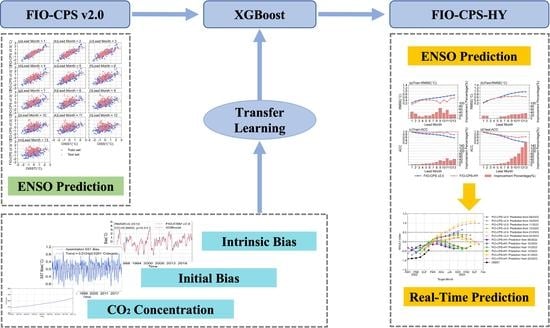
A Hybrid ENSO Prediction System Based on the FIO−CPS and XGBoost Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Datasets and Methods
2.1. FIO−CPS v2.0 Bias Correction Ideas
2.2. Datasets
2.3. Machine Learning Model
2.4. Evaluation Metrics
2.5. FIO−CPS−HY’s Establishment
2.5.1. Intrinsic Bias Prediction
2.5.2. Initial Bias
2.5.3. Transfer Correction of FIO−CPS v2.0
3. Results


4. Discussion
4.1. Feature Importance
4.2. Comparison of Observation Data
4.3. Prediction Skill of FIO−CPS−HY
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bjerknes, J. Atmospheric teleconnections from the equatorial Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 1969, 97, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Z. Three-ocean interactions and climate variability: A review and perspective. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 5119–5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.H.; Sumi, A.; Kimoto, M. Impact of El Niño on the East Asian monsoon a diagnostic study of the’86/87 and’91/92 events. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 1996, 74, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W. Impacts of El Niño and La Niña on the cycle of the East Asian winter and summer monsoon. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci.-Chin. Ed. 2002, 26, 609–623. [Google Scholar]
- Timmermann, A.; An, S.; Kug, J.; Jin, F.F.; Cai, W.J.; Capotondi, A.; Cobb, K.M.; Lengaigne, M.; McPhaden, M.J.; Stuecker, M.F. El Niño–southern oscillation complexity. Nature 2018, 559, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.H.; Yu, Y.Q.; Song, Z.Y.; Ren, H.L.; Tang, Y.M.; Qiao, F.L.; Wu, T.W.; Gao, C.; Hu, J.Y.; Tian, F. A review of progress in coupled ocean-atmosphere model developments for ENSO studies in China. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2020, 38, 930–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhaden, M.J.; Zebiak, S.E.; Glantz, M.H. ENSO as an integrating concept in earth science. Science 2006, 314, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kløve, B.; Ala-Aho, P.; Bertrand, G.; Gurdak, J.J.; Kupfersberger, H.; Kværner, J.; Muotka, T.; Mykrä, H.; Preda, E.; Rossi, P. Climate change impacts on groundwater and dependent ecosystems. J. Hydrol. 2014, 518, 250–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, C.Z. Marine heatwaves and cold-spells in global coral reef zones. Prog. Oceanogr. 2022, 209, 102920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.Y.; Zhu, J.; Yang, X.G.; Zhang, X. Y Correlation changes between rice yields in North and Northwest China and ENSO from 1960 to 2004. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Strapasson, A.; Rojas, O. Assessment of El Niño and La Niña impacts on China: Enhancing the early warning system on food and agriculture. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2020, 27, 100208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.L.; Jin, F.F.; Song, L.C.; Lu, B.; Tian, B.; Zuo, J.Q.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.J.; Zhao, C.B.; Nie, Y. Prediction of primary climate variability modes at the Beijing Climate Center. J. Meteorol. Res. 2017, 31, 204–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.M.; Zhang, R.H.; Liu, T.; Duan, W.S.; Yang, D.J.; Zheng, F.; Ren, H.L.; Lian, T.; Gao, C.; Chen, D. Progress in ENSO prediction and predictability study. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 826–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.; Anderson, D.; Barnett, T.; Cane, M.; Kleeman, R.; Leetmaa, A.; O’Brien, J.; Rosati, A.; Schneider, E. A review of the predictability and prediction of ENSO. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1998, 103, 14375–14393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.L.; Zheng, F.; Luo, J.J.; Wang, R.; Liu, M.H.; Zhang, W.J.; Zhou, T.J.; Zhou, G.Q. A review of research on tropical air-sea interaction, ENSO dynamics, and ENSO prediction in China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2020, 34, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.S. Analysis and Prediction of the El Niño Southern Oscillation Phenomenon Using Principal Oscillation Pattern Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Dool, H. Searching for analogues, how long must we wait? Tellus A 1994, 46, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnston, A.G.; Van den Dool, H.M.; Zebiak, S.E.; Barnett, T.P.; Ji, M.; Rodenhuis, D.R.; Cane, M.A.; Leetmaa, A.; Graham, N.E.; Ropelewski, C.R. Long-lead seasonal forecasts—Where do we stand? Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1994, 75, 2097–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.X.; Barnston, A.G. Long-lead forecasts of seasonal precipitation in the tropical Pacific islands using CCA. J. Clim. 1996, 9, 2020–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaff, J.A.; Landsea, C.W. An El Niño–Southern Oscillation climatology and persistence (CLIPER) forecasting scheme. Weather Forecast 1997, 12, 633–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.G.; Jiang, Z.H.; Zhu, Y.F. Experiment on short term climatic prediction to SSTA over the NINO oceanic region. J. Trop. Meteorol. 1998, 14, 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Leetmaa, A. Forecasts of tropical Pacific SST and sea level using a Markov model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 2701–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.A.; Matrosova, L.; Penland, C.; Scott, J.D.; Chang, P. Forecasting Pacific SSTs: Linear inverse model predictions of the PDO. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.L.; Zuo, J.Q.; Deng, Y. Statistical predictability of Nino indices for two types of ENSO. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 5361–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.J. El Nino Physics and El Nino Predictability. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2014, 6, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cane, M.A.; Zebiak, S.E.; Dolan, S.C. Experimental forecasts of EL Nino. Nature 1986, 321, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebiak, S.E.; Cane, M.A. A model el niñ–southern oscillation. Mon. Weather Rev. 1987, 115, 2262–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.K.; Cane, M.A.; Kaplan, A.; Zebiak, S.E.; Huang, D.J. Predictability of El Niño over the past 148 years. Nature 2004, 428, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Zhu, J. Improved ensemble-mean forecasting of ENSO events by a zero-mean stochastic error model of an intermediate coupled model. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 47, 3901–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.J.; Shu, Q.; Bao, Y.; Yang, X.D.; Song, Z.Y. The short-term climate prediction system FIO-CPS v2. 0 and its prediction skill in ENSO. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 759339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, R.H.; Zhou, G.Q. Ensemble hindcasts of SST anomalies in the tropical Pacific using an intermediate coupled model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L19604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, R.H. Impact of altimetry data on ENSO ensemble initializations and predictions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L13611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnston, A.G.; Tippett, M.K.; L’Heureux, M.L.; Li, S.; DeWitt, D.G. Skill of real-time seasonal ENSO model predictions during 2002–11: Is our capability increasing? Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 631–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnston, A.G.; Tippett, M.K.; Ranganathan, M.; L’Heureux, M.L. Deterministic skill of ENSO predictions from the North American Multimodel Ensemble. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 7215–7234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.J.; Stockdale, T.N.; Ferranti, L.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Molteni, F.; Magnusson, L.; Tietsche, S.; Decremer, D.; Weisheimer, A.; Balsamo, G. SEAS5: The new ECMWF seasonal forecast system. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 1087–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.L.; Wu, Y.J.; Bao, Q.; Ma, J.H.; Liu, C.Z.; Wan, J.H.; Li, Q.P.; Wu, X.F.; Liu, Y.; Tian, B. The China multi-model ensemble prediction system and its application to flood-season prediction in 2018. J. Meteorol. Res. 2019, 33, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, Y.G.; Kim, J.H.; Luo, J.J. Deep learning for multi-year ENSO forecasts. Nature 2019, 573, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippett, M.K.; Ranganathan, M.; L’Heureux, M.; Barnston, A.G.; DelSole, T. Assessing probabilistic predictions of ENSO phase and intensity from the North American Multimodel Ensemble. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 7497–7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P. The annual cycle and the predictability of the tropical coupled ocean-atmosphere system. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 1995, 56, 33–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhaden, M.J.; Santoso, A.; Cai, W.J. El Niño Southern Oscillation in a Changing Climate; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; Volume 253. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, M.; Xu, H.; Duan, W.S. A kind of initial errors related to “spring predictability barrier” for El Niño events in Zebiak-Cane model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L03709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.S.; Zhao, P.; Hu, J.Y.; Xu, H. The role of nonlinear forcing singular vector tendency error in causing the “spring predictability barrier” for ENSO. J. Meteorol. Res. 2016, 30, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.W.; Wang, H.; Jiang, H.; Ma, W.T. Evaluation of ENSO prediction skill changes since 2000 based on multimodel hindcasts. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, Q.L.; Zheng, F. Bias corrections of the heat flux damping process to improve the simulation of ENSO post-2000. Sci. Online Lett. Atmos. 2015, 11, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Zhang, W.; Yu, J.; Chen, Q. A possible bias of simulating the post-2000 changing ENSO. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 1850–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichstein, M.; Camps-Valls, G.; Stevens, B.; Jung, M.; Denzler, J.; Carvalhais, N. Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven Earth system science. Nature 2019, 566, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irrgang, C.; Boers, N.; Sonnewald, M.; Barnes, E.A.; Kadow, C.; Staneva, J.; Saynisch-Wagner, J. Towards neural Earth system modelling by integrating artificial intelligence in Earth system science. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2021, 3, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, R.; Bonavita, M.; Geer, A.; Arcucci, R.; Dueben, P.; Vitolo, C.; Le Saux, B.; Demir, B.; Mathieu, P.-P. ESA-ECMWF Report on recent progress and research directions in machine learning for Earth System observation and prediction. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 5, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.H.; Sandoval, L.; Crystal-Ornelas, R.; Mousavi, S.M.; Wang, J.B.; Lin, C.; Cristea, N.; Tong, D.; Carande, W.H.; Ma, X. A review of earth artificial intelligence. Comput. Geosci. 2022, 159, 105034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.P.; Chu, P.S.; He, L.K.; Unger, D. Improving the CPC’s ENSO forecasts using Bayesian model averaging. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 3373–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kwon, M.; Kim, S.D.; Kug, J.S.; Ryu, J.G.; Kim, J. Spatiotemporal neural network with attention mechanism for El Niño forecasts. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.Y.; Liu, W.G.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.X.; Su, T.Y.; Yin, X.Q. Research Progress and Perspective of the Key Technologies for Ocean Numerical Model Driven by the Mass Data. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2019, 37, 161–170. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.M.; Xu, G.J.; Han, G.Q.; Brandon, J.B.; Xie, W.H.; Zhou, S.Y. Recent Developments in Artificial Intelligence in Oceanography. Ocean Land Atmos. Res. 2022, 2022, 9870950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, R.H. A hybrid neural network model for ENSO prediction in combination with principal oscillation pattern analyses. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 39, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, K.; Doi, T.; Oettli, P.; Jayanthi, V.R.; Behera, S. Long Lead Predictions of ENSO Using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, A13I-08, New Orleans, LA, USA, 13–17 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.T. The application of machine learning in ENSO prediction consultation. Mar. Forecast 2022, 39, 91–103. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Y.; Song, Z.Y.; Qiao, F.L. FIO-ESM version 2.0: Model description and evaluation. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2020, 125, e2019JC016036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Duan, W.S. What kind of initial errors cause the severest prediction uncertainty of El Nino in Zebiak-Cane model. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 25, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J. ENSO ensemble prediction: Initial error perturbations vs. model error perturbations. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 2516–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Mu, M.; Duan, W.S. Does model parameter error cause a significant “spring predictability barrier” for El Niño events in the Zebiak–Cane model? J. Clim. 2012, 25, 1263–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.J.; Gao, C.; Zhang, R.H. Model parameter-related optimal perturbations and their contributions to El Niño prediction errors. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 1425–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.J.; Yang, Q. A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2010, 22, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Thorne, P.W.; Banzon, V.F.; Boyer, T.; Chepurin, G.; Lawrimore, J.H.; Menne, M.J.; Smith, T.M.; Vose, R.S.; Zhang, H.-M. Extended reconstructed sea surface temperature, version 5 (ERSSTv5): Upgrades, validations, and intercomparisons. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 8179–8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, R.W.; Smith, T.M.; Liu, C.; Chelton, D.B.; Casey, K.S.; Schlax, M.G. Daily high-resolution-blended analyses for sea surface temperature. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5473–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousky, V.; Higgins, R. An alert classification system for monitoring and assessing the ENSO cycle. Weather Forecast 2007, 22, 353–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Q.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, D. Tree Boosting with xgboost-Why Does Xgboost Win “Every” Machine Learning Competition? NTNU: Trondheim, Norway, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.L.; Liu, H.C.; Zhu, C.F. Thunderstorm weather analysis based on XGBoost algorithm. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, 42, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.L.; Gao, Z.; Xiao, H.; Yang, X.D.; Song, Z.Y. Predicting the Tropical Sea Surface Temperature Diurnal Cycle Amplitude Using an Improved XGBoost Algorithm. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, X.M.; Sun, F.B.; Wang, H.; Wu, L.F.; Zhang, X.Z.; Liu, W.B.; Che, H.Z. Correction of Overestimation in Observed Land Surface Temperatures Based on Machine Learning Models. J. Clim. 2022, 35, 5359–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, Z.Y.; Xu, L.J.; Ou, C.Q. Meteorological drought forecasting based on a statistical model with machine learning techniques in Shaanxi province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Q.F.; Jia, X.J.; Lin, H. Machine learning models for the seasonal forecast of winter surface air temperature in North America. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2020EA001140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.X.; Kang, J.F.; Wan, M.X.; Fang, L.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zeng, Z.L. Solar radiation prediction using different machine learning algorithms and implications for extreme climate events. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 596860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Y.; Wang, H.; Ma, Y.; Xu, M.Y. Prediction of Wave Energy Flux in the Bohai Sea through Automated Machine Learning. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Dataset | Horizontal Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Time Span | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SST | ERSST v5 | 2° × 2° | Monthly | 01/1854–01/2023 |
| OISST v2.1 | 0.25° × 0.25° | Daily | 12/01/1981–12/31/2022 | |
| FIO−ESM v2.0 Historical simulation | 1.1° × (0.27–0.54°) | Monthly | 01/1854–12/2014 | |
| SSP2−4.5 | 01/2015–01/2023 | |||
| Assimilation | 12/01/1981–11/30/2021 | |||
| FIO−CPS v2.0 | 01/1982–12/2022 | |||
| Global Mean CO2 Concentration | —— | 01/1854–01/2023 | ||
| Dataset | Statistical Metrics | |
|---|---|---|
| RMSE | CC | |
| Training Set | 0.1505 | 0.9937 |
| Test Set | 0.3863 | 0.9605 |
| Hindcast Period | 0.2010 | 0.9900 |
| Observations for Initial Bias | Observations for Intrinsic Bias | Observations for Transfer Correction |
|---|---|---|
| Init_OI_198112 | Intri_OI_198201 | TC_OI_198201 |
| Intri_EROI_185401 | ||
| Intri_ER_185401 | ||
| Init_ER_198112 | Intri_ER_198201 | TC_ER_198201 |
| Intri_ER_185401 |
| Statistical Metrics | Observations | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Init_OI_198112 | Init_ER_198112 | ||||
| Intri_OI_198201 | Intri_EROI_185401 | Intri_ER_185401 | Intri_ER_198201 | Intri_ER_185401 | |
| TC_OI_198201 | TC_ER_198201 | ||||
| RMSE | 0.6849 | 0.6500 | 0.6537 | 0.6961 | 0.6930 |
| ACC | 0.5842 | 0.6338 | 0.6297 | 0.6442 | 0.6598 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuang, Z.; Song, Y.; Wu, J.; Fu, Q.; Shu, Q.; Qiao, F.; Song, Z. A Hybrid ENSO Prediction System Based on the FIO−CPS and XGBoost Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071728
Kuang Z, Song Y, Wu J, Fu Q, Shu Q, Qiao F, Song Z. A Hybrid ENSO Prediction System Based on the FIO−CPS and XGBoost Algorithm. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(7):1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071728
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuang, Zhiyuan, Yajuan Song, Jie Wu, Qiuying Fu, Qi Shu, Fangli Qiao, and Zhenya Song. 2023. "A Hybrid ENSO Prediction System Based on the FIO−CPS and XGBoost Algorithm" Remote Sensing 15, no. 7: 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071728
APA StyleKuang, Z., Song, Y., Wu, J., Fu, Q., Shu, Q., Qiao, F., & Song, Z. (2023). A Hybrid ENSO Prediction System Based on the FIO−CPS and XGBoost Algorithm. Remote Sensing, 15(7), 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071728