Energy-Efficient and High-Performance Ship Classification Strategy Based on Siamese Spiking Neural Network in Dual-Polarized SAR Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
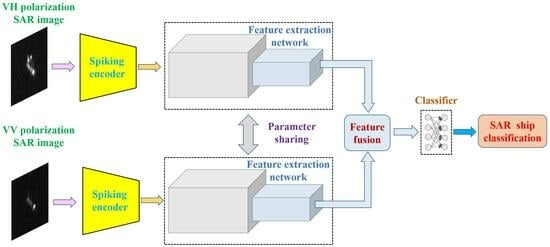
2. Energy-Efficient and High-Performance Ship Classification Strategy
2.1. Input Image Spiking Encoding
2.2. Spiking Neuron Model
2.3. Backbone Network Structure
2.4. Spiking Feature Fusion
2.5. Model Learning Methods
2.5.1. Surrogate Gradient Training
2.5.2. Loss Function
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Evaluating Indicator
3.3. Experiment and Analysis
3.3.1. Ship Classification Performance
3.3.2. Model Parameter Quantity
3.3.3. Model Energy Consumption
3.3.4. Fusion Method Analysis
3.3.5. Simulation Step Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, J.; An, D.; Chen, L.; Feng, D.; Zhou, Z. An NSST-Based Fusion Method for Airborne Dual-Frequency, High-Spatial-Resolution SAR Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 4362–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; An, D.; Liu, J.; Feng, D.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Z. Modified Adaptive 2-D Calibration Algorithm for Airborne Multichannel SAR-GMTI. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 4004805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; An, D.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Huang, X. Local Road Area Extraction in CSAR Imagery Exploiting Improved Curvilinear Structure Detector. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 3172227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Jiang, H.; Wang, G. SAR and Optical Image Registration Based on Deep Learning with Co-Attention Matching Module. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Song, Y.; Jiang, N.; Xie, Z.; Fan, C.; Huang, X. Enhanced Doppler Resolution and Sidelobe Suppression Performance for Golay Complementary Waveforms. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xie, H.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; He, J.; Yi, S.; Jiang, H.; Xie, K. Fast Factorized Backprojection Algorithm in Orthogonal Elliptical Coordinate System for Ocean Scenes Imaging Using Geosynchronous Spaceborne-Airborne VHF UWB Bistatic SAR. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Xie, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Xie, K. Arbitrary-Oriented Ship Detection Method Based on Long-Edge Decomposition Rotated Bounding Box Encoding in SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, B.; Huang, L.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, W. OpenSARShip 2.0: A Large-Volume Dataset for Deeper Interpretation of Ship Targets in Sentinel-1 Imagery. In Proceedings of the SAR in Big Data Era: Models, Methods and Applications (BIGSARDATA), Beijing, China, 13–14 November 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, G.; Xie, K. Lightweight and Anchor-Free Frame Detection Strategy Based on Improved CenterNet for Multiscale Ships in SAR Images. Front. Comput. Sci. 2022, 4, 1012755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Jiang, X.; Hu, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, G.; Xie, K. High-Efficiency and Low-Energy Ship Recognition Strategy Based on Spiking Neural Network in SAR Images. Front. Neurorobot. 2022, 16, 970832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; He, J.; Lu, Z.; Hu, J. Two-Level Feature-Fusion Ship Recognition Strategy Combining HOG Features with Dual-Polarized Data in SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Xiong, G.; Yu, W. Feature-Loss Double Fusion Siamese Network for Dual-Polarized SAR Ship Classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Signal, Information and Data Processing (ICSIDP), Chongqing, China, 11–13 December 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Chang, W.; Wang, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Gan, Y. Polarization Matters: On Bilinear Convolutional Neural Networks for Ship Classification from Synthetic Aperture Radar Images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Natural Language Processing (ICNLP), Xi’an, China, 25–27 March 2022; pp. 315–319. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Chang, W.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, L. Group Bilinear CNNs for Dual-Polarized SAR Ship Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4508405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Zhang, T.; Ke, X. A Dual-Polarization Information-Guided Network for SAR Ship Classification. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X. Squeeze-and-Excitation Laplacian Pyramid Network with Dual-polarization Feature Fusion for Ship Classification in SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 4019905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Ke, X.; Liu, C.; Xu, X.; Zhan, X.; Wang, C.; Ahmad, I.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, D.; et al. HOG-ShipCLSNet: A Novel Deep Learning Network with HOG Feature Fusion for SAR Ship Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5210322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Song, S.; Yang, J. Ship Classification Based on MSHOG Feature and Task-Driven Dictionary Learning with Structured Incoherent Constraints in SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (NAACL-HLT), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Fedus, W.; Zoph, B.; Shazeer, N. Switch Transformers: Scaling to Trillion Parameter Models with Simple and Efficient Sparsity. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2022, 23, 5232–5270. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language Models Are Few-Shot Learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Maass, W. Networks of Spiking Neurons: The Third Generation of Neural Network Models. Neural Netw. 1997, 10, 1659–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Jaiswal, A.; Panda, P. Towards Spike-Based Machine Intelligence with Neuromorphic Computing. Nature 2019, 575, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhmann, J.; Lange, T.; Ramacher, U. Image Segmentation by Networks of Spiking Neurons. Neural Comput. 2005, 17, 1010–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Lin, X.; Xu, M. Coding Method of Image Segmentation in Spiking Neural Network. Comput. Eng. 2012, 38, 196–199. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Park, S.; Na, B.; Yoon, S. Spiking-Yolo: Spiking Neural Network for Energy-Efficient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (CAI), New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 11270–11277. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Shen, H.; Cao, X.; Wang, T.; Feng, Q.; Tan, Z. Conversion of Siamese Networks to Spiking Neural Networks for Energy-Efficient Object Tracking. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 9967–9982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merolla, P.; Arthur, J.; Alvarez-Icaza, R.; Cassidy, A.S.; Sawada, J.; Akopyan, F.; Jackson, B.L.; Imam, N.; Guo, C.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. A Million Spiking-Neuron Integrated Circuit with A Scalable Communication Network and Interface. Science 2014, 345, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Yu, Z.; Masquelier, T.; Chen, Y.; Huang, T.; Tian, Y. Spike-Based Residual Blocks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04159. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, T.; Fang, W.; Ding, J.; Dai, P.; Yu, Z.; Huang, T. Optimal ANN-SNN Conversion for High-Accuracy and Ultra-Low-Latency Spiking Neural Networks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.04347. [Google Scholar]
- Indiveri, G.; Corradi, F.; Qiao, N. Neuromorphic Architectures for Spiking Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), Washington, DC, USA, 7–9 December 2015; pp. 4.2.1–4.2.4. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Li, G.; Wu, Y.; Deng, L. Spiking Neural Networks: A Survey on Recent Advances and New Directions. Control. Decis. 2021, 36, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin, A.; Huxley, A. A Quantitative Description of Membrane Current and Its Application to Conduction and Excitation in Nerve. Bull. Math. Biol. 1989, 52, 25–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, P.; Abbott, L. Theoretical Neuroscience: Computational and Mathematical Modeling of Neural Systems. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2003, 15, 154–155. [Google Scholar]
- Gerstner, W.; Kistler, W.; Naud, R.; Paninski, L. Neuronal Dynamics: From Single Neurons to Networks and Models of Cognition; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Eshraghian, J.; Ward, M.; Neftci, E.; Wang, X.; Lenz, G.; Dwivedi, G.; Bennamoun, M.; Jeong, D.S.; Lu, W.D. Training Spiking Neural Networks Using Lessons from Deep Learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.12894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H. Ship Classification in High-resolution SAR Images Using Deep Learning of Small Datasets. Sensors 2018, 18, 2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Li, W. Ship Classification in High-Resolution SAR Images via Transfer Learning with Small Training Dataset. Sensors 2018, 19, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rueckauer, B.; Lungu, I.; Hu, Y.; Pfeiffer, M.; Liu, S.-C. Conversion of Continuous-Valued Deep Networks to Efficient Event-driven Networks for Image Classification. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2261–2269. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Tang, H.; Pan, G. Spiking Deep Residual Networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 34, 5200–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonidas, L.; Jie, Y. Ship Classification Based on Improved Convolutional Neural Network Architecture for Intelligent Transport Systems. Information 2021, 12, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; AbdelTawab, A. A Transfer Learning and Optimized CNN Based Maritime Vessel Classification System. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Fusion Methods | Operation |
|---|---|
| Method 1 | |
| Method 2 | |
| Method 3 | |
| Method 4 | |
| Method 5 | |
| Method 6 |
| Methods | Models | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mainstream classification networks | ResNet18 | 0.6267 | 0.6590 | 0.6331 |
| ResNet34 | 0.6212 | 0.6545 | 0.6312 | |
| ResNet50 | 0.6210 | 0.6597 | 0.6152 | |
| DenseNet121 | 0.6332 | 0.6630 | 0.6389 | |
| DenseNet161 | 0.6371 | 0.6706 | 0.6436 | |
| VGG16 | 0.6319 | 0.6670 | 0.6306 | |
| MobileNet-v2 | 0.5989 | 0.6438 | 0.5974 | |
| AlexNet | 0.6332 | 0.6653 | 0.6258 | |
| Transformer | ViT | 0.6078 | 0.6434 | 0.5826 |
| ResNet50ViT | 0.6213 | 0.6586 | 0.6261 | |
| SNN | Spiking-ResNet18 (T = 16) | 0.6189 | 0.6521 | 0.6272 |
| Proposed method | Siam-SpikingShipCLSNet | 0.6395 | 0.6735 | 0.6365 |
| Methods | Models | Parameter Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Mainstream classification networks | ResNet18 | 11.80 M |
| ResNet34 | 21.29 M | |
| ResNet50 | 23.52 M | |
| DenseNet121 | 6.96 M | |
| DenseNet161 | 26.48 M | |
| VGG16 | 134.28 M | |
| Mobillenet-v2 | 5.64 M | |
| AlexNet | 57.02 M | |
| Transformer | ViT | 12.76 M |
| ResNet50 ViT | 9.95 M | |
| SNN | Spiking-ResNet18 (T = 16) | 11.18 M |
| Proposed method | Siam-SpikingShipCLSNet | 2.19 M |
| Methods | Models | FLOPs/SOPs | Energy Consumption (J) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mainstream classification networks | ResNet18 | 148.71 M | 1.858 × 10−3 |
| ResNet34 | 300.01 M | 3.75 × 10−3 | |
| ResNet50 | 336.32 M | 4.204 × 10−3 | |
| DenseNet121 | 235.24 M | 2.941 × 10−3 | |
| DenseNet161 | 638.06 M | 7.976 × 10−3 | |
| VGG16 | 1.38 G | 1.725 × 10−2 | |
| MobileNet-v2 | 26.04 M | 3.255 × 10−4 | |
| AlexNet | 94.17 M | 1.177 × 10−3 | |
| Transformer | ViT | 3.24 G | 4.05 × 10−2 |
| ResNet50ViT | 2.53 G | 3.163 × 10−2 | |
| SNN | Spiking-ResNet18 (T = 16) | 119.16 M | 9.175 × 10−6 |
| Proposed method | Siam-SpikingShipCLSNet | 57.00 M | 4.389 × 10−6 |
| Fusion Methods | Precision | Recall | F1 | T | SOP | SOP/T |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without fusion | 0.6166 | 0.6548 | 0.6136 | 12 | 15.2 M | 1.27 M |
| Method 1 | 0.6395 | 0.6735 | 0.6365 | 8 | 57.0 M | 7.13 M |
| Method 2 | 0.6324 | 0.6664 | 0.6293 | 20 | 116.4 M | 5.82 M |
| Method 3 | 0.6272 | 0.6623 | 0.6182 | 20 | 91.9 M | 4.60 M |
| Method 4 | 0.6305 | 0.6646 | 0.6246 | 16 | 71.6 M | 4.48 M |
| Method 5 | 0.6339 | 0.6668 | 0.6265 | 16 | 101.0 M | 6.31 M |
| Method 6 | 0.6310 | 0.6646 | 0.6289 | 16 | 102.0 M | 6.38 M |
| Simulation Steps | Precision | Recall | F1 | SOP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 0.6339 | 0.6641 | 0.6158 | 19.4 M |
| 8 | 0.6395 | 0.6735 | 0.6365 | 57.0 M |
| 12 | 0.6409 | 0.6682 | 0.6373 | 97.6 M |
| 16 | 0.6339 | 0.6704 | 0.6344 | 103.8 M |
| 20 | 0.6339 | 0.6690 | 0.6380 | 252.9 M |
| Simulation Steps | Precision | Recall | F1 | SOP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 0.6167 | 0.6565 | 0.6072 | 13.3 M |
| 8 | 0.6204 | 0.6579 | 0.6231 | 39.2 M |
| 12 | 0.6284 | 0.6641 | 0.6243 | 54.2 M |
| 16 | 0.6238 | 0.6601 | 0.6231 | 63.3 M |
| 20 | 0.6324 | 0.6664 | 0.6293 | 116.4 M |
| Simulation Steps | Precision | Recall | F1 | SOP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 0.6144 | 0.6512 | 0.5808 | 17.0 M |
| 8 | 0.6138 | 0.6543 | 0.6005 | 47.9 M |
| 12 | 0.6231 | 0.6583 | 0.6043 | 47.7 M |
| 16 | 0.6243 | 0.6574 | 0.6106 | 77.6 M |
| 20 | 0.6272 | 0.6623 | 0.6182 | 91.9 M |
| Simulation Steps | Precision | Recall | F1 | SOP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 0.6190 | 0.6561 | 0.6085 | 16.8 M |
| 8 | 0.6399 | 0.6686 | 0.6216 | 39.1 M |
| 12 | 0.6221 | 0.6579 | 0.6268 | 49.4 M |
| 16 | 0.6305 | 0.6646 | 0.6246 | 71.6 M |
| 20 | 0.6278 | 0.6641 | 0.6234 | 72.1 M |
| Simulation Steps | Precision | Recall | F1 | SOP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 0.6149 | 0.653 | 0.6166 | 16.5 M |
| 8 | 0.6282 | 0.6615 | 0.6206 | 53.7 M |
| 12 | 0.6319 | 0.6619 | 0.6227 | 80.4 M |
| 16 | 0.6339 | 0.6668 | 0.6265 | 101.0 M |
| 20 | 0.6337 | 0.6664 | 0.6201 | 129.4 M |
| Simulation Steps | Precision | Recall | F1 | SOP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 0.6262 | 0.6588 | 0.6071 | 20.6 M |
| 8 | 0.6292 | 0.6632 | 0.6218 | 37.9 M |
| 12 | 0.6318 | 0.6659 | 0.6232 | 47.4 M |
| 16 | 0.6310 | 0.6646 | 0.6289 | 102.0 M |
| 20 | 0.6357 | 0.6628 | 0.6246 | 88.7 M |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, X.; Xie, H.; Lu, Z.; Hu, J. Energy-Efficient and High-Performance Ship Classification Strategy Based on Siamese Spiking Neural Network in Dual-Polarized SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4966. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15204966
Jiang X, Xie H, Lu Z, Hu J. Energy-Efficient and High-Performance Ship Classification Strategy Based on Siamese Spiking Neural Network in Dual-Polarized SAR Images. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(20):4966. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15204966
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Xinqiao, Hongtu Xie, Zheng Lu, and Jun Hu. 2023. "Energy-Efficient and High-Performance Ship Classification Strategy Based on Siamese Spiking Neural Network in Dual-Polarized SAR Images" Remote Sensing 15, no. 20: 4966. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15204966
APA StyleJiang, X., Xie, H., Lu, Z., & Hu, J. (2023). Energy-Efficient and High-Performance Ship Classification Strategy Based on Siamese Spiking Neural Network in Dual-Polarized SAR Images. Remote Sensing, 15(20), 4966. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15204966