Joint Sparse Sub-Pixel Mapping Model with Endmember Variability for Remotely Sensed Imagery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
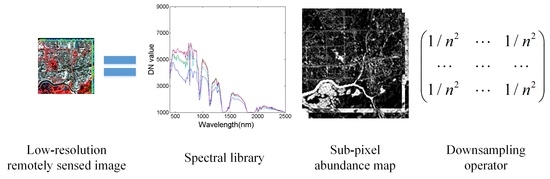
2. Sub-Pixel Mapping Problem
3. The Proposed Joint Sparse Subpixel Mapping Model
3.1. Basic JSSM Model
3.2. Spatial Prior Constraint
3.3. Optimization
4. Experiments and Analysis
4.1. Synthetic Experiments
4.1.1. Synthetic Image 1: HJ-1A
4.1.2. Synthetic Image 2: Flightline C1 (FLC1)
4.1.3. Synthetic Image 3: AVIRIS Indian Pines
4.2. Real Experiment-Nuance Dataset
4.3. Discussion
4.3.1. The Impact of the Penalty Parameter
4.3.2. The Impact of the Regularization Parameter and
4.3.3. The Impact of Different Scale Factors
5. Conclusions and Future Lines
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A.; Camps-Valls, G.; Scheunders, P.; Nasrabadi, N.M.; Chanussot, J. Hyperspectral remote sensing data analysis and future challenges. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A.; Dobigeon, N.; Parente, M.; Du, Q.; Gader, P.; Chanussot, J. Hyperspectral unmixing overview: Geometrical, statistical, and sparse regression-based approaches. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2012, 5, 354–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, P.M. Mapping sub-pixel boundaries from remotely sensed images. In Innovations in GIS IV; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 1997; Volume 12, pp. 166–180. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, P.M. Issues of uncertainty in super-resolution mapping and their implications for the design of an inter-comparison study. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 5293–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, W.R. A computer movie simulating urban growth in the Detroit region. Econom. Geogr. 1970, 46, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, P.M. Sub-pixel target mapping from soft-classified, remotely sensed imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2005, 71, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.F.; Foody, G.M.; Muad, A.M.; Cheng, K.S. Combining pixel swapping and contouring methods to enhance super-resolution mapping. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 1428–1437. [Google Scholar]
- Tatem, A.J.; Lewis, H.G.; Atkinson, P.M.; Nixon, M.S. Super-resolution target identification from remotely sensed images using a Hopfield neural network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 781–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ling, F.; Du, Y.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, Y. A spatial–temporal Hopfield neural network approach for super-resolution land cover mapping with multi-temporal different resolution remotely sensed images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 93, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, K.C.; Baets, B.D.; Verbeke, L.P.C.; Wulf, R.R.D. A sub-pixel mapping algorithm based on sub-pixel/pixel spatial attraction models. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3293–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Zhang, X.; Shan, J.; Xie, H.; Liu, M. Attraction-repulsion model-based subpixel mapping of multi-/hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 2799–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L. A sub-pixel mapping method based on an attraction model for multiple shifted remotely sensed images. Neurocomputing 2014, 134, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, K.C.; Verbeke, L.P.C.; Ducheyne, E.I.; Wulf, R.R.D. Using genetic algorithms in sub-pixel mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 4241–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Xu, T.; Liu, R.; Shi, K.; Huang, C. Super-resolution mapping of wetland inundation from remote sensing imagery based on integration of back-propagation neural network and genetic algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 164, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L. Adaptive sub-pixel mapping based on a multi-agent system for remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 787–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H. Sub-pixel mapping based on a MAP model with multiple shifted hyperspectral imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X. Adaptive MAP sub-pixel mapping model based on regularization curve for multiple shifted hyperspectral imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 96, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L. An adaptive subpixel mapping method based on MAP model and class determination strategy for hyperspectral remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1411–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L. Remote sensing image sub-pixel mapping based on adaptive differential evolution. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B Cybern. 2012, 42, 1306–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Shi, W. Utilizing multiple subpixel shifted images in subpixel mapping with image interpolation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 11, 798–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shi, W.; Atkinson, P.M. Sub-pixel mapping of remote sensing images based on radial basis function interpolation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 92, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y. Vectorial boundary-based sub-pixel mapping method for remote-sensing imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 35, 1756–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Li, S.; Lakhan, V.C. Development and testing of a subpixel mapping algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2155–2164. [Google Scholar]
- Kasetkasem, T.; Arora, M.; Varshney, P. Super-resolution land cover mapping using a Markov random field based approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, F.; Fang, S.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Y. Post-processing of interpolation-based super-resolution mapping with morphological filtering and fraction refilling. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 5251–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ling, F.; Du, Y. Super-resolution mapping based on the supervised fuzzy c-means approach. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 3, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, F.; Du, Y.; Xiao, F.; Li, X. Subpixel land cover mapping by integrating spectral and spatial information of remotely sensed imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Du, Y.; Ling, F.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Spectral–spatial based sub-pixel mapping of remotely sensed imagery with multi-scale spatial dependence. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 2831–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ge, Y.; Jia, Y. Integrating object boundary in super-resolution land-cover mapping. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Xu, X.; Plaza, A.; Xie, H.; Pan, H.; Cao, W.; Lv, D. A new genetic method for subpixel mapping using hyperspectral images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 4480–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, F.; Du, Y.; Xiao, F.; Xue, H.; Wu, S. Super-resolution land-cover mapping using multiple sub-pixel shifted remotely sensed images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 5023–5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, F.; Li, X.; Xiao, F.; Fang, S.; Du, Y. Object-based sub-pixel mapping of buildings incorporating the prior shape information from remotely sensed imagery. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2010, 18, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y. Spatial continuity and self-similarity in super-resolution mapping: Self-similar pixel swapping. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 7, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, B.; Asner, G.; Tits, L.; Coppin, P. Endmember variability in spectral mixture analysis: A review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, A.; Ho, K.C. Endmember variability in hyperspectral analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2014, 31, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.; Gardner, M.; Church, R.; Ustin, S.; Scheer, G.; Green, R.O. Mapping chaparral in the Santa Monica mountains using multiple endmember spectral mixture models. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 65, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateson, C.A.; Asner, G.P.; Wessman, C.A. Endmember bundles: A new approach to incorporating endmember variability into spectral mixture analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrodad, A.; Xing, Z.; Greer, J.; Bosch, E.; Carin, L.; Sapiro, G. Learning discriminative sparse representations for modeling, source separation, and mapping of hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4263–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, A.; Gader, P.; Dranishnikov, D.; Glenn, T. Spectral unmixing using the beta compositional model. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing, Gainesville, FL, USA, 25–28 June 2013.
- Nascimento, J.M.P.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M. Vertex component analysis: A fast algorithm to unmix hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, M. N-FINDR: An algorithm for fast autonomous spectral endmember determination in hyperspectral data. Proc. SPIE 1999, 3753, 266–277. [Google Scholar]
- Iordache, D.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A. Sparse unmixing of hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2014–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordache, D.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A. Total variation spatial regularization for sparse hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 4484–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candès, E.; Tao, T. Decoding by linear programming. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2005, 51, 4203–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candès, E.; Tao, T. Near-optimal signal recovery from random projections: Universal encoding strategies. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 5406–5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dópido, I.; Zortea, M.; Villa, A.; Plaza, A.; Gamba, P. Unmixing prior to supervised classification of remotely sensed hyperspectral images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dópido, I.; Villa, A.; Plaza, A.; Gamba, P. A quantitative and comparative assessment of unmixing-based feature extraction techniques for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.; Shen, H.; Lam, E.; Zhang, L. A total variation regularization based super resolution reconstruction algorithm for digital video. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2007, 2007, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, J.; Bertsekas, D. On the Douglas-Rachford splitting method and the proximal point algorithm for maximal monotone operators. Math. Program. Ser. A/B 1992, 55, 293–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, D.C.; Chang, C.I. Fully constrained least square linear spectral unmixing analysis method for material quantification in hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNemar, Q. Note on the sampling error of the difference between correlated proportions or percentages. Psychometrika 1947, 12, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debeir, O.; Van den Steen, I.; Latinne, P.; Van Ham, P.; Wolff, E. Textural and contextual land-cover classification using single and multiple classifier systems. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2002, 68, 597–606. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L. An adaptive artificial immune network for supervised classification of multi-/hyperspectral remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 894–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpaydin, E. Introduction to Machine Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, G. China environmental and disaster monitoring and forecasting small satellite—HJ-1A/B. Aerosp. China 2009, 5, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffer, R.M. Computer-aided analysis of multispectral scanner data-the beginnings. In Proceedings of the ASPRS 2009 Annual Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 9–13 March 2009.









| Accuracy Indexes | Methods | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCLS | SUnSAL-TV | MRF | JSSM | ||||||
| AM | HC | HNN | AM | HC | HNN | ||||
| IA (%) | Urban area | 60.14 | 64.66 | 67.61 | 61.33 | 73.05 | 73.75 | 77.14 | 75.36 |
| Agricultural land | 86.90 | 93.45 | 95.84 | 79.81 | 89.79 | 93.72 | 93.80 | 94.49 | |
| Water | 71.89 | 61.35 | 75.30 | 66.51 | 65.92 | 71.08 | 72.05 | 73.20 | |
| Vegetation | 51.49 | 56.67 | 50.26 | 55.86 | 61.26 | 57.54 | 56.43 | 60.03 | |
| AA (%) | 67.61 | 69.03 | 72.25 | 65.88 | 72.51 | 74.02 | 74.86 | 75.77 | |
| OA (%) | 64.23 | 65.82 | 69.42 | 63.60 | 71.30 | 72.55 | 74.22 | 74.33 | |
| Kappa | 0.504 | 0.523 | 0.571 | 0.493 | 0.589 | 0.607 | 0.628 | 0.632 | |
| RMSE | 0.192 | 0.180 | Null | ||||||
| McNemar’s Test | 901.3 | 1068.4 | 336.2 | 962.7 | 236.4 | 55.65 | 0.187 | Null | |
| Accuracy Indexes | Methods | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCLS | SUnSAL-TV | MRF | JSSM | ||||||
| AM | HC | HNN | AM | HC | HNN | ||||
| IA (%) | Red Cover | 76.53 | 86.01 | 88.49 | 81.55 | 94.63 | 93.97 | 95.39 | 96.81 |
| Oats | 58.95 | 74.70 | 80.73 | 55.07 | 94.23 | 79.58 | 85.83 | 94.70 | |
| Wheat | 93.80 | 94.94 | 96.16 | 94.20 | 99.35 | 98.20 | 98.20 | 99.67 | |
| Soybeans | 78.63 | 92.14 | 92.53 | 77.09 | 91.48 | 93.46 | 93.68 | 96.65 | |
| Hay | 41.74 | 55.51 | 56.89 | 43.89 | 86.91 | 73.32 | 65.24 | 88.84 | |
| Pasture | 62.42 | 75.88 | 78.79 | 62.52 | 77.43 | 76.95 | 80.58 | 85.71 | |
| Alfalfa | 65.54 | 78.24 | 75.93 | 65.54 | 79.66 | 74.78 | 83.30 | 82.42 | |
| Corn | 87.60 | 97.24 | 94.49 | 94.88 | 97.24 | 95.28 | 98.62 | 98.23 | |
| AA (%) | 70.65 | 81.83 | 83.00 | 71.84 | 90.12 | 85.69 | 87.61 | 92.88 | |
| OA (%) | 67.14 | 78.99 | 80.84 | 67.83 | 89.27 | 84.27 | 85.54 | 92.39 | |
| Kappa | 0.623 | 0.757 | 0.779 | 0.631 | 0.876 | 0.818 | 0.833 | 0.912 | |
| RMSE | 0.142 | 0.134 | Null | ||||||
| McNemar’s Test | 2893.4 | 1463.8 | 1193.1 | 2742.5 | 216.7 | 736.4 | 513.3 | Null | |
| Accuracy Indexes | Methods | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCLS | SUnSAL-TV | MRF | JSSM | |||||||
| AM | HC | HNN | AM | HC | HNN | |||||
| IA (%) | Corn-notill | 44.00 | 48.73 | 49.92 | 65.46 | 79.98 | 83.70 | 53.72 | 89.86 | |
| Corn-min | 12.52 | 15.38 | 5.43 | 55.05 | 66.97 | 66.82 | 6.18 | 79.03 | ||
| Grass/Pasture | 6.79 | 4.96 | 2.61 | 86.42 | 92.69 | 89.56 | 2.61 | 95.04 | ||
| Grass/Trees | 52.87 | 53.22 | 73.91 | 82.09 | 92.00 | 98.96 | 85.91 | 96.00 | ||
| Hay-windrowed | 92.70 | 99.16 | 100 | 94.38 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| Soybeans-notill | 61.86 | 66.27 | 64.80 | 56.55 | 83.36 | 84.68 | 66.57 | 80.71 | ||
| Soybeans-min | 25.58 | 33.02 | 35.60 | 49.89 | 70.70 | 75.19 | 39.70 | 67.85 | ||
| Soybeans-clean | 39.56 | 46.44 | 41.28 | 64.13 | 87.47 | 92.38 | 46.68 | 98.28 | ||
| woods | 94.78 | 100 | 99.90 | 86.07 | 100 | 100 | 99.81 | 100 | ||
| Bldg | 48.68 | 56.23 | 61.89 | 52.08 | 61.13 | 63.77 | 73.58 | 63.40 | ||
| AA (%) | 47.93 | 52.34 | 53.53 | 69.21 | 83.43 | 85.51 | 57.48 | 87.02 | ||
| OA (%) | 46.41 | 51.30 | 52.54 | 65.97 | 81.93 | 84.50 | 56.04 | 84.77 | ||
| Kappa | 0.391 | 0.443 | 0.457 | 0.611 | 0.792 | 0.821 | 0.496 | 0.825 | ||
| RMSE | 0.213 | 0.127 | Null | |||||||
| McNemar’s Test | 2486.6 | 2180.2 | 2026.1 | 965.9 | 77.9 | 0.52 | 1727.7 | Null | ||
| Accuracy Indexes | Methods | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCLS | SUnSAL-TV | MRF | JSSM | ||||||
| AM | HC | HNN | AM | HC | HNN | ||||
| IA (%) | Soil | 72.50 | 67.77 | 84.96 | 69.20 | 84.19 | 84.69 | 85.36 | 79.62 |
| Fresh vegetation | 87.94 | 96.97 | 94.58 | 83.58 | 95.65 | 95.31 | 94.94 | 96.61 | |
| Withered vegetation | 70.03 | 78.52 | 77.73 | 72.84 | 80.28 | 79.33 | 80.66 | 86.01 | |
| Paper | 78.23 | 86.31 | 84.03 | 75.08 | 86.03 | 86.33 | 85.60 | 87.73 | |
| AA (%) | 77.18 | 82.39 | 85.33 | 75.18 | 86.54 | 86.42 | 86.64 | 87.49 | |
| OA (%) | 77.79 | 82.53 | 86.20 | 75.52 | 87.23 | 87.12 | 87.36 | 87.75 | |
| Kappa | 0.699 | 0.764 | 0.812 | 0.669 | 0.827 | 0.825 | 0.828 | 0.834 | |
| RMSE | 0.190 | 0.160 | Null | ||||||
| McNemar’s Test | 1508.9 | 808.7 | 84.4 | 1927.5 | 17.3 | 17.2 | 5.85 | Null | |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Tong, X.; Plaza, A.; Zhong, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhang, L. Joint Sparse Sub-Pixel Mapping Model with Endmember Variability for Remotely Sensed Imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9010015
Xu X, Tong X, Plaza A, Zhong Y, Xie H, Zhang L. Joint Sparse Sub-Pixel Mapping Model with Endmember Variability for Remotely Sensed Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xiong, Xiaohua Tong, Antonio Plaza, Yanfei Zhong, Huan Xie, and Liangpei Zhang. 2017. "Joint Sparse Sub-Pixel Mapping Model with Endmember Variability for Remotely Sensed Imagery" Remote Sensing 9, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9010015
APA StyleXu, X., Tong, X., Plaza, A., Zhong, Y., Xie, H., & Zhang, L. (2017). Joint Sparse Sub-Pixel Mapping Model with Endmember Variability for Remotely Sensed Imagery. Remote Sensing, 9(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9010015