Future Scenarios of Urban Nighttime Lights: A Method for Global Cities and Its Application to Urban Expansion and Carbon Emission Estimation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Projection of Future Urban Area Expansion
2.2. Urban Structures and GHG Emission Estimates Using Nighttime Light Data
2.3. Contribution of This Study
3. Materials and Methods
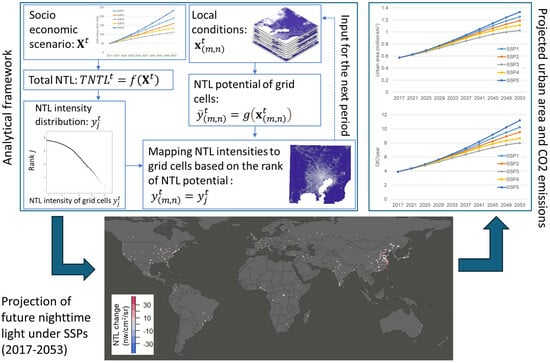
3.1. Conceptual Framework of Nighttime Light Scenario Generator
- (1)
- The total nighttime light intensity for urban areas is calculated based on socioeconomic indicators such as population and per capita GDP;
- (2)
- The intensity distribution of nighttime light that aligns with the calculated total nighttime light intensity is determined;
- (3)
- Grid-level nighttime light potentials are computed based on previous period nighttime light intensity, geographical conditions, and transportation conditions;
- (4)
- Nighttime light intensity is allocated from the highest values in the intensity distribution obtained in step 2 to grid cells based on the potentials derived in step 3, in descending order of intensity.
3.2. Data
3.3. Specification of the Model
3.4. Model Validation
3.5. Estimation Model for Urban Areas and Carbon Emissions from Nighttime Light
4. Results
4.1. Nighttime Light Projection and Urban Area for Selected Cities
4.2. Estimated Urban Expansion and Carbon Emissions by SSPs
5. Discussion
5.1. Features of the Nighttime Light Estimation Method
5.2. Estimation of Urban Areas and Carbon Emissions
5.3. Limitations and Future Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krayenhoff, E.S.; Moustaoui, M.; Broadbent, A.M.; Gupta, V.; Georgescu, M. Diurnal interaction between urban expansion, climate change and adaptation in US cities. Nat. Clim. Change 2018, 8, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Zuo, L.; Wen, Q.; Yi, L.; Xu, J.; Hu, S.; Liu, B. Chinese cropland losses due to urban expansion in the past four decades. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Wu, J. The Relationship between Habitat Loss and Fragmentation during Urbanization: An Empirical Evaluation from 16 World Cities. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, R.I.; Mansur, A.V.; Ascensão, F.; Colbert, M.l.; Crossman, K.; Elmqvist, T.; Gonzalez, A.; Güneralp, B.; Haase, D.; Hamann, M.; et al. Research gaps in knowledge of the impact of urban growth on biodiversity. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 3, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.; Alatalo, J.M.; Thapliyal, K.; Chauhan, S.; Archie, K.M.; Gupta, A.K.; Jha, S.K.; Kumar, M. Climate change vulnerability in urban slum communities: Investigating household adaptation and decision-making capacity in the Indian Himalaya. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 90, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vliet, J. Direct and indirect loss of natural area from urban expansion. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, C.; Chen, W.; Huang, G. Effect of urban expansion on summer rainfall in the Pearl River Delta, South China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, A.H.; Förster, M.; Kleinschmit, B. The spatial dimension of urban greenhouse gas emissions: Analyzing the influence of spatial structures and LULC patterns in European cities. Landsc. Ecol. 2015, 30, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudipudi, R.; Fluschnik, T.; Ros, A.G.C.; Walther, C.; Kropp, J.P. City density and CO2 efficiency. Energy Policy 2016, 91, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Kammen, D.M. Spatial distribution of U.S. household carbon footprints reveals suburbanization undermines greenhouse gas benefits of urban population density. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, B. Comparing the impacts of local land use and urban spatial structure on household VMT and GHG emissions. J. Transp. Geogr. 2020, 84, 102694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Madden, M.; Liu, X. Exploring the Relationship between Urban Forms and CO2 Emissions in 104 Chinese Cities. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2017, 143, 04017014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lwasa, S.; Seto, K.C.; Bai, X.; Blanco, H.; Gurney, K.R.; Kılkış, Ş.; Lucon, O.; Murakami, J.; Pan, J.; Sharifi, A.; et al. Urban Systems and Other Settlements. In Climate Change 2022—Mitigation of Climate Change; Shukla, P.R., Skea, J., Slade, R., Al Khourdajie, A., van Diemen, R., McCollum, D., Pathak, M., Some, S., Vyas, P., Fradera, R., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 861–952. [Google Scholar]
- Croft, T.A. Nighttime Images of the Earth from Space. Sci. Am. 1978, 239, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.D.; Mills, S.P.; Elvidge, C.D.; Lindsey, D.T.; Lee, T.F.; Hawkins, J.D. Suomi satellite brings to light a unique frontier of nighttime environmental sensing capabilities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 15706–15711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Seto, K.C. Projecting global urban land expansion and heat island intensification through 2050. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 114037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Eom, J.; Yu, S.; Asrar, G.R. Projecting Global Urban Area Growth Through 2100 Based on Historical Time Series Data and Future Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. Earth’s Future 2019, 7, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liang, X.; Leng, J.; Xu, X.; Liao, W.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, Q.; et al. Global projections of future urban land expansion under shared socioeconomic pathways. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; O’Neill, B.C. Mapping global urban land for the 21st century with data-driven simulations and Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Varquez, A.C.G.; Kanda, M. High-resolution global urban growth projection based on multiple applications of the SLEUTH urban growth model. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Asrar, G.R.; Smith, S.J.; Imhoff, M. A global record of annual urban dynamics (1992–2013) from nighttime lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Fragkias, M.; Guneralp, B.; Reilly, M.K. A meta-analysis of global urban land expansion. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guneralp, B.; Zhou, Y.; Urge-Vorsatz, D.; Gupta, M.; Yu, S.; Patel, P.L.; Fragkias, M.; Li, X.; Seto, K.C. Global scenarios of urban density and its impacts on building energy use through 2050. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 8945–8950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Große, J.; Fertner, C.; Groth, N.B. Urban Structure, Energy and Planning: Findings from Three Cities in Sweden, Finland and Estonia. Urban Plan. 2016, 1, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahtta, R.; Mahendra, A.; Seto, K.C. Building up or spreading out? Typologies of urban growth across 478 cities of 1 million+. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 124077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Song, W.; Liu, H.; Wu, Q.; Shi, K.; Wu, J. A New Approach for Detecting Urban Centers and Their Spatial Structure with Nighttime Light Remote Sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6305–6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kii, M.; Tamaki, T.; Suzuki, T.; Nonomura, A. Estimating urban spatial structure based on remote sensing data. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Li, C. Potential of NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Imagery for Modeling the Regional Economy of China. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3057–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yin, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, J. Evaluating the Ability of NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Data to Estimate the Gross Domestic Product and the Electric Power Consumption of China at Multiple Scales: A Comparison with DMSP-OLS Data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1705–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sutton, P.C.; Qi, B. Global Mapping of GDP at 1 km2 Using VIIRS Nighttime Satellite Imagery. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Chen, Y.; Yu, B.; Xu, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, R.; Li, L.; Wu, J. Modeling spatiotemporal CO2 (carbon dioxide) emission dynamics in China from DMSP-OLS nighttime stable light data using panel data analysis. Appl. Energy 2016, 168, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letu, H.; Nakajima, T.Y.; Nishio, F. Regional-Scale Estimation of Electric Power and Power Plant CO2 Emissions Using Defense Meteorological Satellite Program Operational Linescan System Nighttime Satellite Data. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 1, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.; Jiao, J.; Zhu, W.; Guo, Z.; Cao, X.; Liu, J.; Xi, G.; Wei, W. How to accurately assess the spatial distribution of energy CO2 emissions? Based on POI and NPP-VIIRS comparison. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 402, 136656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Song, J.; Chi, Y.; Yu, Q. Differential Spatiotemporal Patterns of CO2 Emissions in Eastern China’s Urban Agglomerations from NPP/VIIRS Nighttime Light Data Based on a Neural Network Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Sun, C. Refined Carbon Emission Measurement Based on NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Data: A Case Study of the Pearl River Delta Region, China. Sensors 2022, 23, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Li, W. Evaluation of NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Data for Mapping Global Fossil Fuel Combustion CO2 Emissions: A Comparison with DMSP-OLS Nighttime Light Data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Wu, R.; Cai, T. Revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve for city-level CO2 emissions: Based on corrected NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 121575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Pozzi, F.; Elvidge, C. Spatial analysis of global urban extent from DMSP-OLS night lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Lang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhu, M.; Na, J.; Zheng, J. Using Dual Spatial Clustering Models for Urban Fringe Areas Extraction Based on Night-time Light Data: Comparison of NPP/VIIRS, Luojia 1-01, and NASA’s Black Marble. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Shi, S.; Wu, J.; Yu, B. Global spatial patterns between nighttime light intensity and urban building morphology. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 124, 103495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kii, M.; Matsumoto, K. Detecting Urban Sprawl through Nighttime Light Changes. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, R.; Barabási, A.-L. Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 47–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabasi, A.L.; Albert, R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 1999, 286, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kii, M.; Akimoto, K.; Doi, K. Random-growth urban model with geographical fitness. Phys. A: Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2012, 391, 5960–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummu, M.; Taka, M.; Guillaume, J.H.A. Gridded global datasets for Gross Domestic Product and Human Development Index over 1990–2015. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, K.; van Vuuren, D.P.; Kriegler, E.; Edmonds, J.; O’Neill, B.C.; Fujimori, S.; Bauer, N.; Calvin, K.; Dellink, R.; Fricko, O.; et al. The Shared Socioeconomic Pathways and their energy, land use, and greenhouse gas emissions implications: An overview. Glob. Environ. Change 2017, 42, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, B.C.; Kriegler, E.; Ebi, K.L.; Kemp-Benedict, E.; Riahi, K.; Rothman, D.S.; van Ruijven, B.J.; van Vuuren, D.P.; Birkmann, J.; Kok, K.; et al. The roads ahead: Narratives for shared socioeconomic pathways describing world futures in the 21st century. Glob. Environ. Change 2017, 42, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kii, M. Projecting future populations of urban agglomerations around the world and through the 21st century. NPJ Urban. Sustain. 2021, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Zhizhin, M.; Ghosh, T.; Hsu, F.-C.; Taneja, J. Annual Time Series of Global VIIRS Nighttime Lights Derived from Monthly Averages: 2012 to 2019. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESA. Land Cover CCI Product User Guide Version 2; European Space Agency: Brussels, Belgium, 2017; p. 105.
- Oda, T.; Maksyutov, S. A very high-resolution (1 km × 1 km) global fossil fuel CO2 emission inventory derived using a point source database and satellite observations of nighttime lights. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Maksyutov, S.; Andres, R.J. The Open-source Data Inventory for Anthropogenic Carbon dioxide (CO2), version 2016 (ODIAC2016): A global, monthly fossil-fuel CO2 gridded emission data product for tracer transport simulations and surface flux inversions. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Estimate | t Value | |
|---|---|---|
| −6.289 | −12.96 | |
| 0.893 | 18.80 | |
| 0.928 | 25.22 | |
| N | 555 | |
| R2 | 0.663 | |
| F-statistic | 542.1 | |
| Estimate | t Value | |
|---|---|---|
| 0.212 | 19.24 | |
| 0.510 | 5.30 | |
| −3.64 × 10−4 | −3.54 | |
| 0.109 | 8.43 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explanatory Variables 1 | Estimate | t Value | Estimate | t Value | Estimate | t Value |
| (Intercept) | −1.29 | −52.43 | −1.29 | −52.65 | −0.705 | −33.35 |
| NTL.b | 0.907 | 2687.30 | 0.907 | 2688.50 | 0.907 | 2691.25 |
| RTC | −0.888 | −114.02 | −0.888 | −114.24 | −0.925 | −124.47 |
| RDD | −6.41 × 10−5 | −48.51 | −6.41 × 10−5 | −48.75 | −5.66 × 10−5 | −43.44 |
| TDS | 2.76 × 10−2 | 18.92 | 2.76 × 10−2 | 18.91 | ||
| PTC | −2.77 × 10−2 | −18.95 | −2.77 × 10−2 | −18.94 | −5.49 × 10−5 | −32.58 |
| WBD | 1.66 × 10−3 | 0.08 | ||||
| TMP.a | 0.155 | 205.38 | 0.155 | 205.79 | 0.140 | 226.77 |
| TMP.v | 8.31 × 10−4 | 55.69 | 8.31 × 10−4 | 55.70 | 5.13 × 10−4 | 40.15 |
| PRC.a | −4.22 × 10−4 | −71.83 | −4.22 × 10−4 | −71.86 | −5.09 × 10−4 | −95.50 |
| PRC.v | −4.84 × 10−4 | −4.98 | −4.82 × 10−4 | −4.96 | ||
| talt.m | 2.98 × 10−4 | 45.24 | 2.98 × 10−4 | 45.72 | ||
| talt.sd | 5.89 × 10−4 | 0.83 | ||||
| tslp.m | 0.962 | 5.42 | 1.09 | 12.68 | ||
| tslp.sd | −4.30 | −20.14 | −4.32 | −20.35 | −0.566 | −6.71 |
| PRC | −3.39 × 10−2 | −3.28 | −3.38 × 10−2 | −3.28 | −3.41 × 10−2 | −3.32 |
| NTL.fc.b | 8.64 × 10−3 | 27.63 | 8.64 × 10−3 | 27.63 | 8.56 × 10−3 | 27.34 |
| POP | 4.37 × 10−5 | 84.89 | 4.37 × 10−5 | 84.94 | 4.48 × 10−5 | 87.38 |
| GDPp | 5.99 × 10−6 | 48.11 | 5.99 × 10−6 | 48.18 | 5.18 × 10−6 | 43.91 |
| N | 2,555,832 | |||||
| DF | 2,555,813 | |||||
| R2 | 0.915 | 0.915 | 0.915 | |||
| Linear Regression | Log-Linear Regression | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | t Value | Estimate | t Value | ||
| (Intercept) | 438.1 | 312.5 | (Intercept) | 5.261 | 9200.6 |
| ntl | 117.3 | 1146.2 | log (ntl) | 0.830 | 2212.0 |
| n | 3,468,619 | n | 3,468,619 | ||
| R2 | 0.275 | R2 | 0.585 | ||
| R2~ntl | 0.302 | ||||
| Source | Period | Estimated Urban Area Increase |
|---|---|---|
| This study | 2017 to 2053 | 79% to 132% |
| Huang et al. [16] | 2015 to 2050 | 78% to 171% |
| Li et al. [17] | 2013 to 2050 | 40% to 67% |
| Chen et al. [18] | 2015 to 2100 | 53.8% to 110.6% |
| Gao and O’Neill [19] | 2010 to 2050 | 51% to 168% |
| Zhou et al. [20] | 2012 to 2050 | About 40% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kii, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Sugita, S. Future Scenarios of Urban Nighttime Lights: A Method for Global Cities and Its Application to Urban Expansion and Carbon Emission Estimation. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061018
Kii M, Matsumoto K, Sugita S. Future Scenarios of Urban Nighttime Lights: A Method for Global Cities and Its Application to Urban Expansion and Carbon Emission Estimation. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(6):1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061018
Chicago/Turabian StyleKii, Masanobu, Kunihiko Matsumoto, and Satoru Sugita. 2024. "Future Scenarios of Urban Nighttime Lights: A Method for Global Cities and Its Application to Urban Expansion and Carbon Emission Estimation" Remote Sensing 16, no. 6: 1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061018
APA StyleKii, M., Matsumoto, K., & Sugita, S. (2024). Future Scenarios of Urban Nighttime Lights: A Method for Global Cities and Its Application to Urban Expansion and Carbon Emission Estimation. Remote Sensing, 16(6), 1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061018