Monitoring Urban Clusters Expansion in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River, China, Using Time-Series Nighttime Light Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
2.2. DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data and Preprocessing
2.3. Auxiliary Data Sets
3. Methodology
3.1. Extraction of Urban Extents
3.2. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Urban Expansion
3.2.1. Urban Expansion Intensity
3.2.2. Expansion Direction
3.2.3. Landscape Metrics
3.3. Relationship between NTL Intensity and Urbanization Variables
4. Results
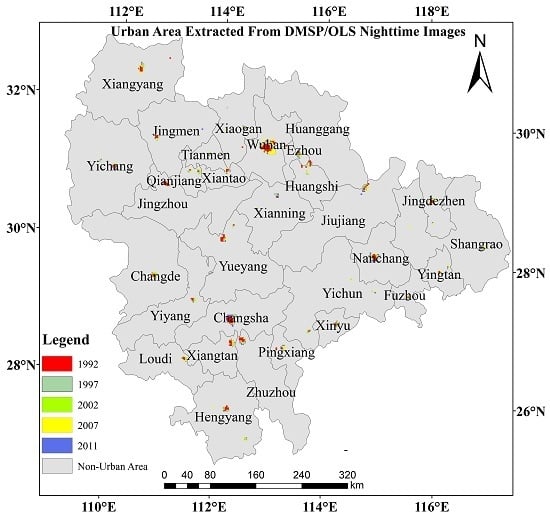
4.1. Urban Spatial Sprawl and Accuracy Assessment
4.2. Spatiotemporal Variations in Urban Expansion
4.2.1. Dynamic of Urban Expansion Intensity
4.2.2. Urban Expansion Direction
4.2.3. Urban Expansion Form
4.3. Relationship between Nighttime Light Brightness and Urbanization
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Imhoff, M.L.; Bounoua, L.; DeFries, R.; Lawrence, W.T.; Stutzer, D.; Tucker, C.J.; Ricketts, T. The consequences of urban land transformation on net primary productivity in the United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, B. Urbanization in developing countries: Current trends, future projections, and key challenges for sustainability. Technol. Soc. 2006, 28, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, M. The urban transformation of the developing world. Science 2008, 319, 761–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantakonstantis, D.; Mountrakis, G. Urban Growth Prediction: A Review of Computational Models and Human Perceptions. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2012, 4, 555–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Urban-rural Linkages and Spatial-temporal Land Use Change in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Metropolitan Region: A New Perspective. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 4, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Fang, C.; Lin, G.; Gong, H.; Qiao, B. Tempo-Spatial Patterns of Land Use Changes and Urban Development in Globalizing China: A Study of Beijing. Sensors 2007, 7, 2881–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milesi, C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Nemani, R.R.; Running, S.W. Assessing the impact of urban land development on net primary productivity in the southeastern United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, M. The effects of urban patterns on ecosystem function. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2005, 28, 168–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Weng, Q. World energy consumption pattern as revealed by DMSP-OLS nighttime light imagery. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L. China’s urban economic regions in the open context. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2003, 58, 271–284. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, T.; Anderson, S.; Powell, P.L.; Sutton, P.C.; Eividge, C.D. Estimation of Mexico’s Informal Economy and Remittances Using Nighttime Imagery. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 418–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Kuang, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; Yu, D.; Wu, S. Spatial patterns and driving forces of land use change in China during the early 21st century. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, B. Mapping and evaluation the process, pattern and potential of urban growth in China. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 71, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. A remote sensing? GIS evaluation of urban expansion and its impact on surface temperature in the Zhujiang Delta, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 1999–2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, W.; Ma, J.; Twibell, R.W.; Underhill, K. Characterizing urban sprawl using multi-stage remote sensing images and landscape metrics. Comput. Environ. Urban. Syst. 2006, 30, 861–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jat, M.K.; Garg, P.K.; Khare, D. Monitoring and modeling of urban sprawl using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2008, 10, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Remote sensing of impervious surfaces in the urban areas: Requirements, methods, and trends. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y. Regional differences of China’s urban expansion from late 20th to early 21st century based on remote sensing information. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubenböck, H.; Wegmann, M.; Roth, A.; Mehl, H.; Dech, S. Urbanization in India—Spatiotemporal analysis using remote sensing data. Comput. Environ. Urban. Syst. 2009, 33, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.M.; Loveland, R.T. A review of large area monitoring of land cover change using Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Weng, Q. Impervious surface area extraction from IKONOS imagery using an object-based fuzzy method. Geocarto Int. 2011, 26, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Imhoff, M.L.; Baugh, K.E.; Hobson, V.R.; Nelson, I.; Safran, J.; Dietz, J.B.; Tuttle, B.T. Night-time lights of the world: 1994–1995. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2001, 56, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, P.C. A scale-adjusted measure of “urban sprawl” using nighttime satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, S.; Camara, G.; Miguel, A.; Monteiro, V.; Quintanilha, J.A.; Elvidge, C.D. Estimating population and energy consumption in Brazilian Amazonia using DMSP night-time satellite data. Comput. Environ. Urban. Syst. 2005, 29, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keola, S.; Andersson, M.; Hall, O. Monitoring economic development from space: Using nighttime light and land cover data to measure economic growth. World Dev. 2015, 66, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, M.; Yeh, E.T.; Gong, P.; Elvidge, C.; Baugh, K. Validation of urban boundaries derived from global night-time satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Shi, P.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhuo, L.; Ichinose, T. Restoring urbanization process in China in the 1990s by using non-radiance-calibrated DMSP/OLS nighttime light imagery and statistical data. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 1614–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Smith, S.J.; Zhao, K.; Imhoff, M.; Thomson, A.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Asrar, G.R.; Zhang, X.; He, C.; Elvidge, C.D. A global map of urban extent from nightlights. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 054011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Yang, Y.; Yue, X.; Zhao, X. Mapping urban areas with integration of DMSP/OLS nighttime light and MODIS data using machine learning techniques. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12419–12439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tang, L. Measuring urban sprawl in China by night time light images. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 52, 012111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Seto, K.C. Mapping urbanization dynamics at regional and global scales using multi-temporal DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2320–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y. Extracting the dynamics of urban expansion in China using DMSP-OLS nighttime light data from 1992 to 2008. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 106, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, C.H.; Pei, T.; Haynie, S.; Fan, J.F. Quantitative estimation of urbanization dynamics using time series of DMSP/OLS nighttime light data: A comparative case study from China’s cities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.W.; Su, S.L. Determinants of urban expansion and their relative importance: A comparative analysis of 30 major metropolitans in China. Habitat Int. 2016, 58, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Weng, Q. Detecting urban-scale dynamics of electricity consumption at Chinese cities using time-series DMSP-OLS (Defense Meteorological Satellite Program-Operational Linescan System) nighttime light imageries. Energy 2016, 100, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, T. Comparative estimation of urban development in China’s cities using socioeconomic and DMSP/OLS night light data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7840–7856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Huang, Q.; He, C.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, D. How does sprawl differ across cities in China? A multi-scale investigation using nighttime light and census data. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 148, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Liu, C. The integrated use of DMSP-OLS nighttime light and MODIS data for monitoring large-scale impervious surface dynamics: A case study in the Yangtze River Delta. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9359–9378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Min, X. Quantifying spatiotemporal patterns of urban expansion in China using remote sensing data. Cities 2013, 35, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.G.; Jiao, W.L.; Long, T.F.; Liu, H.C.; Yi, Y.Q.; Wu, M.M.; Wang, W.; He, G.J. Analysis of spatial and temporal characteristics of urban expansion about Wuhan city in the year of 2000–2014. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2016, 25, 1034–1042. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xin, X.; Liu, B.; Di, K.C.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Liu, J.; Yue, Z.Y.; Guo, Z. Monitoring urban expansion using time series of night-time light data: A case study in Wuhan, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.X.; Lin, J.; Bao, G.S.; Chen, B.S. A study of Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan urban extension based on remote sensing. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2005, 17, 74–77. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, L.J.; Zhang, Z.X.; Tan, W.B.; Wang, C.Y. Analysis on the Urban Land Use Sprawl and Its Driving Forces by Using Remote Sensing and GIS: The Case of Nanchang City, China. Geo-Inform. Sci. 2007, 9, 116–122. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Run, J.; Zhuo, R.; Wang, X. Evolution process of urban spatial pattern in Hubei Province based on DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.N.; He, L.L.; Jin, W.P.; Wu, K.J.; Xu, Y.Y.; Yu, F.F. Quantitative Analysis of the Urban Expansion Models in Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan Metroplan Areas. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2012, 32, 544–549. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Chen, J.; Imura, H.; Higashi, O. A SVM-based method to extract urban areas from DMSP-OLS and SPOT VGT data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2205–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Cai, C. Regional urban extent extraction using multi-sensor data and one-class classification. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7671–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, C.; Yue, H. Urban Land Extraction Using VIIRS Nighttime Light Data: An Evaluation of Three Popular Methods. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Smith, S.J.; Elvidge, C.D.; Zhao, K.; Thomson, A.; Imhoff, M. A cluster-based method to map urban area from DMSP/OLS nightlights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Weng, Q. Updating urban extents with nighttime light imagery by using an object-based thresholding method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Liao, J.; Ye, Y.; Wang, C. A new method for extracting built-up urban areas using DMSP-OLS nighttime stable lights: A case study in the Pearl River Delta, southern China. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2015, 52, 218–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Liao, J.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, N.; Kuang, Y. China’s 19-year city-level carbon emissions of energy consumptions, driving forces and regionalized mitigation guidelines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 35, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 1992–2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.; Weifeng, Q.; Song, J. Researches on Comprehensive Measurement of Compactness of Urban Agglomerations in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2008, 63, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Triantakonstantis, D.; Stathakis, D. Examining urban sprawl in Europe using spatial metrics. Geocarto Int. 2015, 30, 1092–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, M.; Longley, P.A. The morphology of urban land use. Environ. Plan. B 1988, 15, 461–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Huang, Q.; He, C.; Ma, Q. Dynamics of urbanization levels in China from 1992 to 2012: Perspective from DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1721–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, Y. Characterizing spatio-temporal dynamics of urbanization in China using time series of DMSP/OLS night light data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7708–7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantakonstantis, D.; Stathakis, D. Cokriging areal interpolation for estimating economic activity using night-time light satellite data. In Computational Science and Its Applications—Iccsa 2014; Murgante, B., Misra, S., Rocha, A., Torre, C., Rocha, J.G., Falcao, M.I., Taniar, D., Apduhan, B.O., Gervasi, O., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; Volume 8582, pp. 243–252. [Google Scholar]
- York, R.; Rosa, E.A.; Dietz, T. STIRPAT, IPAT and ImPACT: Analytic tools for unpacking the driving forces of environmental impacts. Ecol. Econ. 2003, 46, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, R.; Rosa, E.A.; Dietz, T. A rift in modernity? Assessing the anthropogenic sources of global climate change with the STIRPAT model. Int. J. Sociol. Soc. Policy 2003, 23, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Wang, Z. Influencing factors of carbon emissions from energy consumptions in Chongqing based on STIRPAT model. Acta Sci. Circum. 2013, 33, 602–608. [Google Scholar]














| Year | Satellite | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F10 | F12 | F14 | F15 | F16 | F18 | |
| 1992 | F101992 | |||||
| 1993 | F101993 | |||||
| 1994 | F101994 | F121994 | ||||
| 1995 | F121995 | |||||
| 1996 | F121996 | |||||
| 1997 | F121997 | F141997 | ||||
| 1998 | F121998 | F141998 | ||||
| 1999 | F121999 | F141999 | ||||
| 2000 | F142000 | F152000 | ||||
| 2001 | F142001 | F152001 | ||||
| 2002 | F142002 | F152002 | ||||
| 2003 | F142003 | F152003 | ||||
| 2004 | F152004 | F162004 | ||||
| 2005 | F152005 | F162005 | ||||
| 2006 | F152006 | F162006 | ||||
| 2007 | F152007 | F162007 | ||||
| 2008 | F162008 | |||||
| 2009 | F162009 | |||||
| 2010 | F182010 | |||||
| 2011 | F182011 | |||||
| Units | Total Pixels | Number of Urban Pixels | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1992 | 1997 | 2002 | 2007 | 2011 | ||
| Wuhan | 11,404 | 194 | 205 | 214 | 428 | 502 |
| Changsha | 8495 | 104 | 112 | 131 | 157 | 274 |
| Nanchang | 7408 | 65 | 88 | 89 | 111 | 210 |
| Wuhan metropolitan area | 58,202 | 353 | 381 | 463 | 697 | 771 |
| Chang-Zhu-Tan urban agglomeration | 27,880 | 202 | 211 | 247 | 308 | 431 |
| Poyang Lake city group | 50,044 | 223 | 288 | 316 | 470 | 588 |
| All cities | 308,679 | 1084 | 1244 | 1535 | 2105 | 2645 |
| City | Fractal Dimension | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1992 | 1997 | 2002 | 2007 | 2011 | |
| Zhuzhou | 1.129 | 1.139 | 1.141 | 1.091 | 1.101 |
| Changsha | 1.128 | 1.125 | 1.110 | 1.125 | 1.117 |
| Yueyang | 1.333 | 1.196 | 1.191 | 1.125 | 1.139 |
| Yingtan | 1.262 | 1.204 | 1.161 | 1.158 | 1.181 |
| Yiyang | 1.136 | 1.163 | 1.116 | 1.131 | 1.131 |
| Yichun | 1.235 | 1.262 | 1.262 | 1.128 | 1.226 |
| Yichang | 1.113 | 1.215 | 1.186 | 1.083 | 1.241 |
| Xinyu | 1.265 | 1.196 | 1.123 | 1.112 | 1.109 |
| Xiaogan | 1.180 | 1.226 | 1.139 | 1.136 | 1.133 |
| Xiangyang | 1.152 | 1.152 | 1.220 | 1.151 | 1.140 |
| Xiangtan | 1.221 | 1.205 | 1.106 | 1.125 | 1.101 |
| Xianling | 1.365 | 1.088 | 1.116 | 1.178 | 1.083 |
| Xiantao | 1.443 | 1.265 | 1.238 | 1.183 | 1.179 |
| Wuhan | 1.135 | 1.217 | 1.196 | 1.179 | 1.139 |
| Tianmen | 1.179 | 1.140 | 1.271 | 1.144 | 1.131 |
| Shangrao | 1.111 | 1.322 | 1.136 | 1.168 | 1.135 |
| Qianjiang | 1.306 | 1.140 | 1.120 | 1.197 | 1.177 |
| Pingxiang | 1.156 | 1.085 | 1.235 | 1.089 | 1.116 |
| Nanchang | 1.116 | 1.099 | 1.094 | 1.125 | 1.112 |
| Loudi | 1.177 | 1.149 | 1.127 | 1.118 | 1.118 |
| Jiujiang | 1.345 | 1.253 | 1.234 | 1.237 | 1.216 |
| Jingdezheng | 1.156 | 1.125 | 1.100 | 1.262 | 1.204 |
| Jingzhuo | 1.248 | 1.253 | 1.168 | 1.176 | 1.153 |
| Jingmen | 1.236 | 1.190 | 1.129 | 1.135 | 1.170 |
| Huangshi | 1.239 | 1.211 | 1.116 | 1.132 | 1.254 |
| Wugang | 1.283 | 1.283 | 1.104 | 1.111 | 1.168 |
| Hengyang | 1.191 | 1.124 | 1.203 | 1.107 | 1.102 |
| Fuzhou | 1.156 | 1.322 | 1.133 | 1.100 | 1.089 |
| Ezhou | 1.250 | 1.214 | 1.323 | 1.214 | 1.262 |
| Changde | 1.100 | 1.153 | 1.109 | 1.053 | 1.046 |
| Cites | L | D | P | I | E | U | S | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wuhan | L | 0.864 | 0.852 | 0.787 | 0.785 | 0.832 | 0.836 | |
| D | 0.823 | 0.846 | 0.875 | 0.801 | 0.796 | |||
| P | 0.884 | 0.951 | 0.873 | 0.826 | ||||
| I | 0.86 | 0.841 | 0.714 | |||||
| E | 0.818 | 0.872 | ||||||
| U | 0.853 | |||||||
| S | ||||||||
| Changsha | L | 0.784 | 0.839 | 0.804 | 0.79 | 0.853 | 0.863 | |
| D | 0.853 | 0.841 | 0.784 | 0.824 | 0.826 | |||
| P | 0.862 | 0.851 | 0.873 | 0.847 | ||||
| I | 0.854 | 0.839 | 0.884 | |||||
| E | 0.748 | 0.785 | ||||||
| U | 0.868 | |||||||
| S | ||||||||
| Nanchang | L | 0.816 | 0.773 | 0.765 | 0.804 | 0.841 | 0.886 | |
| D | 0.859 | 0.813 | 0.882 | 0.797 | 0.872 | |||
| P | 0.824 | 0.891 | 0.873 | 0.877 | ||||
| I | 0.873 | 0.805 | 0.827 | |||||
| E | 0.823 | 0.864 | ||||||
| U | 0.836 | |||||||
| S |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, Y.; Peng, H.; Liu, G.; Yang, K.; Xie, Y.; Weng, Q. Monitoring Urban Clusters Expansion in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River, China, Using Time-Series Nighttime Light Images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101007
Zou Y, Peng H, Liu G, Yang K, Xie Y, Weng Q. Monitoring Urban Clusters Expansion in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River, China, Using Time-Series Nighttime Light Images. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(10):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101007
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Yanhong, Haiquan Peng, Geng Liu, Kuanda Yang, Yanhua Xie, and Qihao Weng. 2017. "Monitoring Urban Clusters Expansion in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River, China, Using Time-Series Nighttime Light Images" Remote Sensing 9, no. 10: 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101007
APA StyleZou, Y., Peng, H., Liu, G., Yang, K., Xie, Y., & Weng, Q. (2017). Monitoring Urban Clusters Expansion in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River, China, Using Time-Series Nighttime Light Images. Remote Sensing, 9(10), 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101007