A Lightweight SAR Image Ship Detection Method Based on Improved Convolution and YOLOv7
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Most of their SAR image ship target detection frameworks are designed for small ships in SAR images, and in the process of designing, the performance of recognizing large, medium, and small ships is not simultaneously well-considered. Therefore, the detection accuracy decreases for the presence of large, medium, and small ships in the SAR image.
- Some networks use complex feature fusion in the neck part, and it is the fusion of features extracted from high-level convolutions of the backbone network, while the semantic details about the ship extracted from low-level convolutions are easily drowned out due to the stacking of the convolutions, which is not friendly to ship detection.
- All of the above methods are mainly dedicated to the improvement of the detection accuracy of ship targets in SAR images, but do not consider the reduction in redundant parameters. Among the papers mentioned above that utilize the parameters to measure the model, the model with the least number of parameters also has 32.5 M [15]. The redundancy in the feature maps of convolutional neural networks leads to a large consumption of memory [19].
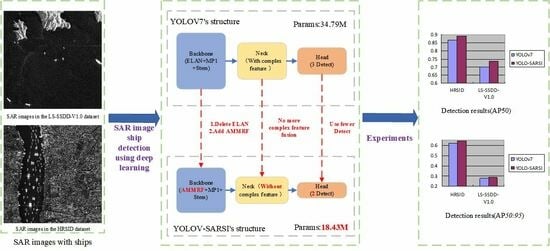
- A new convolutional block, which we name AMMRF, is proposed. For SAR images containing ships, it obtains feature information from different sensory fields and filters this feature information, making the network more focused on information useful for ship detection.
- The addition of AMMRF to the backbone network of YOLOv7 makes the backbone network more dexterous. The addition of AMMRF makes the whole detection framework complete with feature fusion in the backbone network. Therefore, we modified the neck part of YOLOv7 by removing the complex feature fusion. We named the new detection framework YOLO-SARSI.
- The number of parameters in YOLO-SARSI is very small, only 18.43 M, which is 16.36 M less compared to YOLOv7. Even so, the average precision of YOLO-SARSI in SAR images of ship targets is still higher than that of YOLOv7.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Analysis of SAR Image Features
- SAR images are grayscale images that carry less information than optical images. Complex detection frameworks are not necessarily suitable for SAR image ship target detection, and there may be redundancy of convolution when using these detection frameworks in recognizing ships.
- There are many small ships in the SAR images, and the small ships carry less semantic information, which can easily be confused with other interference, leading to missed or wrong detection.
- As can be seen from the human approach to ship detection, the network model requires global information about the image as well as high-quality semantic detail information about the ship itself.
2.2. Improved Convolution Block: AMMRF
2.3. Network Structure
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Evaluation Metrics
3.2. YOLO-SARSI Recognition Accuracy Evaluation
3.3. Instance Testing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, H.; Du, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. A Modified CFAR Algorithm Based on Object Proposals for Ship Target Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1925–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Xiang, D.; Xie, H. Multiscale salient region detection and salient map generation for synthetic aperture radar image. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 083501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.I.; Ouchi, K. On a Novel Approach Using MLCC and CFAR for the Improvement of Ship Detection by Synthetic Aperture Radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Yang, X.; Gao, X.; Hong, W.; Fu, K.; Sun, X. A Densely Connected End-to-End Neural Network for Multiscale and Multiscene SAR Ship Detection. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 20881–20892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Li, Q.; Cao, Z.; Liu, N. Dense Attention Pyramid Networks for Multi-Scale Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 8983–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X. High-Speed Ship Detection in SAR Images Based on a Grid Convolutional Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Shen, L.; Guo, W.; Wang, J. Ships Detection in SAR Images Based on Anchor-Free Model with Mask Guidance Features. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Dong, F.; Wang, Y. Small-Target Ship Detection in SAR Images Based on Densely Connected Deep Neural Network with Attention in Complex Scenes. Appl. Intell. 2022, 53, 4162–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Liu, J.M.; Miao, Y.H.; He, Z.J. A High-Effective Implementation of Ship Detector for SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gao, S.; Zhou, L.; Liu, R.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Jia, Y.; Qian, J. YOLO-SD: Small Ship Detection in SAR Images by Multi-Scale Convolution and Feature Transformer Module. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Chen, Y.; Xu, B.; Yin, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, J. A Patch-to-Pixel Convolutional Neural Network for Small Ship Detection with PolSAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 6623–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Liu, B.; Liu, P. Detection of Small Ship Objects Using Anchor Boxes Cluster and Feature Pyramid Network Model for SAR Imagery. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Fu, K. An Anchor-Free Method Based on Feature Balancing and Refinement Network for Multiscale Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 1331–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, M.; Wu, C. Deep learning for autonomous ship-oriented small ship detection. Saf. Sci. 2020, 130, 104812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, N.; Gao, X. A CenterNet++ model for ship detection in SAR images. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 112, 107787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, W. A coupled convolutional neural network for small and densely clustered ship detection in SAR images. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2018, 62, 42301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Chen, C.; Liu, S.; Zeng, B. SlimConv: Reducing Channel Redundancy in Convolutional Neural Networks by Weights Flipping. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 6434–6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.02696. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Bourdev, L.; Girshick, R.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Zitnick, C.L.; Dollár, P. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1405.0312. [Google Scholar]
- Everingham, M.; Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The Pascal Visual Object Classes (VOC) Challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2010, 88, 303–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Xu, Y.; Qian, L.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, W.; Wang, N.; Liu, X.; Xiang, X. The QXS-SAROPT Dataset for Deep Learning in SAR-Optical Data Fusion. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.08259. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.; Zeng, X.; Qu, Q.; Wang, M.; Su, H.; Shi, J. HRSID: A High-Resolution SAR Images Dataset for Ship Detection and Instance Segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 120234–120254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Ke, X.; Zhan, X.; Shi, J.; Wei, S.; Pan, D.; Li, J.; Su, H.; Zhou, Y.; et al. LS-SSDD-v1.0: A Deep Learning Dataset Dedicated to Small Ship Detection from Large-Scale Sentinel-1 SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate Attention for Efficient Mobile Network Design. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.02907. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going Deeper with Convolutions. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.4842. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2261–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Vasconcelos, N. Cascade R-CNN: Delving Into High Quality Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6154–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1506.01497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1703.06870. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1708.02002. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer Using Shifted Windows. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.14030. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Pang, J.; Cao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Feng, W.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. MMDetection: Open MMLab Detection Toolbox and Benchmark. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.07155. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image Is Worth 16 × 16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2019, 128, 336–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Dataset | Model | (%) | (%) | Params (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRSID | Cascade R-CNN | 65.1 | 41.2 | 68.93 |
| Faster R-CNN | 69.8 | 43.6 | 41.12 | |
| Mask R-CNN | 69.9 | 43.9 | 41.12 | |
| SDD 300 | 56.5 | 36.8 | 23.75 | |
| Swin Transformer | 57.1 | 32.6 | 36.82 | |
| RetinaNet | 70.9 | 45.5 | 36.10 | |
| YOLOv7 | 86.7 | 61.8 | 34.79 | |
| YOLO-SARSI | 89.3 | 64.0 | 18.43 | |
| LS-SSDD-V1.0 | Cascade R-CNN | 55.4 | 20.1 | 68.93 |
| Faster R-CNN | 63.4 | 23.9 | 41.12 | |
| Mask R-CNN | 63.3 | 24.1 | 41.12 | |
| SDD 300 | 32.5 | 10.1 | 23.75 | |
| Swin Transformer | 37.0 | 10.2 | 36.82 | |
| RetinaNet | 64.9 | 24.8 | 36.10 | |
| YOLOv7 | 69.8 | 27.7 | 34.79 | |
| YOLO-SARSI | 73.7 | 28.5 | 18.43 |
| Model | Figure 8 | Figure 9 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correct | Wrong | Missed | Correct | Wrong | Missed | |
| Ground Truth | 19 | 0 | 0 | 44 | 0 | 0 |
| YOLOv7 | 15 | 8 | 4 | 20 | 5 | 24 |
| YOLO-SARSI | 19 | 8 | 0 | 34 | 3 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, H.; Gao, S.; Li, S.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Qian, J. A Lightweight SAR Image Ship Detection Method Based on Improved Convolution and YOLOv7. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16030486
Tang H, Gao S, Li S, Wang P, Liu J, Wang S, Qian J. A Lightweight SAR Image Ship Detection Method Based on Improved Convolution and YOLOv7. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(3):486. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16030486
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Hongdou, Song Gao, Song Li, Pengyu Wang, Jiqiu Liu, Simin Wang, and Jiang Qian. 2024. "A Lightweight SAR Image Ship Detection Method Based on Improved Convolution and YOLOv7" Remote Sensing 16, no. 3: 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16030486
APA StyleTang, H., Gao, S., Li, S., Wang, P., Liu, J., Wang, S., & Qian, J. (2024). A Lightweight SAR Image Ship Detection Method Based on Improved Convolution and YOLOv7. Remote Sensing, 16(3), 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16030486