Joint Local Abundance Sparse Unmixing for Hyperspectral Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
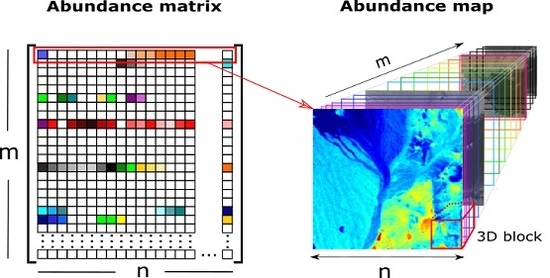
- is the hyperspectral data,
- is the spectral library,
- is the abundance matrix,
- is the 3D abundance data,
- m is the number of spectral signatures,
- l is the number of spectral bands,
- n is the number of pixels in ,
- is the number of columns in ,
- is the number of rows in ,
- B is the number of all local blocks in ,
- N is the number of pixels in each local abundance matrix,
- is the b-th local block,
- is the b-th local abundance matrix.
2. Hyperspectral Unmixing
2.1. Sparse Unmixing
2.2. Spatial Regularization
3. Proposed Algorithm
3.1. Local Abundance Correlation
3.2. Collaborative Sparsity Regularization
3.3. Local Abundance Regularizer
3.4. J-LASU
| Algorithm 1: ADMM in pseudocode for solving problem in Equation (10) |
 |
4. Experiment and Analysis
4.1. Simulated Data Sets
4.2. Real Data Sets
4.3. Parameters Setting and Evaluation Metrics
4.4. Simulated-Data Experiment
4.5. Real-Data Experiment
5. Discussion
5.1. Sensitivity Test
5.2. Effect of Block Size
5.3. Computational Complexity
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rizkinia, M.; Okuda, M. Local abundance regularization for hyperspectral sparse unmixing. In Proceedings of the 2016 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA), Jeju, Korea, 13–16 December 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Keshava, N.; Mustard, J.F. Spectral unmixing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2002, 19, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhuang, L.; Gao, L.; Luo, W.; Ran, Q.; Du, Q. PSO-EM: A hyperspectral unmixing algorithm based on normal compositional model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 7782–7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Ma, Q.; An, J.; Chang, C.I. An improved NMF algorithm based on spatial and abundance constraints. In Proceedings of the 2016 Progress in Electromagnetic Research Symposium (PIERS), Shanghai, China, 8–11 August 2016; pp. 4532–4537. [Google Scholar]
- Shippert, P. Why use hyperspectral imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2004, 70, 377–396. [Google Scholar]
- Landgrebe, D. Hyperspectral image data analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2002, 19, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiden, U.; Iwasaki, A.; Müller, A.; Schlerf, M.; Udelhoven, T.; Uto, K.; Yokoya, N.; Chanussot, J. Foreword to the special issue on hyperspectral remote sensing and imaging spectroscopy. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 3904–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.M.; Duran, O.; Zweiri, Y.; Smith, M. Hybrid spectral unmixing: Using artificial neural networks for linear/non-linear switching. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licciardi, G.A.; Sellitto, P.; Piscini, A.; Chanussot, J. Nonlinear spectral unmixing for the characterisation of volcanic surface deposit and airborne plumes from remote sensing imagery. Geosciences 2017, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoya, N.; Chanussot, J.; Iwasaki, A. Nonlinear unmixing of hyperspectral data using semi-nonnegative matrix factorization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Feng, R.; Zhang, L. Non-local sparse unmixing for hyperspectral remote sensing imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1889–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A.; Dobigeon, N.; Parente, M.; Du, Q.; Gader, P.; Chanussot, J. Hyperspectral unmixing overview: Geometrical, statistical, and sparse regression-based approaches. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 354–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, J.M.P.; Dias, J.M.B. Vertex component analysis: A fast algorithm to unmix hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, M.; Kiiveri, H.; Lagerstrom, R.; Ernst, A.; Dunne, R.; Huntington, J.F. ICE: A statistical approach to identifying endmembers in hyperspectral images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 2085–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.D.; Seung, H.S. Learning the parts of objects by nonnegative matrix factorization. Nature 1999, 401, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pauca, V.P.; Piper, J.; Plemmons, R.J. Nonnegative matrix factorization for spectral data analysis. Linear Algebra Appl. 2006, 416, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Du, B.; Zhang, L. Hyperspectral unmixing via double abundance characteristics constraints based NMF. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordache, M.D.; Plaza, A.J. A Sparse Regression Approach to Hyperspectral Unmixing. Ph.D. Thesis, Instituto Superior Tecnico, Lisbon, Portugal, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Ma, Y.; Mei, X.; Liu, C.; Ma, J. Hyperspectral unmixing with robust collaborative sparse regression. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasrodashti, E.K.; Karami, A.; Heylen, R.; Scheunders, P. Spatial resolution enhancement of hyperspectral images using spectral unmixing and bayesian sparse representation. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili Salehani, Y.; Gazor, S.; Kim, I.M.; Yousefi, S. ℓ0-norm sparse hyperspectral unmixing using arctan smoothing. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Shi, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, C. Sparse unmixing of hyperspectral data using spectral a priori information. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 770–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Jia, X.; Somers, B.; Wu, J.; Coppin, P. A quantitative analysis of virtual endmembers’ increased impact on the collinearity effect in spectral unmixing. Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2945–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Themelis, K.E.; Rontogiannis, A.A.; Koutroumbas, K. Semi-supervised hyperspectral unmixing via the weighted Lasso. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Dallas, TX, USA, 14–19 March 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Figueiredo, M.A.T. Alternating direction algorithms for constrained sparse regression: Application to hyperspectral unmixing. In Proceedings of the 2010 2nd Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), Reykjavik, Iceland, 14–16 June 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Iordache, M.D.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A. Sparse unmixing of hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2014–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordache, M.D.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A. Total variation spatial regularization for sparse hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 4484–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordache, M.D.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A. Collaborative sparse regression for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Liu, K.; Deng, C.; Liu, L.; Plaza, A. Hyperspectral unmixing based on local collaborative sparse regression. IEEE. Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Q.; Nasrabadi, N.M.; Tran, T.D. Abundance estimation for bilinear mixture models via joint sparse and low-rank representation. IEEE. Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 4404–4423. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, J. Hyperspectral image denoising via sparsity and low rank. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 1091–1094. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; He, W.; Zhang, L.; Shen, H.; Yuan, Q. Hyperspectral image restoration using low-rank matrix recovery. IEEE. Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 4729–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Q.; Yang, J. Hyperspectral image denoising via sparse representation and low-rank constraint. IEEE. Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampouras, P.V.; Themelis, K.E.; Rontogiannis, A.A.; Koutroumbas, K.D. Simultaneously sparse and low-rank abundance matrix estimation for hyperspectral image unmixing. IEEE. Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4775–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S.; Yamada, I. Color-line regularization for color artifact removal. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2016, 2, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Chan, J.C.W.; Kong, S.G. Coupled sparse denoising and unmixing with low-rank constraint for hyperspectral image. IEEE. Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 1818–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candes, E.J.; Tao, T. Decoding by linear programming. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theor. 2005, 51, 4203–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizkinia, M.; Baba, T.; Shirai, K.; Okuda, M. Local spectral component decomposition for multi-channel image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 3208–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza, J.; Hendrix, E.M.T.; García, I.; Martín, G.; Plaza, A. On endmember identification in hyperspectral images without pure pixels: A comparison of algorithms. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 2012, 42, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, J.J. Fonctions convexes duales et points proximaux dans un espace hilbertien. C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris Ser. A Math. 1962, 255, 2897–2899. [Google Scholar]
- Combettes, P.L.; Pesquet, J.C. Proximal splitting methods in signal processing. In Fixed-Point Algorithms for Inverse Problems in Science and Engineering; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 185–212. [Google Scholar]
- USGS Digital Spectral Library 06. Available online: https://speclab.cr.usgs.gov/spectral.lib06/ (accessed on 10 June 2016).
- AVIRIS Data. Available online: https://aviris.jpl.nasa.gov/data/free_data.html (accessed on 10 June 2016).
- Cuprite, Nevada AVIRIS 1995 Data USGS. Available online: https://speclab.cr.usgs.gov/cuprite95.tgif.2.2um_map.gif (accessed on 11 January 2017).
- Datasets and Ground Truths. Available online: http://www.escience.cn/people/feiyunZHU/Dataset_GT.html (accessed on 10 November 2017).
- Jia, S.; Qian, Y. Spectral and spatial complexity-based hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3867–3879. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, S.; Qian, Y. Constrained nonnegative matrix factorization for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, S.; Fan, B.; Pan, C. Structured sparse method for hyperspectral unmixing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 88, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Wang, Y.; Fan, B.; Meng, G.; Xiang, S.; Pan, C. Spectral unmixing via data-guided sparsity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 5412–5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Wang, Y.; Fan, B.; Meng, G.; Pan, C. Effective spectral unmixing via robust representation and learning-based sparsity. arXiv, 2014; arXiv:1409.0685. [Google Scholar]
- Zortea, M.; Plaza, A. Spatial preprocessing for endmember extraction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2679–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| SUnSAL-TV | J-LASU | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS | 10 dB | 1 × 10 | 1 × | 1 × | 1 × 10 | 1 × 10 | 5 × | 5 × | 5 × |
| 20 dB | 1 × 10 | 5 × | 5 × | 1 × 10 | 1 × 10 | 2.5 × | 5 × | 3 × | |
| 30 dB | 1 × 10 | 5 × | 1 × | 1 × 10 | 1 × | 5 × | 1 × | 8 × | |
| FR | 10 dB | 1 × 10 | 5 × | 1 × | 1 × 10 | 5 × 10 | 5 × | 1 × | 2.5 × |
| 20 dB | 1 × 10 | 5 × | 5 × | 1 × 10 | 3 × 10 | 2.5 × | 1 × | 1 × | |
| 30 dB | 1 × 10 | 5 × | 2.5 × | 1 × 10 | 1 × | 5 × | 5 × | 5 × | |
| Cuprite | - | 5 × | 5 × | 1 × | 1 × 10 | 1 × 10 | 5 × | 5 × | 1 × |
| Urban | - | 1 × | 1 × | 1 × | 1 × | 1 × | 1 × | 1 × | 1 × |
| SUnSAL-TV | J-LASU | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS | 10 | 0.0084 | 0.0078 | 0.0097 | |
| 20 | 0.0102 | 0.0046 | 0.0053 | ||
| 30 | 0.0039 | 0.0023 | 0.0038 | ||
| FR1 | 10 | 0.0130 | 0.0119 | 0.0140 | |
| 20 | 0.0129 | 0.0087 | 0.0107 | ||
| 30 | 0.0062 | 0.0068 | 0.0073 | ||
| FR2 | 10 | 0.0140 | 0.0119 | 0.0149 | |
| 20 | 0.0138 | 0.0083 | 0.0115 | ||
| 30 | 0.0062 | 0.0061 | 0.0066 | ||
| FR3 | 10 | 0.0136 | 0.0118 | 0.0130 | |
| 20 | 0.0128 | 0.0077 | 0.0107 | ||
| 30 | 0.0056 | 0.0058 | 0.0057 | ||
| FR4 | 10 | 0.0123 | 0.0120 | 0.0135 | |
| 20 | 0.0126 | 0.0089 | 0.0090 | ||
| 30 | 0.0057 | 0.0075 | 0.0058 | ||
| FR5 | 10 | 0.0118 | 0.0112 | 0.0139 | |
| 20 | 0.0119 | 0.0080 | 0.0106 | ||
| 30 | 0.0049 | 0.0062 | 0.0061 |
| SUnSAL-TV | J-LASU | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS | 10 | 2.5467 | 5.1021 | 0.3110 | |
| 20 | 2.1617 | 6.3470 | 4.5515 | ||
| 30 | 6.3299 | 10.5770 | 6.1799 | ||
| FR1 | 10 | 0.6435 | 2.018 | 0.851 | |
| 20 | 1.3116 | 3.5071 | 2.1257 | ||
| 30 | 4.2204 | 4.8625 | 4.0937 | ||
| FR2 | 10 | 0.3457 | 2.2395 | 0.2493 | |
| 20 | 1.1915 | 3.8690 | 1.0974 | ||
| 30 | 4.4628 | 5.604 | 4.5908 | ||
| FR3 | 10 | 1.6928 | 4.0113 | 2.1009 | |
| 20 | 3.1706 | 5.8611 | 2.3815 | ||
| 30 | 6.8354 | 6.9782 | 7.0605 | ||
| FR4 | 10 | 0.3417 | 1.3213 | 0.2092 | |
| 20 | 1.0942 | 2.5735 | 0.3275 | ||
| 30 | 4.1734 | 3.263 | 3.5545 | ||
| FR5 | 10 | 1.005 | 2.4054 | 0.2591 | |
| 20 | 1.5711 | 4.1026 | 1.228 | ||
| 30 | 6.3324 | 5.6279 | 6.0702 |
| SUnSAL-TV | J-LASU | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 0.2135 | 0.2003 | 0.2077 | |
| SRE | 4.6831 | 5.4738 | 5.0805 |
| SUnSAL-TV | J-LASU | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time/iteration (s) | 0.92 | 0.54 | 0.24 | 2.77 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rizkinia, M.; Okuda, M. Joint Local Abundance Sparse Unmixing for Hyperspectral Images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121224
Rizkinia M, Okuda M. Joint Local Abundance Sparse Unmixing for Hyperspectral Images. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(12):1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121224
Chicago/Turabian StyleRizkinia, Mia, and Masahiro Okuda. 2017. "Joint Local Abundance Sparse Unmixing for Hyperspectral Images" Remote Sensing 9, no. 12: 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121224
APA StyleRizkinia, M., & Okuda, M. (2017). Joint Local Abundance Sparse Unmixing for Hyperspectral Images. Remote Sensing, 9(12), 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121224