Retrieval of High-Resolution Atmospheric Particulate Matter Concentrations from Satellite-Based Aerosol Optical Thickness over the Pearl River Delta Area, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Author | Study Area | Date | Model description | Linear Regression | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang et al. [17] | Alabama | 2002 | MODIS 10 km AOT and PM2.5 | 77τ − 0.23 (Terra) 68.6τ + 1.93 (Aqua) | 0.67 0.76 |
| Chu et al. [18] | Italy | August–October 2000 | AOT from AERONET and PM10 | 54.7τ + 8 | 0.82 |
| Engel-cox et al. [11] | Eastern United States | Summer 2004 | MODIS 10 km AOT and PM2.5 | 25.329τ + 11.091 | 0.574 |
| Gupta et al. [20] | Global urban areas | 2002 | MODIS 10 km AOT and PM2.5 | 166.7τ − 25 | 0.96 |
| Li et al. [21] | Hong Kong | 15–17 September 2001 | MODIS 1 km AOT and PM2.5 | 171.3τ + 0.4 | 0.77 |
| Zheng et al. [22] | Pearl River Delta | 2006 to 2008 | MODIS 1 km AOT and PM10 | 63.35τ + 39.94 | 0.458 |
| Guo et al. [23] | Eastern China | 2007 | MODIS 10 km AOT and hourly PM | NA | 0.46 (PM1) 0.61 (PM2.5) 0.52 (PM10) |
| Schaap et al. [14] | Cabauw, Netherlands | August 2006 to May 2007 | MODIS 10 km AOT and PM2.5 | 120τ+5.0926 | 0.518 |
| Wang et al. [24] | Beijing | July 2007 to October 2008 | MODIS 1 km AOT and PM10 | 361.1τ + 19.6 | 0.65 |
| You et al. [25] | Xi’an | 2013 | MODIS 10 km AOT, MISR 17.6 km AOT and PM2.5 | NA | 0.816 0.847 |

2. Data
2.1. Station Monitoring Data of PM10
| Stations | Type | (Lat, Lon) | City |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tianhu | Rural | (23.646° N, 113.638° E) | Guangzhou |
| Luhu Park | City | (23.156° N, 113.277° E) | Guangzhou |
| Haogang school | Mixed residential/commercial/industrial | (23.017° N, 113.734° E) | Dongguan |
| Xiapu | Urban: commercial | (23.054° N, 114.41° E) | Huizhou |
| Jinguowan | Residential | (23.074° N, 114.406° E) | Huizhou |
| Liyuan | City | (22.545° N, 114.089° E) | Shenzhen |
| Tamen | Rural | (22.477° N, 114.361° E) | Hong Kong |
| Quanwan | Mixed residential/commercial/industrial | (22.375° N, 114.115° E) | Hong Kong |
| Tangjia | Mixed educational/commercial and residential/commercial | (22.354° N, 113.58° E) | Zhuhai |
| Zimaling Park | Mixed residential/commercial | (22.509° N, 113.406° E) | Zhongshan |
| Wanqinsha | Mixed educational/commercial and residential/industrial | (22.709° N, 113.55° E) | Guangzhou |
| Donghu | City | (22.59° N, 113.087° E) | Jiangmen |
| Jinjuzui | Tourist and cultural/educational | (22.804° N, 113.291° E) | Foshan |
| Huijingcheng | Mixed residential/commercial/industrial | (22.978° N, 113.106° E) | Foshan |
| Chengzhong | Mixed residential/commercial | (23.053° N, 112.476° E) | Zhaoqing |
2.2. Ground-Based Sampling Observations of AOT and PM
| Places | Type | Latitude(° N) | Longitude(° E) | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry | Urban | 23.133 | 113.350 | 28 |
| Guangzhou Luhu park | Borders of urban and suburb | 23.15 | 113.283 | 66 |
| Maofeng Mountain Forestry Park | Suburb | 23.3 | 113.467 | 4 |
| Conghua city | Urban | 23.55 | 113.583 | 60 |
| Liuxihe National Forest Park | Suburb | 23.75 | 113.783 | 104 |
| Zhongshan forest | Suburb | 22.4 | 113.467 | 21 |
| Zhongshan college | Urban | 22.533 | 113.383 | 8 |
| Nansha wetland park | Suburb by the sea | 22.617 | 113.650 | 14 |
2.3. Satellite Data
2.4. Atmospheric Boundary Layer (ABL) Height and Relative Humidity (RH)
3. Analyses on Particulate Concentration in the PRD
3.1. Ground Observations of Particulate Matter
3.2. Station Monitoring Data of Particulate Matters in PRD
| Stations | 1 January | 2 January | 3 January | 4 January | 5 January |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tianhu | 40 | 43 | 54 | 110 | 104 |
| Luhu Park | 31 | 27 | 34 | 39 | 79 |
| Haogang school | 48 | 73 | 152 | 174 | 200 |
| Xiapu | 101 | 122 | 133 | 147 | 186 |
| Jinguowan | 28 | 40 | 53 | 58 | 54 |
| Liyuan | 68 | 95 | 122 | 88 | 120 |
| Tamen | -- | 89 | 92 | 64 | 111 |
| Quanwan | -- | 64 | 91 | 52 | 101 |
| Tangjia | 33 | 34 | 77 | 61 | 79 |
| Zimaling Park | 52 | 67 | 119 | 79 | 233 |
| Wanqinsha | 88 | 125 | 151 | 23 | 232 |
| Donghu | 54 | 73 | 118 | 197 | 336 |
| Jinjuzui | 60 | 62 | 91 | 63 | 190 |
| Huijingcheng | -- | 119 | 197 | 265 | 311 |
| Chengzhong | 62 | 78 | 119 | 157 | 146 |
3.3. Correlation Test between Particulate Concentration and AOT

4. Retrieval of Atmospheric Particulate Concentrations

4.1. Retrieval of the Instantaneous Particulate Distribution








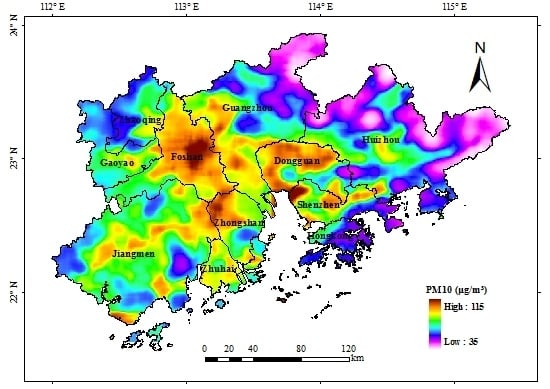
4.2. Retrieval of Yearly Average PM10 Distributions



| Sites | AOT | Measured PM10 (µg/m3) | Predicted PM10 (µg/m3) | Deviation (µg/m3) | Relative Errors (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tianhu | 0.238 | 62 | 54 | −8 | −12.90 |
| Luhu Park | 0.575 | 65 | 77 | 12 | 18.46 |
| Haogang school | 0.701 | 90 | 86 | −4 | −4.44 |
| Xiapu | 0.506 | 91 | 72 | −19 | −20.88 |
| Jinguowan | 0.274 | 45 | 56 | 11 | 24.44 |
| Liyuan | 0.544 | 59 | 75 | 16 | 27.12 |
| Tamen | 0.3 | 57 | 58 | 1 | 1.75 |
| Quanwan | 0.202 | 57 | 51 | −6 | −10.53 |
| Tangjia | 0.35 | 50 | 61 | 11 | 22.00 |
| Zimaling Park | 0.677 | 82 | 84 | 2 | 2.44 |
| Wanqinsha | 0.566 | 93 | 76 | −17 | −18.28 |
| Donghu | 0.68 | 75 | 84 | 9 | 12.00 |
| Jinjuzui | 0.669 | 80 | 84 | 4 | 5.00 |
| Huijingcheng | 0.734 | 103 | 88 | −15 | −14.56 |
| Chengzhong | 0.533 | 66 | 74 | −8 | −12.12 |
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- King, M.D.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Nakajima, T. Remote sensing of tropospheric aerosols from space: Past, present and future. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 80, 2229–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Boucher, O. A satellite view of aerosols in the climate system. Nature 2002, 419, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dockery, D.W.; Pope, C.A.; Xu, X.P.; Spengler, J.D.; Ware, J.H.; Fay, M.E.; Ferris, B.G., Jr.; Speizer, F.E. An association between air pollution and mortality in six U.S. cities. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, J.; Dockery, D.W.; Neas, L.M. Is daily mortality associated specifically with fine particles? J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1996, 46, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A., III. Review: Epidemiological basis for particulate air pollution health standards. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2000, 32, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samet, J.M.; Dominici, F.; Curriero, F.C.; Coursac, I.; Zeger, S.L. Fine particulate air pollution and mortality in 20 U.S. cities, 1987–1994. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1742–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, L. Correlations of personal exposure to particles with outdoor air measurements: A review of recent studies. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2000, 32, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husar, R.B.; Tratt, D.M.; Schichtel, B.A.; Falke, S.R.; Li, F.; Jaffe, D.; Gassó, S.; Gill, T.; Malm, W.C. Asian dust events of April 1998. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 2001, 106, 18317–18330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, K.D. Applications of MODIS satellite data and products for monitoring air quality in the state of Texas. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2403–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Christopher, S.A.; Reid, J.S.; Maring, H.; Savoie, D.; Holben, B.N.; Livingston, J.M.; Russell, P.B.; Yang, S.-K. GOES 8 retrieval of dust aerosol optical thickness over the Atlantic Ocean during PRIDE. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel-Cox, J.A.; Holloman, C.H.; Coutant, B.W.; Hoff, R.M. Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of MODIS satellite sensor data for regional and urban scale air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2495–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel-Cox, J.A.; Young, G.S.; Hoff, R.M. Application of satellite remote-sensing data for source analysis of find particulate matter transport events. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2005, 55, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kacenelenbogen, M.; Léon, J.F.; Chiapello, I.; Tanré, D. Characterisation of aerosol pollution events in France using ground-based and POLDER-2 satellite data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 4843–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaap, M.; Apituley, A.; Timmermans, R.M.A.; Koelemeijer, R.B.A.; de Leeuw, G. Exploring the relation between aerosol optical depth and PM2.5 at Cabauw, The Netherlands. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 909–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malm, W.C.; Sisler, J.F.; Huffman, D.; Eldred, R.A.; Cahill, T.A. Spatial and seasonal trends in particle concentration and optical extinction in the United States. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 1347–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Richards, L.W. Comparability between PM2.5 and particle light scattering measurements. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2002, 79, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Christopher, S.A. Intercomparison between satellite-derived aerosol optical thickness and PM2.5 mass: Implications for air quality studies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Zibordi, G.; Chern, J.D.; Mao, J.T.; Li, C.C.; Holben, B.N. Global monitoring of air pollution over land from the Earth Observing System-Terra Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS). J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel-Cox, J.A.; Hoff, R.M.; Rogers, R.; Dimmick, F.; Rush, A.C.; Szykman, J.J.; Al-Saadi, J.; Chu, D.A.; Zell, E.R. Integrating lidar and satellite optical depth with ambient monitoring for 3-D dimensional particulate characterisation. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 8056–8067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Christopher, S.A.; Wang, J.; Gehrig, R.; Lee, Y.C.; Kumar, N. Satellite remote sensing of particulate matter and air quality assessment over global cities. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5880–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.C.; Lau, A.K.-H.; Mao, J.T.; Chu, D.A. Retrieval, validation and application of the 1-km aerosol optical depth from MODIS measurement over Hong Kong. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2650–2658. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.Y.; Che, W.W.; Zheng, Z.Y.; Chen, L.F.; Zhong, L.J. Analysis of spatial and temporal varialility of PM10 concentrations using MODIS aerosol optical thickness in the Pearl River Delta region, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 862–876. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.P.; Zhang, X.Y.; Che, H.Z.; Gong, S.L.; An, X.; Cao, C.X.; Li, X.W. Correlation between PM concentrations and aerosol optical depth in eastern China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5876–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.F.; Chen, L.F.; Tao, J.H.; Zhang, Y.; Su, L. Satellite-based estimation of regional particulate matter (PM) in Beijing using vertical-and-RH correcting method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.; Zang, Z.; Pan, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D. Estimating PM2. 5 in Xi’an, China using aerosol optical depth: A comparison between the MODIS and MISR retrieval models. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 1156–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.S.; Xu, J.H.; Zhang, S.Q. Valuing the health risks of particulate air pollution in the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Policy 2012, 15, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Deng, X.J.; Bi, X.Y.; Li, F.; Tan, H.B.; Liao, G.L. Study on the visibility reduction caused by atmospheric haze in Guangzhou area. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2007, 23, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.J.; Tie, X.X.; Wu, D.; Zhou, X.J.; Bi, X.Y.; Tan, H.B.; Li, F.; Jiang, C.L. Long-term trend of visibility and its characterizations in the Pearl River Delta (PRD) region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, D.; Huang, M.H.; Li, F.; Bi, X.Y.; Tan, H.B.; Deng, X.J. Visibility variations in the Pearl River Delta of China during the Period of 1954–2004. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2008, 19, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, P.; Liu, X.Y.; Liu, Z.R.; Li, T.T.; Zhong, L.J.; Xiang, Y.R. Human health impact of exposure to airborne particulate matter in Pearl River Delta, China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 215, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.G.; Chow, J.C.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.L.; Merrifield, T.M.; Fine, P.M.; Barker, K. Measurement system evaluation for upwind/downwind sampling of fugitive dust emissions. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2011, 11, 331–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (CFSR) 6-hourly Products, January 1979 to December 2010. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.5065/D69K487J (accessed on 5 January 2008).
- Saha, S.; Suranjana, M.; Pan, H.L.; Wu, X.G.; Wang, J.D.; Sudhir, N.; Patrick, T.; Glenn, R.; Mitch, G. The NCEP Climate Forecast System Reanalysis. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 1015–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Bi, X.Y.; Deng, X.J.; Li, F.; Tan, H.B.; Liao, G.L.; Huang, J. Effect of atmospheric haze on the deterioration of visibility over the Pearl River Delta. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2006, 64, 510–517. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Lau, A.K.-H.; Leung, Y.K. Hazy weather formation and visibility deterioration resulted from fine particulate (PM2.5) pollutions in Guangdong and Hong Kong. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2012, 32, 2660–2669. [Google Scholar]
- Kotchenruther, R.B.A.; Hobbs, P.V.; Hegg, D.A. Humidification factors for atmospheric aerosols off the mid-Atlantic coast of the United States. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 1999, 104, 2239–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.C.; Mao, J.T.; Liu, Q.H.; Yuan, Z.B.; Wang, M.H.; Liu, X.Y. Application of MODIS aerosol product in the study of air pollution in Beijing. Sci. China Series D Earth Sci. 2005, 35, 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.L.; Yang, J.X.; Wang, Y.P. An improved dark object method to retrieve 500 m-resolution AOT (Aerosol Optical Thickness) image from MODIS data: A case study in the Pearl River Delta area, China. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 89, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Vermote, E.F.; Kaufman, Y.J. Second-generation operational algorithm: Retrieval of aerosol properties over land from inversion of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer spectral reflectance. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Remer, L.A.; Vermote, E.F.; Chu, A.; Holben, B.N. Operational remote sensing of tropospheric aerosol over land from EOS moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 1997, 102, 17051–17067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Wald, A.E.; Remer, L.A.; Gao, B.C.; Li, R.R.; Flynn, L. The MODIS 2.1-μm channel-correlation with visible reflectance for use in remote sensing of aerosol. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelemeijer, R.B.; Homan, C.D.; Matthijsen, J. Comparison of spatial and temporal variations of aerosol optical thickness and particulate matter over Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5304–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sarnat, J.A.; Kilaru, V.; Jacob, D.J.; Koutrakis, P. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 in the eastern United States using satellite remote sensing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3269–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.G.; Cheng, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.H.; Jung, J.S.; Sugimoto, N.; Chang, S.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Fan, S.J.; Zeng, L.M. Influences of relative humidity and particle chemical composition on aerosol scattering properties during the 2006 PRD. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1525–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.S.; Saxena, V.K.; Wenny, B.N. An assessment of hygroscopic growth factors for aerosols in the surface boundary layer for computing direct radiative forcing. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 2001, 106, 20213–20224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Wang, Y.P. What drives the aerosol distribution in Guangdong-the most developed province in Southern China? Sci. Rep. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, B.N.; Prados, A.I.; Lamsal, L.N.; Liu, Y.; Streets, D.G.; Gupta, P.; Hilsenrath, E.; Ziemba, L.D. Satellite data of atmospheric pollution for US air quality applications: Examples of applications, summary of data end-user resources, answers to FAQs, and common mistakes to avoid. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergin, M.H.; Schwartz, S.E.; Halthore, R.N.; Ogren, J.A.; Hlavka, D.L. Comparison of aerosol optical depth inferred from surface measurements with that determined by Sun photometry for cloud-free conditions at a continental U.S. site. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 6807–6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y. Retrieval of High-Resolution Atmospheric Particulate Matter Concentrations from Satellite-Based Aerosol Optical Thickness over the Pearl River Delta Area, China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7914-7937. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70607914
Li L, Yang J, Wang Y. Retrieval of High-Resolution Atmospheric Particulate Matter Concentrations from Satellite-Based Aerosol Optical Thickness over the Pearl River Delta Area, China. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(6):7914-7937. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70607914
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Lili, Jingxue Yang, and Yunpeng Wang. 2015. "Retrieval of High-Resolution Atmospheric Particulate Matter Concentrations from Satellite-Based Aerosol Optical Thickness over the Pearl River Delta Area, China" Remote Sensing 7, no. 6: 7914-7937. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70607914
APA StyleLi, L., Yang, J., & Wang, Y. (2015). Retrieval of High-Resolution Atmospheric Particulate Matter Concentrations from Satellite-Based Aerosol Optical Thickness over the Pearl River Delta Area, China. Remote Sensing, 7(6), 7914-7937. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70607914