A Collection of SAR Methodologies for Monitoring Wetlands
Abstract
:1. Introduction


2. Surface Water
2.1. Case Study—Peace-Athabasca Delta

2.2. SAR Data Acquisition and Processing
| Spring 2012 | Summer 2012 | Fall 2012 |
|---|---|---|
| 28 April | 15 June | 19 September |
| 22 May | 9 July | 13 October |
| - | 2 August | - |
| - | 26 August | - |
2.3. Results and Discussion



| Date | Daily Total Precipitation (mm) | Daily Mean Temperature (°C) | Month | Monthly Total Precipitation (mm) | Monthly Mean Daily Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28 April 2012 | 0.0 | 10.0 | April 2012 | 20.6 | 3.3 |
| 22 May 2012 | 0.0 | 13.6 | May 2012 | 20.8 | 12.2 |
| 15 June 2012 | 0.0 | 13.3 | June 2012 | 58.0 | 16.9 |
| 9 July 2012 | 0.0 | 25.3 | July 2012 | 87.6 | 20.6 |
| 2 August 2012 | 5.7 | 17.2 | August 2012 | 33.3 | 18.3 |
| 26 August 2012 | 0.0 | 17.2 | September 2012 | 101.1 | 13.4 |
| 19 September 2012 | 0.3 | 12.5 | October 2012 | 44.4 | 0.7 |
| 13 October 2012 | 0.0 | 1.5 |
3. Flooded Vegetation
3.1. Case Study—Whitewater Lake

3.2. Data Acquisition and Processing
| 2010 | 2012 | 2013 |
|---|---|---|
| 6 May | 19 May | 14 May |
| 30 May | 12 June | 7 June |
| 17 July | 6 July | 1 July |
| 3 September | 16 September | 18 August |
| 21 October | 10 October | 11 September |
| − | − | 5 October |
3.3. Results and Discussion
| Land Cover, Time 1 | Land Cover, Time 2 | % Correct Change Detection Freeman-Durden | % Correct Change Detection m-χ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annually | |||
| Wet soil | Open water | 100% | 100% |
| Upland | Open water | 100% | 100% |
| Upland | Flooded vegetation | 80% | 80% |
| Open water | Flooded vegetation | 87% | 69% |
| Seasonally | |||
| Wet soil | Open water | 73% | 80% |
| Upland | Open water | − | − |
| Upland | Flooded vegetation | 67% | 67% |
| Open water | Flooded vegetation | 100% | 67% |
| Overall | |||
| Any | Any | 89% | 81% |


4. Curvelet-Based Change Detection for Mapping Flooded Vegetation
4.1. Case Study—Dong Ting Lake

4.2. Data Acquisition and Processing
4.3. Results and Discussion


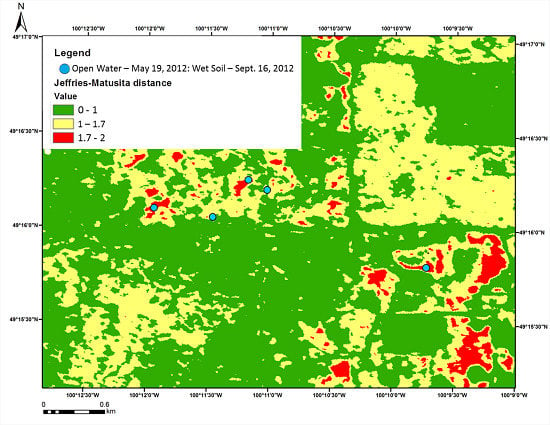
5. Wishart-Chernoff Distance
5.1. Case Study—Whitewater Lake
5.2. SAR Data Acquisition
5.3. Results and Discussion

6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vymazal, J. Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Ecol. Eng. 2005, 25, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsch, W.; Gosselink, J. The value of wetlands: Importance of scale and landscape setting. Ecol. Econ. 2000, 35, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.C.; Watt, W.E.; Marsalek, J. Critical issues for stormwater ponds: Learning from a decade of research. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 45, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gedan, K.B.; Kirwan, M.L.; Wolanski, E; Barbier, E.B.; Silliman, B.R. The present and future role of coastal vegetation in protecting shorelines: Answering recent challenges to the paradigm. Clim. Chang. 2010, 106, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.D. A Naturalist’s Guide to Wetland Plants: An Ecology for Eastern North America; Syracuse University Press: Syracuse, NY, USA, 2002; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Natural Resources Canada. Sensitivity of Peatlands to Climate Change. Available online: http://atlas.nrcan.gc.ca/site/english/maps/climatechange/potentialimpacts/sensitivitypeatlands/1 (accessed on 5 August 2014).
- IUCN. 2007 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Available online: www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 21 December 2014).
- Prigent, C.; Papa, F.; Aires, F.; Jimenez, C.; Rossow, W.B.; Matthews, E. Changes in land surface water dynamics since the 1990s and relation to population pressure. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L08403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrati, R.; Canziani, G.A.; Moreno, D.R. Estero del Ibera: Hydrometeorological and hydrological characterization. Ecol. Model. 2005, 18, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scientific and Technical Review Panel of the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands. New guidelines for management planning for Ramsar sites and other wetlands. “Wetlands: water. Life, and culture”. In Proceedings of 8th Meeting of the Conference of the Contracting Parties to the Convention on Wetlands (Ramsar, Iran, 1971), Valencia, Spain, 18–26 November 2002.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (US-EPA). Wetlands Treatment Database (North American Wetlands for Water Quality Treatment Database); US-EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1994.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (US-EPA). Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment and Wildlife Habitat: 17 Case Studies; US-EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Environment Canada. Water and Climate Change. Available online: http://www.ec.gc.ca/eau-water/default.asp?lang=En&n=3E75BC40-1 (accessed on 30 December 2014).
- Root, T.L.; Price, J.T.; Hall, K.R.; Schneider, S.H.; Rosenzweig, C.; Pounds, J.A. Fingerprints of global warming on wild animals and plants. Nature 2003, 421, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lettenmaier, D.P.; Su, F. Chapter 9: Progress in hydrological modeling over high latitudes under Arctic Climate System Study (ACSYS). In ARCTIC Climate Change—The ACSYS Decade and Beyond; Lemke, P., Hans-Werner, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 357–380. [Google Scholar]
- Ducks Unlimited. Conserving Waterfowl and Wetlands amid Climate Change; Browne, D.M., Dell, R., Eds.; Ducks Unlimited, Inc.: Memphis, TN, USA, 2007; pp. 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Johns, T.C.; Carnell, R.E.; Crossley, J.F.; Gregory, J.M.; Mitchell, J.F.B.; Senior, C.A.; Tett, S.F.B.; Wood, R.A. The second Hadley Centre coupled ocean-atmosphere GCM: Model description, spinup and validation. Clim. Dyn 1997, 13, 103–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, G.J.; Flato, G.M.; Ramsden, D. A transient climate change simulation with greenhouse gas and aerosol forcing: Projected climate change to the 21st century. Clim. Dyn 2000, 16, 427–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.; Wigley, T.M.L.; Boville, B.A.; Kiehl, J.T.; Buja, L.E. Climates of the twentieth and twenty-first centuries simulated by the NCAR climate system model. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 485–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate change 2001: The scientific basis. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Houghton, J.T., Ding, Y., Griggs, D.J., Noguer, M., van der Linden, P.J., Dai, X., Maskell, K., Johnson, C.A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001; pp. 1–873. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, P.; Hey, M. Analysis of spring high water events in the Mackenzie Delta and implications for lake and terrestrial flooding. Geogr. Ann. 1994, 4, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, P.J.; Best, G.R.; Coutant, C.C.; Hornberger, G.M.; Meyer, J.L.; Robinson, P.J.; Stenbert, J.R.; Turner, R.E.; Vera-Herrera, F.; Wetzel, R.G. Effects of climate change on freshwater ecosystems of the south-eastern United States and the Gulf of Mexico. Hydrol. Process. 1997, 11, 949–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cihlar, J.; Tarnocai, C. Wetlands of Canada and climate change: Observation strategy and baseline data. In Presented at a Natural Resources Canada Workshop, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 24−25 January 2000.
- Fournier, R.A.; Grenier, M.; Lavoie, A.; Hélie, R. Towards a strategy to implement the Canadian Wetland Inventory using satellite remote sensing. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 33, S1–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducks Unlimited Canada. Canadian Wetland Inventory. Available online: http://www.ducks.ca/what-we-do/cwi/ (accessed on 29 August 2014).
- Milne, A.K.; Horn, G.; Finlayson, M. Monitoring wetlands inundation patterns using Radarsat multitemporal Data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 26, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, J.; Knight, J.; Brisco, B.; Kaya, S.; Cull, A.; Murnaghan, K. The integration of optical, topographic and radar data for wetland mapping in northern Minnesota. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 37, 564–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.J.; Wang, L.Z.; Shu, L.F.; Chen, P.Y.; Chen, L.G. Factors affecting the vegetation restoration after fires in cold temperate wetlands: A review. Chin. J. App. Ecol. 2013, 24, 853–860. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsch, W.J.; Gosselink, J.G. Wetands, 2nd ed.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1993; p. 539. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (US-EPA). Design Manual: Nitrogen Control; US-EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Bartzen, B.A.; Dufour, K.W.; Clark, R.G.; Caswell, F.D. Trends in agricultural impact and recovery of wetlands in prairie Canada. Ecol. Appl. 2010, 20, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brisco, B.; Touzi, R.; van der Sanden, J.J.; Charbonneau, F.; Pultz, T.J.; D’Iorio, M. Water resource applications with RADARSAT-2—A preview. Int. J. Digital Earth 2008, 1, 130–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisco, B.; Short, N.; van der Sanden, J.; Landry, R.; Raymond, D. A semi-automated tool for surface water mapping with RADARSAT-1. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 35, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, L.L.; Melack, J.M.; Simonett, D.S. Radar detection of flooding beneath the forest canopy: A review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1990, 11, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzi, R.; Deschamps, A.; Rother, G. Wetland characterization using polarimetric RADARSAT-2 capability. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 33, S56–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallant, A.L.; Kaya, S.G.; White, L.; Brisco, B.; Roth, M.F.; Sadinski, W.; Rover, J. Detecting emergence, growth, and senescence of wetland vegetation with polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Data. Water 2014, 6, 694–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, L.; Brisco, B.; Pregitzer, M.; Tedford, B.; Boychuk, L. RADARSAT-2 beam mode selection for surface water and flooded vegetation mapping. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 40, 135–151. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.C. Satellite remote sensing of river inundation area, stage, and discharge: A review. Hydrol. Process. 1997, 11, 1427–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.B. Introduction to Remote Sensing; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; p. 206. [Google Scholar]
- Töyrä, J.; Pietroniro, A. Towards operational monitoring of a northern wetland using geomatics-based techniques. Remote Sen. Environ. 2005, 97, 174–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, S.; Wiebe, J.; Collins, M.; Pietroniro, A. RADARSAT flood mapping in the Peace-Athabasca Delta, Canada. Can. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 24, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crevier, Y.; Pultz, T.J. Analysis of C-Band SIR-C radar backscatter over a flooded environment, Red River, Manitoba. In Proceedings of the Third International Workshop (NHRI Symposium)—Applications of Remote Sensing in Hydrology, Greenbelt, MD, USA, 16−18 October 1996; pp. 47–60.
- Töyrä, J.; Pietroniro, A.; Martz, L.W. Multisensor hydrologic assessment of a freshwater wetland. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2001, 75, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Baldassarre, G.; Schumann, G.; Brandimarte, L.; Bates, P. Timely low resolution SAR imagery to support floodplain modeling: A case study review. Surv. Geophys. 2011, 32, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, T.G. Chapter 5: Radar interactions with geologic surfaces. In Guide to Magellan Image Interpretation; Ford, J.P., Plaut, J.J., Weitz, C.M., Eds.; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; pp. 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Sanden, J.J.; Geldsetzer, T.; Short, N.; Brisco, B. Advanced SAR APPLICATIONS FOR CANADA’S CRYOSphere (freshwater ice and permafrost); Final Technical Report for the Government Related Initiatives Program (GRIP); Natural Resources Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2012; p. 80.
- Hess, L.; Melack, J.; Novo, E.; Barbosa, C.; Gastil, M. Dual season mapping of wetland inundation and vegetation for the central Amazon Basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 87, 404–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, C.R.; D’Amico, E. Calculating the ecosystem service of water storage in isolated wetlands using LiDAR in North Central Florida, United States. Wetlands 2010, 30, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisco, B.; Kapfer, M.; Hirose, T.; Tedford, B.; Liu, J. Evaluation of C-band polarization diversity and polarimetry for wetland mapping. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 37, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisco, B.; Li, K.; Tedford, B.; Charbonneau, F.; Yun, S.; Murnaghan, K. Compact polarimetry assessment for rice and wetland mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 1949–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wdowinski, S.; Kim, S.W.; Amelung, F.; Dixon, T.H.; Miralles-Wilhelm, F.; Sonenshein, R. Space-based detection of wetlands’ surface water level changes from L band SAR interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadian Space Agency. RADARSAT Constellation. Available online: http://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/satellites/radarsat/ (accessed on 2 August 2014).
- Raney, R.K. Hybrid-polarity SAR architecture. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3397–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, C.M.; Davidson, N.C.; Spiers, A.G.; Stevenson, N.J. Global wetland inventory—Current status and future priorities. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1999, 50, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.R.M.; Dwivedi, R.S.; Kushwaha, S.P.S.; Bhattacharya, S.N.; Anand, J.B.; Dasgupta, S. Monitoring the spatial extent of coastal wetlands using ERS-1 SAR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 2509–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, N.; Bernier, M.; Gauthier, R.; Neeson, I. Evaluation of C-band SAR data for wetlands mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasischke, E.S.; Bourgeau-Chavez, L.L. Monitoring South Florida wetlands using ERS-1 SAR imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Rem. Sens. 1997, 63, 281–291. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.E.; Kim, D.; Lee, H.S.; Moon, W.M.; Wagner, W. Tidal wetland monitoring using polarimetric synthetic aperture RADAR. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2010, 38, 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Reschke, J.; Bartsch, A.; Schlaffer, S.; Schepaschenko, D. Capability of C-band SAR for operational wetland monitoring at high latitudes. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 2923–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerner, W.M.; Mott, H.; Luneburg, E.; Livingstone, C.; Brisco, B.; Brown, R.J.; Paterson, J.S. Polarimetry in radar remote sensing: Basic and applied concepts, in principles and applications of imaging radar. IEEE Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 3, 1401–1403. [Google Scholar]
- Horritt, M.S.; Mason, D.C.; Luckman, A.J. Flood boundary delineation from synthetic aperture radar imagery using a statistical active contour model. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 2489–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvoven, J.; Simila, M.; Makynen, M. Open water detection from Baltic Sea ice RADARSAT-1 SAR imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2005, 2, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, G.; Li, J.; Zhiguo, H. Detecting water bodies on RADARSAT imagery. Geomatica 2011, 65, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulvirenti, L.; Chini, M.; Pierdicca, N.; Guerriero, L.; Ferrazzoli, P. Flood monitoring using multi-temporal COSMO-SkyMed data: Image segmentation and signature interpretation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 990–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhoff, R.S.; Kleuskens, M.P.H.; Winsemius, H.C.; Huizinga, H.J.; Brakenridge, G.R.; Bishop, C. Automated global water mapping based on wide-swath orbital synthetic-aperture radar. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nico, G.; Pappalepore, M.; Pasquariello, G.; Refice, A.; Samarelli, S. Comparison of SAR amplitude vs. coherence flood detection methods—A GIS application. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 1619–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.C.; Alsdorf, D.E. Control on sediment and organic carbon delivery to the Arctic Ocean revealed with space-borne synthetic aperture radar: Ob’ River, Siberia. Geology 1998, 26, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsdorf, D.E.; Rodríguez, E.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Measuring surface water from space. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, RG2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahmann, T.; Wessel, B. Surface water body detection in high-resolution TerraSAR-X data using active contour models. In Proceedings of the 8th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 7−10 June 2010; pp. 1–4.
- Hess, L.L.; Melack, J.M.; Filoso, S.; Wang, Y. Delineation of inundated area and vegetation along the Amazon floodplain with the SIR-C synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, J.B.; Chastanet, P.; Fellah, K.; Desnos, Y.L. Envisat multi-polarized ASAR data for flood mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, S.; Twele, A.; Voigt, S. Towards operational near real-time flood detection using a split-based automatic thresholding procedure on high resolution TerraSAR-X data. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulvirenti, L.; Pierdicca, N.; Chini, M.; Guerriero, L. An algorithm for operational flood mapping using Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) using fuzzy logic. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GAMMA Remote Sensing Research and Consulting AG. Gamma Remote Sensing. Available online: http://www.gamma-rs.ch/gamma.html (accessed 30 December 2014).
- Goodman, J.W. Some fundamental properties of speckle. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1976, 66, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Jurkevish, I.; Dewaele, P.; Wambacq, P; Oosterlinck, A. Speckle filtering of synthetic aperture radar images: A review. Remote Sens. Rev. 1994, 8, 313–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olthof, I.; Latifovic, R.; Pouliot, D. National scale medium resolution land cover mapping of Canada from SPOT 4/5 data. In Proceedings of the 34th Canadian Symposium on Remote Sensing, Victoria, BC, Canada, 27−29 August 2013.
- Vachon, P.W.; Wolfe, J. C-band cross-polarization wind speed retrieval. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 8, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeau-Chavez, L.L.; Kasischke, E.S.; Brunzell, S.M.; Mudd, J.P.; Smith, K.B.; Frick, L.A. Analysis of space-borne SAR data for wetland mapping in Virginia riparian ecosystems. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 3665–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, P.A.; Foster, J.R. A synthetic aperture radar-based model to assess historical changes in lowland floodplain hydroperiod. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjusree, P.; Kumar, L.P.; Bhatt, C.M.; Rao, G.S.; Bhanumurty, V. Optimization of threshold ranges for rapid flood inundation mapping by evaluating backscatter profiles of high incidence angle SAR images. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2002, 3, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuchl, B.; Flett, D.; Caves, R.; Cumming, I. Potential of RADARSAT-2 data for operational sea ice monitoring. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 30, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, H.C.; Waite, W.P.; Demarcke, J.S. Use of Seasat satellite radar imagery for the detection of standing water beneath forest vegetation. In Proceedings of the American Society of Photogrammetry Fall Technical Meeting, Niagara Falls, NY, USA, 7−10 October 1980.
- Pope, K.O.; Rejmankova, E.; Paris, J.F.; Woodruff, R. Detecting seasonal flooding cycles in marches of the Yucatan Peninsula with SIR-C polarimetric radar imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 59, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, P.A. Relationship between forest structure and the detection of flood inundation in forested wetlands using C-band SAR. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzi, R.; Boerner, W.M.; Lee, J.S.; Luenberg, E. A review of polarimetry in the context of synthetic aperture radar: Concepts and information extraction. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 30, 380–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SARs. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.; Durden, S.L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zyl, J.J. Unsupervised classification of scattering behaviour using radar polarimetry data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1989, 27, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raney, R.K.; Cahill, J.T.S.; Patterson, G.W.; Bussey, D.B.J. The m-chi decomposition of hybrid dual-polarimetric radar data with application to lunar craters. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 17, E00H21. [Google Scholar]
- Geomatica 2010; PCI Geomatics Enterprises, Inc.: Richmond Hill, ON, Canada, 2010.
- Da Silva, A.Q.; Waldir, W.R.; Freitas, C.C.; Oliveira, C.G. Evaluation of digital classification of polarimetric SAR data for iron-mineralized laterites mapping in the Amazon region. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3101–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Space Agency. Radar and SAR Glossary. Available online: https://earth.esa.int/handbooks/asar/CNTR5-2.htm (accessed on 29 December 2014).
- Ramsey, E. Radar remote sensing of wetlands. In Remote Sensing Change Detection: Environmental Monitoring Methods and Applications; Lunetta, R., Elvidge, C., Eds.; Ann Arbor Press: Chelsea, MI, USA, 1998; pp. 211–243. [Google Scholar]
- Pope, K.; Sheffner, E.; Linthicum, K.; Bailey, C.; Logan, T.; Kasischke, E.; Birney, K.; Njogu, A.; Roberts, C. Identification of central Kenyan Rift Valley fever virus vector habitats with Landsat TM and evaluation of their flooding status with airborne radar. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 40, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbonneau, F.J.; Brisco, B.; Raney, R.K.; McNairn, H.; Liu, C.; Vachon, P.W.; Shang, J.; DeAbreu, R.; Champagne, C.; Merzouki, A.; et al. Compact polarimetry overview and applications assessment. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 36, 298–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois-Fernandez, P.; Souyris, J.C.; Angelliaume, S.; Garestier, F. The compact polarimetry alternative for spaceborne SAR at low frequency. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 46, 3208–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, E.M.; Costa, M.F.; Mantovani, J.; Lima, I. Relationship between macrophyte stand variables and radar backscatter at L and C band, Tucuruí Reservoir, Brazil. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 1241–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandus, P.; Karszenbaum, H.; Pultz, T.; Parmuchi, G.; Bava, J. Influence of flood conditions and vegetation status of the radar backscatter of wetland flood conditions and vegetation status on the radar backscatter of wetland ecosystems. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 27, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leconte, R.; Pultz, T. Evaluation of the potential of Radarsat for flood mapping using simulated satellite SAR imagery. Can. J. Remote Sens. 1991, 17, 241–249. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.; Brisco, B.; D’Iorio, M.; Prevost, C.; Ryerson, R.; Singhroy, V. RADARSAT applications: Review of GlobeSAR Program. Can. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 22, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, A.; Brisco, B. Wetland monitoring using the curvelet-based change detection method on polarimetric SAR imagery. Water 2013, 5, 1036–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, A.; Brisco, B.; Kaya, S.; Murnaghan, K. Polarimetric change detection for wetlands. In IAHS Publication Series (Red Book); Centre for Ecology and Hydrology: Jackson Hole, WY, USA, 2010; pp. 375–379. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, A.; Wessel, B.; Roth, A. An innovative curvelet-only-based approach for automated change detection in multi-temporal SAR imagery. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 2435–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candès, E.J.; Donoho, D.L. Curvelets—A surprisingly effective nonadaptive representation for objects with edges. In Curve and Surface Fitting. Innoivations in Applied Mathematics; Schumaker, L., Ed.; Vanderbilt University Press: Saint-Malo, France, 1999; pp. 105–120. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, A.; Wessel, B.; Roth, A. Curvelet approach for SAR image denoising, structure enhancement, and change detection. In CMRT09—Object Extraction for 3D City Models, Road Databases and Traffic Monitoring—Concepts, Algorithms and Evaluation; Stilla, U., Rottensteiner, F., Paparoditis, N., Eds.; CMRT09: Paris, France, 2009; pp. 151–156. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.L. The change of wetland and analysis of flood control in Dong Ting Lake. In The Symposium of Flooding Disaster and Scientific and Technological Countermeasure of the Yangtze River; Xu, H.Z., Zhao, Q.G., Eds.; Science Press of China: Beijing, China, 1999; pp. 106–112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dabboor, M.; Collins, M.; Karathanassi, V.; Braun, A. An unsupervised classification approach for polarimetric SAR data based on the Chernoff distance for the complex Wishart distribution. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4200–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabboor, M.; Yackel, J.; Hossain, M.; Braun, A. Comparing matrix distance measures for unsupervised polarimetric SAR data classification of sea ice based on agglomerative clustering. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 1492–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabboor, M.; White, L.; Brisco, B.; Charbonneau, F. Change detection with compact polarimetric SAR for monitoring wetlands. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2015. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, J.A.; Jia, X. Remote Sensing Digital Image Analysis an Introduction, 3rd ed.; Springer Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, J.R. Introductory Digital Image Processing: A Remote Sensing Perspective; Prentice Hall: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 1996; pp. 372–373. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
White, L.; Brisco, B.; Dabboor, M.; Schmitt, A.; Pratt, A. A Collection of SAR Methodologies for Monitoring Wetlands. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7615-7645. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70607615
White L, Brisco B, Dabboor M, Schmitt A, Pratt A. A Collection of SAR Methodologies for Monitoring Wetlands. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(6):7615-7645. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70607615
Chicago/Turabian StyleWhite, Lori, Brian Brisco, Mohammed Dabboor, Andreas Schmitt, and Andrew Pratt. 2015. "A Collection of SAR Methodologies for Monitoring Wetlands" Remote Sensing 7, no. 6: 7615-7645. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70607615
APA StyleWhite, L., Brisco, B., Dabboor, M., Schmitt, A., & Pratt, A. (2015). A Collection of SAR Methodologies for Monitoring Wetlands. Remote Sensing, 7(6), 7615-7645. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70607615