P.; Zhu, Z. A Spectral Index for Estimating Soil Salinity in the Yellow River Delta Region of China Using EO-1 Hyperion Data. Pedosphere 2010, 20, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Shu, H.; Lei, L.; Xu, J. Estimating soil salt components and salinity using hyperspectral remote sensing data in an arid area of China. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 016043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Du, Y.; Yin, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J. Radar remote sensing-based inversion model of soil salt content at different depths under vegetation. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurmemet, I.; Sagan, V.; Ding, J.L.; Halik, U.; Abliz, A.; Yakup, Z. A WFS-SVM Model for Soil Salinity Mapping in Keriya Oasis, North-western China Using Polarimetric Decomposition and Fully PolSAR Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzone, A.; Cotrozzi, L.; Lorenzini, G.; Nali, C.; Pellegrini, E. Hyperspectral Detection and Monitoring of Salt Stress in Pomegranate Cultivars. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turhan, H.; Genc, L.; Smith, S.E.; Bostanci, Y.B.; Turkmen, O.S. Assessment of the Effect of Salinity on the Early Growth Stage of the Common Sunflower (Sanay Cultivar) Using Spectral Discrimination Techniques. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 761–767. [Google Scholar]
- Gorji, T.; Tanik, A.; Sertel, E. Soil Salinity Prediction, Monitoring and Mapping Using Modern Technologies. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 15, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerardo, R.; de Lima, I.P. Sentinel-2 Satellite Imagery-Based Assessment of Soil Salinity in Irrigated Rice Fields in Portugal. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, O.M.; Budak, M.; Gunal, E.; Acir, N.; Halbac-Cotoara-Zamfir, R.; Alfarraj, S.; Ansari, M.J. Soil salinity assessment of a natural pasture using remote sensing techniques in central Anatolia, Turkey. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharsallah, M.E.; Aichi, H.; Stambouli, T.; Ben Rabah, Z.; Ben Hassine, H. Assessment and mapping of soil salinity using electromagnetic induction and Landsat 8 OLI remote sensing data in an irrigated olive orchard under semi-arid conditions. Soil Water Res. 2022, 17, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Qin, R.; Chen, X. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle for Remote Sensing Applications—A Review. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Cerro, J.; Cruz Ulloa, C.; Barrientos, A.; de León Rivas, J. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Agriculture: A Survey. Agronomy 2021, 11, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melendez-Pastor, I.; Navarro-Pedreño, J.; Koch, M.; Gómez, I. Applying Imaging Spectroscopy Techniques to Map Saline Soils with ASTER Images. Geoderma 2010, 158, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Tsanis, I.K.; Koutroulis, A.G.; Kourgialas, N.N.; Varouchakis, A.E.; Karatzas, G.P.; Ritsema, C.J. The threat of soil salinity: A European scale review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.; Chan, N.W.; Kung, H.; Ariken, M.; Wang, Y. Regional suitability prediction of soil salinization based on remote-sensing derivatives and optimal spectral index. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ma, F.; Li, J.; Gu, Q.; Yang, S.; Wu, D.; Ding, J. Characterizing and modeling regional-scale variations in soil salinity in the arid oasis of Tarim Basin, China. Geoderma 2017, 305, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Zhang, J.; He, W.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, R.; Zamanian, K.; Jia, K.; Zhao, X. Combination of Hyperspectral and Machine Learning to Invert Soil Electrical Conductivity. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudiero, E.; Skaggs, T.H.; Corwin, D.L. Regional-scale soil salinity assessment using Landsat ETM+ canopy reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, N.; Barman, A.; Sundha, P.; Rai, A.K. Recent Trends in Soil Salinity Appraisal and Management. In Soil Analysis: Recent Trends and Applications; Rakshit, A., Ghosh, S., Chakraborty, S., Philip, V., Datta, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholdorov, S.; Gopakumar, L.; Katsura, K.; Jabbarov, Z.; Jobborov, O.; Shamsiddinov, T.; Khakimov, A. Soil salinity assessment research using remote sensing techniques: A special focus on recent research. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1068, 012037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; ITPS. Status of the World’s Soil Resources (SWSR)—Main Report; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and Intergovernmental Technical Panel on Soils: Rome, Italy, 2015; Available online: https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/c6814873-efc3-41db-b7d3-2081a10ede50/ (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- FAO. Salt-Affected Soils. Available online: http://www.fao.org/soils-portal/soil-management/management-of-some-problem-soils/salt-affected-soils/more-information-on-salt-affected-soils/en/ (accessed on 8 March 2023).
- FAO. Legacy Soil Maps and Soils Databases. Available online: https://www.fao.org/soils-portal/data-hub/soil-maps-and-databases/en/ (accessed on 8 March 2023).
- Ivushkin, K.; Bartholomeus, H.; Bregt, A.K.; Pulatov, A.; Kempen, B.; de Sousa, L. Global Mapping of Soil Salinity Change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, G.; Bakacsi, Z.; Laborczi, A.; Petrik, O.; Pataki, R.; Tóth, T.; Pásztor, L. Elaborating Hungarian Segment of the Global Map of Salt-Affected Soils (GSSmap): National Contribution to an International Initiative. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. World Map of Salt-Affected Soils Launched at Virtual Conference. 2021. Available online: www.fao.org/newsroom/detail/salt-affected-soils-map-symposium/en (accessed on 8 March 2023).
- Omuto, C.T.; Vargas, R.R.; El Mobarak, A.M.; Mohamed, N.; Viatkin, K.; Yigini, Y. Mapping of Salt-Affected Soils: Technical Manual; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L.; Yemoto, K. Measurement of soil salinity: Electrical conductivity and total dissolved solids. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2019, 83, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Soil Salinization Management for Sustainable Development: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, G.; Al-Hawas, I.A. Salinity sensor: A reliable tool for monitoring in situ soil salinity under saline irrigation. Int. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 3, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaw, E.; Suryabhagavan, K.V.; Argaw, M. Soil salinity modeling and mapping using remote sensing and GIS: The case of Wonji sugar cane irrigation farm, Ethiopia. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2018, 17, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradipta, A.; Soupios, P.; Kourgialas, N.; Doula, M.; Dokou, Z.; Makkawi, M.; Alfarhan, M.; Tawabini, B.; Kirmizakis, P.; Yassin, M. Remote Sensing, Geophysics, and Modeling to Support Precision Agriculture—Part 1: Soil Applications. Water 2022, 14, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafik, A.; Ibouh, H.; El Alaoui El Fels, A.; Eddahby, L.; Mezzane, D.; Bousfoul, M.; Amazirh, A.; Ouhamdouch, S.; Bahir, M.; Gourfi, A.; et al. Soil Salinity Detection and Mapping in an Environment under Water Stress between 1984 and 2018 (Case of the Largest Oasis in Africa-Morocco). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqasemi, A.; Ibrahim, M.; Fadhil Al-Quraishi, A.; Saibi, H.; Al-Fugara, A.; Kaplan, G. Detection and Modeling of Soil Salinity Variations in Arid Lands Using Remote Sensing Data. Open Geosci. 2021, 13, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmetwalli, A.M.H.; Tyler, A.N.; Hunter, P.D.; Salt, C.A. Detecting and distinguishing moisture-and salinity-induced stress in wheat and maize through in situ spectroradiometry measurements. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 3, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, S.; Shamsi, S.R.; Abtahi, S.M. Weakly-coupled geostatistical mapping of soil salinity to Stepwise Multiple Linear Regression of MODIS spectral image products. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 152, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Shi, Z.; Biswas, A.; Yang, S.; Ding, J.; Wang, F. Updated information on soil salinity in a typical oasis agroecosystem and desert-oasis ecotone: Case study conducted along the Tarim River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 135387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantaravikorn, Y.; Ongsomwang, S. Soil Salinity Prediction and Its Severity Mapping Using a Suitable Interpolation Method on Data Collected by Electromagnetic Induction Method. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Weston, S.; Keefer, C.; Coulter, N.; Quinlan, R. Cubist: Rule-and Instance-Based Regression Modeling, R Package Version 0.0.18; CRAN: Vienna, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Li, E.; Wei, H.; Li, C.; Qiao, Q.; Armaghani, D.J. Random Forests and Cubist Algorithms for Predicting Shear Strengths of Rockfill Materials. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, R. Combining instance based and model based learning. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Machine Learning, Amherst, MA, USA, 27–29 June 1993; pp. 236–243. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Biswas, A.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, R.; Hu, J.; Hu, B.; Shi, Z. Estimating soil salinity from remote sensing and terrain data in southern Xinjiang Province, China. Geoderma 2019, 337, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Li, S.; Makar, R.S.; Li, H.; Feng, C.; Luo, D.; Shen, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Fang, L. Proximal Soil Sensing of Low Salinity in Southern Xinjiang, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahbeni, G.; Székely, B. Spatial Modeling of Soil Salinity Using Kriging Interpolation Techniques: A Study Case in the Great Hungarian Plain. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. 2022, 11, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hateffard, F.; Balog, K.; Tóth, T.; Mészáros, J.; Árvai, M.; Kovács, Z.A.; Szűcs-Vásárhelyi, N.; Koós, S.; László, P.; Novák, T.J.; et al. High-Resolution Mapping and Assessment of Salt-Affectedness on Arable Lands by the Combination of Ensemble Learning and Multivariate Geostatistics. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Li, S.; Wu, R.; Shen, D. Study on the Scale Effect of Spatial Variation in Soil Salinity Based on Geostatistics: A Case Study of Yingdaya River Irrigation Area. Land 2022, 11, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeri, F.; Mariethoz, G. A review of geostatistical simulation models applied to satellite remote sensing: Methods and applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 259, 112381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahbeni, G.; Székely, B. Machine Learning Models for Estimating Soil Salinity Using Sentinel-1 SAR and Landsat-8 OLI Data. J. Adv. Geospat. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Garajeh, M.K.; Malakyar, F.; Weng, Q.; Feizizadeh, B.; Blaschke, T.; Lakes, T. An automated deep learning convolutional neural network algorithm applied for soil salinity distribution mapping in Lake Urmia, Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Ji, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Fan, J.; Wang, H. Prediction of soil salinity parameters using machine learning models in an arid region of Northwest China. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 204, 107512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Xing, A.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X. Spatial prediction of soil salinity in a Semi-arid Oasis: Environmental Sensitive Variable Selection and Model Comparison. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 784–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Mao, Z.; Qi, S.; Zhang, C.; Yin, Z. The Role of Soil Salinization in Shaping the Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Soil Organic Carbon Stock. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, E.J.; Banks, A.C.; Gurney, R.J. Remote sensing of soil-vegetation- atmosphere transfer processes. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 1997, 21, 549–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, G.; Zeng, W.; Yu, J.; Huang, J. A comparison of physical-based and machine learning modeling for soil salt dynamics in crop fields. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 277, 108115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, B.; Yabar, H.; Faruque, M.J. Exploring the Potential of Soil Salinity Assessment through Remote Sensing and GIS: Case Study in the Coastal Rural Areas of Bangladesh. Land 2022, 11, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadl, M.E.; Jalhoum, M.E.M.; Abdelrahman, M.A.E.; Ali, E.A.; Zahra, W.R.; Abuzaid, A.S.; Fiorentino, C.; D’Antonio, P.; Belal, A.A.; Scopa, A. Soil Salinity Assessing and Mapping Using Several Statistical and Distribution Techniques in Arid and Semi-Arid Ecosystems, Egypt. Agronomy 2023, 13, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Ding, J.; Teng, D.; Wang, J.; Huo, T.; Jin, X.; Wang, J.; He, B.; Han, L. Updated soil salinity with fine spatial resolution and high accuracy: The synergy of sentinel-2 MSI, environmental covariates and hybrid machine learning approaches. CATENA 2022, 212, 106054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, M.A.E.; Afifi, A.A.; D’Antonio, P.; Gabr, S.S.; Scopa, A. Detecting and Mapping Salt-Affected Soil with Arid Integrated Indices in Feature Space Using Multi-Temporal Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hihi, S.; Ben Rabah, Z.; Bouaziz, M.; Chtourou, M.; Bouaziz, S. Prediction of Soil Salinity Using Remote Sensing Tools and Linear Regression Model. Adv. Remote Sens. 2019, 8, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngabire, M.; Wang, T.; Xue, X.; Liao, J.; Sahbeni, G.; Huang, C.; Duan, H.; Song, X. Soil Salinization Mapping across Different Sandy Land-Cover Types in the Shiyang River Basin: A Remote Sensing and Multiple Linear Regression Approach. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 23, 100618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleymanov, A.; Gabbasova, I.; Komissarov, M.; Suleymanov, R.; Garipov, T.; Tuktarova, I.; Belan, L. Random Forest Modeling of Soil Properties in Saline Semi-Arid Areas. Agriculture 2023, 13, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.A.; Metwaly, M.M.; Metwalli, M.R.; AbdelRahman, M.A.E.; Badreldin, N. Integrating Active and Passive Remote Sensing Data for Mapping Soil Salinity Using Machine Learning and Feature Selection Approaches in Arid Regions. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Nurmemet, I.; Muhetaer, N.; Xiao, S.; Abulaiti, A. Monitoring Soil Salinity Using Machine Learning and the Polarimetric Scattering Features of PALSAR-2 Data. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Wang, S.; Gao, Z.; Lv, Y. Dynamic Prediction of Soil Salinization in an Irrigation District Based on the Support Vector Machine. Math. Comput. Model. 2013, 58, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Rusuli, Y.; Amuti, T.; He, Q. Quantitative Assessment of Soil Salinity Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data Based on the Support Vector Machine and Artificial Neural Network. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 40, 284–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.S.; El-Hady, M.A.; Rahim, I.S. Soil Salinity Mapping Utilizing Sentinel-2 and Neural Networks. Indian J. Agric. Res. 2018, 52, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, E.I.; Melendez-Pastor, I.; Navarro-Pedreño, J.; Gómez, I. Spectral Indices for the Detection of Salinity Effects in Melon Plants. Sci. Agric. 2014, 71, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matinfar, H.R.; Zandieh, V. Efficiency of Spectral Indices Derived from Landsat-8 Images of Maharloo Lake and Its Surrounding Rangelands. J. Rangeland Sci. 2016, 6, 334–343. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Q.; Han, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ge, H.; Li, X. Extraction of Saline Soil Distributions Using Different Salinity Indices and Deep Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadifar, A.; Gholami, H.; Golzari, S. Assessment of the Uncertainty and Interpretability of Deep Learning Models for Mapping Soil Salinity Using DeepQuantreg and Game Theory. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnaggar, A.; Noller, J. Application of Remote-sensing Data and Decision-Tree Analysis to Mapping Salt-Affected Soils over Large Areas. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Vincent, B.; Yang, J.; Bouarfa, S.; Vidal, A. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Changes in Soil Salinity: A Case Study in Inner Mongolia, China. Sensors 2008, 8, 7035–7049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, W. Sensing Biodiversity. Science 2014, 346, 301–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Kayem, K.; Hao, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, C.; Peng, J.; Liu, W.; Zuo, Q.; Ji, W.; Li, B. Mapping the Levels of Soil Salination and Alkalization by Integrating Machining Learning Methods and Soil-Forming Factors. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Yu, D. Monitoring and evaluating spatial variability of soil salinity in dry and wet seasons in the werigan–kuqa oasis, China, using remote sensing and electromagnetic induction instruments. Geoderma 2014, 235–236, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Lu, M.; Fan, Y.; Wu, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C. A novel remote sensing monitoring index of salinization based on three-dimensional feature space model and its application in the Yellow River Delta of China. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2022, 14, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Tashpolat, N. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Soil Salinity in Weigan River–Kuqa River Delta Oasis Based on Two-Dimensional Feature Space. Water 2023, 15, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapov, P.; Hansen, M.C.; Kommareddy, I.; Kommareddy, A.; Turubanova, S.; Pickens, A.; Adusei, B.; Tyukavina, A.; Ying, Q. Landsat Analysis Ready Data for Global Land Cover and Land Cover Change Mapping. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiam, S.; Villamor, G.B.; Faye, L.C.; Sène, J.H.; Diwediga, B.; Kyei-Baffour, N. Monitoring land use and soil salinity changes in coastal landscape: A case study from Senegal. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, P.; Zhang, J.; He, W.; Yuan, D.; Hu, Y.; Zamanian, K.; Jia, K.; Zhao, X. Inversion of Different Cultivated Soil Types’ Salinity Using Hyperspectral Data and Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagacherie, P.; Gomez, C.; Bailly, J.; Baret, F.; Coulouma, G. The Use of Hyperspectral Imagery for Digital Soil Mapping in Mediterranean Areas. In Digital Soil Mapping; Progress in Soil Science; Boettinger, J.L., Howell, D.W., Moore, A.C., Hartemink, A.E., Kienast-Brown, S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, K.J.; Chabrillat, S.; Brell, M.; Castaldi, F.; Spengler, D.; Foerster, S. Mapping Soil Organic Carbon for Airborne and Simulated EnMAP Imagery Using the LUCAS Soil Database and a Local PLSR. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mzid, N.; Castaldi, F.; Tolomio, M.; Pascucci, S.; Casa, R.; Pignatti, S. Evaluation of Agricultural Bare Soil Properties Retrieval from Landsat 8, Sentinel-2 and PRISMA Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasmi, A.; Gomez, C.; Chehbouni, A.; Dhiba, D.; El Gharous, M. Using PRISMA Hyperspectral Satellite Imagery and GIS Approaches for Soil Fertility Mapping (FertiMap) in Northern Morocco. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Weng, Y.; Tao, J. Towards decadal soil salinity mapping using Landsat time series data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 52, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eibedingil, I.G.; Gill, T.E.; Van Pelt, R.S.; Tong, D.Q. Combining Optical and Radar Satellite Imagery to Investigate the Surface Properties and Evolution of the Lordsburg Playa, New Mexico, USA. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, E.A.; Subburayalu, S.K.; Slater, B.; Dave, R.; Parekh, P.; Zhao, K.; Bhattacharya, B. Assessing the effectiveness of ground truth data to capture landscape variability from an agricultural region using gaussian simulation and geostatistical techniques. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekrecka, A.; Kedzierski, M. Integration of Satellite Data with High-Resolution Ratio: Improvement of Spectral Quality with Preserving Spatial Details. Sensors 2018, 18, 4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.L.; Feng, L.I.U.; Song, X.D. Recent Progress and Future Prospect of Digital Soil Mapping: A Review. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 2871–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safanelli, J.L.; Chabrillat, S.; Ben-Dor, E.; Demattê, J.A.M. Multispectral Models from Bare Soil Composites for Mapping Topsoil Properties over Europe. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Bao, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. A new digital soil mapping method with temporal-spatial-spectral information derived from multi-source satellite images. Geoderma 2022, 425, 116065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, E.; Frauenfelder, R.; Rüther, D.; Nava, L.; Rubensdotter, L.; Strout, J.; Nordal, S. Multi-Temporal Satellite Image Composites in Google Earth Engine for Improved Landslide Visibility: A Case Study of a Glacial Landscape. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; He, B.; Xie, B.; Ge, X.; Han, L. Investigation of the spatial and temporal variation of soil salinity using Google Earth Engine: A case study at Werigan–Kuqa Oasis, West China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, S.; Yildirim, A.; Gorji, T.; Hamzehpour, N.; Tanik, A.; Sertel, E. Assessing the performance of machine learning algorithms for soil salinity mapping in Google Earth Engine Platform using Sentinel-2A and Landsat-8 OLI data. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 69, 1072–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Xu, X.; Klinger, Y.; Van Der Woerd, J.; Tapponnier, P. High-Resolution Mapping Based on an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) to Capture Paleo Seismic Offsets along the Altyn-Tagh Fault, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nex, F.; Armenakis, C.; Cramer, M.; Cucci, D.A.; Gerke, M.; Honkavaara, E.; Kukko, A.; Persello, C.; Skaloud, J. UAV in the Advent of the Twenties: Where We Stand and What Is Next. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 184, 215–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sensor | Spatial Resolution (m) | Spectral Resolution | Temporal Resolution (Day) | Acquisition Cost | Applicable Mapping Scale |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MODIS | 250–500 | 36 | 1 | Free | Regional/Global |
| Landsat | 30–120 | 8–11 | 16 | Free | Local/Regional |
| Sentinel 2 | 10–60 | 13 | 5 | Free | Local/Regional |
| ASTER | 15–90 | 14 | 16 | Low | Local/Regional |
| IKONOS | 4 | 5 | 3 | High | Local |
| PlanetScope | 3 | 8 | 1 | Low/Medium | Local/Pixel plot |
| Worldview | <5 | 9 | 1 | Low/Medium | Local/Pixel plot |
| Sentinel 1 | 5 | 6 | Free | Local/Regional | |
| RADAR | 5 | High | Local/Regional | ||
| Hyperspectral | 1 | >200 | High | Pixel-plot | |
| Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) | ~2.5 cm | >200 | Medium/High | Pixel-plot |
| Modeling Technique/Algorithm | Estimated Accuracy Range (%) | Strengths | Weaknesses | Example Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Regression | 40–50 | Simple and efficient; can identify linear relationships | Assumes only linear relationships | [136] |
| Multiple Linear Regression | 60–80 | Can account for multiple variables | Assumes only linear relationships | [20,137] |
| Decision Trees | 70–85 | Easy to interpret; can handle nonlinear relationships | Prone to overfitting | [23] |
| Random Forest | 80–90 | Good for nonlinear relationships | Can be slow with large datasets | [138,139] |
| Support Vector Machines | 75–90 | Can handle high-dimensional data | Prone to overfitting | [140,141] |
| Artificial Neural Networks | 80–95 | Can learn complex relationships | Can be prone to overfitting | [142,143] |
| Spectral Indices | 60–80 | Simple and fast, it can provide helpful information about vegetation and soil properties. | Limited to specific vegetation and soil types, and sensitive to atmospheric interferences | [144,145] |
| Deep Learning | 90–95 | Can learn complex relationships | Requires large amounts of data and computing power | [146,147] |
| Maximum Likelihood Classification | 60–80 | Simple and easy to implement | Requires accurate training data and assumes a normal distribution of pixel values | [148,149] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sahbeni, G.; Ngabire, M.; Musyimi, P.K.; Székely, B. Challenges and Opportunities in Remote Sensing for Soil Salinization Mapping and Monitoring: A Review. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102540
Sahbeni G, Ngabire M, Musyimi PK, Székely B. Challenges and Opportunities in Remote Sensing for Soil Salinization Mapping and Monitoring: A Review. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(10):2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102540
Chicago/Turabian StyleSahbeni, Ghada, Maurice Ngabire, Peter K. Musyimi, and Balázs Székely. 2023. "Challenges and Opportunities in Remote Sensing for Soil Salinization Mapping and Monitoring: A Review" Remote Sensing 15, no. 10: 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102540
APA StyleSahbeni, G., Ngabire, M., Musyimi, P. K., & Székely, B. (2023). Challenges and Opportunities in Remote Sensing for Soil Salinization Mapping and Monitoring: A Review. Remote Sensing, 15(10), 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102540