MODIS-Based Fractional Crop Mapping in the U.S. Midwest with Spatially Constrained Phenological Mixture Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data Sets


2.2. Methodology
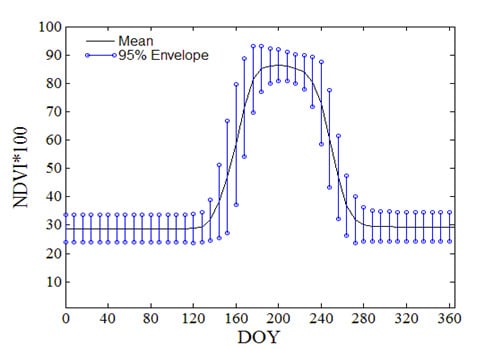
2.2.1. NDVI Time Series and Crop Phenology

| Crops | Corn | Soybean | Spring Wheat | Winter Wheat | Short CSG | Short WSG | Tall CSG | Tall WSG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean | 5.47 | 6.56 | 6.17 | 10.4 | 4.70 | 3.79 | 7.31 | 6.61 |
| stddev * | 3.13 | 2.64 | 2.14 | 2.94 | 1.28 | 1.79 | 3.40 | 2.49 |
2.2.2. Spatially Constrained Phenological Mixture Analysis (SPMA)
2.2.3. Accuracy Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SPMA-Extracted Crop Percent Covers



3.2. Comparison with References at Pixel Level
| Types | Corn | Soybean | Spring Wheat | Winter Wheat | Short CSG | Short WSG | Tall CSG | Tall WSG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 0.163 | 0.162 | 0.195 | 0.160 | 0.187 | 0.165 | 0.136 | 0.156 |
| SE | –0.096 | –0.099 | –0.152 | –0.081 | –0.124 | –0.016 | 0.049 | 0.059 |
| Student’s t | 21.84 | 21.30 | 15.08 | 11.52 | 8.97 | 6.54 | 8.37 | 7.52 |


3.3. Comparison with Crop Census Records at County Level

| Types | County Level | Region-Level (Midwest) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRAE | r | SPMA Results (Million Acres) | NASS Census (Million Acres) | Ratio (SPMA/Census) | |
| Soybean | −0.065 | 0.955 | 61.616 | 52.702 | 116.91% |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- 2007 Corn Crop A Record Breaker. Available online: http://www.nass.usda.gov/Newsroom/2008/01_11_2008.asp (accessed on 15 May 2014).
- Wang, C.; Fritschi, F.B.; Stacey, G.; Yang, Z. Phenology-based assessment of perennial energy crops in North American Tallgrass Prairie. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2011, 101, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.K.; Cleveland, C.C.; Reed, S.C.; Miller, N.L.; Running, S.W. Bioenergy potential of the United States constrained by satellite observations of existing productivity. Environ. Sci. Tech. 2012, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boryan, C.; Yang, Z.; Mueller, R.; Craig, M. Monitoring US agriculture: The US department of agriculture, national agricultural statistics service, Cropland Data Layer Program. Geocarto Int. 2011, 26, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.D.; Barnes, J.R.; Halvorsen, K.E. Grain and cellulosic ethanol: History, economics, and energy policy. Biomass Bioenerg. 2007, 31, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, K.; Hansen, M.C.; Becker-Reshef, I.; Potapov, P.V.; Christopher, O.J. Estimating global cropland extent with multi-year MODIS data. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 1844–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Biradar, C.M.; Noojipady, P.; Dheeravath, V.; Li, Y.J.; Velpuri, M.; Gumma, M.; Reddy, G.P.O.; Turral, H.; Cai, X.L.; et al. Global Irrigated Area Map (GIAM), derived from remote sensing, for the end of the last millennium. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 3679–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Hanjra, M.A.; Dheeravath, V.; Gumma, M.A. A holistic view of global croplands and their water use for ensuring global food security in the 21st century through advanced remote sensing and non-remote sensing approaches. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 211–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, U.L. Spectral identification of native and non-native plant species. In Proceedings of ASD and IEEE GRS; Art, Science and Applications of Reflectance Spectroscopy Symposium, Boulder, CO, USA, 23–25 February 2010.
- Xie, Y.; Sha, Z.; Yu, M. Remote sensing imagery in vegetation mapping: A review. J. Plant Ecol. 2008, 1, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCloy, K.R.; Lucht, W. Comparative evaluation of seasonal patterns in long time series of satellite image data and simulations of a global vegetation model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jamison, B.; Spicci, A. Trajectory-based warm season grass mapping in Missouri prairies with multi-temporal ASTER imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 531–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, D.L.; Price, K.P.; Martinko, E.A. Discriminating between cool season and warm season grassland cover types in Northeaster Kansas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 5015–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlow, B.D.; Egbert, S.L.; Kastens, J.H. Analysis of time-series MODIS 250 m vegetation index data for crop classification in the U.S. Central Great Plains. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 290–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Hunt, E.R.; Zhang, L.; Guo, H. Phenology-assisted classification of C3 and C4 grasses in the U.S. Great Plains and their climate dependency with MODIS time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 138, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homer, C.; Huang, C.; Yang, L.; Wylie, B.; Coan, M. Development of a 2001 national landcover database for the United States. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2004, 70, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerken, R.A. An algorithm to classify and monitor seasonal variations in vegetation phenologies and their inter-annual change. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2009, 64, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlow, B.D.; Egbert, S.L. Large-area crop mapping using time-series MODIS 250 m NDVI data: An assessment for the US Central Great Plains. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1096–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Asner, G.P. Cropland distributions from temporal unmixing of MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Hu, X.; Lu, D. Extracting impervious surface from medium spatial resolution multispectral and hyperspectral imagery: A comparison. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3209–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Remote sensing of impervious surfaces in the urban areas: Requirements, methods, and trends. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Wu, C. A spatially adaptive spectral mixture analysis for mapping subpixel urban impervious surface distribution. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 133, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busetto, L.; Meroni, M.; Colombo, R. Combining medium and coarse spatial resolution satellite data to improve the estimation of sub-pixel NDVI time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdogan, M. The spatial distribution of crop types from MODIS data: Temporal unmixing using independent component analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1190–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, B.; Asner, G.P.; Tits, L.; Coppin, P. Endmember variability in spectral mixture analysis: A review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethanol Facilities’ Capacity by State. Available online: http://www.neo.ne.gov/statshtml/121.htm. (accessed on 15 May 2014).
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cropland Layer Data. Available online: http://nassgeodata.gmu.edu/CropScape/ (accessed on 15 May 2014).
- Hu, X.; Weng, Q. Estimating impervious surfaces from medium spatial resolution imagery using the self-organizing map and multi-layer perceptron neural networks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2089–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhong, C.; Yang, Z. Assessing bioenergy-driven agricultural land use change and biomass quantities in the U.S. Midwest with MODIS time series. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Cheng, J.; Gao, F.; Chen, X.; Masek, J.G. An enhanced spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model for complex heterogeneous regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, C.; Wang, C.; Wu, C. MODIS-Based Fractional Crop Mapping in the U.S. Midwest with Spatially Constrained Phenological Mixture Analysis. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 512-529. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70100512
Zhong C, Wang C, Wu C. MODIS-Based Fractional Crop Mapping in the U.S. Midwest with Spatially Constrained Phenological Mixture Analysis. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(1):512-529. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70100512
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Cheng, Cuizhen Wang, and Changshan Wu. 2015. "MODIS-Based Fractional Crop Mapping in the U.S. Midwest with Spatially Constrained Phenological Mixture Analysis" Remote Sensing 7, no. 1: 512-529. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70100512
APA StyleZhong, C., Wang, C., & Wu, C. (2015). MODIS-Based Fractional Crop Mapping in the U.S. Midwest with Spatially Constrained Phenological Mixture Analysis. Remote Sensing, 7(1), 512-529. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70100512